The cooling system of a modern engine is a combined solution that combines liquid and air cooling. In this case, the main task of the entire complex of devices is to maintain the operating temperature of the engine within strictly specified limits.
In other words, the motor temperature should not be too low or high. In the first case, when the engine does not reach operating temperature, efficiency suffers, the exhaust becomes toxic, power is lost, service life decreases, etc. In the second, when the engine overheats, detonation occurs, and the engine can quickly fail or seize.
It becomes clear that the normal temperature of the coolant of a warm engine directly depends on the quality of the cooling system. Next, we will talk about what coolant temperature is normal for a warmed-up power unit, and also why the indicated operating temperature of antifreeze or antifreeze may deviate from normal or optimal values.
CAUSES OF ENGINE OVERHEATING
Overheating can be caused by many reasons, all of them are related to a malfunction of the cooling system, or the quality of the coolant, as well as contamination of the cooling system jacket, which impairs the fluid throughput. It is important to use high-quality spare parts, otherwise the reasons below will happen suddenly. Let's look at each of the reasons.
LOW COOLANT LEVEL
The most common problem is a lack of coolant in the system. Coolant, in the form of antifreeze or antifreeze, constantly circulates through the system, removing heat from heated engine parts. If the coolant level is insufficient, the heat will not be removed sufficiently, which means an increase in temperature will be inevitable.
If it is not possible to add coolant, then turn on the heater to reduce the likelihood of overheating. As a last resort, add regular or distilled water, after which the cooling system must be flushed and then filled with fresh antifreeze. At temperatures above 90 degrees, you should immediately stop the car, turn off the ignition, and allow the engine to cool.
ELECTRIC COOLING FAN FAILED
The electric fan forces cool air onto the radiator, which is especially necessary when driving at low speeds when there is insufficient air flow. The fan can be installed either in front or behind the radiator. If the temperature arrow starts to rise, stop the car and check the fan for serviceability. Reasons for fan failure:
- electric motor failed
- connector oxidized
- fan relay burnt out
- The internal combustion engine temperature sensor has failed.
To check the fan, remove the connectors from it and connect the wires directly to the battery, which will allow you to determine the cause of the failure.
THERMOSTAT FAULT
The thermostat is one of the main elements of the cooling system. The cooling system has two circuits: small and large. A small circuit means that fluid circulates only through the engine. In a large circuit, fluid circulates throughout the system. The thermostat helps you quickly reach and maintain operating temperature. Thanks to the sensitive element, which opens the valve at 90 degrees, the liquid enters a large circle, and vice versa. The thermostat is considered faulty in two cases:
- operating temperature of the coolant is not reached
- the power unit tends to overheat.
The thermostat can be located directly in the cylinder block, in a separate housing, or as one unit with a temperature sensor and pump.
BROKEN COOLING FAN BELT
On vehicles with a longitudinally mounted engine, the fan can be driven by a drive belt from the crankshaft pulley. In this case, the fan works forcibly. The service life of the drive belt is from 30 to 120 thousand km. Typically, several units are driven by one belt. When a belt breaks, the internal combustion engine immediately tends to overheat, especially when the speed decreases. If you have a domestic car with a belt-driven fan, it is recommended to install an additional electric fan to avoid unpleasant incidents.
3) Thermostat malfunction
The most likely cause of a car overheating at high speeds is a faulty thermostat. If you are driving at high speed, then the load on the car engine increases, that is, at this moment it is much greater than when the car is moving at low speed.
Due to the increased load, the car engine needs more cooling. To do this, the cooling system itself, when driving at high speed, supplies more coolant to the cooling system, thereby cooling the car’s engine. This process is precisely regulated by a thermostat, which can periodically fail.
For example, the thermostat may simply not open, which will lead to a lack of coolant in a certain area of the engine cooling system. In this case, your engine will begin to heat up very quickly and the sensor scale will reach critical values.
CAUSES OF LOW ENGINE TEMPERATURE
Low engine temperature may occur in the following cases:
- use of an inappropriate thermostat (opening temperature too early)
- high performance of cooling fans, or their forced operation from the moment the engine starts
- thermostat malfunction
- non-compliance with the proportion of mixing antifreeze with water.
If you purchase antifreeze concentrate, it must be diluted with distilled water. If in your region the temperature has dropped to a maximum of -30°, then purchase antifreeze marked “-80” and dilute it 1:1 with water. In this case, the resulting liquid will heat and cool in time, and will not lose its lubricating properties, which is extremely necessary for the pump.
Source
Operating coolant temperature on a warm engine
- 1 What is the normal coolant temperature of a warm engine?
- 2 How the cooling system keeps the temperature within specified limits
- 3 Let's summarize
The cooling system of a modern engine is a combined solution that combines liquid and air cooling. In this case, the main task of the entire complex of devices is to maintain the operating temperature of the engine within strictly specified limits.
In other words, the motor temperature should not be too low or high. In the first case, when the engine does not reach operating temperature, efficiency suffers, the exhaust becomes toxic, power is lost, service life decreases, etc. In the second, when the engine overheats, detonation occurs, and the engine can quickly fail or seize.
It becomes clear that the normal temperature of the coolant of a warm engine directly depends on the quality of the cooling system. Next, we will talk about what coolant temperature is normal for a warmed-up power unit, and also why the indicated operating temperature of antifreeze or antifreeze may deviate from normal or optimal values.
What causes engine overcooling?
The phenomenon of hypothermia also negatively affects the quality of operation of the power unit. Most often this happens in winter or when operating a vehicle in difficult climatic conditions of the far north.
The operating temperature of the engine in winter can be sharply reduced while the car is moving. At the same time, flows of cooled air blow over the radiator and the entire power unit. As a result, the coolant sharply lowers the engine temperature, even if it is running at full load.
Reducing the operating temperature of the motor is dangerous for the following reasons:
- When the power system overcools in the carburetor, the nozzle hole through which air enters freezes over, resulting in the spark plugs being filled with gasoline. To continue driving, the driver will have to wait for the spark plugs to dry.
- At sub-zero ambient temperatures in cars running on water, the coolant freezes in the radiator tubes. Stopping coolant circulation leads to engine overheating. Experienced car owners install special fabric partitions or protective shutters on the radiator grille.
- Deterioration in quality or lack of heating of the car interior in winter can lead to impaired driving.
What is the normal coolant temperature for a warm engine?
As a rule, various serious malfunctions and deviations in the operation of the cooling system are immediately recorded by the driver. If the engine does not warm up, then in winter the heater does not work well and the operating comfort of the vehicle decreases.
If the engine overheats, this can be determined by the temperature indicator on the dashboard; on many cars, an alarm sounds, steam may simply come out from under the hood, etc.
In such situations, the problem is obvious, the problems are easier to localize and fix. However, a more complex situation is when the engine warms up, but not completely, and the internal combustion engine can overheat, but only partially. Quite often, drivers also note significant fluctuations in coolant temperature for no apparent reason.
One way or another, this problem needs to be eliminated, since breakdowns in the cooling system tend to progress, and quite quickly. Such deviations from the norm, even minor ones, also do not add service life to the engine.
First of all, you need to understand that for most engines the optimal temperature range for a warmed-up engine (when the engine has fully reached operating temperature) is between 80 and 90 degrees Celsius. This is the normal coolant temperature on a warm engine.
Engine takes a long time to warm up
This is another issue that is very subjective. What do you mean it takes a long time to warm up?
Let's say 20 minutes is a lot or normal? I often hear this exact number when complaining about long warm-up times. Why do people think it takes so long? Are there any standards or regulations and it is clearly written there that the engine must complete, say, 17.5 minutes?
Personally, I have never seen anything like this. And all because the heating conditions are different - coolant temperature, ambient temperature, wind speed, whether the interior heater is on. Whether the car is moving or not. And if it moves, then at what speed? What engine speed, etc.
Therefore, the warm-up time will always be different and I cannot say specifically that 20 minutes is a lot.
But I can only give some average values so that you can at least roughly start from something.
Hundreds of engine management system diagnostic files pass through me every month. Therefore, it is possible to build approximate values over several years.
So here it is:
- From 10 degrees to operating temperature, warming up takes about 10 minutes. Warm up for one minute and then drive at an average speed of 40 km/h in the city.
- From 0 degrees to operating temperature in about 18 minutes. Warm up for six minutes and then drive at an average speed of 30 km/h.
Warming up outside. In a garage, the warm-up time is slightly reduced.
From these average figures we can conclude that if you have minus ten degrees, there is a strong wind and your car is coasting downhill, then 20 minutes is still a quick warm-up
Therefore, draw conclusions and do not interfere with the machine’s work.
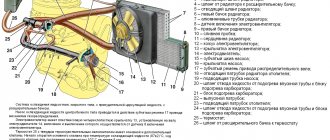
How the cooling system keeps the temperature within specified limits
Let's start with the fact that after starting a cold engine, the pump (water pump) forces coolant to circulate through the channels of the cooling system. In this case, the channels can be divided into a large and small circle.
Small circle? circulation occurs inside the cylinder block and cylinder head. Large circle - liquid enters the cooling radiator. The thermostat is responsible for opening the large circle, which is completely closed when the engine is cold. As the liquid heats up, the thermostat begins to open, after which antifreeze or antifreeze enters a large circle.
By the time the liquid warms up to 80-90 degrees, the thermostat will be completely open and the liquid will begin to circulate only in a large circle. Once the temperature drops, the thermostat will partially or completely close. In a nutshell, this is the scheme for regulating the operating temperature of the engine and coolant.
In parallel, a coolant temperature control sensor is installed on the engine. This sensor, if necessary, activates air cooling by sending a signal to turn on the fan.
As for the properties of the coolant, boiling under atmospheric pressure begins at 108-110 degrees. However, before boiling begins, vapor plugs begin to form in the system, which disrupt the operation of the internal combustion engine cooling system. As a result, the motor may overheat.
We also recommend reading the article about what you need to know about the coolant that is used in the cooling system of an internal combustion engine. From this article you will learn about the properties, composition and features of coolant, different types of liquids, features of their mixing, etc.
To minimize risks, an expansion tank is integrated into the system, which also has special valves. If the system pressure rises above the specified limits, then the release valve opens. This way you can get rid of active steam formation.
Even after heating (while the engine is cooling), the volume of coolant also decreases, and a vacuum forms in the system. In this case, the inlet valve opens to equalize the pressure difference.
It is important to understand that a breakdown of the exhaust valve will result in a lower coolant boiling point in the system. If the valve is completely jammed, then excess pressure can cause rupture of pipes and damage to the radiator, antifreeze leaks, etc.
Let's sum it up
As you can see, the operating temperature of the coolant on a warm engine should not be higher or lower than the average mark of 80-90 degrees. More accurate information can be obtained by studying the manual for a specific car.
The fact is that modern highly accelerated internal combustion engines are characterized by extremely high temperature control, which also needs to be taken into account separately. You also need to remember that on many cars the temperature indicator on the instrument panel displays somewhat average values.
To know exactly how much the coolant and engine heat up under certain conditions, it is recommended to install a separate digital engine temperature sensor. Please note that the cooling system definitely requires regular maintenance. Antifreeze or antifreeze must be changed promptly, since the liquid has a limited service life (usually 2-3 or maximum 4 years for the newest generation of antifreeze) and gradually loses its declared properties.
We also recommend reading the article about what are the main malfunctions that occur in the engine cooling system. From this article you will learn about the main problems, methods of diagnosing and fixing possible problems.
You also need to know what types of antifreeze and antifreeze can be mixed with each other. When replacing the coolant, the cooling system should be flushed in different ways. Experts also recommend that you always change the thermostat at the same time as routinely replacing the pump. This approach allows us to subsequently avoid possible malfunctions in the operation of this device and additional unscheduled work to replace it.
Source
Accepted norm
Generally speaking, the operating temperature should not remain constant. When the engine is turned off and the car has stood motionless for at least several hours, the antifreeze has warmed up to approximately room temperature. This indicator is not the norm, and therefore the internal combustion engine must be warmed up before driving.
How can you understand that the motor has fully assumed working condition and is ready for further movement? This, of course, is evidenced by the device, which has a small pictogram with a thermometer at the bottom of the scale. The markings of its scale, as a rule, vary from 50 to 130 degrees - this interval, with some margin in both directions, centers around the normal coolant temperature indicator. The norm, by the way, is 90 degrees - this is equally true for cars, trucks and any other types of vehicles.
It is quite possible that even after a long period of movement the temperature has not become normal, but is, say, 60–80 degrees. This can happen for two reasons. The first of them is that the device or temperature sensor is faulty, so their readings simply do not coincide with the real ones. The problem, as a rule, is solved by diagnostics from specialists and replacement of inexpensive and rather primitive functional elements and sensors.
The second reason is extreme cold, which does not allow a running engine to warm up to the required temperatures. The fact is that coolant constantly circulates from the internal combustion engine to the radiator, and this process does not stop during operation. In this regard, in some cases, even when the fan is turned off, the antifreeze remains insufficiently heated, and the motor does not reach the required temperatures.
Warm engine coolant temperature
The main function of a car's cooling system is to maintain normal engine temperature while driving. The optimal temperature range for a running motor is between 80 and 90 degrees. An important component of the cooling system is antifreeze or antifreeze, which have anti-corrosion and lubricating properties, begin to freeze at 40 degrees below zero, and boil at temperatures above 108 degrees (unlike water).
During a trip, when the engine reaches a temperature of 100 degrees, you should immediately turn it off and stop, since a critical temperature is reached after which the coolant begins to boil. This can lead to serious damage to the engine and trigger the need for major repairs, so every driver should know what the normal coolant temperature is for a warm engine.
When the engine starts, the thermostat is completely closed and coolant circulates in a small circle. As the engine temperature increases, the thermostat begins to open slightly and antifreeze or antifreeze partially splashes out into a large circle. When the coolant heats up to a temperature range of 80 to 90 degrees, it begins to move only in a large circle due to the full opening of the thermostat. This part will partially or completely close when the engine begins to cool down during operation, and the coolant will again be redirected to the small circle. In this way, the normal operating temperature of the engine is controlled.
As you can see, the cooling system is also an important component in any car, and accordingly, it needs to be given proper attention. For this purpose, it is necessary to undergo regular inspection at a service station, especially before summer and winter. If you don’t have enough free time to visit a car service center, call us. Our technical assistance specialists will be able to come to any district of the Moscow region with all the necessary equipment and conduct a high-quality inspection of all systems of your car!