Story
Many people think that turbocharged engines appeared not so long ago. But this actually happened in the 20th century. In 1911, the American inventor A. Buchi received an official patent for the industrial production of the system, which made it possible to increase the motor power several times.
Although Alfred Büchi figured out how to properly “compress” the intake air, the process first began to work in practice when General Electric began experimenting with gas supercharging. Ten years later, a turbocharger was installed on the Liberty biplane engine. He then managed to rise to a height of more than 10 km.
The first turbines gave a good increase in power, but were very bulky. They increased the already heavy weight of the cars. For this reason, turbocharging did not spread further. For example, in America they were in no hurry to integrate it into manufactured cars.
The turbocharging system was used in European countries. In those years, the gasoline crisis just hit. Turbocharging helped reduce engine displacement and increase its power. Over time, the system was improved, but the problem of high fuel consumption remained. It was only possible to solve it in 1970, when the Mercedes company introduced a car with a turbocharged diesel engine. Now fuel consumption has been reduced, since the diesel unit turned out to be not so “gluttonous”.
By the way, turbochargers were used in aircraft construction even before World War II. A little later they were installed on passenger liners. Thus, we can say that turbocharging appeared in the last century, but received its well-deserved popularity only after more than 100 years.
Pros and cons of turbocharging
The advantages of using turbocharging are:
- The ability to increase the power of a car engine without changing its volume and weight.
- Reduced fuel consumption.
Disadvantages of a turbocharged engine:
- More intensive wear of parts and mechanisms.
- The need to use special grades of oil.
- Strict adherence to maintenance schedules and recommendations.
- Reducing the overall reliability of the engine due to the inclusion of additional elements in the system (turbocharger, etc.).
Device
Turbocharging is used today on different types of engines, including gasoline and diesel. The system is most often used on a diesel engine; it has a high compression ratio and low crankshaft speeds.
As for gasoline engines, the t of exhaust gases in them is higher. This can produce a detonation effect, that is, provoke accelerated wear of the piston group. This phenomenon can be prevented.
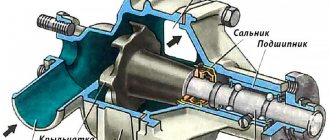
The turbocharging system includes many important elements. The main element is the supercharger. It is also called a turbine compressor. It functions in the intake system, increasing the pressure of the air mass.
The compressor itself consists of wheels (turbine and compressor). The first is designed to process energy, the second is to suck in the air mass, and then to compress and pump it. Another important element is the intercooler and boost pressure regulator.
Specifics of supercharging operation
The principle of operation of the turbine is that the compressor forces air into the cylinders, due to which the gas mixture makes the engine operate more efficiently by up to 30%! With a constant amount of fuel used, the power of the car increases. To understand the features of turbocharging, you must first understand the principles of operation of a conventional engine.
We also recommend reading our expert’s article, which talks about what an air blower is in a car.
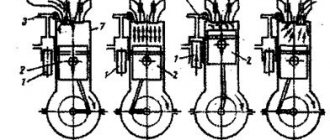
The operation of a four-stroke engine consists of 4 stages.
- Inlet . When the piston moves, the valve opens and a combustible mixture consisting of fuel and air enters the chamber.
- Compression . The air-fuel system is compressed for more efficient combustion.
- Working progress . The spark plugs produce a spark, which ignites the combustible mixture and causes the piston to move downwards, causing the crankshaft to rotate. The energy of expansion of gases is the main force that sets the car in motion.
- Release . The spent mixture is discharged from the chamber. The gas is purified and released from the exhaust system into the atmosphere.
This scheme works for gasoline engines, but diesel engines work somewhat differently. First of all, air enters the engine, which heats up to a temperature of 700 - 800 degrees Celsius. Next, diesel is injected, which self-ignites when compressed, which sets the mechanism in motion.
We recommend: The design of a manual transmission and how it works
In order to understand what turbocharging is, it is necessary to clarify the features of its operation. The turbine forces air into the combustion chamber using a compressor, thereby increasing the oxygen content in the mixture and improving its combustion.
Most compressors are capable of compressing air by 80%! more compared to conventional chamber filling.
How does it work?
Let's take a closer look at the operating principle of turbocharging. The system operates on the energy of exhaust gases. They rotate the turbine wheel, which, in turn, rotates the compressor wheel. It compresses the air, and then it is cooled in the intercooler and passes into the cylinders of the “engine”.
The efficiency of the system depends on the engine speed. It turns out that the more the crankshaft rotates, the greater the energy of the gases, the faster the turbine rotates and a large amount of compressed air goes into the cylinders.
There are some downsides to turbocharging. These include “turbo lag” and “turbo pickup”. The first occurs with a sharp “start” when there is a delay in increasing the power of the “engine”. The second appears when the pressure increases after overcoming the turbo lag.
If the driver knows how a classic internal combustion engine functions, then it will not be difficult for him to understand the process of supplying additional air to the cylinders. It turns out that when the turbocharging is turned on, the engine power increases at standard volumes.
Operating principle of a car turbocharger
A turbocharger is a complex device used to increase engine power by delivering more air to the cylinders. The operating principle of a turbocharger is as follows:
- When the air-fuel mixture enters the engine, it burns, which then exits through the exhaust pipe. At the beginning of the exhaust manifold there is an impeller, firmly connected to another impeller located in the intake manifold;
- the flow of exhaust gases leaving the engine spins the impeller located in the exhaust manifold, which in turn drives the impeller installed on the intake;
- Thus, more air mass enters the engine, which means more fuel is supplied to it. As you know, the more fuel mixture is burned, the more powerful the engine becomes. The task of an automobile turbocharger is precisely to supply more air to the power unit to burn more fuel, due to which a significant increase in power is achieved.
We recommend: So different and so similar: liftback and hatchback, what are the differences
The turbocharging system uses the energy of gases that are formed during the combustion of fuel. The gases provide rotational movements of the turbine wheel, which in turn starts the compressor wheel, which is responsible for compressing and pumping the air mass into the system. Next, the air is cooled using an intercooler and supplied to the cylinders.
It is obvious that although turbocharging is not mechanically connected in any way with the engine crankshaft, its operation and its efficiency are directly dependent on the speed of rotation of the crankshaft. The higher the engine speed, the more efficiently the turbocharger works.
Despite its practicality and efficiency, the turbocharging system has some disadvantages. The key one is the appearance of turbos - a delay in increasing the power of the internal combustion engine.
This phenomenon manifests itself due to the inertia of the system - a delay in increasing the boost pressure when pressing the gas quite sharply, which can lead to a gap between the required engine power and turbine performance.
Features of TD operation
Having understood the principle of operation of turbocharging, the driver must understand the rules for operating the unit. If you follow the recommendations, the “lifetime” of the motor will increase.
The operating features are as follows:
Checking the oil level is the most important condition when operating turbo engines. If there is a lack of lubrication, this leads to rapid wear of the turbine bearings.
Correct pressure on the gas pedal - TDs reach maximum speed immediately after starting, so you should not hold the gas pedal for a long time.
High-quality oil - the turbine wears out quickly also due to low-quality oil. This also negatively affects the condition of the motor.
Checking the engine after repairs - the liquid should be transparent, and the “engine” itself should not make any extraneous sounds.
Raise the engine to high speed. The turbine must be constantly running, otherwise it will cease to function normally. That is why once a week it is necessary to turn on the engine at high speeds.
For diesel engines, only high-quality fuel should be used. Low-grade fluids clog the fuel system, reducing engine power levels.
At low t values, the lubricant turns into a viscous substance. That is why during frost the engine must run at idle speed so that the liquid circulates inside the unit.
Types of systems
There are several types of turbocharging systems. The first type includes VGT and VNT turbines. They are also called variable geometry turbines.
The first type was developed by the then famous company BorgWarner, the second by Garrett. Their operating principle is quite simple. The direction and speed of the exhaust gas flow is regulated by changing the area of the input channel.
The second type is called Twin Turbo or double turbo. Two turbines smooth out inertia and avoid delays. Control occurs through sensors and ECM. This design comes in three different types:
1. Parallel - 2 turbines are fired simultaneously. After compression, the exhaust gases go into the intake manifold, and from there they are distributed among the cylinders.
2. Series - 2 compressors with the same configuration are connected to the engine. The first compressor operates in continuous mode, and the second is only adjusted to operating mode.
3. Staged - 2 different compressors are connected to the inlet and outlet channels. There is also a third type of system, which is called combined (Twincharger). The combination of mechanical and turbocharging creates a combined boost.
Thus, there are three main types of systems. Each of them has certain functions.
Turbo timer
A turbo timer is an electronic device that helps increase the life of a car turbine. In other words, it is a special controller that turns off the engine some time after removing the ignition key from the lock. All this time the unit operates at idle speed. The turbo timer is installed under the dashboard and connected to the ignition switch.
The turbo timer allows the turbine to cool down under elevated temperature conditions. Cooling occurs using machine oil. If the engine stops functioning, the supply of coolant lubricant stops. This all leads to parts failing.
Car enthusiasts who constantly operate turbocharged engines at high speeds first make the turbine idle, and only then turn off the ignition. The turbine cools down on its own, but if you use a turbo timer, you won’t need to sit and wait in the cooling machine. You can remove the key from the lock, and then the electronics will turn off the engine itself.
If a person leaves the turbo timer running and leaves the salon, then another person will not be able to steal the car. The device is blocking control. If a person wants to leave in a car, the alarm will go off.