The degree of charge of a battery by voltage can be characterized as the “force” of charged particles that is transmitted by a source of electrical energy through a cable. In this case, thanks to these charged particles, the machine’s devices are powered. Voltage as a value is not a constant and tends to change in correlation with the battery charge value.
Battery charge level by voltage table
| Battery charge level, % | Voltage (no load), V |
| 100 | 12,66 |
| 94 | 12,60 |
| 87,5 | 12,54 |
| 81 | 12,48 |
| 75 | 12,42 |
| 69 | 12,36 |
| 62,5 | 12,30 |
| 56 | 12,24 |
| 50 | 12,18 |
| 44 | 12,12 |
| 37,5 | 12,06 |
| 31 | 12,00 |
| 25 | 11,94 |
| 19 | 11,88 |
| 12,56 | 11,82 |
| 6 | 11,76 |
| 0 | 11,70 |
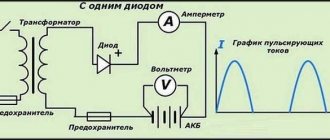
The battery is recharged using a separate charging unit, which is designed for acid-acid machine batteries. The most basic charging functionalities of this type consist of a current transformer and a diode bridge.
Thanks to these components, the alternating voltage goes to the memory, where it is transformed into a direct voltage (15V). This value is enough to recharge the car battery.
Some charger models include current and voltage indicators and adjust them accordingly. There are also devices that adjust these parameters automatically. And the most basic charger models do not include indicators or adjustments.
What parameters to consider when charging a battery?
When charging a car battery yourself, it is worth considering a number of fundamental parameters:
- The suitable current for charging is 10% of the designated capacity of the car battery. For example, the capacity of your battery is 80Ah, in this case the charging current will remain at 8A.
- The voltage at the charging unit terminals should be 10% higher than the battery voltage. When the voltage at the terminals of a 100% charged battery corresponds to 12.6V, at the contacts of the charger this value should be in the range of 13.86V.
- You can reproduce the battery charging more quickly; for this, the current strength increases to 20-30A. However, such recharging is not recommended by professional car owners, as it negatively affects the life of the battery.
- When charging a helium battery, it is forbidden to go beyond the voltage limit of 14.2V, since in this case this value is the critical point for this type of battery.
Correct battery charging
Many car enthusiasts charge an acid battery at home. This process requires certain conditions to be met to ensure safety.
Before the initial stage, you need to make sure that the battery is intact and that the battery does not have a charge. To do this, before the process, make a visual inspection to ensure that there are no flaws in the battery case.
If you find damage, this may mean that the electrolyte has leaked, and such a battery cannot be repaired or restored. The working battery also needs to be freed from dirt, dust and deposits. This can be done using a damp sponge dipped in soapy water. Additionally, the ventilation in the battery cover must be cleaned.
Some batteries contain indicators; a sticker for the meaning of these designations is usually located on the battery cover. Such an indicator can show the electrolyte boundaries, electrolyte density and battery charge level. Additionally, the battery can be tested on the clamps. When the battery is empty, the voltage will show a value lower than that established by the standards.
Do not forget to check the electrolyte boundaries before the work process. To do this, you need to unscrew the tops on the battery banks (you can do it manually). The electrolyte must be pure, homogeneous and completely cover the plates. If the amount of electrolyte is insufficient, you need to add distilled water to the electrolyte manually.
How to check with a charger?
A car charger equipped with a digital or analog voltmeter is designed for charging and diagnosing a battery.
To do this, you need to unplug the device from the outlet and connect it to the battery. The degree of charge of the battery is determined based on the voltage at its terminals .
Chargers with a digital scale do not need to be unplugged. They have a special button for checking the charge level. All you have to do is press it and read the device readings.
Conclusion
To regularly approximate the battery charge level, just look through the indicator window at its covers. If the device is not equipped with an indicator or you want to learn more about the condition of the battery, you should use a multimeter. It will help assess the performance of the car's battery, wiring and alternator.
The load plug should only be used occasionally, when you need to make sure that the battery is capable of delivering enough current to operate the starter. In other cases, it is enough to check the density and measure the voltage at the battery terminals.
Battery charging methods
It is better to recharge the battery in special, well-ventilated rooms. Since the electrolyte evaporates and harmful vapors are released into the air.
To begin with, charging functionality is attached to the battery, and only after that the power from the network is connected. Otherwise, the charging fuses may be damaged.
Battery charging is carried out in three ways:
- The first type of charge involves maintaining a voltage at the border of 16V for a 12-volt battery, varying the current strength. In the early stages of charging, it stays at 20-30A, but then gradually drops as charging progresses. This process usually occurs within 24 hours; the lower the voltage, the longer the recharging time will be. It is not recommended to use high voltage.
- The second type is radically contrasting - the current strength here is a constant value, and the variable value is voltage. This is a more extreme type of charging and requires a professional approach.
- The third type involves a combination of the first two. That is, first charging is carried out using direct current, and then using constant voltage.
At the end of the process, the voltage at the battery terminals is tested. This is done with the operation of a load fork. Or the battery is installed in the car for testing. If the battery is charged, the starter will start without any problems.
Analysis of the causes of battery discharge
With regular use of the car, preventive inspections of the battery and checks of the functionality of the generator, special charging of the battery is not required. The battery must be charged if it is used incorrectly, if it is completely discharged (for example, with electrical appliances not turned off) or during seasonal maintenance.
A charged battery may quickly lose charge. The reasons for this situation are as follows:
- The battery has expired and needs to be replaced.
- The generator that charges the battery during vehicle operation has failed.
- Current leakage in the vehicle electrical network.
- Malfunction of electricity consumers (radio, alarm, electric power steering, lighting and information devices, etc.).
To solve the problem of rapid battery discharge, it is necessary to identify and fix the problem by conducting a technical inspection of the car.
How long to charge a lead acid battery
The battery is perceived to be fully charged when the electrolyte begins to boil. The average charging time is usually 9 hours for standard batteries. But this indicator varies depending on the type of battery and its charge level at the time the charging process begins.
It is not recommended to recharge the battery, as this will cause scale to form on the lead plate. After which the battery may deteriorate beyond repair. In order to avoid this, you need to test the height of the electrolyte and its density before starting the process, especially in the cool season.
At high air temperatures, the battery is charged at a capacity reading of 50%; at colder temperatures, this figure is usually 25%.
The battery should be cleaned of dirt, dust and scale not only before charging, but also after, since traces of acid may remain on the surface during the charging process.
You can clean the battery with soap or soda solution. This procedure should be carried out with gloves for safety reasons. At the same time, try not to let the solution leak into the battery jars.
The whole process is quite simple, and if you follow all the instructions, the battery will last a long time and work well.
Check during operation
During operation, it is necessary to periodically check the performance of the battery. Here you should take into account the fact that if you turn off the engine and immediately take measurements, the result will always be the same - the battery is normal. For reliability, measurements must be taken 6-7 hours after stopping the engine. This is due to the fact that during operation of the generator, the electrolyte inside the battery heats up and therefore its density increases, thereby increasing the voltage at its terminals.
In addition, if the battery is not new, but has been used for several years, it has a certain self-discharge current, which will be compensated by recharging the generator. To reduce natural loss of capacity, keep the battery clean. If there are traces of electrolyte and other wet contaminants on it, the discharge current can flow from the positive terminal to the car body.
Another nuance is that the battery is connected to the on-board network, which, even when the ignition switch is turned off, consumes a certain amount of electricity (radio, alarm, etc.). Therefore, it is necessary to remove the ground terminal going from the car body to the negative terminal before taking measurements, otherwise a certain error will appear.
How to test your battery charge level
Battery endurance is characterized by voltage; this data is fundamental for measuring the battery charge level.
The voltage can be tested in two ways: by measuring the readings at the terminals and by measuring the density of the electrolyte.
Terminal readings
This is the simplest and most accessible method. It focuses on the indicator values that are measured at the battery contacts with a voltmeter - a special measuring device. It will show the exact value, down to hundredths of a volt.
To take measurements, the battery must be at rest for 4-5 hours, and only after that can measurements be taken. The usual voltage level for acid batteries is 12.5-12.9V. For more accurate measurements, refer to the above table.
There is a method for measuring with higher accuracy using special memories with memory and a microprocessor. They have the ability to track several series of battery charge and discharge.
This method is as accurate as possible, and this way you can save money when servicing your battery.
Electrolyte density
The second method is to measure the density of the liquid electrolyte. Accordingly, this method is only suitable for batteries with electrolyte. The electrolyte consists of 65% distillate and 35% sulfuric acid.
When the battery is discharged, the density of sulfuric acid decreases. The higher the discharge, the more the density decreases. These coefficients are in constant relationship.
You can measure the density of the electrolyte with a special device - a hydrometer. With a fully charged battery of 12.7V and average air temperature, the density of the electrolyte will fluctuate between 1.27-1.28 g/cm3.
There is a special data table showing the dependence of battery charge on electrolyte density:
| Charge degree, % | Electrolyte density, g/cm3 |
| 10 | 1,13 |
| 20 | 1,14 |
| 30 | 1,16 |
| 40 | 1,17 |
| 50 | 1,19 |
| 60 | 1,20 |
| 70 | 1,21 |
| 80 | 1,23 |
| 90 | 1,24 |
| 95 | 1,25 |
| 100 | 1,27-1,28 |
The higher the density of the electrolyte, the more resistant the battery will remain in cold mode. In regions with cold climatic conditions, the electrolyte density is forcibly increased to 1.30 g/cm3.
However, the maximum permissible value is 1.35 g/cm3, otherwise the acid may melt the plates.
Battery voltage
First, let’s look at the meaning of the term “tension.” Essentially, it is the “pressure” of charged electrons created by a current source through a circuit (wire). Electrons perform useful work (powering light bulbs, equipment, etc.). Voltage is measured in Volts.
Measuring battery voltage
You can use a multimeter to measure battery voltage. The contact probes of the device are applied to the battery terminals. Formally, a voltage of 12V is considered normal. The actual battery voltage should be between 12.6V -12.7V. These are the indicators for a fully charged battery.
These values may vary depending on environmental conditions and test time. Immediately after charging, the device may show 13V - 13.2V. Although such values are also considered acceptable. To get the correct data, you need to wait an hour or two after charging.
If the voltage drops below 12 Volts, this indicates a low battery. The voltage value and charge level can be compared using the following table.
| Voltage, Volt | Charge degree, % |
| 12,6 + | 100 |
| 12,5 | 90 |
| 12,42 | 80 |
| 12,32 | 70 |
| 12,20 | 60 |
| 12,06 | 50 |
| 11,9 | 40 |
| 11,75 | 30 |
| 11,58 | 20 |
| 11,31 | 10 |
| 10,5 | 0 |
As can be seen from the table, a voltage below 12V indicates a 50% discharge of the battery. The battery needs urgent recharging. You should know that during the discharge process a process of sulfation of the plates occurs. The density of the electrolyte decreases. Sulfuric acid breaks down by participating in a chemical reaction. Lead sulfate forms on the plates. Timely charging starts this process in the opposite direction. If you allow a deep discharge, it will be difficult to revive the battery. It will either fail completely or significantly lose capacity.
The minimum voltage at which the battery can operate is considered to be 11.9 Volts.
Measurements under load
Sometimes the battery has the ability to start the engine even when the voltage drops. But it is important that after starting the generator provides its further charge.
During the ignition process, the charge in the battery goes to the starter, as a high current is supplied. With a well-functioning battery, battery restoration is completed in 5 seconds.
The voltage on a well-functioning battery is in the range of 12.6-12.9V. But these data do not always correctly assess the condition of the battery. An effect can occur when in a quiet state the voltage in the battery is good, but under the influence of a load it drops sharply, and the charge runs out quickly.
Therefore, it makes sense to sometimes take measurements under load. To do this, use a loading fork. This helps you understand how well the battery holds its charge.
The plug is a device with a load spiral, contact probes and a voltmeter. The device creates an imitation of starting current, while producing a voltage that is 2 times higher than the battery capacity.
With a battery capacity of 50 Ah, a load of up to 100A occurs. Such measurements are made on a fully charged battery. After 5 seconds the device produces the result.
Considering that the load voltage indicator is less, with a working battery this indicator will be 10V, and with a poorly functioning battery it will be 9V or less.
Engine running
For the vehicle to operate correctly, all its components must be in good condition. It is possible to test the battery voltage while the engine is running. The indicator will be higher than when the engine is turned off, varying between 13.5 and 14 V. Exceeding the maximum value will indicate that the generator is operating in enhanced mode. If the electrical equipment operates correctly, after 10 minutes the DC charge indicator will return to normal. If the increase in indicators is constant, the power supply will be overcharged. The electrolyte will boil away.
If there is a constant decrease in the DC charge of the battery, the power source does not have time to fully charge. A malfunction of this equipment will be indicated by a drop in readings of more than 2 V. If such situations arise, you should think about purchasing a new device.
Voltage at low temperatures
When the air temperature drops with the change of seasons, the engine starts more difficult. Many drivers solve this problem in this way: they remove the battery at night and take it home.
Low temperatures have an effect on the density of the electrolyte, which reduces its value.
There is more water in the electrolyte, and the liquid is capable of freezing. Therefore, low temperatures slow down the processes in the battery.
With adequate operation, a battery with liquid electrolyte can operate without replacement for 5-7 years. And if in summer the electrolyte density and state of charge need to be tested once every 3-4 months, then in winter such checks are carried out once every 2-3 weeks.
When living in regions with harsh winter climates, the battery needs to be charged every 5-7 days, even if you constantly use the car.