It is very important that the engine operates correctly in any mode, including idling. However, many car owners are faced with a problem: when they release the gas, the engine speed does not drop. As soon as such a defect is discovered, it is necessary to immediately find out the cause and eliminate the malfunction for the smooth operation of the car. Also, the engine may slow down for a long time, which also does not contribute to proper operation.
Typically, upon reaching operating temperature, the speed should drop to its normal level. The manufacturer indicates the indicators for each specific vehicle model in the operating manual. They may vary slightly depending on the mileage and general condition of the car, but usually stay within the range of 650-1000 rpm.
In some cases, the speed drops very slowly or even stays at the same level of 1500-2000 revolutions. In this mode, not only does fuel consumption increase, which affects the driver’s finances, but it also contributes to engine wear.
The cause of the idle failure must be diagnosed by qualified technicians. However, you can also understand on your own why the engine speed does not drop.
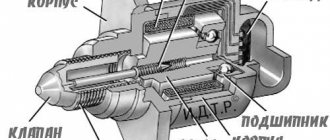
Injector system
If your car has an injection system, there may be many more reasons for high idle speeds. Here, both mechanical elements and electronic devices responsible for adjusting the idle speed can fail.
The main injector malfunctions include:
- Incorrect operation of the temperature sensor installed in the cooling system. Incorrectly received data from this device causes the electronics to recognize the engine as cold and work to warm it up, thereby maintaining high speeds necessary to reach operating temperature. Overheating can often occur, which leads to more serious damage, including major engine repairs. The same effect is possible if the idle speed control is not operating correctly.
- The throttle control cable may become stuck. The higher the mileage of the car, the higher the risk of encountering a similar problem.
- The electronic XX operation sensor often malfunctions, then the speed will either increase or disappear altogether.
- The spring that brings the throttle valve to its original closed position is not functioning properly, is jumping off, or is being stretched too far.
- Too much air enters the fuel combustion chamber due to poor quality or leaky gaskets. It is necessary to carefully check the seals of the manifold and injectors.
- And the simplest reason is usually the incorrect placement of the mat after a visit to a car wash or dry cleaning of the interior. It is often inaccurately placed under the accelerator pedal, which leads to the appearance of improper engine operation.
If the car is oversaturated with various electronics and all the work is based on the correct functioning of the sensors, one of them may well become a problem. It will supply incorrect data to the computer, and as a result, the speed will not drop. You will most likely not be able to detect the problem on your own.
It is necessary to contact a car service for computer diagnostics. The task is best handled by specialists working at a service center that specializes in repairing a specific brand of car. If the diagnosis is carried out on time, then it is quite possible to get away with simply replacing the sensor.
You shouldn’t delay repairs, because a supersaturated mixture has a bad effect on engine performance and significantly shortens its service life.
Let's sum it up
As you can see, in order to accurately determine why the engine speed is not reset, in many cases in-depth diagnostics may be necessary. For carburetor engines, cleaning and adjustment of the carburetor itself is often necessary, while the injector will require computer diagnostics.
If the problem is not on the surface (the throttle cable has become sour, after washing or dry cleaning, the carpet in the cabin is not installed correctly, which presses the gas pedal, etc.), then it is better to take the car to a service center.
The most complex situation is when the design of the power system involves the presence of a large number of sensors and actuators. In this case, even the use of diagnostic equipment does not always allow you to quickly and accurately determine the problem.
If diagnostics are difficult, it is optimal to deliver the car to a service that specializes in repairing a specific brand of car. As a rule, these are official dealer service stations; it is less common to find third-party organizations.
Finally, we note that timely detection of a problem allows you to save the life of the internal combustion engine and other components and assemblies. In other words, high idle speeds, floating speeds and jumps indicate that there are problems with the air/fuel supply or with mixture formation. Ignoring such problems negatively affects the engine and its service life.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Source
Possible causes of malfunction
Floating engine speed at idle is almost always caused by a violation of the composition of the fuel mixture or excessive air intake into the engine. The complexity of this problem lies in the fact that a wide range of malfunctions in the fuel supply system can lead to this.
In carburetor cars
Most problems with floating engine speeds with carburetor injection of the fuel mixture are directly related to the device itself (carburetor). As a rule, jumps in engine speed are associated with depletion of the incoming fuel mixture, caused by:
- incorrect adjustment of the idle speed by “craftsmen” or its failure as a result of operation;
- contamination of jets, fuel and idle air channels;
- breakdown of the solenoid valve of the device;
- sucking in excess air and subsequent depletion of the fuel mixture;
- incorrect fuel level in the carburetor float chamber (high or low);
- breakdown of the throttle valve or oil deposits that prevent the valve from opening and closing correctly;
As a result of these malfunctions in the fuel supply system, the engine begins to stall at idle.
In injection cars
In cars with forced fuel supply, most causes of engine stalling are often associated with electronic malfunctions. The operation of the electronic control unit (ECU), responsible for fuel injection, is based on the data received, which is transmitted by sensors. Jumps in engine speed occur due to the fact that, due to incorrect data transmitted by the mass air flow sensor (MAF), more air enters the injection valves than necessary. Due to excess air in the engine cylinders, the ECU “gives” a command to the injector valves to open slightly to supply fuel. As a result of its combustion, a jump in engine speed occurs. After the fuel burns, the engine speed drops again.
Also, the reasons for speed jumps on injection models can be:
- worn and clogged spark plugs;
- damage to high-voltage wires, causing incorrect operation of all car electronics;
- breakdown of the idle air regulator (IAC);
- malfunction of the EGR exhaust gas recirculation system;
- The oil pan ventilation valve is clogged.
In diesel cars
In cars with a diesel engine, the reasons for jumps in engine speed can be the same as in a gasoline unit. However, another reason may be the failure of the high pressure fuel pump (HPF). Corrosion or mechanical damage to the moving fuel injection pump blades leads to floating engine speeds, both at idle and while driving at low engine speeds.
When releasing the gas, the speed is increased or “freezes”: common malfunctions
Let's start with the fact that on many cars with an injector, the ECU raises the speed while the internal combustion engine is warming up. This is necessary to ensure that the power unit operates stably after a cold start.
However, after the temperature rises, the control unit reduces the idle speed, bringing it to normal. On many cars with a carburetor, the driver independently increases the speed during warm-up, using the so-called “choke”.
Moreover, after the engine is warmed up, the normal idle speed is, on average, 650-950 rpm. If you press the gas and release the accelerator, the speed should increase, and then decrease again to the specified values.
Also, a situation often arises when the speed drops slowly or is constantly kept at around 1.5 thousand rpm, 2 thousand revolutions, etc. Naturally, in such cases, consumption increases and the internal combustion engine wears out more, which indicates the need for diagnostics.
So, let's start with common carburetor problems. Often the engine speed does not drop due to problems with the throttle valve. For example, when the driver steps on the gas, the throttle must be opened wider to allow more air to enter the cylinders to burn fuel. After the gas pedal is released, the throttle closes and the speed decreases.
If the damper does not close completely, an over-enriched mixture enters the cylinders, and the speed is increased. The cause may be severe contamination of the throttle assembly or damage to the valve itself (deformation). First you need to clean the damper; carburetor cleaning liquid is suitable as a cleaner.
We also note that the damper does not close tightly even when the drive cable is worn out. In this case, the cable must be replaced. On carburetor cars, engine speed often does not drop even if the gasket between the carburetor and the cylinder head has failed. The culprit may also be an intake manifold that is damaged.
It should be noted that after cleaning the carburetor and fuel system, the engine speed slowly drops due to a failure in the adjustments of the idle system itself. In other words, after any manipulations with these components, the carburetor should be separately configured and adjusted.
The main task is to find the correct ratio of fuel and air. Often, a high level of fuel in the carburetor float chamber also leads to increased speed. The check should begin with the needle valve.
Now let's move on to the injector
Please note that on many injection cars, after cleaning the throttle valve, the assembly also needs to be additionally “trained”. As for problems, the injection system itself is more complex, that is, there are more reasons for high speeds compared to a carburetor
As a rule, problems with speed can be caused by problems with both mechanical elements and electronic components. In the list of main malfunctions, experts highlight malfunctions of the coolant temperature sensor, which is installed in the cooling system.
Currently reading
In simple words, if the specified sensor gives an incorrect signal, the ECU considers that the engine is cold and activates the warm-up mode. In this case, the control unit raises the speed so that the power unit operates stably and reaches operating temperature faster.
Also, problems with speed can begin due to problems and malfunctions in the operation of the IAC (idle air regulator). It also happens that the throttle cable gets stuck and becomes wedged. The spring that closes the throttle valve may also become stretched or damaged.
Special attention should be paid to gaskets, since air leaks can lead to disruption of mixture formation. This means that you need to separately inspect manifold gaskets, injector seals, etc.
Let's sum it up
As you can see, in order to accurately determine why the engine speed is not reset, in many cases in-depth diagnostics may be necessary. For carburetor engines, cleaning and adjustment of the carburetor itself is often necessary, while the injector will require computer diagnostics.
If the problem is not on the surface (the throttle cable has become sour, after washing or dry cleaning, the carpet in the cabin is not installed correctly, which presses the gas pedal, etc.), then it is better to take the car to a service center.
The most complex situation is when the design of the power system involves the presence of a large number of sensors and actuators. In this case, even the use of diagnostic equipment does not always allow you to quickly and accurately determine the problem.
Finally, we note that timely detection of a problem allows you to save the life of the internal combustion engine and other components and assemblies. In other words, high idle speeds, floating speeds and jumps indicate that there are problems with the air/fuel supply or with mixture formation. Ignoring such problems negatively affects the engine and its service life.
The main causes of the third stage of hypertension
With arterial hypertension (AH) grade 3, blood pressure increases to 180/110 mmHg, and sometimes exceeds them. In this situation, it is impossible not to use medical help, otherwise more serious disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system are possible.
Most often, this pathology develops in older people. It happens that the upper numbers on the tonometer exceed 180 mmHg, while the lower ones drop to normal. This can significantly complicate treatment. This pathology may be accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of vital organs, which corresponds to risk grade 3 or 4.
The development of a disease such as stage 3 hypertension, risk 3 or 4, is caused by various factors influencing from the outside and from the inside.
Causes of high blood pressure:
- kidney pathologies, disruptions in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels;
- obesity, diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorders;
- poor nutrition;
- age restrictions, gender;
- chronic fatigue, stress, psycho-emotional overload;
- alcohol abuse, smoking addiction;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- hereditary factor.
Some of these reasons can be influenced, others should simply be taken into account. In this case, therapy will be easier to carry out and the risk of more serious complications will be reduced.
Electronics
The most common cause of unstable speed is a violation in the engine management system. Therefore, the first thing to do is to conduct computer diagnostics. In most cases, this can identify errors in specific sensors and check their operation. Below we look at the most common causes of the problem.
Check the throttle position sensor. Sometimes it may give incorrect signals, causing the RPM to increase. To check, you will have to remove the sensor from the car. It is also recommended to check the condition of the damper itself. Possibly due to contamination
I don't close it completely. If a malfunction is detected, the sensor should be replaced. Just don't buy a cheap Chinese part; most likely, you'll need to buy it again soon. It's better to buy a normal sensor right away.
{banner_content}Damage to the engine control unit bus. Sometimes the wires
, which send a signal to the on-board computer, may be damaged. This happens when the repair is unsuccessful, when a car enthusiast accidentally breaks them. A breakdown can also occur due to a large amount of dirt accumulated on the tire. Be sure to check the functionality of these wires. The easiest way to do this is to install a known working tire. If this cannot be arranged, then you can ring them with a tester in resistance measurement mode. The problem may also be caused by the idle air control valve. Diagnosis of this part is complicated by the lack of response to a malfunction of the engine control unit. Therefore, you will have to remove it in any case. It is essentially a small electric motor that drives a needle that regulates power to the motor. After removal, measure the resistance at the opposite terminals. The device should show 40-80 Ohms
. When measuring resistance at adjacent terminals, the indicator should tend to infinity. If this is not the case, then the regulator is faulty and requires replacement. It must be said that an increase in speed when it fails is rarely observed; usually there are options with a missing idle speed.
If your car has a mass air flow sensor, then this is probably the cause. It rarely fails, but when it breaks down, in most cases it supplies the cylinders with a mixture that is too rich. An indirect sign is the presence of engine detonation. This sensor is quite expensive, and if the TPS can be bought and checked by simply replacing it, then it is better to carry out a thorough diagnosis. The first thing to do is try to disconnect the sensor from power. In this case, the control unit begins to work, starting from the throttle position. If the sensor is faulty, then the motor operation returns to normal. Some sensor models can be checked using a multimeter. To do this, remove the mass air flow sensor, connect it to power, and measure the voltage at the terminals. It should match the recommended one for your sensor. For example, on the Bosch DMRC the permissible voltage is 1.01-1.03 V
. The figure may vary on other models.
How to find the reason and fix it?
Before you can fix the problem, you need to find its source, that is, the part, mechanism or electronic device that causes the speed to triple.
- In a car with carburetors, first you need to check whether the cause of the jumps is a breakdown of the solenoid valve. In this case, the engine will idle only on choke, and if you remove it, the engine will stall. If it breaks, you will have to replace the valve.
- If the reason is not in the valve, then it is necessary to remove the carburetor, thoroughly clean the jets and channels, and replace the carburetor air filter. The jet and channels are cleaned using special aerosols for carburetors.
- You also need to evaluate the fuel level in the float chamber and, if necessary, adjust the flow correctly. Adjusting the carburetor is not the easiest procedure, so if you lack experience, it is better to entrust this work to specialists.
It is more difficult to detect the causes of speed jumps in injection engines, since problems are often caused by the electronic “brains” of the car.
In injection engines, the search for the cause of the breakdown can begin with the idle air regulator (IAC). The condition of the regulator can be checked using a multimeter; if the readings differ from the standard readings of 40–80 ohms, the IAC is broken and will have to be replaced. For minor deviations, you can try to adjust it with a screwdriver, loosening or tightening the screws that control the speed. Diagnostics at a service station can help determine that the mass air flow sensor (MAF) has failed. The reason for contacting may be symptoms of a malfunction (jumps in engine speed) in combination with the Check Engine light coming on. As a rule, modern service stations are equipped with software to determine that it is the mass air flow sensor that has failed. Since the sensor cannot be repaired, it will have to be replaced. You can also check the sensor for malfunction at home: using a multimeter (if the readings are above 1.04, it can be changed) or by turning off the mass air flow sensor. If, with the sensor disconnected, the surges have stopped and the engine speed remains at 1500 RPM, the problem is in the mass air flow sensor. The EGR valve is located in the intake manifold and connects to the exhaust manifold. You can check its operation using a multimeter; you can also carry out a visual inspection of the adjacent tubes and connectors. When replacing the valve, the adjacent tubes must be cleaned of carbon deposits. Testing high-voltage wires can be carried out in several ways. First, you should inspect them for external damage (cracks, cuts). You can also take a closer look at them at night with the headlights off and the engine running. Sparks in the wires indicate breakdowns. The presence of damage can be checked using a wire with stripped ends; one side is applied to the car body, the other must be routed along the explosive wires. An insulation failure can also be detected by the appearance of sparks. Another way to determine insulation failure is to check with a multimeter in ohmmeter mode. Resistance values should not exceed 10 kOhm. In case of any damage, it is necessary to completely replace the high-voltage wires in the set. Checking spark plugs is carried out first visually - a spark plug wet from gasoline or large carbon deposits on it requires immediate action. You can also make sure that the spark plug is working correctly using a special spark plug test gun, which can be purchased at auto stores.
If necessary, the candles are carefully but carefully cleaned of carbon deposits or replaced with new ones. In order to wash the oil crankcase ventilation valve, you need to disassemble the crankcase itself and then remove the valve. The valve is washed to remove oil deposits in kerosene or another chemical.
After drying, the valve can be reinstalled. Flushing the throttle valve from oil deposits can be carried out either with or without removing the unit. Washing is carried out with special chemical aerosols.
The high pressure fuel pump used in diesel cars can be treated with an anti-corrosion agent. To do this, the aerosol is sprayed directly into the neck of the fuel tank before refueling. If you plan to park a diesel car for a long time, then before that you can fill the tank with 200–300 ml of motor oil and drive for 1 day. Naturally, the car will smoke and smoke, but this will prevent corrosion. If the fuel injection pump blades fail, then the entire pump assembly will have to be replaced.
Floating speed
In addition to slowly falling revs, car enthusiasts may encounter a phenomenon called floating revs, when they drop and then rise sharply. The reason is excessive air supply into the system, which causes the engine to spin up to 2 thousand revolutions at idle.
This often happens in cars that have a fuel injection sensor. It calculates how much air the mixture needs. When its operation is disrupted, different amounts of oxygen are supplied at different times, as a result, speed jumps are observed approximately every 3 seconds.
Faced with a similar phenomenon, the same computer diagnostics will be a prerequisite
It is very important that this and all subsequent work is carried out by experienced, qualified specialists. By contacting a service that does not specialize in breakdowns of this kind, you may be faced with the need to carry out expensive engine overhauls ahead of time.
VISITING A CAR SERVICE
In a situation where you specifically do not have enough experience in car maintenance, there is a fairly high probability of aggravating the problem by unqualified intervention in the operation of various on-board systems.
It is important to objectively assess your own capabilities, and if you don’t have faith in yourself, then it is better to entrust the repairs to specialists. In a situation where it turns out that the problem is not particularly serious, they won’t take much money from you
But in any case, you will be able to avoid many of the troubles associated with unqualified attempts to repair the vehicle.
- Why does the car jerk when accelerating?
There is a special offer on our website. You can get a free consultation with our corporate lawyer by simply submitting your question in the form below.
What are the consequences of high idle speed?
The first thing the driver should remember is the high fuel consumption at high speeds. Accordingly, if high speeds remain at idle, this means that part of the fuel “flies into the pipe.” Moreover, this problem directly affects the life of the engine, which suffers as a result of such a malfunction. The node itself, which led to the occurrence of the malfunction in question, may also suffer. That is why, if this problem is identified, it should be eliminated as soon as possible.
Normal or not
By default, the idle speed is in the range of 650-950 rpm. This is provided that the engine is warmed up to operating temperature. And if not, then the tachometer needle may deviate to large values. So, in warm-up mode, 1,500 rpm is completely normal. As the antifreeze warms up, they will gradually drop to the default values.
If there is no decrease in speed on a hot engine, then this is a malfunction. The main danger is that stuck speeds increase the risk of engine overheating, and this is a problem with far from cheap results. However, there is a case when the engine behaves ambiguously even when cold. Let's start with this!
Problems with the injector
Separately, we should consider situations due to which the speed at idle can increase on injection types of engines.
Unlike carburetor internal combustion engines, where all the problems lie in the mechanical part, the injector has a high probability of having electronic faults.
- Malfunction or failure of the sensor that monitors the coolant temperature. This leads to constant operation in the internal combustion engine warm-up mode. You need a diagnostic scanner and probably a controller replacement;
- Malfunction or breakdown of the XX sensor. It's also a mass air flow sensor. Diagnostics with special equipment will help. Eliminate broken wiring using a multimeter, replace the unit as necessary;
- The same problems, but with the throttle position sensor. That is, the throttle valve. The controller is either jammed or broken;
- Damper return spring. It can stretch or jump off, causing the engine to behave correspondingly at idle. The unit is returned to its place or replaced with a new one;
- Hall throttle cable. Relevant for older cars. Replacing or lubricating will help solve the problem;
- Sealing gaskets on injectors. They don't get damaged that often. Diagnosing the problem is difficult. They usually check it last.
Be careful when starting and observing the behavior of the tachometer in your car. If you see that the speed is floating, rising to abnormal levels and behaving uncharacteristically, do not ignore such symptoms.
High engine speeds at idle, in addition to completely unnecessary excessive fuel consumption, also interfere with driving the car - for example, when driving through a particularly rough section of the road, when you want to carefully “sneak” among potholes in first gear, and the car boldly takes blows to the suspension. In addition, during long periods of idle time in traffic jams, the engine will always operate at elevated temperatures. Let's look at several reasons why high idle speeds do not drop on a warm engine. The reasons may be malfunctions in both the mechanical and electronic components of the engine power supply system, so we will describe possible failures separately. But since in a car these components interact in a complex manner, you may be able to independently find the answer to the question of why your engine has high idle speeds, taking the material in this article as “food for thought.”
Checking the intake manifold for leaks
Excess air leakage can cause high idle speeds. Moreover, depending on where excess air penetrates into the intake manifold, the idle speed will either simply be increased or begin to “float” - .
If there is simply a violation of the tightness of the intake manifold gaskets, damage to the vacuum hoses or sealing rings, then the speed will “float”. This happens due to the fact that the amount of gasoline supplied to the cylinders will be constant, and the quality of the mixture becomes either “richer” or “poorer”. When a certain critical value (air content in the fuel mixture) is reached, the engine will begin to slow down - until it stops. But as the speed decreases, the amount of air entering the manifold will decrease, i.e. the mixture will become richer and the engine will “come to life” - the idle speed will increase. This will continue until the leak in the intake manifold is eliminated. On turbocharged engines, air leaks can also occur through damage to the intercooler or air pipe connections. If there is significant suction (for example, if the pipe has come off the intercooler), the engine begins to operate with a whistling (or hissing) sound. But sometimes it is possible to identify the location of a violation in the intake tract only by cutting off the air supply to the intake manifold in different places in turn - from the air filter to the manifold itself.
Main reasons
The reasons that the speed of the power unit does not decrease differ for cars with injection and carburetor engines.
On carburetor engines
In cars equipped with carburetors, it is this unit that is responsible for preparing and supplying the air-fuel mixture to the combustion chambers. Most often, problems with high speeds are associated with an over-enrichment of the fuel-air mixture, but other causes of malfunction may also occur.
The effect of increased speed can be caused by the following problems.
- Incorrect operation of the throttle valve responsible for the air supply. If the damper, after releasing gas or warming up the engine, cannot close tightly, and a gap forms in it, then an enriched fuel-air mixture enters the engine.
- Open suction. Choke is a control knob for adjusting the air damper, which is responsible for the flow of air into the carburetor. With its help, you can enrich the fuel-air mixture with air. If the suction is not working correctly, the mixture becomes over-enriched with air.
- Needle valve position. In this case, the incorrect dose of fuel will enter the combustion chamber. A malfunction of the needle valve can manifest itself in different ways, including the absence of a drop in speed.
- Incorrect idle speed adjustment. This problem is often encountered by car owners who have changed or repaired the carburetor.
- A fairly rare cause is a burnt-out cylinder head gasket. The problem is manifested not only by increased engine speeds, but also by the appearance of white smoke from the engine compartment.
On injection engines
For cars equipped with injection engines, the range of reasons for increased speed is wider. This is due to the fact that such cars have many more electronic devices and sensors that are responsible for transmitting information to the electronic control unit that regulates engine speed. Therefore, disturbances in engine operation can be associated with both mechanical damage and malfunction of electronic systems.
The reason for the increased speed of injection engines may be one of the following problems.
- Incorrect operation or failure of the coolant temperature control sensor. With such a malfunction, the engine constantly operates in warm-up mode, since the ECU (electronic control unit) does not receive information from the sensor that the engine is already warmed up. As mentioned above, in this mode the engine speed is increased.
- Failure of the mass fuel flow sensor (MAF), which is also called the idle speed sensor. A malfunction of the mass air flow sensor can manifest itself in different ways - a loss of speed or an increase in speed. In the latter case, the engine also goes into constant warm-up mode.
- Throttle position sensor malfunction. In this case, a sensor malfunction may be perceived by the ECU as information about an open throttle valve. Then the control unit gives a command to increase the speed.
Also, the reasons for the increased speed of injection engines can be associated with mechanical damage.
- Broken throttle return spring.
- Sticking throttle cable.
- Damage to the injector gaskets.
Excess fuel supply
Cleaning the throttle body
A completely different situation will arise if not just excess air, but an air-fuel mixture enters - for example, through a gap formed as a result of loose closing of the throttle valve. In this case, the high idle speed of the engine will be stable. The fuel systems of some engines provide semi-automatic control of the fuel supply during engine warm-up mode - due to this, high idle speeds are maintained until the engine warms up to the set temperature. Fuel is supplied through a channel that bypasses the throttle valve. Such a channel can be closed/opened in various ways - the valve in it has either an electric drive (solenoid), or it can be arranged like a refrigerator thermostat - when the engine warms up, the channel is locked.
At high idle speeds, you should check the entire throttle valve assembly with sensors and idle control.
In any case, such a valve may break, and then excess fuel will always flow into the intake manifold, which will cause high idle speeds after the engine has warmed up. In all such cases, first of all, you need to remove the throttle body and wash it with a special solution - there are a lot of similar “chemicals” sold in stores. After washing, you need to carefully inspect the assembly - especially for sticking or, on the contrary, excessive looseness of the throttle valve. The throttle valves of some injection engines also have a screw for adjusting the idle speed of the engine or limiting the closing of the valve - you should also pay attention to them - whether the unit can be adjusted. Often, the engine speed does not drop at idle due to the gas cable getting stuck or foreign objects getting under the pedal - the corner of the mat, for example. Of course, almost all of the above can also apply to carburetor engines. In addition, a typical malfunction (or, more precisely, a deviation from the norm) for them is incomplete opening of the air damper - mainly due to incorrect installation of the choke cable. In the absence of breakdowns, the normal idle speed of a carburetor engine is set by adjustment using two screws - the “quantity” and “quality” of the mixture.