The question of comparison in terms of “which is better” between injection and carburetor fuel supply has not been raised for a long time. There are fewer cars equipped with a carburetor every day, and new ones are no longer produced.
Novice motorists do not understand the structure of a car engine, fuel supply system, etc. The terms “carburetor” and “injector” mean nothing to them. Inexperienced motorists do not see the difference between their purposes. Those who buy a new car no longer face the question of which is better: a carburetor or an injector. They don’t need to know anything about the carburetor, since it has long been discontinued and does not pass the Euro-3 environmental standard.
This is associated with the massive transition of automakers to cars with an injection power system. The requirements for exhaust gas cleaning are becoming higher, and the carburetor cannot meet them.
But this is not the only reason for abandoning carburetors. Compared to an injector, it has many disadvantages and few advantages.
Pros and cons of the injector
First of all, the injector is different in that it is capable of providing much more engine power than the classic version. The injector is not a carburetor, so even in winter it starts without any problems - you don’t have to invent anything to make the car go. In terms of reliability, it is still at a fairly high level - the system rarely fails on its own, since it is completely isolated from the external environment.
But there are also disadvantages, and there is no escape from them. The first and most significant is the inability to independently diagnose and fix faults if they arise. The system includes a lot of complex elements:
- Fuel rail.
- Injectors.
- Electronic sensors and more.
Each of them is practically impossible to repair; in the event of a breakdown, the unit will have to be completely replaced - and unlike the classical system, the parts here are by no means cheap. A power system of this type requires extremely high-quality fuel. If you use a cheap one, then impurities, undissolved residues of petroleum products and residues from production will quickly clog the injectors and they will have to be cleaned. And this can only be done at a special stand in a service station.
At the same time, if you constantly drive on low-quality fuel, then after a while cleaning the injectors will no longer help - they will completely fail. Since they are sold in sets, their price will be approximately a quarter of the entire engine. Accordingly, we can conclude that the use of engines with such a power system costs owners significantly more. This is the difference between a carburetor and an injector.
Types of injection injection
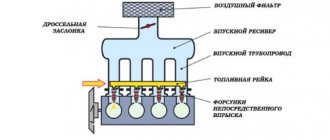
As soon as car manufacturers decided to move away from the carburetor injection system, the injection nozzle was installed alone, directly in place of the carburetor, and injection was carried out into the intake manifold. This method of fuel injection was called mono-injection and its usefulness did not greatly exceed the effect of a carburetor. The next stage of evolution was distributed injection, the injectors were installed closer to the cylinders, but also in the intake manifold. The pinnacle of injection injection was full-fledged direct injection into the engine cylinders through the intake valve. This ensures maximum engine efficiency, increased power and efficiency.
Comparative analysis of gasoline systems
To identify the fundamental differences between a carburetor and an injector, you need to know that the carburetor's job is to create the rich fuel mixture that the engine needs to perform a specific task. To do this, a prepared combustible volume enters the chamber, independent of the current speed. This negatively affects fuel consumption and creates emissions pollution.
Understanding the difference between an injection engine and a carburetor engine helps to understand the design of a modern injection system. Injection engines are characterized by the supply of a lean mixture with a precise dosage, which is selected by the electronic unit (the main computer in the car).
Important! The most accurate fuel dosage is characterized by economical operation of the vehicle and a minimum level of toxicity of exhaust gas emissions.
Thanks to the built-in injector, cars receive an additional increase in engine power by 10-12% and an increase in dynamic characteristics. When choosing the optimal fuel supply system, it is necessary to take into account that the injector is more demanding of fuel quality than its competitor. Also, modern injection systems are not affected by temperature changes, unlike carburetors, which can overheat in hot weather and can freeze in severe frosts.
There is a noticeable difference in maintenance, diagnostics and repair between a carburetor and an injector. Fuel systems equipped with carburetors have a fairly simple design and are undemanding during operation if the following rules are followed:
- High-quality gasoline is poured into the car;
- there is a reliable fuel filter;
- the air filter is not dirty.
In practice, motorists may encounter frequent carburetor breakdowns due to the use of low-quality fuel. Car owners have the opportunity to carry out almost all types of repairs of this unit on their own, even in a garage, and the cost of spare parts will be minimal.
A motorist can identify an injector not only visually or by an increase in power, but also by greater reliability of operation. It is worth knowing that these advantages of the injector are compensated by the sufficient complexity of repairing the unit. Diagnostic work is usually performed on special expensive stands available to professional service stations. Also, individual built-in sensors and fuel unit elements are expensive.
How does a carburetor work?
The carburetor is one of the most important mechanical parts of a car. All engines require the correct mixture of gasoline and air to burn gasoline. And it is this vital device that controls the ratio of the fuel-air mixture entering the engine. For effective output inside it, all components must work perfectly. The correct fuel to air ratio is critical to engine performance.
Air enters the device from the air intake or through the air filter, and is gradually accelerated due to the narrowing of the internal walls. This air blows perpendicular to the throttle valve, controlled by a cable. When tensioned, the cable lifts the throttle located inside the main body of the device. When the flapper rises, fast moving air pulls gasoline upward from the float chamber.
The quality of the mixture of air and fuel to power the engine depends on the speed of air entering through the device. And, although most modern car manufacturers have switched to fuel injection, there are still many models equipped with outdated engines.
Strengths and weaknesses of the carburetor
This is a simple and inexpensive fuel supply system for two-stroke and four-stroke engines. The simplicity and mechanicalness of its maintenance and repair are possible and quite simple. It can be easily customized according to user needs and environmental conditions. Being a mechanical device, it reacts uniquely to every possible position and action of the fuel. Frequent response to speed is a very common feature and advantage of such a fuel supply system. The problem of fuel contamination can be ignored in a carburetor engine, although this reduces performance. A very suitable fuel supply system for low-cost and low-capacity automobile engines.
The amount of fuel supplied is not precise, as it allows the flow to be supplied according to the suction speed and the amount of air in the combustion chamber. Fuel economy is significantly lower in a carbureted engine. With this fuel supply system, cold starting of the engine is a big problem. Dry and rich mixture often becomes a problem. Due to inefficient combustion, emissions are significantly higher. In some cases, the engine gets vibration, and the problem of dirty spark plugs is also quite common.
Carburetor design
Carburetor - is the simplest type of device for supplying and spraying gasoline. The process of mixing fuel with air is performed mechanically, and adjusting the supply of the mixture requires careful adjustment. Thanks to the use of simple mechanisms, the carburetor system is easy to maintain. An experienced motorist can perform such repairs independently, which provides certain advantages in operation. For such operations, it is not difficult to purchase a repair kit, and all work is carried out with standard tools available in the car.
The carburetor is located on the intake manifold, and its design consists of a float and mixing chambers. To supply fuel, a spray tube is used, connecting the chambers to each other. Fuel is supplied to the float chamber using a gasoline pump, and a stable supply of gasoline is ensured by a needle filter and a float. The mixing chamber is also called the air chamber and consists of a diffuser, atomizer and throttle valve. When the pistons move, a vacuum is created, which ensures the suction of atmospheric air and gasoline. This mixing ensures stable engine operation.
How does an injection engine work?
In addition to its simpler design, the injector differs from the carburetor in its operating principle. Here the main element is the nozzle - a sprayer with an electromagnetic drive that supplies the combustible mixture directly into the combustion chamber or into the intake manifold. The injectors are controlled by an electronic unit that collects readings from the following sensors:
- crankshaft position;
- mass air flow (abbreviated as MAF);
- lambda probe (read more about the sensor here);
- throttle position (TPV);
- speed;
- detonation.
Reference. Air flow meters are gradually being replaced by a new type of device - absolute pressure sensors (APS).
Gasoline and air are injected into the combustion chambers forcibly . The pressure in the fuel rail, where all the injectors are connected, is provided by an electric fuel pump. When the sprayers consume little fuel, the pressure in the fuel line is limited by a valve that dumps gasoline back into the tank.
We recommend: TSI engines from Volkswagen - what they are, their pros and cons
“Seeing” the position of the crankshaft, the controller selects the moment to turn on the injector when the piston in the cylinder moves down. The amount of mixture supplied depends on the duration of operation of the sprayer and is determined by the control unit using the throttle position sensors and mass air flow sensor. The remaining meters are needed to adjust the proportions of gasoline and air in the mixture.
Thanks to the lambda probe mounted in the exhaust pipe, the controller is aware of the quality of fuel combustion. Speed and detonation meters provide a more complete picture of the operation of the power unit. The engines of more modern cars are equipped with additional devices - camshaft sensors, which allow the electronic unit to monitor valve timing.
How the injector works and works
The injector design assumes the presence of the following basic system components:
- electronic control unit (ECU);
- electric fuel pump;
- injection nozzles;
- fuel rail with pressure regulator;
- electronic sensors for temperature, throttle opening angle TPS, DPKV, mass air flow sensor, etc.
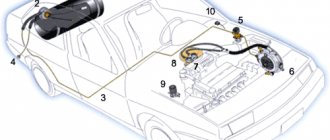
To better understand the principle of operation of the injector, let's take a superficial look at how the components of the system interact with each other using the example of a common type of injection engines with multipoint distributed injection. After turning the ignition key, power is supplied to the electric fuel pump, which is located in the fuel tank and immersed in fuel. This pump supplies fuel to the fuel line at a certain pressure. The injection nozzles are installed in the fuel rail (rail), through which fuel is supplied to the injectors, and the injectors themselves are fixed to the intake manifold. The rail also contains a fuel pressure regulator, which serves to maintain the difference between the air pressure in the intake and in the injectors themselves.
Thanks to the installed sensors of the electronic engine control system (ECM), the ECU controller receives information on the basis of which it is possible to synchronize injection in accordance with the modes and operating conditions of the internal combustion engine. The control unit receives readings from the engine temperature sensor, oxygen sensor, knock sensor, camshaft position sensor (Hall sensor) and crankshaft sensor. This makes it possible to adjust the amount of fuel supplied to each cylinder, flexibly and dynamically change the composition of the fuel-air mixture, etc.
Sensors record various changes in engine operation and changing conditions, constantly transmitting signals to the control unit. This scheme allows you to spend a strictly defined amount of fuel during startup, warming up, idling, quiet or dynamic driving, etc.
The specified accuracy during fuel dosing is possible only thanks to the operation of the vehicle’s control electronics in the form of a set of sensors and the engine ECU. The control unit has microprograms embedded in it, and the operation itself is based on so-called fuel maps. Sensors continuously provide information about the engine operating mode, vehicle speed, etc. The controller receives and processes the data, after which it determines the required number of fuel injections and their duration. Any changes in the operation of the internal combustion engine are read by sensors and force the ECU to dynamically make adjustments to the operation of the injector.
The outstanding environmental friendliness of the injector is made possible thanks to the presence of an oxygen sensor (lambda probe). This sensor is located in the exhaust system and “assesses” the condition of the exhaust gases. Based on its readings, the ECU leans or enriches the fuel-air mixture (changes the ratio of air and fuel in the working mixture) while the engine is running in most standard modes.
Selecting the optimal fuel supply system
In debates about which is better - an injector or a carburetor, car enthusiasts always have differing opinions. Some people think that only the carburetor copes with the engine's operation, while others are convinced of the need to use an injector. So which of these options is the best?
It seems like an injector is the best option. Although most small engines use a carburetor system due to its simplicity and low prices, as well as lower maintenance costs, fuel injection is the ideal choice for modern vehicles to improve performance, reduce emissions and save fuel.
If power and performance are your main criteria when choosing an engine, you'll be firmly on the side of carburetors. This is due to the fact that a carburetor engine has no restrictions on the amount of fuel that can be pumped out of the tank. This means that modifications to the cam will allow more fuel to flow through the carburetor and into the cylinders. This results in a denser mixture in the chamber and higher power levels.
The only way to compete with a fuel injector is to turbocharge it to achieve the same fuel elasticity and performance. For normal daily driving, however, the extra power won't make much difference. Excess power will always lead to increased fuel consumption, which in turn will cause increased costs.
While the carburetor may have been around for over a century, the fuel injector is clearly superior in functionality and performance, delivering better power, fuel economy and lower emissions. For a modern driver, this is enough to make a choice. If you are a fan of the latest technology, then you will definitely prefer fuel injection instead of carburetor. Carburetors are old school, but that doesn't mean they're bad. Carburetors offer simplicity, whereas fuel injection is much more complex. If you're looking at a classic Mustang or vintage Chevy C10, chances are it will be equipped with a carburetor. It’s not for nothing that many old car enthusiasts would prefer to replace it with a proven carburetor instead of a new system.
How to replace the generator on a VAZ 2108-VAZ 21099?
Removal: You will need to remove the generator from the bottom of the car, but there is usually a crankcase protection at the bottom, so you will definitely need to remove it, as soon as the bolts securing the protection are unscrewed and it is removed, remove the minus terminal from the battery (How to do this, read “here in this article”, in paragraph 1) and first of all, disconnect the wiring from the generator (two terminals are attached to it and a block of wires is connected in addition, to disconnect the terminals, you will need to unscrew the nut that secures them, see the large photo, but you are near the block you will find it, you just need to pull it out by hand), immediately after which loosen the upper nut of the adjusting bar, and then the lower one a little (see small photo) and as soon as this is done, move the generator by hand closer to the engine and remove it from it the belt that is put on it, but that’s not all, and until the generator is removed, all that remains is to completely unscrew only three bolts, one is the one that secures the adjustment bar (Indicated by a blue arrow, you will have to completely unscrew it), and the other two are located at the bottom ( More on them a little later, namely in paragraph 2).
Note! When the belt is removed, take it out and inspect it, under no circumstances should there be traces of oil or other types of liquids on it, and it should not be cracked or have any obvious defects, otherwise the belt will need to be replaced with new!
2) At the very bottom of the generator (You will have to crawl under the car), you will find two bolts, but remember, one of them is long and the other is short, remember where each one is wrapped, so that later you do not match them with each other, but immediately wrap them on those places where needed, well, both bolts must be unscrewed, and when they are completely unscrewed, carefully remove the generator and place it on the ground or wherever you need it.
Installation: The new generator is installed in place of the old one in exactly the same way, but just don’t forget to unscrew the nut that secures the adjusting bar on the generator and move this bar to another one, and that’s all in essence, the replacement of the generator on the car has been completed successfully.
Additional video clip: To see in more detail the process of how the generator is checked for serviceability using a device such as a multi-meter, you can watch the video clip located just below:
Pros and cons of carburetor and injector
Electronic control of power and ignition systems allows for more precise tuning and consistency.
A gasoline injection engine certainly has a number of advantages over a carburetor engine. Electronic control of power and ignition systems allows for more precise tuning and consistency. Keeping mechanical moving parts to a minimum has improved engine reliability. The service life of an injection engine is generally longer than a carburetor engine and because the electronics, adjusting the fuel supply and timing of spark formation, selects the optimal operating mode, which eliminates detonation due to the presence. In addition, injection power systems continue to improve. Cars with turbocharged injection engines have been driving on the roads for several years now and this is not a new thing. Naturally, innovations require some “breaking in” in order to become more perfect, but there are still prospects for development. The disadvantage of the injector is that it requires more complex diagnostics, requiring special equipment, which often makes repairing the injector more expensive, and the cost of some components is quite high. Therefore, the cost of carburetor repair is usually lower. In order to safely go on a long journey, it is enough to have carburetor and fuel pump repair kits. The weak point of these units are the diaphragms, the replacement of which does not require special skills. Therefore, as a car for fishermen, hunters, as well as for military equipment, a car with a carburetor power system is still more reliable - ease of diagnosis and repair allows you to quickly put it “on wheels”.
Everyone knows that gasoline engines either have a fuel injector or are equipped with a carburetor. But if you ask the first car enthusiast you come across the question of how an injector differs from a carburetor, you are unlikely to get a clear answer. Many people only know that these units perform the same function - they form a combustible mixture to supply it to the engine. But how do these units differ?
What is the difference between an injection engine and a carburetor engine?
Every car enthusiast who is interested in the design of his car knows that modern gasoline engines are equipped with a carburetor or fuel injector. However, if you take the first driver you meet and ask him a question about how these systems differ, you most likely will not get a clear answer. General erudition, as a rule, is limited to the fact that the systems perform the same function - they form a combustible mixture for supply to the engine.
So, what is the difference between an injection engine and a carburetor engine? How do they function? Our note is devoted to these issues.
How to distinguish an injection car from a carburetor
If you know what a carburetor looks like, then all you have to do is open the hood and look under it. But if you have no idea about it, then a number of signs will help you identify it:
- a new car sold at a car dealership is 100% fuel-injected;
- look at the nameplate at the rear of the car - for example, it says BMW 525i. This “i” is the designation of an injection car;
- year of car manufacture. Injectors began to be installed on foreign cars in the mid-90s, on domestic ones - from the beginning of the 2000s;
- The air filter housing is mounted directly on the carburetor. If you see air ducts (for example, black plastic corrugated boxes), then most likely you have an injection machine in front of you;
- If the indicators that light up on the dashboard when you turn the key contain a “Check Engine” indicator, then the car in front of you is fuel-injected.
Carburetor or injector. Which is better and what is the difference between them?
It seems to me that this topic has long been “worn out” and, with the development of new environmental standards, has long been removed from the agenda. BUT IT TURNS OUT NOT! Many people write - what is really better, a carburetor or an injector? And “newcomers” to cars also ask the following question: what’s the difference between them? Everything is already obvious to me (I closed this question a long time ago), but if there is such interest, then I will write an article and shoot a video, and there will be a vote below. So read and watch, it will be interesting...
I have almost 20 years of driving experience. During this time, I had a lot of fun with the carburetor (there were several VAZs, such as 2101, 2103, 2105, etc.), and already had a lot of fun with injection modifications of cars (not only ours, but also imported ones). Therefore, I really have the opportunity to evaluate both units, although I think this is not correct, it’s like comparing a tube TV and a modern LCD panel.
Difference between power systems
So, both the carburetor and the injector perform the same function - they generate a fuel-air mixture, which is then supplied to the engine cylinders. But the way the mixture is created in these systems is fundamentally different. The difference is that in a classic engine, a ready-made mixture is supplied to the cylinders, which is drawn in under the action of vacuum. As air passes through the carburetor, it mixes with the fuel inside. The only negative here is that all actions occur completely mechanically.
The difference between an injector is that here every moment and step is controlled by a computer, many different sensors are used.
There are plenty of them here:
- Mass air flow sensor.
- Air temperatures.
- Positions of the camshaft and crankshaft.
- Throttle position, etc.
Based on sensor readings, the on-board computer decides when it is best to inject the fuel mixture and what its composition should be for optimal engine operation. This is precisely the difference between carburetor and injection power systems.
Generator circuit for injection engines
In fact, the design of the generator set is not much different from those installed on carburetor engines. Only the type of excitation and serviceability monitoring differ. The dashboard contains not only a warning lamp, but also a voltmeter; these two devices allow you to assess both the presence and level of charging. Current flows through the lamp filament and is supplied to the field winding when the engine starts. The connection diagram for the VAZ-2107 generator, regardless of the year of manufacture, implies operation in the following mode:
- When the ignition is turned on, power is supplied to the excitation winding. A magnetic field appears around the armature.
- When the crankshaft rotates with the starter, the generator armature also begins to move. With the help of movement and a magnetic field, a potential difference arises at the ends of the stator windings.
- From the windings, voltage (alternating, three-phase) is supplied to the rectifier unit, and from it to terminal “30” of the generator.
- Pin “30” is connected to the battery (positive terminal). Consequently, the entire electrical system is powered and the battery is charged.
In this case, the battery and generator G221A work in parallel. The connection diagram for the VAZ-2107 with carburetor and injection engines is almost identical, with only minor features.
Main differences between systems
The differences between a carburetor and an injector appear when determining their strengths and weaknesses. You can choose the best option by comparing their pros and cons, as well as functionality according to several parameters:
- Power and performance.
We recommend: Injection injection system
Electronically controlled injector provides more accurate results. Since it can provide the required amount, the engine runs at optimal power and provides the best performance.
A carburetor differs from an injector in that it cannot calculate the exact amount of fuel. They cannot be adjusted when atmospheric pressure or fuel temperature changes.
- Emissions and fuel economy.
Again, the injector wins in this regard. It can accurately calculate the required amount of fuel and air and adjust it according to changes in several parameters, resulting in lower consumption, higher fuel efficiency and lower carbon emissions. Carburetors cannot produce the same results because they provide an average fuel-to-air ratio that is independent of engine conditions.
Emissions are a major factor in modern automotive manufacturing and are likely to become even more important in the future. Here the injector has many advantages. The carburetor was fine when little attention was paid to the amount of CO2 emitted, but these days car emission restrictions mean that more and more manufacturers will lean towards fuel injection for their vehicles.
Injection engine intake system design
- Operating costs.
If you choose which is more economical - a carburetor or an injector, then the first one wins in this regard. You can even rebuild the entire system in the garage! All you need are a few simple hand tools, a carburetor cleaner, and some spare parts.
On the other hand, the injector is a complex system. If the system is burned out, you will need outside help to transport the car to a repair shop. In addition, repairing the fuel injector system requires professional skills.
- Simplicity.
The carburetor is very complex and must be adjusted correctly to operate effectively. On the contrary, installing the injector is extremely simple. The carburetor rests on a float and must regulate the amount of fuel flowing through the engine. With a carbureted engine, one cylinder will receive more fuel than the other. In a fuel injected engine, each cylinder receives the same amount of fuel. In this particular case, there is little that can be done to improve the carburetor design.
The difference between an injector and a carburetor is that in injectors, fuel passes through a line under pressure to the fuel injectors. The car's computer instructs each injector when it should open, at which point fuel enters the cylinders. As it passes through the cylinder, the fuel is atomized, resulting in more efficient combustion.
- Structural difference.
The design of a carburetor is completely different from an injector. The carburetor is an air intake through an air filter, after which there is an air valve, and after that the air passes through a pipe in which it is mixed with fuel. then comes the throttle valve, after which the air-fuel mixture passes into the engine. The injector structure consists of the following elements: o-ring, filter, electrical connector, electrical coil, magnet, spring, o-ring, valve and cap.
- Price
An engine with a carburetor costs about five times less than an engine with an injection, which provides very large savings. However, maintenance costs for a carbureted engine tend to be higher than for a fuel injected engine, so in the short run this can all be taken into account.
Prices for injectors versus carburetors can vary greatly. In particular, direct fuel injection is usually significantly more expensive than central or multipoint injection.
- Device category.
A carburetor is a purely mechanical device, where the fuel injector can be a purely mechanical or electrical device (most are now electrical).
- Diagnosis of the problem.
The fully electronic nature of the electric fuel injector allows problems to be identified by simply connecting the engine control unit to a diagnostic device or computer where, as with carburetors, maintenance and tuning require special expertise as it must be done manually.
Computer engine diagnostics
Advantages and disadvantages of systems
Advantages of carburetors:
- Carburetors are cheaper, simpler to operate, and easy to repair or replace.
- Carburetors allow you to customize them to suit your requirements.
- Because carburetors are not built into engines, they can be repaired or replaced without touching the engine.
Disadvantages of carburetors:
- Not the most efficient systems, outdated design.
- Most carburetors have a slight lag, resulting in relatively slow throttle response.
- Some components, such as the diaphragm, are relatively delicate and susceptible to damage.
Advantages of an injector over a carburetor:
- Optimized, reliable air-fuel mixture and atomization ensure cleaner, more efficient combustion.
- Throttle response is much quicker.
- Better fuel efficiency and slightly more power than carbureted systems.
- Usually do not require maintenance and do not fail.
Injector disadvantages:
- Significantly more expensive than carburetors.
- Cannot be repaired with simple tools and must be replaced, which is expensive.
- Cannot be configured unless you have the appropriate hardware and software, which is again expensive.
What is the difference between an injector and a carburetor?
During the operating cycle, a saturated air-fuel mixture is formed in the carburetor, which is necessary for the engine to operate. In this case, an equal amount of mixture enters the engine, regardless of how many revolutions the “heart” of the car is operating at at a particular moment. Due to this, the system consumes a large amount of fuel and, consequently, the environment is unnecessarily polluted by exhaust gases.
When using injection systems, a lean air-fuel mixture is supplied to the engine in a dosage calculated by the central control unit. Precise dosage can significantly reduce consumption, provide cost savings and reduce the amount of harmful emissions into the atmosphere.
We recommend: Cleaning the carburetor - choosing the fluid and washing it yourself
The use of an injector allows in modern projects to increase engine power by up to 10%! and modernize the dynamic properties of the machine. The injector is not affected by temperature changes, it does not freeze in the cold autumn-winter period and does not overheat in the summer heat. However, the injector is more “picky” about the quality of fuel than the carburetor.
Carburetor engine
At the same time, using low-quality fuel on the carburetor is also not recommended in order to avoid serious problems with the chassis. It can be unpretentious in maintenance, compared to an injector, but only on condition that the driver fills the car with exclusively high-quality fuel. In the harsh Russian realities, such systems are subject to frequent breakdowns as a result of the use of low-quality gasoline. The advantages in such a situation include the ability to carry out repairs yourself and the affordable cost of spare parts for the unit.
The injector, on the contrary, breaks down less often and is generally more reliable, but its repair is a complex procedure. It is not possible to carry out diagnostics without special service equipment, and replacing components may require serious investment.
We recommend: Symbols, icons, indicators and symbols of the car dashboard
The design and principle of operation of the carburetor
About the design and operation of the car Is it possible to change the engine. Engine replacement
Carburetor operation diagram
The fundamental differences between a carburetor and an injector lie in the method of supplying the combustible mixture to the combustion chambers and the design of the ignition system.
The figure shows the most simplified diagram of a carburetor. However, with its help it is quite possible to understand how the air-fuel mixture is supplied to the cylinders. Let us briefly describe how such a device works. The carburetor is mounted on the intake manifold (lower plane), and the air filter is installed on top (upper plane). Gasoline is supplied by the fuel pump through inlet 1. To maintain the required fuel level in the float chamber of the carburetor 11, the inlet is equipped with a needle valve 2. Upon reaching a certain level, the float rises and, through a small lever, presses on the valve, closing it. Fuel and air, under the influence of the vacuum created by the piston as it moves down (with the cylinder inlet valve open), rush through the intake manifold into the engine cylinder. To improve the mixing of fuel with air and to make the mixture more dense, the cross-section of the chamber in the lower part of the carburetor has the shape of a cone - this is the simplest diffuser. The supply of the fuel mixture is regulated by the throttle valve 7, the axis of which is connected (using rods or a cable) to the gas pedal, and the amount of air in the combustible mixture is regulated by the throttle sensor. The amount of gasoline coming from the float chamber is determined by the diameter of the fuel nozzle 9. To start a cold engine, a richer mixture is required, that is, the air/gasoline mixture ratio should have a lower value. To do this, an air damper 5 is installed in the upper part of the carburetor. When it is closed (with a small gap), the amount of air participating in the formation of the combustible mixture is significantly limited, and it becomes enriched, which makes it easier to start the engine. After the engine warms up, the air damper opens. Manipulation is carried out manually - with a special cable, the handle of which is installed in the car interior.
Solex carburetors
Solex carburetor operation diagram
A two-chamber carburetor has a number of parts that help supply the fuel mixture to the combustion chamber under various operating conditions.
- not only fuel (39 and 29), but also air jets (14 and 7);
- adjustable idle system;
- air damper control system. That is, the damper closes and opens manually, using a cable, but its position is adjusted by the diaphragm 3 of the trigger;
- accelerator pump - to enrich the mixture during acceleration by injecting an additional portion into the chambers. Its diaphragm 42 is driven by lever 42. Gasoline is supplied through channels to the sprayer 11.
However, a detailed description is now completely unnecessary. The purpose of the material is to show the differences between an injector and a carburetor. From what is said above, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- To supply the mixture, the vacuum created by the engine pistons is used; its composition is determined by the diameter of the nozzle holes.
- All actuators, including the fuel pump, are mechanically driven, with the exception of the forced idle solenoid valve 5.
The principle of operation of the injector and carburetor
The main difference between an injection engine and a carburetor engine is the technology for supplying air and fuel to the engine. The carburetor creates an air-fuel mixture and regulates its flow; the combustible fuel-air mixture is sucked into the engine due to the difference in pressure between the atmosphere and the intake manifold.
Injection engine
The injector is a modern electronic fuel supply system. In it, the composition of the air-fuel mixture is regulated by an electronic system. Fuel is injected into the air stream using special nozzles. The combustible mixture is injected into the combustion chamber and enters the engine cylinders. Most modern cars are equipped with injectors due to the advantages described below.
Main differences between systems
The purpose of both systems is to saturate the cylinders with a combustible mixture. The system pre-determines and prepares the mixture for delivery to the engine; inefficient fuel distribution affects overall consumption and the environment. Which is better, a carburetor or an injector? The first is popular in remote areas from services, as they can be adjusted without specialized tools. What is the difference between an injector and a carburetor is found out by many car owners before purchasing a new or used iron friend.
Injector device
Injector - has a more advanced fuel supply control system. All operations are monitored by an electronic system. Such equipment calculates with high accuracy the portion of fuel required for engine operation. To determine the required flow rate, readings are taken from many vehicle sensors, and the microcontroller instantly makes the necessary calculation. To understand which is better, a carburetor or an injector, it is worth comparing their design and giving preference to a more practical model.
Fuel is supplied to the injector using special nozzles. This principle of operation differs from carburetor injection, and almost all modern cars are equipped with it. Fuel injection into the air flow is automatic and depends on the engine operating mode. The nozzle itself opens due to the action of an electromagnet, and closes using a spring. In such a system, constant pressure is maintained by a special valve on the ramp, which discharges excess fuel.
Depending on the make of the car and the characteristics of the engine, the following injector connection options can be used:
- Single-point (mono-injection);
- Multipoint (distributed);
- Direct (direct injection).
Such a system requires precise injection control and depends on the quality of the fuel. For such purposes, the injector uses an electronic control unit that coordinates the supply of gasoline with driving conditions.