Spark plugs and their types
Depending on the engine for which the spark plug is intended, it differs in diameter and thread pitch, sealing method, and heat rating.
Spark plugs with different threads and seal types
In the picture, the left candle has a larger thread diameter than the right one. The left spark plug has a conical seal, while the right spark plug has a washer. On the right, the central electrode is moved further out of the housing. All these and other differences and characteristics are encrypted in the candle markings. Each engine has a specific manufacturer's spark plug. There are almost always analogues from different manufacturers with similar characteristics. The manufacturer installs spark plugs from one of the manufacturers on the conveyor, and these spark plugs are considered original and may have two markings. Manufacturer and automobile manufacturer
Original candles
These spark plugs are supplied as original WV ,AUDI spark plugs. Manufacturer: NGK. For the engine on which they were installed by the factory, in addition to these spark plugs, the installation of Bosch, Champion, Beru spark plugs is allowed. Naturally a specific model.
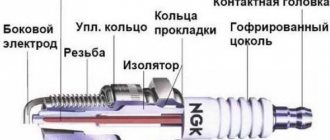
Spark Plug Components
Picture taken from the Internet
Components of a spark plug
The spark plug contact sleeve is fitted with a high-voltage wire or the tip of the ignition coil. A high-voltage spark discharge is supplied through it from a coil. The discharge passes through a conductor located in the body of the spark plug insulator. It breaks through the gap between the central and side electrodes and ignites the fuel-air mixture, which, burning and expanding, pushes the piston and our engine runs.
How to check that spark plugs are working correctly
Having realized that the engine is not working correctly, inspect the spark plugs. There are several ways.
Rolling power off
The easiest test method is to remove the ignition coils from the spark plugs one by one with the engine running.
In this case, you need to listen closely to the operation of the engine: if after removing the wire from the spark plug the sound of the engine has not changed, then it is the spark plug that has failed. For example, if a four-cylinder engine seizes up and you disconnect the spark plug wire, the engine will only run on two cylinders. Changes in the operation of the internal combustion engine will be immediately noticeable - it will, figuratively speaking, “sneeze and choke.”
Checking for spark
To do this, you need to unscrew the spark plug, put a wire on it, place the spark plug on the metal part of the valve cover and turn it with the starter. A spark will be visible on a working spark plug: clear and bright.
Checking with a tester
Spark plugs can be checked using a special tester (piezoelectric spark tester), which is sold in automotive stores.
To do this, you need to remove the tip with the high-voltage wire from the spark plug, and in its place install the sleeve of the flexible connector of the probe until it stops. Press the device forcefully with a spring-loaded probe in its nose part to the engine “ground”. Press and release the probe key several times, checking for the presence or absence of flashes of the indicator lamp located in the rear of the device body, and the characteristic crackling sound of spark discharges. The flashing of the lamp at the moment of pressing indicates the serviceability of the spark plug; if there are no flashes, then the spark plug is inoperative. In addition, the appearance of candles can also tell a lot about their condition:
- Electrode insulation cracked
. Easily determined visually. Manifests itself in the form of deep detonation, regardless of temperature. The breakdown is “treated” by replacing the spark plugs. - Deposits and velvety soot on the candle
. The reason for this wear is poor quality gasoline. If deposits accumulate on the spark plugs, the gas station should be changed - otherwise these deposits will damage other engine parts. To correct the breakdown, the spark plugs can be cleaned or replaced. - Overheating
. Identified by severe wear of the top electrode and the bright white color of the insulator. Overheating may be caused by valves not closing tightly or using gasoline with a high octane number. It is also necessary to check the labeling: perhaps these spark plugs are simply not suitable for your engine. - Gloss or golden surface on candles
. It is necessary to replace the spark plugs with those suitable for the given engine. - Red soot
. Appears with excessive use of various fuel or oil additives that contain manganese or lead. If red carbon deposits appear on the spark plugs, it is recommended to remove it and also change the oil or gasoline, depending on where the additive was poured. - Natural wear of the spark plug
. At the end of its service life, the spark plug becomes covered with scale (iron and copper oxides) and rust - in this case it must be replaced with a new one.
Some spark plug faults
Candles with lean and rich mixture
The insulator on the right spark plug is covered with carbon deposits and because of this it has become a conductor. Therefore, the discharge flows down the insulator and there is no spark between the electrodes.
There is a large gap between the electrodes. Naturally, much more voltage is needed to break through the increased air gap. The coil is overloaded and subsequently fails.
Malfunction of the noise suppression resistance. The discharge flows along the surface of the spark plug insulator, since the conductor in the spark plug body is destroyed. The consequence is that the coil is overloaded and fails.
Symptoms of malfunctions
Worn and new SZ.
Additional factors influencing the condition of the spark plug, as well as its operating temperature:
- fuel quality;
- increased compression;
- change in ignition timing;
- temperature conditions of the region in which the vehicle is operated;
- humidity.
The following symptoms in vehicle operation may indicate a faulty spark plug:
- Poor engine starting when cold. Moisture concentration forms on unheated spark plugs in the cylinders when starting the power unit. If the interelectrode gap is large, there is a need to increase the breakdown voltage; electricity tends to lower resistance, that is, to moistened electrodes. Also affected by a decrease in battery capacity in the cold, as a result, a very small amount of energy is required for the formation of a spark, and the engine does not start.
- Increased consumption of the fuel mixture by the machine. Insufficient ignition in the cylinders leads to a decrease in power; to compensate for it, an excess amount of fuel enters the remaining cylinders (in which the spark plugs are working).
- Extraneous noises emitted while the power unit is warming up or at idle speed.
- Increase in harmful emissions from the exhaust pipe.
- Filled with SZ fuel.
- Reduced traction of the car, the vehicle does not gain enough speed.
Unpleasant consequences of untimely replacement of SZ:
- Reduced catalyst life. Insufficient ignition of the fuel mixture in the cylinders leads to the ingress of unburnt fuel residues into the catalyst. Once in the catalyst, the fuel burns out, and the layer on the catalyst honeycomb burns out. Damage can also be caused to the lambda probe.
- Broken ignition coil. An increased breakdown voltage contributes to an increase in the distance between the spark plug electrodes - this leads to a breakdown of the insulation of the coil layers, and it fails.
- Reducing the operating period of the motor. The entry of the fuel mixture into a faulty cylinder leads to fuel entering the crankcase, which reduces the oil life and wears out the cylinder.
When driving with faulty spark plugs, explosive popping noises can occur inside the combustion chamber. This is fraught with replacement: the crankshaft, piston group, connecting rod.
Troubleshooting
The first step, if you have diagnostic equipment, is to read the error codes.
Errors on the scanner monitor
We received a hint from the scanner, in the picture these are errors P300 and P304. Checking the spark plugs.
Checking spark plugs in a tester
High voltage wires, coils.
Checking high voltage wires
Diagnostics is the most difficult moment if you repair it yourself. We need tools and diagnostic equipment. To read errors and data, in a stripped-down version, you can use an ELM327 scanner and a smartphone. There will be a minimal hint. After repair, using ELM327, you can remove errors. This is the most budget option for a diagnostic scanner, and if you understand the process of engine operation, you can use it to solve many problems. To check high-voltage wires, you need a multimeter with the ability to measure resistance up to 20 Kom. To check spark plugs - a spark plug tester. This tool is quite expensive and not even every service has it.
Another option is to contact a specialist
How to replace spark plugs yourself
In older vehicles, replacing the spark plugs yourself is much easier compared to newer vehicles where it is not so easy to access the spark plugs under the hood. On older cars, after you open the hood, you immediately have access to dismantle them.
On new vehicles, in order to gain access to the spark plugs, you must first remove the protective plastic panel covering the engine. Also, on some cars, ignition coils may be installed above the spark plugs, which can also be removed. Accordingly, replacing spark plugs on such cars will take longer.
Required tools for replacement:
— Spark plug wrench or socket wrench with extension and spark plug head
— Large brush (brush) for cleaning dirt around the candle
— Clean cloth for cleaning
It is also convenient to use a torque wrench with a torque of 10 to 50 Newton meters to replace spark plugs . Thanks to this wrench, you will screw the spark plug into the cylinder head exactly as much as necessary and avoid damage to the threaded connection of the cylinder head.
Attention !!! Replacement of spark plugs is carried out only when the engine is cold, to avoid burns and other thermal injuries.
Each spark plug, as we have already said, is connected to the ignition coils using high-voltage wires. When disconnecting the wires, you must remember that each wire must be installed on the same engine cylinder after replacing the spark plugs. In some cars, high-voltage wires are numbered. If there is no numbering, then you can remember the location of the wires along their length or stick adhesive tape on each wire, which will need to be numbered.
Once you have removed the wires, you will see that the spark plug consists of a cap nut, a ceramic shell, and a hex nut.
Before unscrewing the spark plug, you must use compressed air to clean the dirt around the spark plug. You can also use a stiff brush for cleaning.
This way you will prevent dirt from getting into the engine after you remove the spark plug.
After cleaning the area around the spark plug, it's time to install the spark plug wrench and unscrew the spark plug from the engine block head . Unscrew the spark plug with care so as not to damage the threads in the cylinder head.
After this, screw in the new spark plug by hand. Next, tighten the spark plug with a spark plug or torque wrench.
Thanks to the torque tool, you will completely screw the spark plug into the cylinder head. Remember that if you do not tighten the spark plug, the spark plug may be damaged due to vibration.
In addition, the spark plug is responsible for sealing the combustion chamber. If you do not fully tighten the spark plug, it will result in loss of compression of the fuel mixture.
Excessive tightening of spark plugs is also dangerous, which can lead to failure of the expensive engine cylinder head. So we advise you to use a torque wrench to replace spark plugs, which allows you to control the tightening level (torque).
How to start servicing your car yourself?
Each vehicle requires a different level of torque when replacing the spark plugs when installing the spark plugs. The torque of the spark plug depends on the type of engine, the shape of the spark plug sockets, the thread in the cylinder head, as well as its material. Below we provide a table showing the most common spark plug tightening torques in common engines.
However, remember that this table is not universal. Therefore, look at the spark plug tightening level on their original packaging. Also, sometimes car manufacturers indicate similar parameters in the car’s operating manual. In addition, such data is available in car repair books.
Torque for spark plugs with a flat seat (with seal - gasket)
| Thread diameter | ||||
| Cylinder head material | 18 mm | 14 mm | 12 mm | 10 mm |
| Cast iron head | 35 - 45 Nm | 25 - 35 Nm | 15 - 25 Nm | 10 - 15 Nm |
| Aluminum head | 35 - 40 Nm | 25 - 30 Nm | 15 - 20 Nm | 10 - 12 Nm |
Torque for tapered spark plugs (without seal - gasket)
| Thread diameter | ||
| Cylinder head material | 18 mm | 14 mm |
| Cast iron head | 20 - 30 Nm | 15 - 25 Nm |
| Aluminum head | 20 - 30 Nm | 10 - 20 Nm |
What are the problems when operating a car with faulty spark plugs and what are the consequences?
The car doesn't drive well. No power, no acceleration, no speed. Increased fuel consumption. You can say poor ride quality and extra money on fuel.
Ignition system. The spark plug has failed, the coil is overloaded. After some time the coil fails. It is necessary to change not only the spark plugs, but also the coil. Candles cost from 500 rubles for 4 pieces to 1000 rubles for 1 piece. Reel from 1500 rubles.
In a cylinder where the air-fuel mixture does not ignite, the oil film is washed off from the cylinder walls. The consequence is increased wear of the cylinder walls, piston rings and piston. Further increased oil consumption, engine repair. Yes, yes, and this is possible if problems with the ignition system are not corrected in a timely manner. Engine repairs start from about 80 thousand rubles.
All modern cars have a catalyst. It is part of the exhaust system. Its operating temperature is 350 degrees. The unburnt air-fuel mixture entering the catalyst begins to burn. The catalyst temperature rises to 700 degrees. The consequences are a whole bunch. The car may catch fire. The catalyst filling may melt and close the passage for exhaust gases and the car will stop starting. The solution to this problem is replacing the catalyst. The catalyst costs from 50 thousand rubles, replacement from 5 thousand rubles.
Why do spark plugs fail?
Unfortunately, the longevity of candle service is affected by many factors and it is not possible to eliminate everything. However, some of them can be eliminated and unfavorable developments and breakdowns can be prevented.
Worth taking action
if the external description of the candle corresponds to the following characteristics:
- the spark plug is covered with soot deposits;
- there are oil deposits;
- there is a yellow or red coating on the candle;
- the electrode quickly becomes unusable;
- rapid wear of the spark plug connector itself;
- fill with low-quality fuel;
- poor engine condition;
- poor condition of the fuel supply system;
- aggressive vehicle operation.
Let's look at each point in more detail.
The spark plug is covered with soot deposits
- the first reason is low-quality fuel, the second reason is an incorrect ratio of the proportions of the air-fuel mixture, resulting from the second there may be a malfunction of the fuel injection system, the third reason is a faulty oxygen sensor
When there are oil leaks on the spark plug
- the first reason is a banal oil overflow above the norm, the second is wear of the piston group, and as a result, a major overhaul of the engine is required, and the third reason is a faulty turbocharger.
There is a yellow, red coating
— the main reason for the appearance of yellow and red deposits is the use of additives in the engine or fuel, this is not a serious malfunction, but it is worth thinking about their further use!
The spark plug electrode quickly becomes unusable
— the main reason for a spark plug malfunction is unregulated ignition or valve wear; secondary reasons are the quality of the fuel and the use of oil with aggressive additives. All this can lead to the rapid destruction of the candle.
Rapid wear of the spark plug connector
— it is worth noting that this malfunction is characterized by overheating of the spark plug and its destruction. Quite often, connector wear occurs due to poor-quality spark plug materials.
Quality of fuel used
— additives with a high iron content, which are used to increase the octane number, contribute to the formation of deposits on the electrodes, which makes sparking difficult.
Condition of engine parts
— the breakthrough of crankcase gases and oil into the engine cylinders due to a malfunction of the piston rings contributes to the deposition of carbon deposits on the spark plugs, which worsens their operating conditions.
Fuel supply system condition
— the over-enriched mixture does not burn completely, which also leads to the formation of soot and failure of the spark plugs.
Operating mode
— frequent starts, short trips, engine operation in low temperatures reduce the service life of spark plugs.
As you can see, the causes of spark plug malfunctions are very diverse.
.