Briefly about pistons: how to select a piston to a cylinder
Let's start with the fact that the gap between the piston and the cylinder is determined by clearly defined standards. For parts in a new engine, this gap ranges from 0.05 to 0.07 mm. For engines that are in operation, the gap between the piston and cylinder should not exceed 0.15 mm.
Restoring the engine's CPG will require boring the cylinder block to the repair size, after which a piston is selected from the group of so-called repair pistons. The main requirement for the cylinder boring process is the final result, which is as close as possible to the clearly indicated repair size.
It is also necessary to take into account that the size after boring the block will additionally decrease by an average of 0.03 mm after the honing process (honing the cylinder surface). For this reason, when honing cylinders, it is necessary to adhere to such a diameter that after installing the piston, the gap is as close as possible to 0.045 mm, which is the gap indicator for new parts.
To accurately select a new piston in size, you must first troubleshoot the cylinders and pistons. To measure the diameters of the piston and cylinder you will need the following measuring instruments:
- micrometer;
- bore gauge;
A micrometer measures the diameter of the piston, and a bore gauge measures the diameter of the cylinder. It is necessary to measure the diameter of the cylinder in four zones, and also measure two perpendicular planes. A clearly defined gap between the piston and the cylinder makes it easy to select the required piston size for cylinder boring, and also ensures ease of installation of the piston during assembly.
Further selection is carried out on the basis of a special table, which indicates the nominal sizes of cylinders and pistons. The diameter of the repair pistons received a special division into classes depending on the outer diameter of the part. There are 5 such classes in total, each class is designated by letters from A to E in alphabetical order (A, B, C, D, E) separated by 0.01 mm in size. Also, division into classes provides for changing the diameter of the hole for the piston pin every 0.004 mm.
This information about the classification of repair pistons is applied in the form of markings on the piston crown. The digital designation indicates the category of the pin hole, and the letter designation indicates that the piston belongs to a particular class (repair piston class). Also, in the process of selecting nominal sizes or repair piston sizes, it is additionally necessary to pay attention to the mass of the piston. Pistons can have either a standard weight or a weight increased or decreased by several grams. In parallel with the selection of new pistons, it is necessary to select repair piston rings, which also have repair dimensions.
Replacement
If you decide that installing piston rings is exactly what you need for a complete engine overhaul, then the next step is to purchase them. Usually, quality goods are packaged appropriately and tastefully
When choosing, you should pay attention to the appearance of the product and the quality of its coloring. There must also be a marking
To begin the repair correctly, you need to open the cylinder head. After this, you need to carefully analyze the condition of the parts and decide whether it is necessary to bore the cylinders themselves or grind the valves. How to prepare piston rings, how to install them without much difficulty, etc. - all this will be described below.
Preparation
The device itself for installing piston rings is sold in relevant stores, and it is in the form of pliers. If it is not possible to purchase them, then a small flat-head screwdriver will do, but when using it you should be as careful and careful as possible. Old piston parts can either be broken or removed.
However, piston rings, which are extremely easy to install, require the grooves to match their dimensions as closely as possible. Therefore, at least one old compression part can be broken, since carbon deposits form under it during operation, which will make installing a new one very difficult. A piece of such an old broken part would be perfect for tidying up his previous workplace.
Installation on piston
This is precisely the moment when a device for installing piston rings is indispensable, since repair work of this type is an extremely responsible matter and making mistakes is simply unacceptable. The elements of the piston group themselves are fragile, so you need to be careful and attentive. The middle one is considered the most fragile. When installing it, there is a high risk of breakdown.
The upper piston rings, which are installed first, are marked “TOP” and this side of the marking should be directed towards the piston bottom.
As for such a scraper-type part, it is installed with the scraper down. Installation of parts with chamfers should be carried out so that these same chamfers “look” upward. If you are dealing with assembled oil scraper elements that have a special two-function spring-type expander, then the upper and middle ones must be installed first. After this repair scheme is completed, it is necessary to check the ease of their rotation in the grooves themselves.
Installing pistons into the cylinder
During major repair work, the obsolete cylinder is bored or honed. They also use new repair-size pistons and ring elements of the same type, but with a larger diameter, with their subsequent compression. They should be lubricated with oil before installation so that they can easily “sit” in place. The fit should also not be too tight, since thermal expansion due to heating will cause the piston itself to jam.
Why do piston rings fail?
It may seem to the reader that due to their simple design and the use of wear-resistant materials, piston rings should have a huge, practically inexhaustible service life. Practice has shown that the rings of even the most reliable engines occasionally need to be replaced, although there are cases where the engine has been operated for many years without replacing the main components. It is worth understanding that piston rings, and especially the upper compression rings
, suffer from:
- Pressure changes;
- The influence of a chemically aggressive environment;
- Temperature changes;
- Dry friction.
The last point is worth examining in more detail. When the piston approaches the critical point, at the location of the compression ring
the amount of lubricant quickly decreases.
At the same time, pressure and temperature increase. As soon as the piston stops, the oil film breaks. The compression ring may travel further to the bottom point under conditions of dry friction, which leads to its rapid wear. For this reason, it is the top rings that are checked first - they wear out faster than the others. Compression and oil scraper rings
experience much less stress, so they fail much less often than conventional compression rings. Since the rings perform two functions at once, they have a special shape: conical with a slight angle of inclination. This has virtually no effect on their operational life.
In fact, oil scraper rings
– they experience light loads, since they are only responsible for draining excess oil. In the previous section it was already indicated that such rings have a more complex shape than compression rings: two belts that collect residual oil, as well as a special edge for draining lubricant. Complicating the design negatively affects the service life of the product, but due to low loads, it rarely needs to be replaced.
Parameters influencing the choice of ring size
Width of shank (hoop)
The width of the main part of the ring is an important point that many simply do not pay attention to. But in vain. Our fingers have a conical shape, so the high cylinder rings easily slip through the joint, but cannot sit properly on the phalanx, getting stuck halfway and causing discomfort while wearing.
1. If you are buying jewelry with a wide neck, take a model half a size larger.
2. Thin rings must be held very tightly on your finger, otherwise they will twist and fly off.
3. The size is selected closely for rings with large stones, so that the jewelry does not dangle from side to side (this is annoying).
Influence of air temperature and time of day
The timing of ring fitting is also important. In the morning, late evening and after heavy physical activity, the human body swells and blurs a little, although outwardly it is not noticeable. At such moments, there is no point in taking measurements from your fingers or trying to put a ring you like on your hand in a store.
It is better to postpone a trip to the jewelry store until the middle of the day, when we are in an active state and our muscles and blood vessels are in good shape. It is ideal if you have the opportunity to try on the product you like three times during the day (morning, afternoon and evening) - especially if you are choosing an engagement ring or jewelry for every day.
The weather outside can also affect our body size. In summer, due to dilated vessels, it increases slightly, and in winter it decreases in volume. Please take this fact into account when purchasing a ring.
Size charts from different manufacturers
Above, we determined the sizes of rings in those units used by domestic manufacturers. The same designations for jewelry products are provided in Germany. But other countries have their own measurement systems, and there are so many of them that it doesn’t take long to get confused about them.
1. In France, the ring size corresponds to the circumference of the finger in millimeters. In Switzerland, the same scheme is used, but the marking is written slightly differently: 40 mm is subtracted from the circumference and only the remainder is indicated.
2. Very similar meshes are used by Italian and Japanese manufacturers, although there are still slight differences between them. Here the sizes range from 4 (our 14th) to 26 - corresponding to a diameter of 22.5 mm. The pitch varies greatly.
3. The USA and Canada have their own system - North American manufacturers label rings from 3 to 13 sizes.
To determine the appropriate one, you can use the formula:
(Finger diameter – 11.5) ÷ 0.83
The result obtained is rounded to the nearest whole or half number.
Design and principle of operation
The design of the compression ring is simple: it is a ring that has a gap so that its elasticity allows the ring to diverge and maintain the pressure of the working edge against the cylinder walls. Material – high-strength cast iron, less often – high-alloy steel.
The operating conditions of the upper compression ring are harsh: high temperature and pressure. At the moment the mixture ignites, the pressure reaches 90 bar, the temperature approaches 1500 degrees. As the cylinder wears, it loses its uniform diameter, and with each up-and-down stroke of the piston, the ring has to compress and expand, which contributes to the accumulation of fatigue stresses. To increase the service life, at least the upper ring is coated with a layer of chromium, which has high hardness.
The second compression ring operates in lighter conditions - in this place the piston is already colder, and direct heat transfer from hot gases no longer affects it. Therefore, it may not be chrome plated.
Oil scraper rings were initially made of solid cast iron; they had two working edges with a groove between them. The oil that passed through the lower edge was collected by the upper edge into this groove, and through the radial holes in it fell into the holes in the piston skirt and was discharged inside it. This design had a serious drawback: both edges worked simultaneously; in worn-out engines, where the ring was warped along with the piston, oil leaked past the ring. Therefore, composite structures were invented: in them, two thin rings are pressed against the edges of the groove with a spring expander, through which the collected oil flows into the piston. Due to the small width of the individual rings and their operation, this design remains effective when the piston is misaligned.
Video “Checking the gap in the piston ring lock”
By studying the notes, you will learn how to select piston rings.
Sooner or later, your engine will wear out and require replacement of the piston rings or the entire piston.
It seems that replacing piston rings is a common task, accessible to anyone who is more or less familiar with the structure and principle of operation of a primitive four-stroke engine. But unfortunately, people are afraid to spend 15 minutes of their incredibly expensive time reading literature and charging everything in the engine according to the principle (as it was. It will probably work). Well, the flag is in your hands and contact the service as soon as possible.
So, we take the piston and see 3 grooves for installing piston rings. On 4-stroke engines, such as 2-stroke engines, there are no restriction plugs.
There are two types of piston rings on 4-stroke engines. The first two, which are installed in the two upper grooves, are compressive. As the name suggests, they are responsible for the presence of compression in your engine and must contain the gases produced during the flash due to the combustion of fuel in the combustion chamber.
Next three rings. These are oil scrapers. And here their goal is clear. They are responsible for removing the oil that coats the cylinder walls when the piston returns down. If these rings are missed, the oil will remain on the cylinder walls, threatening the engine to start eating oil and, of course, smoking.
How to install first? Yes, in principle, as they were from the factory, in the same order, but to avoid mistakes, we will show them again.
First we install the main oil scraper ring: the one that has a wavy structure. It is the easiest to install because it is the most flexible of all.
Then place the top and bottom rings of the SHADOW scraper. They are a little more complicated, but installing them doesn't have to happen either.
Now put the piston compression rings: those that are thicker and “firm”, Install the lower one first, then the upper one. They are a little more difficult to put on as they are less elastic and stronger. You're unlikely to break them, but don't bend them with perfectly crooked hands.
Do you think that's all? No!
The fact is that the rings still need to be positioned correctly on the piston so that the retaining rings (cutting points) do not fall on top of each other. Simply put, you need to cut the bottom ring that is not directly above the cut top ring.
Let's start with the upper piston rings.
The lower locking ring is located in the middle above the valve cavity, for example, at the inlet (can also be removed, there is no difference).
The lock of the upper ring is located strictly in the opposite direction to the lower ring. Accordingly, if the lock of the lower ring is above the cavity under the intake valve, the lock of the upper ring is above the cavity under the exhaust valve.
Now let's move on to the oil scraper rings. These rings should also be positioned in the same way so that there is no overlap with the lock. Therefore, the top ring is located above the piston pin hole on the right side.
The second (lower) is located on the opposite side, also approximately in the middle of the piston pin hole.
The last wavy oil scraper ring fits into any of the four sections created between the pin hole and the cavity under the valve.
And now to your question: what the hell is the author losing here? And why are the positions of all 5 rings so carefully established?
We explain. We did all this so that it would not turn out that when one lock is located above another, gases do not pass through these locks (in the case of piston rings) and no oil remains on the walls (in the case of an oil scraper). Ring).
If you take into account the piston rings, there is a loss of compression and the passage of hot operating gases to the oil control rings, which are not designed to withstand such sudden high operating temperatures. As a result, the rings may burn out after some time.
If we turn the oil scrapers towards the rings and the locks on them coincide, the oil will not be completely removed: it will reach the piston rings, which will cause the ring grooves to coke, and as a result they will shake and then burn.
As a result, you end up with burnt rings and a worn piston.
Bottom line: Pre-installation of ring locks takes only 2 minutes, and engine life can be extended by tens of hours.
Ring design
Before considering malfunctions and finding out when replacement or decarbonization of oil scraper rings is required, you need to know their design features. One-piece parts are no longer produced today, as they are no longer popular. Such parts have increased rigidity, which is why they do not adhere well to the surface and do not remove oil well. Today, parts are produced that consist of two or three parts. Such parts are called “stacked oil scraper rings”.
The first option consists of the oil scraper ring itself and a spiral spring. The advantages of such a product: it is quite flexible, which is why it fits tightly to the walls of the cylinder. The spring is pressed against the ring so tightly that the part looks solid. Three-piece rings consist of the following elements: a spacer spring and two steel plates. They are usually used in cars with gasoline engines. The advantage of this design is that it fits as tightly as possible to the cylinder.
Types of rings
Simple
Engagement rings, wedding rings, religious rings, hollow rings, solid rings are all considered simple rings. There are no large stones here, but they can be replaced by a scattering of small ones. Also, such jewelry is often made from different precious metals.
Pros:
- Large selection of both female and male models;
- Simple, elegant design;
- Suitable for everyday wear;
- Do not cling to clothes and hair;
- Do not require complex care;
- If necessary, you can reduce the size or, on the contrary, roll out the ring if you have gained weight.
Minuses:
To some, their appearance seems too modest.
Complex
Rings, rings with large stones, as well as products of non-standard shapes are complex. They are distinguished by rich decor, so they are usually worn only “on going out”
Such models invariably attract the attention of others - they are quite large and always look luxurious
Pros:
- Chic design that will not go unnoticed;
- Self-sufficient and do not require the use of additional decorations;
- A huge range of models to suit every taste and budget.
Minuses:
- Such rings are difficult to clean, and this will have to be done often due to the abundance of decorative elements;
- They can cling to hair or clothing, tear stockings and tights.
Thermal clearance requirements
Functional requirements for thermal clearance include:
- Heat removal from the piston at the moment of ignition of the mixture . Otherwise, the piston will burn out under the temperature of the combustion chamber.
- Piston space sealing function . The resulting pressure should evenly press the rings against the cylinder walls. Achieving such touch requires setting the correct distance.
- Requirements for oil scraper discs responsible for supplying the required amount of lubricant. Compliance with this rule keeps oil and gasoline consumption at the level of factory standards.
Options
Set gaps on rings
The established gap should correspond to 0.6-0.3 mm, and the side gap between the wall should not exceed 0.08-0.04 mm.
The value comes from the fact that exhaust gases act on the rings from the inside of the groove, pressing them against the wall. The coordinated functioning of compression and oil scraper rings allows for complete combustion of the mixture. This depends on how they are placed in the piston groove.
Therefore, a small value between the ends after warming up will lead to scuffing of the cylinder mirror.
The gap is measured with a feeler gauge and is regulated at 0.2-0.5 mm. For VAZ model engines, a value of 0.25-0.04 mm is provided on the sealing rings. Oil scrapers have 0.25-0.5 mm.
The first ring on top (compression), as loaded from alloy cast iron, is sprayed with chromium. The porous coating of this metal is capable of holding the required mass of engine oil.
Plasma coating of a layer of molybdenum on the rings promotes wear resistance and low friction with the cylinder.
Memo
The lock on the separator is painted blue
When choosing a repair size, you need to be guided by the product designation, including the engine model, kit number, product size. Additionally, the markings, which are located in a certain place of the product (close to the end), are checked. Expansion springs with a ground surface are carefully considered.
Checking piston rings during engine repairs after the car has driven 60,000 - 80,000 km
Although the service life of piston rings is 0 km, it is recommended to replace the piston rings in all cases of engine disassembly with a mileage of more than 20,000 km. This, on the one hand, will eliminate the need to re-disassemble the engine after a relatively short mileage of the car, and on the other hand, it will be a preventative measure to increase the overall service life of the engine.
If the cylinder mirrors have minor wear and do not require repair, then repair rings of normal size or increased in diameter by 0.25 mm can be used instead of the previous piston rings. The choice of one or another ring is determined by the size of the gap in the lock, measured at the ring installed in the cylinder in which it will work. Normal size piston rings can be used if the gap in their lock does not exceed 0.75 mm. Otherwise, you need to use rings increased by 0.25 mm, ensuring gaps in their locks of at least 0.4 mm. To do this, it is allowed to file the joints of the lock.
In cases where the cylinder mirrors require repair, the old piston rings are replaced with repair rings having increased outer diameters.
Table. Piston ring kits for repair (quantity per engine)
| Kit number | Repair ring size | Nominal outer diameter of the ring, mm | Caliber diameter for external operations, D1 + (0.6 - 0.8) mm |
| 407-1000101 -P | Normal | 75,875 | 75,875 |
| 407-1000101-RZ | Increased by 0.25 mm | 76,125 | 76,125 |
| 407-1000101-Р6 | Increased by 0.5 mm | 76,375 | 76,375 |
| 407-1000101-Р8 | Increased by 1.0 mm | 76,875 | 76,875 |
| 407-1000101-Р9 | Increased by 1.5 mm | 77,375 | 77,375 |
The table shows the numbers of sets of repair piston rings (for spare parts) of both normal and repair sizes. At the same time, rings of normal size and those enlarged by 0.25 mm are designed to work in cylinders whose mirrors do not require repair. Accordingly, rings increased by 0.5; 1.0; 1.5 mm, intended for cylinders repaired by grinding or boring. These rings are installed on enlarged pistons of the same size as the repair rings.
Table. Repair dimensions of cylinders
| Repair dimensions of cylinders, mm | Piston numbers and sizes | Cylinder repair technology |
| 75,875-75,925 | 408-1004015 normal size | Not repairable or just honing |
| 76,375—76,425 | 408-1004016-Р6 increased by 0.5 mm | Boring, grinding and subsequent honing |
| 76,875-76,1925 | 408-1004015-Р8-А increased by 1.0 mm | Same |
| 77,375-77,425 | 408-1004015-P9-A increased by 1.5 mm | » » |
Table. Main parameters of piston rings of normal and repair sizes
| Options | Compression rings | Oil scraper rings | |
| upper and middle | lower | ||
| Height, mm | 2,173—2,185 | 2,165—2,185 | 3,97—3,99 |
| Radial thickness, mm | 3,2-3,4 | 3,2-3,4 | 3,2—3,34 |
| Gap in the lock of a ring installed in a caliber having an internal diameter D, mm | 0,41-0,76 | 0,41—0,76 | 0,41—0,76 |
| The difference in diameters in directions A A and B B when the ring is compressed with tape until a gap in the lock is 0.41-0.76 mm | 0,2—0,6 | 0,2—0,6 | 0,2-0,6 |
| Elasticity of the ring compressed with tape until a gap in the lock is 0.41–0.76 mm, kg | 1,3-1,8 | 1,3—1,8 | 1,4-2,0 |
The geometric parameters of the piston rings are given in the tables above. In all cases of replacing piston rings, it is necessary:
- In the two upper grooves on the piston bottom, install compression rings that have a groove on the inner cylindrical surface facing towards the piston bottom.
- Install a compression ring with a groove (on the outer cylindrical surface) facing the piston skirt into the third groove on the piston bottom.
- Install the oil scraper ring into the fourth groove on the piston crown.
- After replacing the rings, you must follow the engine break-in rules.
Symptoms of a problem
The first thing the reader should focus on is the size of the piston ring gap. Taking the shape of the piston grooves, the rings form a gap of 0.15-0.50 mm
. The technical documentation of the engine indicates the exact size of the gap, but on average it falls within the specified range. If the gap increases significantly, problems with the engine will occur. The main signs of piston ring failure usually include:
- A drop in power of the power unit due to a decrease in compression;
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Serious increase in oil consumption.
The mileage of inexpensive piston rings usually does not exceed 150 thousand km
.
More expensive analogues from the known ones are about 300 thousand km
, although there are many cases where the mileage of the rings exceeded the 500 thousand km mark. Piston ring failure can be difficult to identify without directly inspecting the pistons. However, the degree of wear can be determined by subtle signs. These include:
- Black smoke appears. The reason lies in the fact that some of the gases from the combustion chambers pass through the compression rings and enter the engine crankcase. At the same time, the pressure in the cylinders drops and, accordingly, the engine power;
- The appearance of blue smoke with a bluish tint. Indicates the fact that lubricant has entered the combustion chambers;
- White exhaust appears. Typically, white exhaust is caused by moisture. If the color of the exhaust has not changed after prolonged warming up of the engine, it makes sense to check the oil scraper rings;
- Changing the composition of the fuel-air mixture. Often the mixture is over-rich, as indicated by acrid black smoke and popping noises in the exhaust system.
Even if a car enthusiast observes any of the above, you should not immediately proceed with partial disassembly of the engine and inspection of the piston rings. First, you should check the spark plugs. If they are covered with oil deposits and fresh lubricant, the integrity of the piston rings is most likely compromised. It also makes sense to check the air filter and air corrugation - there should be no traces of oil on them.
There is one fairly reliable test: start the engine and leave it idling .
, listening. Change gear. If the engine is unstable and shaking, then the pressure in its cylinders is uneven - this indicates wear on the first two piston rings. Clearly audible knocking noises may indicate a lack of lubrication. The components responsible for this malfunction can be either oil scraper rings or, for example, an oil pump. In this case, inspection and diagnostics at a service station are required.
Basic faults
Decarbonization of engine piston rings
Since these CPG elements are in constant contact with the cylinder wall, their main malfunction is the wear of the working surfaces. The service life of these elements largely depends on the material of manufacture and operating conditions, and it can vary from 150 thousand to 1 million km.
But failure to comply with operating rules can significantly reduce their service life. The resource can be affected by:
- Untimely replacement of lubricant in the power plant.
- Use of low quality fuel.
- Frequent use of the car in traffic jams or short trips.
- Creating excessively large loads on the power plant.
- Motor overheating.
The main signs of severe wear of the piston rings are a strong drop in compression, as a result of which the power and dynamic performance of the car decrease and fuel consumption increases, as well as a significant increase in lubricant consumption.
How to choose piston rings
The selection of piston rings means that the dimensions of the piston rings must necessarily correspond to both the dimensions of the pistons and the dimensions of the cylinders. Let us add that selecting piston rings by size is a little easier compared to selecting the pistons themselves. This is due to the fact that repair piston compression and oil scraper rings for various engine models are more or less interchangeable today. This means that you can purchase both original piston rings and select parts from a third-party manufacturer.
Selection of rings by size
It is necessary to select rings taking into account the following basic parameters:
- piston ring height;
- piston ring diameter;
Any high-quality analogue that has the required dimensions often becomes available without any problems. To be completely sure, it is also necessary to take into account the radial width of the piston rings, or rather, the correspondence of this width to the piston grooves. In other words, the depth of the grooves in some cases may be insufficient.
As for compression rings, such rings are structurally similar, often have the same or almost the same radial width, so problems usually do not arise after installing correctly sized rings from this group. The selection of oil scraper rings, on the contrary, requires increased attention both to the design of the ring itself (box-shaped, stacked oil scraper rings), and additional clarification of their radial width according to special catalogs of the ring manufacturer.
We also recommend reading the article about
what to do if the piston rings are stuck
. From this article you will learn about the reasons for the occurrence of rings, self-diagnosis of the problem and how to repair this problem yourself.
I would like to add that selecting piston rings for diesel engines is more difficult. Compression rings for diesel engines are molybdenum coated and also have a trapezoidal profile, which can additionally have different angles. Oil scraper rings in diesel engines are usually box-shaped, but this fact must also be checked in catalogs, since there are cases of installation of set rings on a diesel engine.
Please note that it is highly not recommended to install piston rings from a gasoline engine on a diesel engine. At the same time, in some cases, it is possible to install piston rings from a diesel engine to a gasoline engine.
Which piston rings are better
In addition to choosing from the available nominal and repair sizes of rings, you will also need to separately select the material of manufacture. It is quite fair to say that piston rings for a low-power, low-speed engine, which was developed 10-15 years ago (even taking into account their full compliance in size), will be able to function normally and for a long time in a highly accelerated turbocharged power unit.
The fact is that the materials, coating applied and tolerances on the geometry of the rings may well differ. During the selection process, close attention should be paid to these factors, especially in the absence of accurate data in the manufacturer’s catalogs. It should also be added that rings for new engines usually work well in older internal combustion engines, but not vice versa.
The upper ring is the most heavily loaded during the operation of the internal combustion engine. For this reason, such rings are made of alloy cast iron, which is also plasma sprayed with chromium or molybdenum. Chrome has a porous structure, which allows it to effectively retain the required amount
motor oil
. Coating with chromium or molybdenum increases the wear resistance of the rings and also provides a low coefficient of friction during contact with the cylinder walls.
Cast iron piston rings are considered to be of sufficient quality. Such parts are made of high-strength cast iron, which has improved properties and actively resists wear. Oil scraper rings are available in chrome plated and also without chrome coating. Steel rings additionally equipped with a spring element are also on sale.
Chrome rings are usually installed on engines with a high compression ratio, which implies more severe loads on the internal combustion engine and CPG. Foreign-made civilian cars often have stainless steel piston oil rings. Such rings are characterized by a long service life, low weight and reasonable cost.
Types of rings
Modern jewelry store windows sparkle and shimmer with an abundance of wedding jewelry for every taste and budget. Among all this diversity, from which the eyes run wild, several options can be distinguished.
Designer models
For those who prefer exclusive, expensive and stylish jewelry to their traditional favorite classics. They are made in a variety of stylistic directions, and a variety of materials and stones are used to make them. The main thing in such an accessory is its unusualness and bright individuality.
Engraved models
Very often, wedding rings are decorated with memorable inscriptions. This could be a ring with initials or a tender wish, with a memorable date or with the inscription “Save and preserve.”
Smooth rings
Ordinary, simple, straight models that have not gone out of fashion for many hundreds of years. There is no decor or corrugated surface - just a perfectly even and smooth decoration. A pair of rings most often differs only in width.
Diamond Cut Jewelry
A very popular option in recent years. It is a variation of the classic smooth ring, only decorated with small notches in the form of a specific pattern or ornament. Such grooved rings are often made in two colors.
Ring with stone
This can be one large stone or a scattering of small stones along the rim or wide part of the decoration. Among the most popular models are accessories with emerald, ruby, sapphires, diamond, cubic zirconia.
Muslim rings
Muslims do not have a strict tradition regarding wearing wedding rings. In addition, men are forbidden to wear gold, so Muslims perceive a wedding ring not as part of the wedding ceremony, but as a gift to a lover or lover. A man can wear a ring made of silver, and a woman can wear a ring made of gold or other metal.
Slavic
We are talking not only about engagement rings, but also about wedding rings. The bride is required to wear silver jewelry, and the groom - gold. Church rings should be as simple as possible, without designs or stones.
In appearance, rings can be wide or thin. Thick, massive models look most natural on men's hands. By the way, the weight of the ring itself also plays an important role. A too massive, heavy ring will constantly pull your hand back, causing discomfort. Those with graceful fingers should not forget about this.
Ring with rotating middle part
This decoration looks very unusual and original. It can be made of gold or silver, and the rotating insert can be made of metal of a contrasting color.
It gives the impression of several jewelry on one finger.
The surface of the jewelry itself can be different: some prefer matte rings, others like shiny ones. The decorations themselves can be smooth or openwork. Carved rings always look very interesting and stylish, especially on a woman’s hand.
Rings are most often round in shape, but sometimes there are square jewelry or models made in more complex geometric shapes.
The color scheme of wedding rings is quite laconic. Yellow or white rings are common. White jewelry can be decorated with a gold plated insert or jewelry made of precious stones. Sometimes there are more unusual models, for example, black ones.
Typically, wedding rings are not decorated with ornaments; they differ from other rings in their simplicity. But modern fashion offers interesting and unusual options with different patterns: with a braid, floral patterns, images of butterflies, birds, architectural structures.
The appearance of jewelry can vary significantly among different peoples of the world, for example, among representatives of European and Asian countries. The design of the accessory is influenced by the traditions and customs of each nation.
It is traditionally accepted that wedding rings are worn on the hand all the time. While removing them from your hand, the jewelry is stored in a ring box, which, by the way, can be immediately purchased along with the rings.
After a divorce, the old wedding ring is not given to another person. The decoration can be melted down into a new accessory.
Which rings are better
The question of which piston rings are best to purchase for replacement haunts many car owners. With the variety available, it is not easy to make a choice. You can answer this: if the purpose of the replacement is to restore the normal performance of the engine, the standard ones are quite sufficient, but if the owner wants to improve the performance of the engine, it is better to pay attention to more “sophisticated” products, for example, chrome-plated or molybdenum.
Passenger cars are equipped with different types of engines; power units may differ in volume, power, and design.
If oil consumption in an engine increases, the most common reason for this is worn or broken piston rings; replacing them is quite labor-intensive work, and also requires certain plumbing skills.
Fitting and installation of new piston rings [edit | edit code]
After prolonged operation, the engine cylinder develops oval wear and a step in the upper part of the cylinder, where the upper ring reaches. Both rings and pistons wear out, gas breakthrough gradually increases and oil consumption increases. The time has come for intermediate or major repairs.
During a major overhaul, a worn cylinder is usually bored and/or honed, new repair pistons of a slightly larger diameter are installed (on automobile engines, the next repair size is usually 0.5 mm larger) and repair-size rings. If the condition of the cylinders is still acceptable, the rings and sometimes the pistons must be replaced. According to modern instructions, the installation of rings for subsequent repairs with a point is not allowed, but in order to reduce repair costs, it is used.
Note: when installing the rings for the next repair, you need to carefully check the fit on the mirror.
Usually, after sharpening and setting the minimum gap in the joint,
slightly
work on the piston ring
in the area of the lock along the outer diameter
(!), preferably with an emery block. If this is not controlled, then there will be increased oil consumption for some time, and the risk of overheating during break-in will increase.
The piston must have clearance in the cylinder according to the instructions. Typically, a piston lubricated with engine oil should move easily in the cylinder under its own weight (at room temperature). If the piston has a tighter fit, thermal expansion due to heating will lead to scuffing and a decrease in engine life. On the other hand, if the gap between the piston and the cylinder walls is too large, the piston will knock during operation, and due to increased gaps in the ring locks, the service life before repair will be reduced. The piston rings themselves, due to the presence of a gap, can change their diameter within small limits, which avoids jamming. This small change in diameter is enough to compensate for thermal expansion and contraction. If rings without a piston are inserted into a new or repaired cylinder, the gap should be about 0.2-0.4 mm (for more specific data, see the operating instructions)
. If the gap is smaller, the rings are sharpened with a file; if it is larger, they are installed from a larger repair kit.
The rings are passed over the grooves by placing thin metal plates under them (several pieces along the circumference), or using a ring puller. When installing a piston with rings into a cylinder, the latter are compressed using a mandrel or a homemade tin clamp.
The piston and cylinder of an internal combustion engine have similar dimensions, however, no matter how high precision they are manufactured, there is still a gap between them through which gases generated as a result of combustion of the working mixture could freely pass into the crankcase, and from the crankcase into the chamber combustion would involve engine oil. To prevent these extremely undesirable phenomena, piston rings are used.
They are open rings, seated with a small gap in the piston grooves intended for this purpose. According to their purpose, they are divided into two groups:
- compression, the task of which is to prevent the breakthrough of gases from the combustion chamber into the engine crankcase;
- oil scrapers designed to remove excess engine oil from the cylinder walls.
Compression piston rings have an outer diameter slightly larger than the cylinder diameter. In order for the part to fit inside, a cutout called a lock is made in it. The surface of the compression ring is made smooth, without any grooves. Oil scraper rings, in contrast, have through slots designed to drain oil.
The number of rings installed on one piston may vary. At the dawn of the automobile era, when engines were low-speed in order to cope with compression losses as best as possible, their number reached seven. In modern engines, for each piston, as a rule, three are used: two compression and one oil scraper. For sports cars with high-speed forced engines, engineers quite often limit themselves to just two.
Replacing piston rings
On VAZ cars, as well as on all other models of passenger cars, it is advisable to change only the piston rings only if:
- there is no exhaust in the cylinders;
- there are no signs of damage to their inner surface.
If the liners are significantly worn, they need to be bored, and if the last size was already used before, the cylinder block needs to be relined. You can replace the PC on any VAZ engine without removing the internal combustion engine; this will require removing the cylinder head and oil sump. PCs are replaced if the gap at the joints does not exceed 1 mm.
For example, let's consider replacing piston rings on a VAZ-2114 car with an 8-valve internal combustion engine; such work must be carried out on a pit or a car lift:
- turn off the ignition, put the gearbox in neutral, disconnect the negative terminal from the battery;
- drain the antifreeze, remove the air filter housing along with the pipe (injector corrugation);
- remove the valve cover, camshaft, loosen the timing belt and move it to the side;
- disconnect the wires and cooling system pipes from the cylinder head, unscrew the head bolts;
- unscrew the nuts of the exhaust pipe of the muffler;
- We completely free the cylinder head from all fasteners that prevent it from being removed, and we remove the cylinder head;
- if there is protection under the engine, remove it;
- place a container under the engine sump, unscrew the plug on the crankcase, drain the oil;
- remove the lower hatch of the gearbox housing (three bolts);
- Using a 10 mm wrench or a socket wrench, unscrew all the oil pan bolts;
- dismantle the pan, remove the oil receiver;
- Unscrew the connecting rod nuts, remove the lower connecting rod caps, and carefully knock the pistons and connecting rods upward. Pistons should be knocked out through a soft metal drift or through a wooden block. First, you need to carefully knock out the connecting rod bolt without damaging the threads on it, then place the drift on the end of the connecting rod - in no case should you hit the bearings or the seat underneath them;
- It is recommended to remove the connecting rods one at a time, and immediately attach the caps to them; the caps should not be confused with each other, they are placed back strictly in their places, and a lock to the lock is required;
- remove the PC from the pistons, use a piece of the old ring to clean the piston grooves to bare metal. Be sure to check the cleanliness of the groove all around; there should be no coke left in it;
- We install new rings in the grooves, start with the lower MPC, then install the middle compression PK, and lastly the upper one. For installation, you can use a special device, but it is still more convenient to install the rings by hand. If the MPCs are cast iron, they cannot be bent along their axis, they can only be carefully moved apart. Compression rings also need to be bent carefully, to a minimum;
- we install the piston in place using a special mandrel, hammer it in with a wooden hammer handle or a brass or bronze drift;
- We install one piston-rod at a time, and immediately attach a connecting rod cap to each one. The connecting rod nuts should be tightened with a torque wrench, force - from 4.5 to 5.5 kg;
- then we put everything in place - the oil receiver, the engine sump, the cylinder head. We fill the radiator with antifreeze, oil into the crankcase, and start the engine to check. After replacing the PC, the internal combustion engine may initially smoke and consume oil - the engine needs to be run in for approximately 2 thousand km. It happens that despite the seemingly normal condition of the liners, the internal combustion engine continues to smoke even after replacing the rings after break-in. In this case, you will have to bore the cylinders and install a repair piston group.
Disassembling the engine to replace rings
Before replacement, it is necessary to perform a number of preparatory work:
- it is necessary to drain the used engine oil, because after installing new rings you need to fill in fresh working fluid;
- We loosen the exhaust pipe of the muffler;
- you need to remove the valve mechanism cover and align the engine to the marks;
- we dismantle the camshaft star, and for front-wheel drive VAZs we remove the bolt securing the belt drive pulley, and then the timing belt itself with the pulley;
- in the classics, we loosen the tensioner, and then also dismantle the chain and sprocket mounted on the camshaft;
- then we dismantle the rocker with springs, laying everything out in the correct order to assemble the parts into place;
- remove the block head, before this you need to disconnect the manifold;
- unscrew and get rid of the pan and oil pump;
- remove the connecting rod caps, and then push the connecting rods up so that they can be pulled out along with the piston.
Operation of diesel and gasoline internal combustion engines
To better understand the importance of piston ring clearance in engine operation, let's consider how the two most common systems work. In reality, the difference between them is not that great, at least in terms of design.
The main difference is the ignition process. In diesel engines it occurs due to increased pressure. As a result, the temperature rises, after which the nozzle injects fuel inside, and ignition occurs on its own.
The gasoline engine is designed a little differently. Instead of an injector, spark plugs are installed at the top of the pistons, which supply sparks. Naturally, with such a design, normal piston ring clearance is very important.
This is interesting: How to disassemble a bicycle fork with a shock absorber
Piston group: equipment and device
The piston group is a piston and a group of sealing rings. It also includes the piston pin and fastening parts. It is worth considering the purpose of this mechanism.
Due to it, gas pressure is sensed and transmitted through the connecting rod to the crankshaft. Also, thanks to a mechanism such as a piston group, the above-piston cavity of the cylinder is sealed. This way it will be protected from excessive lubricating oil and gases entering the crankcase. This function is of great importance for good engine performance. The technical condition it is in is judged by its sealing ability. For example, in machine engines it is not allowed for oil consumption to be more than three percent of fuel consumption.
The piston group also carries out its work in difficult climatic conditions. That is why the parts of this mechanism have high thermal stress, and this is taken into account when choosing material and design for them. Manufacturers usually develop their elements, taking into account the type of engine and purpose (transport, stationary, diesel, formed, etc.). However, the general structure still remains the same. So, we should consider what the piston group is made of.
The trunk part (guide) is also called the piston skirt. It has bosses on the inside, with holes drilled in them for the piston pin. The lower edge of the skirt is often used as a technological base when machining the piston. For this purpose it is equipped with a bored collar. In addition, the walls of the skirt still perceive lateral pressure forces, and this increases their friction against the cylinder walls and increases the heating of the cylinder and piston.
The piston head carries the piston rings and has a bottom. The lower groove has drainage holes through which lubricating oil escapes so that it does not accidentally enter the combustion chamber. Its bottom is one of the chamber walls. It perceives significant gas pressure. The bottom itself can be flat, concave, convex or shaped. Again, its shape is chosen taking into account the type of engine as well as the combustion chamber.
It is impossible not to mention such a mechanism as the cylinder-piston group. The main defects in cylinder blocks are cracks, chips and wear. These faults are determined after a thorough inspection, crimping and measuring of the cylinder. In this process, you need to install a head or a cast iron plate on the block (a rubber gasket is required). In general, this group is distinguished by heat-resistant steel and oil cooling, which is carried out through the circulation general lubrication system of the main diesel engine. If you provide good care to the mechanism and high-quality oil, you can easily increase the life of the pistons and cylinders.
And another mechanism is the connecting rod and piston group. The piston is cast and aluminum. The outer surface has a very complex shape. The piston pin is hollow and steel and rotates freely in the connecting rod bushing and piston bosses. And the piston rings are made of cast iron. And, of course, the connecting rod is forged and steel. Its upper head has a bushing made of a mixture of steel and bronze, which has a positive effect on the work of the entire group.
2020 Engagement Ring Trends
- Breaking stereotypes. Open rings, unusually cut stones, futuristic design... No wonder: the millennial generation is approaching the altar. Engagement rings are becoming more and more unusual and far from the classics. Or maybe this is how a new classic is born?..
- Yellow and rose gold. What is familiar to Russia has become fashionable in the West. Let's take note.
- A combination of two or more metals. This trend is not going to lose ground, if only for the reason that such a ring fits very well into any set.
- Instead of a single solitaire diamond, groups of stones with an unusual arrangement are becoming increasingly popular.
- Center stone cuts such as pear, marquise and asscher are gaining popularity.
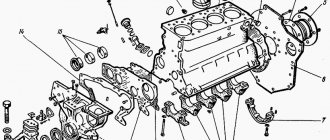
Dimensions and markings of piston rings VAZ 2109 – 2115
I will now give you the main dimensions of the connecting rod and piston group below in the figure.
The piston is cast aluminum. According to the outer diameter, the pistons are divided into five classes (A, B, C, D, E) every 0.01 mm. The outer surface of the piston has a complex shape. Therefore, it is necessary to measure the piston diameter only in a plane perpendicular to the piston pin, at a distance of 55 mm from the piston bottom.
Main dimensions of the connecting rod VAZ 2109 – 2115
Based on the diameter of the hole for the piston pin, pistons are divided into three classes (1, 2, 3) every 0.004 mm.
The classes of piston diameters and holes for the piston pin are stamped on the bottom of the piston (Fig. 4).
The piston is cast aluminum. According to the outer diameter, the pistons are divided into five classes (A, B, C, D, E) every 0.01 mm. The outer surface of the piston has a complex shape. Therefore, it is necessary to measure the piston diameter only in a plane perpendicular to the piston pin, at a distance of 55 mm from the piston bottom.
Dimensions of piston rings VAZ 2109 – 2115
Based on the diameter of the hole for the piston pin, pistons are divided into three classes (1, 2, 3) every 0.004 mm.
The classes of piston diameters and piston pin holes are stamped on the piston crown.
Piston markings VAZ 2109 – 2115
VAZ piston rings
The Volzhsky Automobile Plant produces engines for front-wheel drive and rear-wheel drive cars; piston rings for VAZ engines were originally supplied by the Michurinsky plant. The Michurins produced a lot of defects in their products, and since 1986, their own production was established in Tolyatti. Currently, there are many different manufacturers that produce PCs for VAZ engines, in particular, these are:
- AVTOVAZ (Tolyatti);
- STK (Samara);
- GOETZE (Germany);
- MAHLE (Germany);
- NPR EUROPE (formerly SM, Japan).
Tips and tricks
It is quite obvious that the most convenient option for selection would be to use original piston rings. By original we mean piston rings, which are positioned as original spare parts by the engine manufacturer itself. At the same time, the original parts available for sale do not always allow the implementation of the assigned tasks during engine tuning or repair. In such cases, it is necessary to carry out a competent selection from a group of high-quality analogues.
- When selecting non-original piston rings, it is advisable to choose rings that were originally intended for an engine with similar characteristics. Such characteristics should be understood as volume, power, degree of engine boost, maximum crankshaft speed, compression ratio, etc.
- It should be noted that the installation of so-called “soft” rings, which have a shorter service life, allows you to minimize wear on the cylinder walls, thereby increasing the service life of the BC. In parallel with this, replacing the piston rings in this case will require an average of every 35-45 thousand kilometers traveled, which casts doubt on the feasibility of such a solution. Good quality piston rings have a service life of about 170-220 thousand km. When replacing them at such mileage, the engine still often requires crankshaft repair, restoration of the CPG, etc.
Finally, we would like to add that correctly selected and professionally installed non-original piston rings can, in some cases, last longer compared to original parts. It is also worth considering that high-quality analogues usually cost 10-25% less.
Capture in the ring
Our respondents immediately excitedly began to produce stories, for example: “If you know a girl’s friend, then ask her to help. A friend invites your girlfriend to the store to buy a ring. If she goes, she will get involved in the process, and it’s easy to find out the size.” The idea that a friend, as soon as she received the task, would dial the number of the girl being measured and blurt out about the “surprise” did not occur to any man.
There were more complex multi-steps:
As soon as the detective schemes failed, the men switched to practical methods.
• “Break an old ring and volunteer to take it to a repair shop and take it to a jewelry shop.”
• “Start tying a knot, ask to hold the loop so that your finger is inside the loop, supposedly then insert a pen or stick, and fix the loop in this position. It is important that the rope does not stretch.”
• “Write an email from a jewelry store that sends out advertisements. Copy the html and edit it a little. Promise in it a free distribution of rings after reporting the size in the answer.”
Review of popular models of piston rings VAZ 2109 – 2115
There are many companies that produce piston rings, as well as many fakes, and there is simply not enough time to look through them all. Therefore, let's look at those manufacturers of piston rings that differ from others in normal quality and price. The first thing I want to recommend is SM piston rings.
Piston rings from “SM” Piston rings from “Mahle”.
These companies produce piston rings for VAZ cars of various diameters and are perfect for us. They are most likely produced in China, because the original ones will cost much more. But this does not mean that everything is so bad, their quality is excellent. I still recommend rings from “SM”, because their price is much lower than that of “Mahle”, and the quality is the same, so why pay more and overpay for the brand.
The upper compression ring from these manufacturers is chrome-plated steel, but from the “SM” company it is copper-plated, this is clearly visible in the top photographs. The second compression ring is black and made of cast iron, but the ring from Mahle has a darker color. On the picture
The lower oil scraper rings are metal typesetting. The graphics on the left are “SM”, and on the right “Mahle”.
I recommend using metal oil scraper rings, because, unlike box-type rings, they fit perfectly in the cylinder, are resistant to overheating (they do not lose their spring properties) and their main advantage is that they work as two rings independent of each other. The rings are box-type, very afraid of overheating. When they overheat, they lose their spring properties and do their job poorly. And one more serious disadvantage: they require very careful running-in. At the slightest deviation from the running-in conditions, the working edges of the ring may break off in some places and allow oil to leak through.
Of course, there are other manufacturers of piston rings, but as usual they are complete fakes and sometimes it’s not possible to choose quality ones
How to Determine Ring Size
There is no difficulty in choosing a ring for yourself. You just go to any jewelry store and ask a specialist to measure your finger and choose the appropriate ring size. But what to do when the jewelry is chosen as a gift? How to determine the size of a ring on a finger and not declassify the plan? “head-on” is not an option, and not everyone knows about ways to find out the size on their own. But don't worry - in this article we'll share some great ways to take your measurements. Choose the one that suits you and go get a gift fully prepared!
Additional recommendations
There are a few important things to keep in mind when measuring your fingers.
Firstly, for the most accurate results, it is ideal to measure your finger three times: morning, afternoon and evening. Depending on the time of day, your hands may swell or swell, so you need to choose a ring that will not pinch even with swollen fingers. You should not measure your fingers on hot days or after active sports. Take measurements several times and on different days - if at least two values are similar to each other, then you have found the exact size.
Secondly, it is important to know the thickness of the gift ring. If it is thin (up to 7mm), round the value obtained during measurements to the nearest one. For example, if during your measurements you get a value of 15.8, then the required size will be 16. If the ring is thicker than 7mm, it is worth making a reserve of 0.5mm. With the same value of 15.8, it would be better to choose size 16.5.
Table of nominal sizes of cylinders and pistons
| Size group | Engine model VAZ 2109 – 21099 | Engine model VAZ 2113 – 2115 | ||
| Cylinder diameter mm | Piston diameter mm | Cylinder diameter mm | Piston diameter mm | |
| A | 76,00 – 76,01 | 75,965 – 75,975 | 82,00 – 82,01 | 81,965 – 81,975 |
| B | 76,01 – 76,02 | 75,975 – 75,985 | 82,01 – 82,02 | 81,975 – 81,980 |
| C | 76,01 – 76,03 | 75,985 – 75,995 | 82,02 – 82,03 | 81,980 – 81,985 |
| D | 76,03 – 76,04 | 75,995 – 76,000 | 82,03 – 82,04 | 81,985 – 81,995 |
| E | 76,04 – 76,05 | 76,000 – 76,005 | 82,04 – 82,05 | 81,995 – 82,000 |
By weight, pistons are sorted into three groups: normal, increased and decreased by 5 g. These groups correspond to markings on the bottom of the piston: “G”, “+” and “-”.
All pistons on the engine must be of the same mass group. Repair size pistons are manufactured with an outer diameter increased by 0.4 and 0.8 mm.
An increase of 0.4 mm corresponds to a marking in the form of a triangle, and an increase of 0.8 mm corresponds to a marking in the form of a square. The arrow on the piston crown shows how to properly orient the piston when installing it into the cylinder. It should be directed towards the camshaft drive.
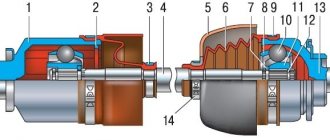
Marking of the connecting rod: 1 – class of the connecting rod by weight and by the hole in the upper head. 2 – cylinder number
The piston pin is a hollow steel, floating type, which rotates freely in the piston bosses and connecting rod bushing. The pin is secured in the piston hole by two retaining rings. According to the outer diameter, the fingers are divided into three classes every 0.004 mm. The class is marked with paint on the end of the finger: a blue mark is the first class, a green mark is the second class, and a red mark is the third class.
Places where metal can be removed when adjusting connecting rod heads
The piston rings are made of cast iron. The upper compression ring has a chrome-plated barrel-shaped outer surface. The lower compression ring is scraper type. The oil scraper ring has chrome-plated working edges and an expansion coil spring. Repair size rings are marked digitally “40” or “80”, which corresponds to an increase in the outer diameter by 0.4 or 0.8 mm.
The connecting rod is steel, forged. The connecting rod is processed together with the cover and therefore they are individually non-interchangeable. To avoid mixing up the caps and connecting rods during assembly, they are marked with number 2 (Fig. 5) of the cylinder in which they are installed. A steel-bronze bushing is pressed into the upper head of the connecting rod.
Based on the diameter of the hole in this bushing, the connecting rods are divided into three classes every 0.004 mm. The class number 1 is stamped on the connecting rod cover. Based on the weight of the upper and lower heads, connecting rods are divided into classes, marked either with a letter or with paint on the connecting rod cover. Connecting rods of the same weight class must be installed on the engine.
495+3 501+3
Green
| Classes of connecting rods based on the weight of the upper and lower heads | |||
| Mass of connecting rod heads, g | Class | Marking color | |
| top | bottom | ||
| 188+2 | 489+3 495+3 501+3 | X B | |
| 192+2 | 489+3 495+3 501+3 | Ts G | Blue |
The weight of the connecting rods can be adjusted by removing metal from the bosses on the upper head and on the cover to a minimum size of 33 and 32 mm (Fig. 6). After removing the metal from the connecting rod cap, it is necessary to mark the classes of the connecting rod on it by the hole for the piston pin and by weight.
Selection of piston and cylinders
| To make it easier to select pistons, we offer a diagram for measuring piston sizes. | |
| 2T (2 cycles) | 4T (4 cycles) |
| pic 1 | pic 3 |
| x', x" - steel lock pins | |
| ______________________________________________________________ | |
| View from above | Option I (yamaha) |
| a-c - finger axis | |
| A, B, C - angles in degrees (to lock points x', x") | |
| o - center | |
| Mark all points with a marker, measure angles with a protractor. |
Table No. 1
| № | Dmm* | H mm | d mm | h mm | A deg | B deg | C deg | tact | Basic brand | Models/link |
| 1 | 50 | 60 | 14 | 21,5 | 40 | 100 | 40 | 2T | Suzuki | Suzuki AX 100 |
| 2 | 41 | 45 | 10 | 14 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 2T | Honda | Honda Tact |
| 3 | 40 | 48 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 70 | 50 | 2T | Honda | Honda Gyro |
| 4 | 52 | 61 | 12 | 28 | 40 | 90 | 50 | 2T | Yamaha | Yamaha Axis 100 |
| 5 | 40 | 50 | 10 | 21 | 50 | 80 | 50 | 2T | Honda | Honda |
| 6 | 40 | 48 | 10 | 20,5 | 70 | 60 | 50 | 2T | Yamaha | Almost all 50 cc. Yamaha (Yamaha Jog, Next zone, etc. there is also a super repair with a diameter of 42.5 and 43 mm) |
| 7 | 47 | 57 | 12 | 23 | 50 | 90 | 40 | 2T | Yamaha | Yamaha |
| 8 | 41 | 43 | 10 | 17 | 60 | 70 | 50 | 2T | Suzuki | Suzuki Ran, Gemma |
| 9 | 52.5 | 57 | 12 | 22 | 50 | 80 | 50 | 2T | Suzuki | Suzuki Address 100 |
| 10 | 39 | 52 | 12 | 22 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 2T | Honda | Honda dio (except AF34/35) |
| 11 | 43 | 42 | 10 | 14 | 60 | 70 | 50 | 2T | Suzuki | Overrepair of Sepia, Adress old Honda Pal |
| 12 | 50 | 56 | 13 | 19 | 40 | 100 | 40 | 2T | Suzuki | Suzuki K90 piston, 50mm |
| 13 | 40 | 48 | 12 | 19 | 60 | 70 | 50 | 2T | Honda | Stels, Honda DIO ZX (AF34/35) |
| 14 | 52 | 60 | 14 | 26 | 50 | 90 | 40 | 2T | Yamaha | Yamaha BWS 100, pin 14mm |
| 15 | 50 | 60 | 12 | 27 | 30 | 120 | 30 | 2T | Yamaha Axis90, 2-stroke Chinese 90 cc. | —Yamaha |
| 16 | 55 | 64 | 15 | 27 | 70 | 50 | 60 | 2T | Kawasaki,Honda | Piston 16 GTO-125 |
| 17 | 44 | 47 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 2T | Piston No. 17 Yamaha CT-70 | |
| 18 | 52 | 56 | 14 | 19 | 50 | 90 | 40 | 2T | Suzuki | Piston No. 18 Suzuki |
| 19 | 40 | 48 | 12 | 18 | 60 | 70 | 50 | 2T | Yamaha | Yamaha |
| 20 | 48 | 54 | 12 | 20 | 60 | 70 | 50 | 2T | Honda | Honda Lead 90 |
| 21 | 50 | 64 | 14 | 26 | 40 | 100 | 40 | 2T | Kawasaki | Kawasaki |
| 22 | 47 | 40 | 13 | 11 | — | — | — | 4T | Chinese | Chinese 4t 139FMB 72cc |
| 23 | 39 | 32 | 13 | 12 | — | — | — | 4T | Honda | 50 cc Chinese four stroke |
| 24 | 41 | 42 | 10 | 14 | 60 | 70 | 50 | 2T | Suzuki | Suzuki Sepia, Adress, old Honda Pal |
| 25 | 41 | 48 | 10 | 21 | 60 | 70 | 50 | 2T | Yamaha | Yamaha |
| 26 | 41 | 48 | 12 | 21 | 50 | 80 | 50 | 2T | Suzuki | Suzuki |
| 27 | 43 | 43 | 10 | 17 | 60 | 70 | 50 | 2T | Suzuki | Super repair Suzuki Ran , Gemma |
| 28 | 56,5 | 52 | 15 | 17 | — | — | — | 4T | Honda | Honda 4-engine |
| 29 | 41 | 37 | 13 | 13 | — | — | — | 4T | Yamaha | Yamaha 4-engine |
| 30 | 52,4 | 38 | 15 | 12 | — | — | — | 4T | Honda | Honda Spasy 125cc (CH 125) |
| 31 | 61 | 53 | 15 | 17 | — | — | — | 4T | Honda | Honda 4-t |
| 32 | 58 | 66 | 16 | 28 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 2T | Yamaha | Yamaha #32 |
| 33 | 72 | 47 | 17 | 14 | 4T | Honda | Honda CH 250H | |||
| 34 | 47 | 56 | 12 | 19,5 | 40 | 100 | 40 | 2T | Suzuki | Suzuki 2-stroke engine |
| 35 | 56 | 70 | 16 | 32 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 2T | Yamaha | Yamaha 2-stroke engine |
| 36 | 50 | 60 | 14 | 22 | 40 | 100 | 40 | 2T | Suzuki | Suzuki 2-stroke engine |
| 37 | 50 | 44 | 13 | 14 | 4T | Honda | Honda 4-stroke engine | |||
| 38 | 49 | 57 | 12 | 22 | 50 | 80 | 50 | 2T | Yamaha Champ 80 | Yamaha Champ 80 |
| 39 | 50 | 42 | 13 | 13 | — | — | — | 4T | Honda | Honda CH100 |
| 39-1 | 50 | 37 | 15 | 13 | — | — | — | 4T | Honling | 100cc Chinese 4-stroke |
| 40 | 49 | 40 | 13 | 13 | — | — | — | 4T | Yamaha | Yamaha 250cc |
| 41 | 44 | 44 | 13 | 14 | — | — | — | 4T | Honda | Honda 125cc |
| 42 | 52 | 56 | 14 | 18 | 50 | 80 | 50 | 2T | Suzuki | Suzuki K100 |
| 43 | 50 | 57 | 14 | 19 | 40 | 100 | 40 | 2T | Suzuki | Suzuki K90 |
| 44 | 48 | 41 | 14 | 13 | — | — | — | 4T | Yamaha | Yamaha FZR 250 |
| 45 | 44 | 32 | 13 | 13 | — | — | — | 4T | 139QMB | 60 cu. 4 Chinese |
| 46 | 47 | 34 | 13 | 11 | — | — | — | 4T | 139QMB | 80 cu. 4 Chinese |
| 47 | 57.4 | 38 | 15 | 13 | — | — | — | 4T | — | 150 cu. 4 Chinese |
| 48 | 50 | 53 | 12 | 20 | 40 | 100 | 40 | 2T | — | ATV ADLY 100 |
| 49 | 39 | 32 | 13 | 12 | — | — | — | 4T | Honda | Honda Spacy 50 (ch50) |
| 50 | 52,4 | 37 | 15 | 12,5 | — | — | — | 4T | — | 125 cc 4 Chinese |
| 51 | 38 | 30 | 10 | 12 | — | — | — | 4T | — | Honda dio AF-56 |
| 52 | 50 | 34 | 13 | 12 | — | — | — | 4T | — | Piston 139 QMB 82cc - 50 mm |
| 53 | 61 | 38 | 15 | 13 | — | — | — | 4T | — | Piston 152QMI, 157QMJ 170cc - 61 mm |
| 54 | 57 | 38 | 15 | 12 | — | — | — | 4T | Honda, Suzuki | Piston No. 54 Honda Spasy 150 cc, Suzuki vecstar 150 |
| 55 | 59 | 63 | 16 | 22 | 70 | 40 | 70 | 2T | — | Piston TZR 150 59 mm |
| 56 | 43 | 48 | 10 | 20,5 | 50 | 80 | 50 | 2T | — | Piston JS60 43 mm |
| 57 | 47 | 48 | 10 | 21 | 70 | 60 | 50 | — | — | Piston No. 57 - Yamaha Jog tuning 70cc - 47mm, pin -10mm |
| 58 | 47 | 48 | 12 | 20 | 70 | 60 | 50 | — | — | Piston No. 58 – Stels tuning 70cc – 47mm, pin 12 mm |
| 59 | 52,5 | 57 | 14 | 21 | — | — | Piston No. 59 — Suzuki Adress 110 | |||
| 60 | 44 | 48 | 12 | 19 | 60 | 70 | 59 | — | — | Piston No. 60 — Honda dio ZX65 44mm |
| 61 | 48 | 48 | 10 | 21 | 70 | 60 | 50 | — | — | Piston No. 61 – Yamaha Jog tuning 75cc – 48mm, pin 10mm |
| 62 | 43 | 51,5 | 12 | 22 | 60 | 60 | 60 | — | — | Piston No. 62 Honda dio 65cc, 43mm |
| 63 | 48 | 51,5 | 12 | 22,5 | 60 | 60 | 60 | Piston No. 63 Honda dio af18 48mm | ||
| 64 | 48 | 48 | 12 | 19 | 60 | 60 | 60 | Piston No. 64 Honda dio af34 48mm | ||
| 65 | 52 | 38 | 14 | 12,5 | 4T | — | Piston Suzuki Vecstar 125 (AN125) |
Measurements should be taken with a caliper with a scale accuracy of at least 0.1 mm. Measure degrees with a protractor; there is no need for special accuracy. When selecting a piston cylinder, it is advisable to make a cardboard circle along the diameter of the piston (approximate diameter) and marking the points of the locks, having previously drawn according to the degrees given in the table, make sure that the locations of the locks do not fall into the open space of the cylinder windows, or do not lie very close to edge of the window.
* - size D is given for standard pistons; repair pistons come with an increase of 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1.00 mm.
How to find out the finger size for a ring?
Since the option of going to a jewelry store and consulting a specialist is not suitable here, we will tell you about several secret ways to take measurements. Each of them is quite good and accurate - we tried to check everything ourselves. So, how do real detectives determine ring size?
Method one: using thread
Let's start with how to determine your ring size based on the circumference of your finger. If you have enough skill, you can calculate the finger size for a ring at home using a thread.
Determine the size of the ring using a thread
If you want to find out the ring finger size for a wedding ring, unbeknownst to the bride (for example, while she is sleeping), wrap the thread around her finger and mark the point where the ends of the thread meet. In the same way, you will have to measure the girth of the joint. Then straighten the thread and measure the distance between the points of contact. Divide the average of the two resulting numbers by 3.14. Ready!
Now you know the required diameter (aka size) of the ring. And due to the fact that you were able to measure the thickness of the finger and the joint at the same time, the jewelry will neither pinch nor dangle. As you can see, you can find out the finger size for a ring at home.
Method two: using pen and paper
This method is much simpler than the first, since it does not require secret “operations” around other people’s fingers - we find out the size of the ring by the diameter of the other. Take any ring from the person you are preparing a gift for. Place it on paper and trace the decoration around the inner perimeter. The diameter of the resulting circle will be the size of the ring. But be careful - for measurements you need to take the ring from the finger on which you will put the gift in the future, because all fingers have different girths.
Method three: with the help of friends
How to find out your finger size if you are too afraid of being declassified? Very easy - ask your friends. The most difficult part of this method is finding a friend who is guaranteed to keep your plan a secret. Then it’s simpler: either your friend already knows the size and simply tells you it, or he calmly, without arousing suspicion, recognizes it and thus helps you with choosing a gift. Thank your friend for helping you understand the size without a ring!
Method four: using the existing ring
For the most courageous, we will tell you how to determine the size of the ring using an existing ring. It is worth noting that this method is the most accurate, but also the most risky. If you are 100% sure that the “object” will not notice the loss of one of his jewelry, feel free to go into battle! For one day, turn into a brazen thief and steal a ring from a person. Take your jewelry to a jeweler - he will measure the diameter of the ring and tell you what size it is. Don't forget to return what you stole!