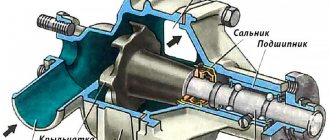
Every detail is important for the smooth operation of a car engine. A special position in the crank mechanism system is occupied by the crankshaft liners. Thin semicircular steel-aluminum plates surrounding the main and connecting rod journals are the outer races of the plain bearings, and the overall performance of the engine depends on their condition.
When is it necessary to replace crankshaft bearings?
Under the conditions of the physical and thermal loads that the crankshaft has to endure, only plain bearings can keep it on the axis and ensure the operation of the crank mechanism. The main and connecting rod journals serve as internal races, and the liners, respectively, serve as external races. The engine block system has a network of oil lines through which engine oil is supplied to the liners under high pressure. It creates a thin oil film that reduces friction and allows the crankshaft to rotate.
Physical wear is the first and main condition due to which the liners have to be changed. No matter how much we would like to avoid wear, the surfaces of the journals and bearings are gradually worn away, the gap between them increases, the crankshaft becomes free to move, and the oil pressure drops sharply. All this leads to engine breakdowns.
Another reason for forced repairs is a situation where the crankshaft liners rotate. Every car owner has heard about such malfunctions, but not everyone knows how and why this happens. A thin plate of the liner is placed in the so-called bed. On the outer walls of the half rings there are special antennae (protrusions), which, after assembly, rest against the end parts of the block or bearing cap.
Sometimes, when certain conditions occur, the antennae are not able to hold the liner and it sticks to the crankshaft journal and rotates. If the crankshaft liners are turned, the engine cannot run. Typical causes of such a breakdown:
- too viscous lubricant, lack of it, abrasive ingress;
- too little interference when installing bearing caps;
- insufficiently viscous lubricant and operation of the motor in overload mode.
Selection of crankshaft liners
Replacing crankshaft bearings
Whatever the reasons why the car owner is forced to disassemble the engine and change the liners, grinding the crankshaft is indispensable. New liners are installed either on a new crankshaft or after grinding it. Even if only one neck is damaged or worn, all of them undergo grinding to the same size.
At the factory, when assembling the motor, standard liners are installed. For VAZ engines, liners are available in 4 repair sizes. Accordingly, grinding the crankshaft can be carried out no more than 4 times. The step between sizes is 0.25 mm. Accordingly, after the first grinding it is necessary to buy inserts marked “0.25”, after the second - 0.5, after the third - 0.75, after the fourth - 1.0. Motors that are installed on GAZ and Moskvich cars have two more borings available, up to 1.25 and 1.50 mm.
The dimensions of the crankshaft liners that need to be purchased can only be calculated by a specialist who grinds the crankshaft. Sometimes it happens that damaged necks require grinding not to the next size, but after one. Inserts are sold only as a set for all main or connecting rod journals.
How to replace crankshaft bearings with your own hands
Considering that to access the crankshaft you will have to completely disassemble the engine, such repairs can only be started if the car owner has the necessary knowledge and skills in this matter. First of all, you need to remove and completely disassemble the motor. This can be done in a garage, but it requires a full set of car keys and other tools, as well as a mechanical winch. To remove the motor, do the following:
- remove the hood and battery;
- drain the oil and coolant;
- remove the engine from attachments: carburetor, starter, generator, fuel pump and cooling system pump, ignition distributor, remove the radiator and cylinder head;
- then unscrew the clutch cover, the nuts of the pillows and remove the block;
- Having placed the engine on the workbench, you should remove: the flywheel, pulley, camshaft drive cover, oil pump drive chain and gear, auxiliary drive shaft, flywheel, and rear cuff holder;
- after the 14 bolts of the pan are unscrewed, the crankshaft itself will become available to us;
- in order to remove it you will need to unscrew the bolts of the five main bearing caps and the bolts of the four connecting rod caps.
By removing the bearing caps, you can immediately notice where the bearings have rotated. It is strongly recommended that you do not remove the covers or remove the crankshaft until it has been seen by a professional. Based on the characteristic signs of uneven wear, a specialist will be able to determine where the displacement or curvature has occurred. To do this, it is necessary that each liner remains in its place.
Is it worth it to install the crankshaft yourself?
A car engine is a rather complex and specific device. Many car enthusiasts successfully carry out its complete disassembly and repair. However, in order to correctly install the crankshaft liners, you must have certain skills. It is better if this work is performed by an experienced mechanic. This is necessary primarily in order to avoid excessive or insufficient tension, which can cause the liners to rotate.
An internal combustion engine is a complex mechanism consisting of hundreds of parts. And each and every one of them is important for the balanced and correct operation of a complex system, to one degree or another. But at the same time, in no case can the degree of importance of each of them be assessed equally. One of the most important elements, of course, is the crankshaft and all its parts that interface with it, which transmits the energy of the burning fuel to the wheels, thereby rotating them. We will further discuss the components of this mechanism, namely the crankshaft liners, which are small half-rings made of soft metal with an anti-friction coating. During long-term operation of the car’s engine, they should be the very first to leave their post, and not the crankshaft journals.
- What are crankshaft repair liners, their types
- Reasons for replacing crankshaft bearings?
- How to determine the wear of the crankshaft liners and help the mechanism?
- How to install liners on the crankshaft - procedure?
- How to choose the right crankshaft bearings?
What are crankshaft repair liners, their types
Essentially, crankshaft bearings are plain bearings for the connecting rods that rotate the crankshaft. This rotation is the result of a micro-explosion in the combustion chambers of the engine cylinders. This system is dominated by high speed and heavy loads, as a result of which it is necessary to minimize the friction of parts, otherwise the engine will simply fail, and instantly. In order for friction to be reduced as much as possible, all significant parts of the internal combustion engine are coated in a so-called “oil film” - a thin micron film, which is ensured by a special lubrication system of the automobile engine. The appearance of a film that envelops metal parts is only possible if the oil pressure is strong enough. And between the crankshaft journal and its bearings there is also a similar oil layer. And only thanks to it the friction force is minimized as much as possible. From this we can conclude that the crankshaft liners represent a certain protection, the effect of which increases the service life of such an important part for the engine.
We recommend: Review of the best station wagon models
To begin with, the crankshaft liners must be divided into two categories:
connecting rod and main. The connecting rod bearings, as we said above, are located between the crankshaft connecting rods and its journals.
The radicals, in turn, play a similar role, but they are located between the crankshaft and the places where it passes through the engine body.
For different engines, factories produce crankshaft liners that differ in their inner diameter. Repair inserts differ from each other and, of course, from new ones installed on a newly released car. Their minimum difference is calculated from a quarter of a millimeter and increases with a similar step. Thus, we have a size range of crankshaft repair liners in increments of 0.25 mm along the internal diameter: 0.25; 0.5; 0.75; 1 mm, etc.
Reasons for replacing crankshaft bearings?
Under conditions of extreme temperature and physical stress that the crankshaft constantly endures, only the crankshaft liners help it stay on the axis, ensuring the operation of the crank mechanism. The main and connecting rod journals operate on the principle of internal races, and the crankshaft liners serve as external races, respectively. The engine block system has a whole network of oil lines through which engine oil is supplied to the bearings under high pressure. It is this that creates the very microscopic film mentioned above, which allows the crankshaft to rotate.
The primary reason for replacing crankshaft bearings is their physical wear . Whatever the desire to protect the liners from wear, physics is physics. The surfaces of the journals of the crankshaft liners wear out over time, increasing the gap between them, which leads to free movement of the crankshaft and less oil supply due to a sharp decrease in pressure. And this already leads to breakdowns of car engines.
The second reason for forced repairs is the rotation of the crankshaft liners . Probably every car owner has heard about such situations, but, alas, not everyone knows about the reasons for this state of affairs. So how and why does this happen? The thinnest plate of the liner goes into a makeshift bed. The outer walls of the half rings are framed by special protrusions, which in the new engine rest against the front parts of the block. Under certain conditions, the antennae simply cannot withstand the liner, and it begins to rotate, sticking to the crankshaft journal. If this happens and the liner turns, the engine simply stops functioning. Typical causes of such failure are:
- extreme viscosity of the lubricant, penetration of abrasive compounds into it or its disappearance altogether;
— insufficient tension of installed bearing caps;
- too thin lubricant and operation of the engine in constant overload modes.
How to determine the wear of the crankshaft liners and help the mechanism?
Once it has happened that engine repair is already inevitable, the question arises of how to further determine the wear of the crankshaft liners and what size will they need to be purchased for the next replacement? Basically, a micrometer is used for measurements, but it is still calculated quite accurately visually, as they say, “by eye.” Immediately evaluate the possibility of the next crankshaft boring.
Immediate replacement is necessary if the crankshaft bearings are rotated. An indicator of this problem will be a loud knocking of the crankshaft and constant attempts by the engine to stall. If the necks jam, then you won’t be able to drive any further. In any case, a detailed inspection of the mechanisms should be carried out. If you find wavy potholes on the journals that you can easily feel with your hands, then you cannot avoid boring the crankshaft and then installing repair liners of the appropriate size. We strongly recommend that you purchase inserts only after boring them. After all, a lot of wear can lead to carrying out this procedure by one, or even two sizes.
How to choose the right crankshaft bearings?
Whatever the reason for disassembling a car engine and replacing the crankshaft liners, grinding it is indispensable. New liners are mounted either on a new crankshaft or on an already bored one. Even if only one neck is subject to damage, then all the others must undergo grinding adjustments for it.
When assembling the engine on a conveyor, standard crankshaft liners are installed. For example, for VAZ models, liners are produced in four repair variations. Consequently, it will be possible to bore the crankshaft no more than four times. For engines installed on GAZ and Moskvich, fifth and sixth borings of up to 1.25 and 1.50 mm are available.
The dimensions of the crankshaft liners are determined only by the person who bored the crankshaft. Depending on the depth of damage to the necks, grinding may go two sizes forward. Inserts are sold as a set for all, both for main and connecting rod journals.
Subscribe to our feeds on social networks such as Facebook, Vkontakte, Instagram, Pinterest, Yandex Zen, Twitter and Telegram: all the most interesting automotive events collected in one place.
Required special tools and accessories:
- micrometer;
- passimeter;
- torque wrench with 15, 17 and 19 mm heads;
- probe plate 0.08 mm thick.
When deciding whether to replace the bearing shells, it should be borne in mind that the diametric wear of the bearing shells and journals of the crankshaft does not always serve as a determining criterion. During engine operation, a significant amount of solid particles (wear products of parts, abrasive particles sucked into the engine cylinders with air, etc.) is embedded in the antifriction layer of the liners. Therefore, such liners, often having insignificant diametrical wear, can cause further accelerated and increased wear of the crankshaft journals. It should also be taken into account that connecting rod bearings operate under more severe conditions than main bearings. The intensity of their wear is slightly higher than the intensity of wear of the main bearings. Thus, to resolve the issue of replacing bearings, a differentiated approach is required in relation to the main and connecting rod bearings.
In all cases of satisfactory condition of the surface of the antifriction filling of the main bearing shells, the criterion for the need to replace them is the size of the diametrical clearance in the bearing.
We recommend: Fuel supply system for a gasoline (carburetor) engine
When deciding whether to replace connecting rod bearing shells, you must be guided by the following rule.
If the connecting rod bearing shells at the time of disassembling or repairing the engine have worked for a time corresponding to a vehicle mileage of 45,000 km or more, they should be replaced with new ones, regardless of the condition of the surface and the degree of wear. In such cases, liners of normal or first repair sizes are suitable for replacement. Preventative replacement of liners allows you to maintain the connecting rod journals in a state of preservation for a long time.
When assessing the condition of the liners by inspection, it should be borne in mind that the surface of the antifriction layer is considered satisfactory if there are no scuffs, chipping of the antifriction alloy and foreign materials (inclusions) pressed into the alloy. The dark color of the pouring surface is not a rejection sign.
To replace worn or damaged bearings, spare parts include main and connecting rod bearing shells in standard and six repair sizes. Repair size liners differ from normal size liners by being reduced by 0.05; 0.25; 0.50; 0.75; 1.00 and 1.25 mm internal diameter. The liners are sold as a set, in quantities required for one engine.
After replacing the liners, either with or without simultaneous regrinding of the crankshaft journals (and for the main journals also if the old liners are used in the engine), be sure to check the diametrical clearance in each bearing. This will allow you to check the correct choice of repair inserts.
You can check the diametrical clearance in a bearing by measuring the diameters of the crankshaft journal and liners (in pairs) of a given bearing, followed by simple calculations. The diameter of the bearing is measured with the liners inserted and the bearing cover bolts tightened with the required force.
The diametrical clearances in the main bearings should be in the range of 0.025-0.082 mm, and in the connecting rod bearings - in the range of 0.025-0.076 mm.
You can also check the diametrical clearance in the bearing using a feeler plate placed between the shaft journal and the liner.
The plate for both connecting rod and main bearings should have a thickness of 0.08 mm, a width of 13 mm and a length 5 mm less than the length of the bearing. The plate is cleaned along the edges with a whetstone, lubricated with engine oil, and placed on the surface of the liner so that its long side is located along the longitudinal axis of the bearing.
Rice. Laying the control plate-feel in the connecting rod bearing: a - plate-feel
When checking, tighten the bolts of the cover of only the bearing in which the probe plate is placed, while the bolts of the covers of the remaining bearings remain untightened. The bolts must be tightened carefully, turning the crankshaft from time to time.
If significant resistance is felt when turning the crankshaft by hand on the flywheel, the diametrical clearance in the bearing is within acceptable limits. If the crankshaft turns almost as easily as without the control plate, the clearance in the bearing is greater than normal.
In some cases, the required diametrical clearance in the bearing can be achieved without regrinding the journal, only by using repair liners reduced by 0.05 mm. In all other cases, the required clearances are obtained by grinding the journals and installing repair liners in the bearings.
If, as a result of repeated grinding, the diameters of the crankshaft journals are reduced so much that the liners of the last repair size turn out to be unsuitable, then during the next repair it is necessary to assemble the engine with a new shaft. For such a case, spare parts kit 408-1000107 is supplied, consisting of a crankshaft from a set of normal-sized bearings.
Thin-walled replacement liners for connecting rod and main bearings of the crankshaft are manufactured with high precision. The required value of the diametrical clearance in the bearing is ensured only by the proper diameters of the crankshaft journals obtained during grinding. Therefore, when repairing an engine, the liners are replaced without any adjustment operations and only in pairs. Replacing one earbud from a pair is not allowed. It also follows from the above that in order to obtain the required diametrical clearance in the bearing, it is strictly forbidden to saw off or scrape the joints of the bearing liners or caps, solder the joints of these parts with babbitt, or install gaskets between the liner and its bed.
Failure to follow these instructions leads to the fact that the correct geometric shape of the bearings will be disrupted, the heat removal from them will deteriorate and the liners will quickly fail. But what is more dangerous is that new bearings of repair sizes cannot be installed in the future in bearings with sawed off or scraped caps. At the same time, bearing caps damaged by mechanical adjustment cannot be replaced with new ones, since at the factory they are processed together with the cylinder block and connecting rod. Since the bearing caps are not interchangeable, they are not supplied as spare parts, and therefore an engine with damaged caps cannot be repaired later.
When installing connecting rod and main bearings, you need to ensure that the locking protrusions a at the joints of the liners fit freely (by hand) into the sockets b in the cover (or body) of the bearing.
Rice. The fixing protrusion of the liner and its socket in the bearing cover
After replacing the connecting rod or main bearing shells (or both) and assembling the engine, you must follow the break-in rules.
What are liners for internal combustion engines
An internal combustion engine is indeed a very complex device; its design was achieved thanks to the engineering mind of many designers and motorists.
It consists of a huge variety of different parts, the purpose of which is to best help the engine operate. Each detail has its place and its shape. However, the expression - there is no limit to perfection, is also relevant for the engine. The rotation of wheels or shafts in any unit, not only in a car, is ensured by parts such as bearings. These can be either rolling bearings or plain bearings. The latter are more often used in internal combustion engines for such a rotating part as the crankshaft.
The designers, working on the perfection of the engine, made a proposal to replace this bearing with a liner. This is the same bearing, but very modified. It is a steel sheet, which, thanks to calculations, has a special shape and size. It is lubricated with an antifriction compound. This is the same bearing in essence, but not in shape.
The liner is installed in a certain place, which is also called the bed, and is strictly fixed. The surface on which the liners are installed must be prepared; the holes for the lubricant on the liner and on the beds must match.
To prevent the liners from turning and moving out of their places, there are special antennae. In addition, the interference must be structurally specified for each liner.
The liners are divided into the following types: connecting rod and main. The connecting rods are located between the crankshaft connecting rod and its journal. The radicals play the same role, but their place is in the passage of the crankshaft through the engine housing.
Each engine is provided with its own liner size, which is determined by the internal diameter. Additionally, there is a size difference between new liners and repair liners. Conventionally, with each repair we add a step plus 0.25 mm. Indeed, despite the lubrication and accuracy of installation, the liner wears out and the surface of the neck where it is installed wears out.
At the same time, the clearance increases, the crankshaft has a larger stroke, the pressure decreases and little oil is supplied. This is already an emergency situation.
Sometimes it is necessary to change the liner because it rotates. This occurs due to breakage of the antennae. This happens in case of poor quality or poorly selected lubricant or in case of poor selection of liner tension.
Usually, engine repairs and replacement of liners, if you do not have sufficient experience in disassembling and assembling the engine, are carried out by a service station. The main thing is the correct selection and quality of liners.
Read more about inserts on the website.
Source
Questions about choosing and replacing crankshaft liners
When selecting sliding bearings, it is necessary to take into account the engine model, wear of associated parts and the presence of repair liners. As a rule, liners are made for one model range or even one engine model, so they cannot be replaced with parts from another engine (with rare exceptions). Also, you cannot use liners without taking into account the wear of the crankshaft journals, otherwise the repair will result in even bigger problems.
Before choosing the repair size of bearings, you need to determine the wear of the crankshaft journals and other associated parts (beds, connecting rod heads, although they are less subject to wear). Usually, the wear of the journals occurs unevenly, some of them wear out more intensively, some less, however, for repairs, a set of identical liners is purchased, so all journals must be ground down to the same size. The choice of the value to which the crankshaft journals will be ground depends on the availability of bearings of certain repair sizes suitable for this particular engine. For engines with low mileage, repair sizes of +0.25 or +0.5 are selected; for engines with significant mileage, it may be necessary to grind down to repair size +1.0; in older engines, even more - up to +1.5. Therefore, for new engines, liners are usually produced in three or four repair sizes (up to +0.75 or +1.0), and for old engines you can find liners up to +1.5.
The repair size of the crankshaft liners must be such that when assembling the engine, a gap remains within 0.03-0.07 mm between the crankshaft journal and the bearing surface. With a smaller gap, there is a high risk of jamming; with a larger gap, the crankshaft runout increases, the wear rate of parts and the overall noise of the power unit increases.
With the correct choice of sleeve bearings for the crankshaft, the engine, even with high mileage, will operate efficiently and effectively in various modes.
The internal combustion engine works by rotating the crankshaft. It rotates under the influence of connecting rods, which transmit forces to the crankshaft from the translational movements of the pistons in the cylinders. In order for the connecting rods to work in tandem with the crankshaft, a connecting rod bearing is used. This is a plain bearing in the form of two half rings. It ensures the ability to rotate the crankshaft and long-term engine operation. Let's take a closer look at this detail.
Crankshaft bearings: faults and selection of new parts (video)
One of the most important elements of the internal combustion engine we are used to is the crankshaft. Due to it, the energy from fuel combustion can be transferred to adjacent elements and ensure the rotation of the wheels. The key point here is that the shaft rotates. At first glance, nothing special, but any engineer will confirm that working with rotating elements requires a special approach. After all, it is necessary to provide rotation for vibrations, as well as heating due to the action of friction forces. The crankshaft liners, which are half rings with the so-called, are very helpful with this. anti-friction coating. At first glance, this is a very simple thing, but a competent car enthusiast needs to know everything about these crankshaft elements.
You will learn about the structure of the liners, their malfunctions, as well as the replacement method from the material Avto.pro.
More details about the part
Liners are essentially sliding bearings, which are needed by the connecting rods that rotate the crankshaft, and individual parts of the shaft itself. Rotation is ensured by a mixture of air and fuel burning in the engine cylinders. Of course, the engine operates under heavy loads and strives to spin the crankshaft as much as possible. The problem of possible friction of parts is especially acute here, and the emergence of the so-called. dry
(oil-free)
friction
can damage the engine very quickly. The solution is simple: ensure that a thin oil film is always present. It turns out that the crankshaft liners are only a kind of protection that maintains an oil film in friction areas. Ideally, the liners should fail for adequate reasons. Let us immediately note that the crankshaft liners are as follows:
- Indigenous
. Such liners are placed between the shaft itself and the places where it passes through the engine housing; - Connecting rods
. They are installed between the connecting rods and journals of a car crankshaft.
As mentioned above, crankshaft bearings do not look like classic roller or ball bearings - they look like ordinary half rings. The fact is that ordinary bearings will not withstand the loads generated by the car’s power unit. Only some low-power motors have rolling bearings installed, while the most common are plain bearings. To summarize, the purpose of the crankshaft bearings is as follows:
- Ensure normal transmission of forces and moments that arise during operation of the power unit;
- Minimization of friction forces that arise at the contact points of the crankshaft, cylinder block supports, and connecting rods;
- Centering of parts, correct positioning;
- Oil distribution.
Description of crankshaft bearings
All crankshaft main and connecting rod journals have their own dimensions; we are talking about the parameters that the journals take after the grinding process. The dimensions of these elements must fully correspond to the dimensions of the crankshaft repair liners. Accordingly, when purchasing such spare parts, you must take into account the parameters of your vehicle, because each individual engine has its own dimensions.
Exhausted crankshaft bearings
For example, if you own a classic VAZ car, you should keep in mind that domestic cars have four different sizes of liners. This means that the crankshaft can, in principle, be bored no more than four times. You also need to take into account that the crankshaft liners also have an outer size, which never changes, but the inner one can be adjusted due to an increase in the thickness of the elements.
Purpose of the inserts
In fact, the crankshaft main bearings, regardless of the markings, act as bearings designed to improve the sliding of the connecting rods. Connecting rods, as you know, are designed to rotate the crankshaft under the influence of a micro-explosion of the combustible mixture in the combustion chambers of the engine. Since the elements periodically wear out, the motorist must promptly remove and replace them, which should also be accompanied by boring the shaft.
It is no secret that when the engine is running, internal components are subjected to high loads and rotation speeds. This means that the motor simply needs to reduce friction, otherwise the unit may fail almost immediately. To ensure that the friction force is significantly lower, all the necessary components inside the motor operate in a micron film, which is oil.
Worn and new liner
This layer, which envelops the metal components of the unit, is formed only with sufficient pressure of the working fluid. In particular, the film should always be between the crankshaft journal and the liner, as a result of which the friction index is not as high as it could be. Accordingly, the liners, which are made of metal, provide reliable protection that allows you to increase the service life of the shaft as a whole.
Design
It would seem that the crankshaft liner is a common part, but its manufacture is carried out using several different metals.
Accordingly, the liner consists of several layers, which we will consider below:
- the first layer is made from copper, its percentage can be from 69 to 75%;
- the second layer is made from lead, its percentage ranges from 21 to 25%;
- third layer - tin, about 2-4%.
In general, the total thickness of the liner is 250-400 microns. It should be noted that sometimes not copper, tin and lead are used to make the liner, but a specialized aluminum alloy. Labeling in this case will depend solely on the manufacturer.
Kinds
As for the types, the marking here will depend on the type of component.
In general, crankshaft bearings are divided into several groups:
- Indigenous. Regardless of the marking, the main bearings perform similar functions. They are mounted between the crankshaft and the place where this shaft passes through the engine housing.
- Connecting rods. The connecting rod components are located directly between the connecting rods and the shaft journals.
In principle, bearings, both connecting rod and main, are produced for each type of engine, but they all differ in internal diameter. Depending on the engine model, the diameters of the elements will be different, even for the same engine. As a rule, the difference in diameter, that is, the pitch, is 0.25 mm. This means that the size range of parts is compiled as follows: 0.25 mm, 0.5 mm, 0.75 mm, etc.
Causes and symptoms of malfunction
Inserts can fail for a number of reasons. Of course, the service life of the liners is very long, so car enthusiasts are not so often faced with the need to replace them. But if a breakdown does occur, you need to act immediately
. It is recommended to immediately contact a service station, where the engine can be inspected by a specialist. However, the car enthusiast can extend the service life of the liners. Here are the reasons why these parts may fail:
- Entry of foreign bodies;
- Metal fatigue;
- Wear due to tin penetration;
- Surface corrosion;
- Mud erosion;
- Insufficient lubrication;
- Erosion due to cavitation;
- Misalignment.
As you can see, there are quite a few reasons for failure. Let's look at them in order. Regarding
the first reason
: if foreign bodies or dirt get on the working surface of the liner, further wear of the liner occurs at an accelerated rate.
It is strictly recommended to clean the system and replace the bearings if they are critically worn. Regarding the second
: fatigue can be caused by both long-term use and excessive load on the part.
You should be wary of installing low-quality liners, not burning enough fuel in the chambers, and improperly tuning the engine. In addition, it makes sense to check the shape of the shaft journal. Regarding the third
: if the liner moves in its seat, in places where the tin layer is significant, it can wear out much more.
Inspection, cleaning work and adjustments are recommended here. Regarding the fourth reason
: accelerated wear of a part and the appearance of traces of corrosion on it are often associated with the use of low-quality motor oil.
At the same time, the failure of the liners due to mud erosion ( the fifth item
on the list) stands out. Everything seems simple: due to the accumulation of dirt on the liners, and in other cases in the area around the oil holes, the parts wear out faster. In fact, there are several reasons why so much dirt appears in the system. It is recommended to change the oil, as well as oil and air filters.
One of the most common reasons why any liners have to be changed more often than usual lies in the low quality of lubrication ( sixth point
list).
Due to dry friction, the liners can wear out very badly. It is recommended to check the lubrication system of the unit, and also make sure that the bearings are supported and the overall integrity of the shaft. Regarding the seventh reason
: check if there are any antifreeze impurities in the engine oil from a leak.
It also makes sense to make sure the liner clearances are correct. In other cases, erosion due to cavitation can be caused by frequent fuel detonation and too high a flow rate of engine oil in the system. The liner itself will have clearly visible washout points. And finally, regarding the eighth reason
: if the liner wears out a lot closer to the edge, you need to check the correct location of the axes of the liners and the neck.
It is often possible to detect a broken liner only at the very last moment. It is for this reason that car manufacturers recommend periodically diagnosing the engine, changing bearings, and optionally grinding the crankshaft journals. If you hear a dull metallic knock in the engine area, there is a critically high probability that its source is a shaft with worn bearings. As practice has shown, the knock of connecting rod bearings is highly sharp and can be heard very well if you hold idle speed and then sharply accelerate.
Connecting rod liner
Dual mass flywheel. What is it, how does it work? Breakdowns and repairs, there will be a video version
When boring the connecting rod bearings, it is necessary to maintain the distance between the centers of the holes in the upper and lower heads of the connecting rod within 202 in. mm.
When examining the connecting rod bearings after experiment No. 4, it turned out that their antifriction layer was covered with a dark brown film, which, when pressed, separated from the base metal in some places, which indicates its weak connection with this metal.
Gaskets made of sheet brass are installed between the halves of the connecting rod bearings. Oblique gaskets are not allowed for installation.
The change in the surface structure of the connecting rod bearings is also characterized by the refinement of the grains, which are oriented in the direction of rotation of the shaft. The change in hardness in a thin babbitt layer is insignificant; the difference in hardness across the cross section does not exceed 1 5 units. A thin layer of babbitt is more uniform, less susceptible to shrinkage during running-in, and more durable than a thick layer.
| Change in mileage ( L until repeated cleaning of spark plugs as the overall duration of their operation increases. |
The wear on cylinder liners and connecting rod bearings is approximately the same. As for the wear of the piston rings, with the exception of one engine, the data of which were discarded during averaging, the wear is also approximately equal.
The upper and lower halves of the connecting rod bearings of four-stroke engines operate under different conditions. The lower half of the liner is loaded by the inertial forces of the translationally moving and rotating masses of the connecting rod, acting on the liners for a much longer time - about 75% of the operating cycle time.
Annular grooves on the working surfaces of the main and connecting rod bearings make it possible to ensure continuous supply of lubricant to these units, but they divide the working surface of the bearing into two parts, making two narrow ones in each support instead of one wide one. This significantly reduces the bearing's ability to provide sufficient load-bearing capacity.
Before assembly, lubricate the surfaces of the connecting rod bearings, pistons, piston rings and cylinders with engine oil. The pistons in the assembly with connecting rods are installed in accordance with the serial numbers of the cylinders indicated on the piston heads or connecting rods.
| The influence of temperature on the corrosion of alloys - tin babbitt and cadmium-nickel. |
The table shows average data only for the lower frame and upper connecting rod bearings.
The corrosive activity of oils is assessed by the weight loss of a set of connecting rod bearings and the condition of their working surfaces.
The corrosive activity of oils is assessed by the weight loss of a set of connecting rod bearings and the condition of their working surfaces.
Тс - coefficient equal to 0 02 for steel bodies of connecting rod bearings without reinforcements, 0 05 for tin bronze bodies, for connecting rod bearings and main bearings without reinforcements; when the liner body is made of aluminum, the same values can be maintained, but strengthening of the liner bodies must be provided.
Conducted laboratory and operational tests show that BT babbit can be used for filling the main and connecting rod bearings of gas generator and carburetor automotive engines, successfully replacing high-tin babbitt in some cases.
A little about the selection of liners
Selecting bearings on your own is a rather risky business, since it will be difficult to choose a part that does not quite fit the crankshaft of your car. The fact is that it is important for a potential buyer to take into account not only the compatibility of the spare part with the car, but also the condition of some of its components. In this case we are talking about the crankshaft
, which will also have to be polished. So, you often cannot do without turning to an expert who will disassemble the engine and carry out diagnostics. It is likely that you will have to install repair liners of large thickness. Such details can be searched using the following parameters:
- Vehicle data;
- VIN code;
- Code for a suitable insert.
The easiest way to search is in online store catalogs. There, a car enthusiast will be able, for example, to find original bearings and, based on them, select repair ones. If the old liners have simply worn out due to long-term use and significant loads, there is a possibility that troubleshooting the crankshaft will not be necessary. From this it follows that it will be somewhat easier to select suitable earbuds.
If you want to do as much work as possible yourself, then first you will have to determine the clearance indicator. To do this, you need a torque wrench and a special calibration wire. If the gap is large, this indicates the need to bore the shaft and further install repair liners
. Work with the shaft can only be entrusted to professionals. The size of suitable inserts can be determined with a micrometer. You can also find information useful for finding earbuds in technical manuals.
Operating conditions of engine liners
Thanks to the formation of an oil film, local concentration of loads is prevented. But if certain conditions are created, the normal hydrodynamic regime for the bearing will be changed to mixed. This can happen if there is insufficient oil pressure in the engine, the unit experiences enormous loads, the oil viscosity is low, the lubricant overheats, and there is increased roughness on the surface of the shaft and bearing. Also, mixed mode can occur due to dirty oil, deformation and geometric defects of bearings.
Conclusion
Crankshaft bearings are simple and, at first glance, incredibly durable elements of modern engines. Experience has shown that you only encounter the need to replace liners once or twice during the entire period of using a car. But don’t think that this is the part that shouldn’t break. In contrast, bearings are sometimes called crankshaft protectors because they are one of the first to absorb the impact. If you are faced with the need to replace the earbuds, do not hesitate. Contact an engine specialist and trust him to do everything, or try to do some of the work yourself.
You can read the full version of the article here.
Source
Crankshaft liners: purpose, types, features of checking and replacement
The engine is a complex multi-component mechanism, each part of which ensures the correct and balanced operation of the entire system. At the same time, some play a big role, while others do not have such importance. The crankshaft, as well as all the elements related to it, is the most important part of the engine. It ensures the rotation of the wheels by transferring the energy of burning gasoline. Crankshaft liners are small parts in the shape of half rings, made of medium-hard metal and coated with a special anti-friction compound. During long-term use of the car, they are subject to severe wear, which makes it necessary to purchase and install new parts.
Description
The crankshaft bearings act as plain bearings to ensure rotation of the crankshaft. This process occurs as a result of combustion of fuel in the cylinder chambers. Active friction of parts caused by increased loads and high speed conditions can damage the motor. To prevent such a situation and reduce the degree of friction, all the most important components are coated with a thin micron layer of oil. This function is assigned to the engine lubrication system, and a film is formed on existing parts only under conditions of high oil pressure. A layer of lubricant also covers the contact surfaces of the bearings and the crankshaft journal. This significantly reduces the generated friction force.
Selection of pistons and bearing shells (HR15DE and HR16DE)
(Selection for MR16DDT
Description
| Selectable gap | Selectable part | Item of selection | Selection method |
| Between the cylinder block and the crankshaft | Main bearings | Size group of the main liner (Insert thickness) | Selected in accordance with the size groups of the cylinder block (the internal diameter of the bed in the cylinder block) and the crankshaft main journals (the external diameter of the journal) |
| Between the crankshaft and connecting rod | Connecting rod bearings | Size group of connecting rod bearing shells (thickness of shells) | Selected according to the diameter of the connecting rod bearing bed and the diameter of the connecting rod journal. |
• The size group number is stamped on each part and corresponds to a specific size range of the new part. For used parts this size group designation is not valid.
• Repaired or used parts must be micrometered. Comparing the tabular data with the measurement results, determine the size group of the part.
• Information about standards, methods of measurement and selection of parts is given in the text of this manual.
Selection of connecting rod bearings
A) For a new connecting rod and a used crankshaft:
1. Determine the diameter size group using the stamp (C) on the side surface of the lower head of the connecting rod for the line in the “Selection of connecting rod bearing” table.
A. Oil hole, B. Cylinder number, C. Stamp. D. Front label
• Determine the size group of the connecting rod journal stamped on the front cheek of the crankshaft (B) for the column in the table “Selection of connecting rod bearing”
A. Dimensional group of the molar neck (No. 1 - 5 from left to right). B. Size group of the connecting rod journal (No. 1 - 4 from left to right).
3. Find the symbol at the intersection of the corresponding row and column in the “Selection of connecting rod bearing” table.
4. Using the received symbol, select the connecting rod bearing in the table - “Size groups of connecting rod bearings”.
B) For used crankshaft and connecting rods:
1. Measure the diameter of the bed of the connecting rod bearings and the connecting rod journal of the crankshaft.
2. Use the measured values for the “Selection of connecting rod bearings” table.
3. Based on the results of measuring the diameter of the journal, determine its size group in the column “Diameter of the connecting rod journal” of the table “Table for selecting the thickness of connecting rod bearings”.
4. Select a connecting rod bearing of the same size group.
| Label | A | IN | WITH | D | E | F | G | N | J | TO | L | M | N | |
| Label | Bed diameter, mm Neck diameter, mm | 43,000- 43,001 | 43,001- 43,002 | 43,002- 43,003 | 43,003- 43,004 | 43,004 — 43,005 | 43,005- 43,006 | 43,006- 43,007 | 43.007- 43.00V | 43,008- 43,009 | 43,009- 43,010 | 43,010- 43.011 | 43,011- 43.012 | 43,012- 43,013 |
| A | 39,971-39,970 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 |
| IN | 39,970 — 39,969 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| WITH | 39,969 — 39,968 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 |
| D | 39,968 — 39,967 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 |
| E | 39,967 — 39,966 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 |
| F | 39,966-39,965 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 |
| G | 39,964-39,963 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 |
| N | 39,963 — 39,962 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| J | 39,962-39,961 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 46 |
| TO | 39,961 -39,960 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 |
| L | 39,960 — 39,959 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 |
| M | 39,959 -39,958 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 5 |
| N | 39,958-39,957 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 5 |
| R | 39,957 — 39,956 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| R | 39,956-39,955 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 56 |
| S | 39,955 — 39,954 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 56 | 56 |
| T | 39,954-39,953 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 56 | 56 | 56 |
| U | 39,953-39,952 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 56 | 56 | 56 | 56 |
Application of inserts for repair size groups
In the case when the use of standard size group bearings does not ensure the specified oil clearance value, repair size group bearings (US) should be used. Measure the crankshaft beds (with the repair size group bearings installed) and grind the crankshaft main journal to obtain the nominal oil clearance value.
When grinding the neck for repair liners, it is necessary to ensure a fillet radius (A) equal to 0.8-1.2 mm.
Selection of main liners
A) For a new cylinder block and used crankshaft:
1. The horizontal lines in the table “Selection of the thickness of the main liners” correspond to the size group of the main liner bed, which is stamped on the left wall of the cylinder block.
| A. Basic stamped mark, B, Corrected stamped mark. |
The arrow points to the front of the engine.
2. The columns in the table “Selection of the thickness of the main bearings” correspond to the size group of the main journals stamped on the front cheek of the crankshaft.
A. Size group of the molar neck (No. 1 - 5 from left to right). 3. Size group of the connecting rod journal (No. 1 - 4 from left to right).
3. Select the size group of the liner at the intersection point of the selected row and the column of the table “Selection of the thickness of the main liners.”
B) For used cylinder block and crankshaft:
1. Measure the diameter of the bed of the main liners and the diameter of the main journals.
2. Using the measured value, find the line “Bed diameter of the main liners” in the table “Selection of the thickness of the main liners”.
3. Using the measured value, find the column “Main journal diameter” in the table “Selection of the thickness of main liners”
4. Select the size group of the insert at the intersection point of the selected row and table column
| Label | A | IN | WITH | D | E | F | G | N | J | TO | L | M | N | R | R | S | T | And | V | W | |
| Label | Bed diameter, mm \ Neck diameter, mm | 51,997- 51,998 | 51,998- 51,999 | 51,999- 52,000 | 52,000 — 52,001 | 52,001 — 52,002 | 52,002- 52,003 | 52,003 — 52,004 | 52,004 — 52,005 | 52,005 — 52,006 | 52,006 — 52,007 | 52,007 — 52,008 | 52,008 — 52,009 | 52,009 — 52,010 | 52,010- 52,011 | 52,011 — 52,012 | 52,012- 52,013 | 52,013- 52,014 | 52,014- 52,015 | 52,015- 52,016 | 52,016- 52,017 |
| A | 47,979 — 47,978 | 0 | 0 | WITH | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 01 | 01 | 01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 |
| IN | 47,978 — 47,977 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 01 | 01 | 01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 |
| WITH | 47,977 — 47,976 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 01 | 01 | 01 | 1 | 1 | i | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 |
| D | 47,976 — 47,975 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 01 | 01 | 01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 |
| E | 47,975 — 47,974 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 01 | 01 | 01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 |
| F | 47,974 — 47,973 | 0 | 0 | 01 | 01 | 01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| G | 47,973 — 47,972 | 0 | 01 | 01 | 01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 |
| N | 47,972 — 47,971 | 01 | 01 | 01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 |
| J | 47,971 — 47,970 | 01 | 01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 |
| TO | 47,970- 47,969 | 01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 |
| L | 47,969 — 47,968 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 |
| M | 47,968- 47,967 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| N | 47,967 — 47,966 | 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 |
| R | 47,966 — 47,965 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 |
| R | 47,965 — 47,964 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 |
| S | 47,964 — 47,963 | 12 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 5 |
| T | 47,963 — 47,962 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 5 |
| U | 47,962 — 47,961 | 2 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| V | 47,961 — 47,960 | 2 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| W | 47,960 — 47,959 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Application of inserts for repair size groups In the case when, when using liners of standard size groups, the specified value of the oil gap is not ensured, liners of repair size groups (US) should be used. Measure the beds of the connecting rod bearings (with the bearings of the repair size group installed) and grind the crankpin journal of the crankshaft to obtain the nominal value of the oil clearance. When grinding the neck for repair liners, it is necessary to ensure a fillet radius (A) equal to 0.8-1.2 mm. |
Types and sizes
VAZ crankshaft liners act as protective elements that prevent premature wear of mating parts. Depending on their location, they are divided into two types: main and connecting rod. The latter, as mentioned earlier, are located on the journals of the shaft, the main ones are located on the crankshaft at the point where it passes through the internal combustion engine and have a similar purpose. Different types of power devices require the use of appropriate elements; first of all, the internal diametrical size must be selected.
Repair parts both differ from each other and have significant differences compared to the new elements that are equipped with new cars at factories. The parameters differ by at least a quarter of a millimeter; all subsequent options go through a similar step.
How to find out the repair dimensions of VAZ engine parts
The power unit of any domestic car wears out sooner or later.
It is difficult to determine what dictated this, but the fact remains that a VAZ engine cannot live until the complete death of the car itself without a single repair. As you know, the same car can easily change a couple of owners in a year of operation, and everyone is trying to do something. But how can you find out whether the VAZ engine has been repaired? For this purpose, the manufacturer provides for the application of marks on various organs. These are, in a way, generally accepted standards that make life easier for the next owner of the car being repaired. To begin with, you need to decide which engine components need to be repaired. To be honest, there are not so many of them, but sometimes getting to these very marks is not at all easy. In addition, it is advisable to look at their photographs, because the sizes leave much to be desired.
Crankshaft
The main parts of the power unit are pistons. They serve to transfer the energy of the explosion of the combustible mixture to the crankshaft. The latter has journals to which the connecting rods are attached. This is done using a lid, like a clamp. Between the crankshaft journals and connecting rods there are liners made of steel-aluminum alloy. Thus, they are softer than other mating parts and wear out with minimal damage. Here the liners act as piston rings between the cylinder and the piston.
A sure sign of wear of the main and connecting rod bearings is a drop in pressure in the lubrication system, unless, of course, there are other visible reasons for this. Sometimes, to achieve the desired result, it is enough to simply replace them, without grinding the crankshaft journals.
Standard liners have a fixed thickness. The repair ones are thickened in increments of 0.25 mm, which allows, in case of repair, to grind off this thickness from the crankshaft journal. There are cases when the connecting rod journals need repair, but the main journals do not. The opposite cases also occur, but they are very rare. The degree of repair is indicated by marks marked on the counterweights on the side of the camshaft drive gear. If they are not there, then measurements can only be made using a micrometer with appropriate measurement limits.
Pistons
Determining the class of pistons is much easier than following the procedures described above. To do this, just remove the cylinder head and look at the bottom size. A piston size chart is not that hard to find. But don't delude yourself. There are known cases when, for example, instead of 76.4, 76.8 was stuffed on the bottom. In principle, this size does not exist on VAZ engines at all.
To check the achieved result, it is advisable to look at the lower part of the cylinder block, where the oil pan is attached. It has something like “B2” stamped on it. This indicates that the pistons are of the second size. Pistons are mass produced, after which they are measured and divided into classes. Therefore, it is not necessary that such an engine has been overhauled, because the parts could have been installed on it at the factory.
Each class of pistons corresponds to a class of pins, which are selected by color.
Conclusion
Well, a short course has been completed on the topic of how to determine the repair dimensions of parts of the crank mechanism, as well as the piston group. If these marks are not available, then the only way is to take measurements using a bore gauge and micrometers. Here you have to be very meticulous, since the count is in microns...
Purpose
The crankshaft is constantly exposed to high physical and thermal loads during operation, connecting rod bearings hold it on the axis, while the functioning of the crank section is supported only by the elements indicated above. The mechanism of action of the journals is represented by internal races; as a result, the crankshaft liners are external. Lubricant is supplied to them through a special oil pipeline network in which the liquid moves under high pressure. This creates the thinnest film that is so necessary for the crankshaft.
Causes of failure
Structural damage and wear during operation are the most common reasons for replacing parts. Despite the regular supply of lubricant and careful operation of the motor, this process is inevitable. Over time, the surface of the journals becomes thinner, the free space between them becomes larger, because of this the crankshaft acquires free movement, the oil pressure decreases and, as a result, its supply decreases. All this causes premature failure of the entire engine system.
Scrolling is the second reason for repair work. Many people have heard about this or dealt with this problem on their own, but not all car owners know why this situation arises. Connecting rod bearings have thin plates that fit into a special bed. In this case, small protrusions are placed along the entire outer surface of the half rings; they should come into contact with the front part of the block, as is the case in new motors. Some conditions reduce the resistance of the antennae in relation to the liner; it sticks to the crankshaft journal and rotates. In such a situation, engine operation stops. It is worth noting the most common reasons for its development:
- the operation of the motor is associated with constant exceeding of the established loads;
- the lubricant has too liquid a structure;
- bearing caps are installed with low interference;
- lack of oil, its excessive viscosity or the presence of abrasive compounds in the composition.
Connecting rod and main bearings - how to determine wear
The crankshaft of the power unit during operation is influenced by temperature and mechanical influences. The design of the crank mechanism is supported by liners. The latter act as sliding bearings. The elements are made of metal and look in the shape of an even geometric half ring. Since this part bears an increased load, the manufacturer protects it with an additional layer on the surface - an anti-friction coating.
When elements wear out while the engine is running, a knocking noise may occur.
The main rotation parts in an internal combustion engine are secured and operated using these elements. All of them may differ in design and purpose. The main bearings are located inside the engine compartment. The main task of these elements is to fix the crankshaft and facilitate its operation. Parts are made in the shape of half rings that cover the crankshaft journals. This type of liners can be called a crankshaft support inside the engine block. When elements wear out while the engine is running, a knocking noise may occur.
The connecting rod elements are installed in the lower head of the connecting rods to ensure their rotation. For these parts, the liners play the role of support. The crankshaft thrust rings are located in the same place, which prevent axial movement. This type of liner is made of a multilayer structure. It is based on a steel plate with an anti-friction coating.
Another sign of bearing wear is a decrease in oil pressure
Both types of liners must be generously lubricated during operation, so there should be no close contact between the rubbing surfaces during operation. The elements have oil holes and locks. All liners used in the automotive industry can be divided into 2 groups - bimetallic and trimetallic. The former are based on a metal plate, the thickness of which is 0.9 - 4 mm. There is an anti-friction coating on the surface of the plate. The protective layer is made of alloys of copper, lead, tin and aluminum. With this protection, the liners can function even with a surface that has geometric defects. Trimetallic elements have a third layer with a thickness of 0.012 - 0.025 mm in their design. It includes alloys of lead, tin and copper.
You can distinguish worn connecting rod and main bearings by sound alone
Wear of liners. Over time, plain bearings begin to wear out and require replacement. This may be indicated by a loss of engine power and knocking noises during operation. Just by the sound you can distinguish worn connecting rod and main bearings. The first ones make a sharper knock. They can be heard well at idle speed while pressing the gas pedal sharply. To carry out diagnostics, you can turn off the spark plug for each cylinder in turn. Another sign of wear after knocking is a sharp decrease in oil pressure. You need to be especially careful as this may be the only reason. Defects on the surface of the elements may indicate that dirt is entering the system. And garbage here is the first reason for the premature failure of elements.
If the crankshaft journal jams, the car will not be able to move. As a rule, this problem occurs due to wear of the main elements. A distance forms between them and the necks, which leads to knocking and other noises. With this phenomenon, the oil pressure drops sharply.
Bottom line . Connecting rod and main bearings in a car periodically fail. This may be indicated by a knocking sound at idle and a drop in oil pressure.
Preliminary work
If it becomes clear that it is impossible to do without repairing the power device, it is necessary to identify the degree of wear of all elements and determine the required dimensions of the crankshaft liners. Most car enthusiasts solve the problem of selecting dimensions by visual inspection; for greater accuracy, you can use a micrometer. It is also worth paying attention to the possibility of boring. If scrolling of elements is detected, they must be immediately replaced with new ones. Before starting repairs, this can be determined by the operation of the engine, in particular it may often stall, or by specific sounds of the crankshaft. When the necks jam, further movement becomes impossible.
Main liners and their features
Another type of liners is root. The main parts are installed in the engine block in special places, so the surface of their friction with the crankshaft main journals increases noticeably.
The main bearings have special grooves or holes in their design that best carry out the required amount of lubricant. These mechanisms support the crankshaft when it is installed in the engine block. When the crankshaft rotates, the liners also replace classic plain bearings.
Of course, the main bearings also become sliding bearings for the main journals of the mechanism. The entire crankshaft of a truck engine rests on them and rotates. This reason determines the importance of periodically diagnosing the wear condition of the liners.
Installation algorithm
The most common method for solving the problem among many people is to contact a car service. But replacing crankshaft liners can be done by any person who has even the slightest experience in carrying out repairs and has a certain set of tools. To simplify the task, it is worth following a certain procedure.
First you need to check the gap located between the liner and the crankshaft. The test is carried out using a calibrated plastic wire, which can be found on the required neck. Then the cover is mounted together with the liner, they are tightened with a certain force corresponding to a value of 51 Nm. It is worth using a torque wrench to measure. After removing the cover, the size of the gap will be similar to the degree of compression of the wire. Using the nominal gap, you need to evaluate the resulting parameter, the value of which is different for each individual brand. If it becomes clear that the gap exceeds the nominal value, that is, the degree of compression, then you cannot do without installing repair parts.
Boring
All connecting rods are removed after sequentially checking the clearances, and the crankshaft is also dismantled and ground. Boring is possible only on special equipment - a centripetal, which is rarely found among ordinary car owners. Therefore, here you will need to contact specialists. After grinding, the crankshaft liners of the appropriate size are selected. Here you cannot do without a tool such as a micrometer and trying on selected elements. Next, all crankshaft parts are installed in the reverse order and the caps on the main bearings are screwed on.
It is worth noting some features of the reverse installation of connecting rods and bearings. The latter are pre-lubricated with oil, and the lids must also be screwed on. Compared to the preparatory work carried out, installation takes much less time. At the same time, we should not forget about the operation of the crankshaft, which is characterized by high loads, as well as its high cost. Everything possible must be done to increase the period of operation. The main role here is played by grinding carried out at the appropriate time. This procedure ensures the smoothness of the necks and prepares them for further use.
Connecting rod bearings and their features
If we consider each type of liners, the connecting rod mechanisms are installed in special places - beds. They are securely fixed to avoid deformation during active movement. The design of the liners has special holes for oil movement. Fixing the liner also helps with friction on specially designed surfaces. The element itself performs a protective function, thanks to which it is possible to increase the operating time of the crankshaft itself.
The connecting rod bearings have a simple design. They can be classified as support parts, since with the help of these mechanisms large loads are transferred from the connecting rods (from the lower heads) to the journals of the crankshaft parts themselves.
Of course, regardless of the accuracy of operation and the current mileage of the engine, connecting rod bearings are subject to natural wear. The main determinant of such a problem is the formation of extraneous knocks and the lack of the required level of oil pressure.
How to choose
Regardless of the reason for repairing the engine and replacing the liners, boring the crankshaft is a must. Installation of new parts is only possible on a polished or new mechanism. If there is damage and potholes on only one neck, all elements are processed to achieve a single overall size. Standard parts are installed during the engine assembly line. For example, repair crankshaft liners for VAZ cars are sold in four versions. That is, boring can be done a maximum of four times. Motors for cars such as Moskvich and GAZ have an additional fifth and sixth grinding of up to 1.5 and 1.2 mm, respectively. The best option would be for the person who did the grinding to select the required sizes. Boring may lead to the need to select elements whose size will significantly exceed the previous one. This depends on the depth of the potholes on the necks and their number. The inserts are sold as sets for both types of necks.
How to replace bearings without removing the engine?
Many car owners think and write on forums that it is impossible to get to the liners without removing or removing them from the engine hood. However, such operations are carried out by repairmen on ships, where the size of the parts is enormous and too much force is required to remove the engine. And if the technique exists, it can be used for simple cars.
- Park the vehicle on a ramp to gain easy access to the engine. If there is protection installed on it, it should be removed and the lubricant drained.
- Remove the box, front cover and loosen the camshaft chain in advance. If you're not too lazy, it's better to remove it entirely so it doesn't interfere.
- Remove the starter and pan (if the beam does not interfere). If it interferes with operation, you will have to lift the motor and pull out the pan from under it.
- You now have access to the crankshaft. The easiest way is to replace the connecting rod bearings. The old bearings are pulled out after unscrewing the head screws; it’s easy to put new ones in place, just don’t forget to lubricate them well with the same engine oil that is in your engine.
- It is more difficult to replace the main bearings without removing the engine. You will need to lower the crankshaft by loosening its fastening. You don’t need to lower it much, ten, maximum fifteen centimeters.
- Now it will be easier to pull out the earbuds. But you will need an aluminum rivet, which must be inserted into the lubrication hole, so it will push the bearing out. The main thing is that the size of the rivet is suitable and does not scratch the crankshaft.
Features of the work
Replacing crankshaft liners requires compliance with the following rules:
- special dirt traps are located on the connecting rod journals; they must be cleaned during the work;
- the protrusions located at the joints and ensuring the fixation of the liners must fit freely into the grooves (hand effort should be quite enough);
- replacement is carried out without adjustment actions;
- work with the main parts is carried out on a previously removed motor, while when installing connecting rods it is not necessary to remove it;
- Upon completion of all actions, the engine must be run-in.