Today, cars are mainly equipped with two types of brake systems and most of them have a hydraulic one. This means that it has a vacuum brake booster (VUT). Like all other components of a car, it is of great importance - the braking speed, and, consequently, the safety of the driver and other road users depends on its serviceability or malfunction. Today we will talk about the design and principle of operation of the VUT, how to check the vacuum brake booster for malfunction, looking at simple methods for such checking.
Vacuum booster malfunctions
Malfunctions of the vacuum booster result in the driver being unable to apply the necessary force for normal operation of the vehicle's braking system.
Thus, there are only three malfunctions of the vacuum brake booster (abbreviated as VUT). This is depressurization of the pipeline (its connection points), breakdown of the VUT check valve, depressurization of its working chambers. The third reason is quite rare, but the first ones are the main ones. Checking the amplifier is usually not difficult, and even a novice car enthusiast can do it. As for repairs, restoring the tightness makes sense only at joints (clamps); in other cases, as a rule, the entire VUT or its connecting tubes are replaced.
What to do with a faulty device?
As usual, there are two options: repair and replacement . Their choice depends on the degree of damage to the VUT. To eliminate them, you need to know the amplifier well and have a repair kit suitable for the specific model of the device in your garage.
We recommend: Polishing car headlights with toothpaste – is it worth it or not?
If the vacuum booster fails, you will have to spend more effort to brake, and the response of the braking system will be very slow. In some situations, this can lead to an accident, so if signs of failure of the VUT are observed, it should be replaced. Note that at home there is no point in trying to get the amplifier into working condition without a special set of spare parts and tools.
What is VUT and why is it needed?
To determine the malfunction of the VUT, it makes sense to describe its purpose, operating principle, as well as the effect of the vacuum booster on engine operation. So, the main task of the “vacuum man” is to increase the physical force (usually 3...5 times) applied by the driver to the car’s brake pedal. This is vital because even a very strong person is not able to create enough force in the hydraulic brake system so that all the brake pads are compressed to the required value at the critical moment. This force is created due to rarefaction of air, and the area in the engine intake manifold is used as its source or is pumped by an additional pump.
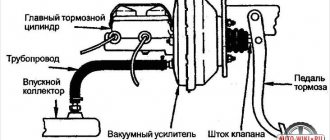
Structurally, the VUT consists of two chambers - atmospheric (on the driver’s side) and vacuum (on the engine side). The vacuum chamber is connected to the intake manifold using an appropriate pipeline. When you press the brake pedal, the vacuum chamber is connected to the atmospheric chamber using a pusher, which has a so-called tracking valve. Next, the diaphragm is connected to the rod and brake fluid is pumped to the brake cylinders. If there is no force on the brake pedal, then under the influence of the return spring the diaphragm returns to its place, the pressure on the brake fluid weakens, which is why the brake pads move apart and braking stops.
In the simplest case, the vacuum brake booster takes vacuum from the intake manifold. To do this, it is connected to it by an appropriate pipeline. However, in many modern cars there are separate vacuum pumps for the vacuum pump. They come in two types. The first is mechanical, it is driven by the engine camshaft. The second is electric and is driven by a separate electric motor. The use of additional pumps not only increases the comfort of using the braking system, but also increases its reliability (for example, in the event of damage and/or depressurization). But still, the pump is only an auxiliary element, and the main vacuum is taken from the intake manifold.
Vacuum booster device
The vacuum booster is a single unit with the STC (brake master cylinder). This node consists of five main segments. Today there are a lot of different design solutions and their modifications, each of which is distinguished by the presence of additional parts, dimensions, configuration, and so on. However, the main components are unchanged; let’s consider them in more detail.
- The body is divided into 2 chambers by a special diaphragm. The first atmospheric cavity is located on the side of the GTZ, and the vacuum chamber is located in the direction of the brake pedal.
- Vacuum chamber . This segment includes parts such as the intake manifold and check valve. The first element is the vacuum sources. In combination with diesel engines, the design has an electric pump that provides a continuous supply of force. In such models, the vacuum booster is in a charged state only when the power unit is running. When the motor is turned off or this unit malfunctions, the collector is disconnected from the amplifier.
- The atmospheric chamber is equipped with a special valve. In the initial position, this element connects it to the vacuum cavity, and when the pedal moves, it correspondingly disconnects it. Together, this and the previous elements are the main mass compensators.
- The pushrod is directly connected to the brake pedal. It is designed to move a tracking valve mounted between the vacuum chamber and the atmospheric cavity. An elastic diaphragm is connected to the end of the GTZ rod and ensures that liquid is supplied to the cylinder under a certain pressure.
- The return spring serves to return the diaphragm to its original position when you remove your foot from the pedal. Provides the initial state of the diaphragm when there is no influence on the brake pedal. In new models of modern cars, the design of which includes an ESP system, active type amplifiers are installed that prevent rollovers.
Signs of VUT malfunction
Partial output of the vacuum brake booster will certainly manifest itself, and from the worst side and quite clearly. So, symptoms of a malfunctioning amplifier include:
Accordingly, the occurrence of one or more signs directly indicates to the car owner that it is necessary to check the vacuum brake booster and its components.
Error p1479
In modern cars equipped with an electronic control unit (ECU), an error code p1479 is often generated in the device’s memory - “Brake booster vacuum system mechanical malfunction.” Owners of a wide variety of cars encounter it - Audi, Volkswagen (Touareg, Passat), Ford and others. The cause of an error in the control unit can be very different. For example, when air is sucked in the hose between the intake manifold and the vacuum brake booster itself.
Another common option is the result of measuring the vacuum value with a vacuum sensor. In particular, it occurs if moisture appears inside the vacuum booster and/or its tubes. The solution is to clean and dry the tubes, and in rare cases, replace the sensor itself.
It also makes sense to check the integrity of the fuse going from the control to the sensor. Each machine will have its own electrical circuit, so it is impossible to provide specific information within the framework of this material.
Another option is the performance of the electric vacuum pump. In particular, its electric motor, impeller, bearings, fastenings, connection blocks, as well as relays and fuses.
Causes of vacuum booster malfunction
The vacuum brake booster and its accompanying elements are fairly simple devices, so experts identify the following main and possible malfunctions of the VUT:
If the car is equipped with an additional vacuum pump, then a fourth fault is usually identified - partial or complete failure of this unit. In this case, the brake system itself will work, but not in optimal mode. In particular, during sharp braking, the force that the driver will need to physically exert on the pedal will increase significantly.
Design and operating features of a vacuum brake booster
If you ask an elderly person who has ever driven a Soviet car what it was like to brake at high speed, he will definitely answer: it was hard. I had to press the brake pedal to the floor, often even stand up, transferring all my weight to one leg. The invention and rapid introduction of brake boosters solved this problem. What's the problem, you ask? The fact is that braking, which strongly depends on the physical condition of the driver, cannot always be effective. And a car with such an imperfect brake will certainly lose to its current brother in terms of ride comfort. Let's look at the design of the most common brake booster and look at what malfunctions it has.
How to check the vacuum brake booster
A logical question arises: how to determine whether the vacuum brake booster is faulty. In fact, this is quite simple to do, and without the use of additional equipment, the test can be performed in a garage or even on the street.
The simplest check is performed using the following algorithm:
It makes sense to perform another check if the brake system seems to be working properly, but when you press the brake pedal, a change in the operating mode of the internal combustion engine is observed. So, the check is performed according to the following algorithm:
Disconnect the pipe from the intake manifold.
If the check reveals the presence of depressurization, then the next step is to localize the location of the damage. This is not always easy to do, since the crack or leak can be very small and sometimes located in the most unexpected places. However, as a check and preventative measure, it is necessary to check the following elements of the vacuum booster system:
If the check does not produce results, then it makes sense to simply replace all the vacuum booster tubes with clamps.
Checking the VUT check valve
The cause of poor performance of the vacuum brake booster may be a malfunction of the check valve to which the hose from the intake manifold is connected. To diagnose the latter, you need to remove the hose, remove the valve from the VUT body and put a rubber bulb from a syringe or hydrometer on it from the outside (to which the hose is connected) and squeeze it. If, after releasing the bulb, it remains compressed, the check valve is working properly.
Otherwise, it must be replaced. In a similar way, you can check the inlet hose for leaks in the absence of a compressor.
Diagnostics of the vacuum brake booster can be easily carried out in just a few minutes through simple manipulations without the use of any measuring instruments or tools. For a more objective check, try the various methods suggested in the article. Before doing this, do not forget to check the condition of the hose leading to the VUT from the intake manifold.
The main signs of failure of the vacuum brake booster control valve are a stiff or, on the contrary, soft brake pedal, as well as complete inoperability of the pedal.
How to troubleshoot
It makes sense to repair the vacuum brake booster system only in the event of partial failure of the booster pipeline, its check valve, or the valve seal. If replacing the listed elements does not produce results, then it is necessary to replace the entire VUT, since its design is non-separable and cannot be repaired.
Replacing a pipeline with mounting clamps makes sense for several reasons:
Replacing the pipeline itself is not difficult, and even a novice car enthusiast can easily handle it. The main thing is to buy a new set of pipes, clamps and appropriate gaskets from the auto store. Next, using plumbing tools, simply change one tube for another.
Repair of auxiliary pumps
As mentioned above, when a mechanical vacuum pump partially fails, some car enthusiasts simply remove their rod, thereby turning them off and eliminating the knocking noise that occurs when the pump operates. In this case, the brake booster will work, but not as effectively, which will result in a harder pedal. Some car enthusiasts get out of the situation by turning the rod 180 degrees. Sometimes this helps because it is only present on one part of them.
As for electric vacuum pumps, these units are usually irreparable; accordingly, they are simply replaced with new ones.
Source
How to check a removed brake booster
A vacuum brake booster (VBR) significantly reduces the pedal effort required to stop the vehicle. This device makes driving the most comfortable and simplest. In addition to the boost function, the vacuum brake booster ensures the safety of road users. That is why, if the function of the amplifier is malfunctioning, it is necessary to start checking in a timely manner. On earlier car models, significant efforts had to be made in order to reduce the speed or completely stop the car. The amplifier makes driving a vehicle more simplified and safe, as a result of which VUT has become widespread in the modern automotive industry.
Why is it necessary to check the brake system boost? The shell of the vacuum assistant is divided into two parts by a special partition. A cylindrical brake rod passes through the housing partition. This element transmits the force acting on the brake pedal to the brake cylinder. An important function of the mechanism in question is to ensure the safety of the driver and road users. This is the main importance of timely inspection of the device. Amplifier malfunctions, in rare cases, adversely affect the function of the entire machine stopping system.
But unexpected difficulty in pedal movement can create an unfavorable situation on the road. The malfunction is not critical for the motorist, but it is so easy to react in time and stop the vehicle in a timely manner. To avoid unforeseen circumstances, it is necessary to promptly diagnose and service the brake booster system. Checking the brake booster is an important part of the vehicle's technical inspection, which should not be neglected. Of course, there is no need to drive the car into the garage every day for diagnostics. A malfunction of the amplification system may be indicated by certain facts that arise during the operation of the vehicle. After reviewing the information provided, it is easy to identify incorrect operation of the amplifier, without expensive diagnostics.
The main signs of dysfunction of the vacuum brake booster. You can check the serviceability of the amplification system without expensive equipment and special knowledge. To do this, you need to stop the engine and bleed the brake system by pressing the car's stop pedal about five to seven times. After this, you need to start the car engine, leaving your foot on the pedal. When starting the engine, the pedal should move forward a little. Otherwise, this indicates some malfunction in the system. Under such circumstances, it is necessary to carefully inspect all conductors and the system valve for mechanical damage. If the operation of the amplifier begins to be accompanied by extraneous sounds, then the range of diagnosed devices expands somewhat. One of the most common areas of damage is the main conductor connecting the brake booster to the car's engine manifold. In this case, it is necessary to carry out a visual diagnosis of the element. If the hose has broken its seal, it must be replaced. Also during diagnostics, it is necessary to check the condition of all holders and tighten them, if necessary. In addition to these damages, internal components of the system, in particular the valve, can cause a malfunction of the VUT. Due to difficult operating conditions, the rubber seals of the system wear out. In this regard, the valve becomes heavier in movement. Sometimes, this leads to partial damage to the flexible septum. If this malfunction is detected, you can independently restore the VUT function using a repair kit. Before doing this, you need to make sure that the amplifier itself is in full working order. Often, improper operation of the brake booster system can lead to disruption of the function of one of the engine cylinders. As a rule, most car enthusiasts explain this problem by wear of the spark plugs, forgetting about the brake assistant. In this case, checking the amplifier is carried out in the following way: We muffle the VUT hose so that no air passes through it. If the engine has restored smooth operation, the reason is clear. Thus, we learned how to check the vacuum brake booster.
Checking the vacuum booster: all methods
There are several effective ways to check VUT. The procedures are simple, you can do it yourself, you don’t need to dismantle anything from the car.
First way
The simplest option:
- start the engine and let it run for about 10 minutes;
- turn off the engine;
- depress the brake completely, creating a vacuum in the booster;
- release the pedal and press it again.
A decrease or heavier pedal stroke when pressed again will indicate problems in the operation of the vacuum pump. On the contrary, if the second pressing occurs without any differences from the first, one can judge the serviceability of the VUT and successful discharge.
Second way
This time, during diagnostics, you should press the pedal several times - 6 or 8. For the last time, press it to the limit and start the engine. If everything is fine with the vacuum system, the pedal should drop even lower - almost halfway. If it does not move, there is a problem with the valve.
Characteristic
So what is this mechanism? A vacuum booster is a part that is used in the braking system of a car. Its main task is to provide additional force on the brake pedal when the latter is pressed. This increases the efficiency of the system and reduces driver fatigue.
If we talk about the design, this element consists of a housing, a pusher, a diaphragm, a sliding valve, a GTZ piston rod and a return spring. The algorithm of operation of the mechanism is based on the pressure difference in the atmospheric and vacuum chambers. Modern amplifiers can increase the energy of pressing the pedal by four to five times. There are also more powerful models. But in their design it is worth noting a larger number of cameras and aperture diameter.
Vacuum booster functions
The main functions of a vacuum cleaner (a common designation for a device) are:
- an increase in the force with which the driver presses the brake pedal;
- ensuring more efficient operation of the braking system during emergency braking.
The vacuum booster creates additional force due to the resulting vacuum. And it is this amplification that, in the event of emergency braking of a car moving at high speed, allows the entire brake system to work with high efficiency.
About malfunctions
The main factor in the malfunction of the “vacuum unit” is the inability to create a vacuum in the chamber. It may not be fully produced or may be completely absent from the system. Often the source of the problem is the loss of tightness of the hose that connects the engine to the amplifier.
But breakdowns are also possible due to loss of elasticity of the valve or damage to the working surface of the diaphragm. In any case, before replacing the vacuum brake booster, it needs to be checked. You can do this yourself.
How to check the vacuum brake booster?
There are several ways to do this. So, you need to start the engine and turn it off after at least 10 seconds of operation. Next, press the brake pedal. With the engine turned off, it will be squeezed out to the fullest extent. Since there is remaining vacuum in the system, it will pull on the diaphragm and increase the force. The second and third press will require more effort. The pedal travel will become shorter. But if it is hard already at the first press, it means that the brake booster valve is not doing its job. Additional force is not implemented in the system.
After completing the operations, you can do one more. The motor must be turned off. Next, press the brake pedal. If this method is done first, you need to press the pedal several times. It is important for us to completely free the system from vacuum. Then, with the brake pedal pressed, we start the engine. In the first seconds of engine operation, you will feel the pedal smoothly begin to press to the floor, with much less effort. If it remains in the same place or only drops slightly, it can be stated that the vacuum brake booster is faulty. If the mechanism is working properly, a vacuum will form in the vacuum chamber. The membrane will press on the rod, and the latter will pull the pusher, which is connected to the pedal.
How to check VUT
In reality, checking the correct operation of a vacuum device is quite simple , which even a beginner can handle. We will give three ways to check the vacuum seal for serviceability.
Option 1
- Start your car and let it idle for about 7 minutes.
- Stop the engine and fully depress the brake pedal to create a vacuum in the brake system.
- First release the pedal and then press it again.
If the vacuum brake device fails, then the second time you press the pedal, you will feel a significant reduction in its travel (compared to the first press). This occurs because airless space can no longer be created. But if when you press again you do not feel a difference, then this indicates that the brake system is working normally . Let's move on to the second verification option.
Option 2
- With the car engine turned off, press the “brake” 6-8 times.
- Depress the brake pedal to the maximum and start the engine.
If there are no problems in the vacuum brake device , airless space begins to create in the system. For this reason, the diaphragm begins to press on the rod, which will pull the pusher connected to the pedal. And the brake pedal (even when it is fully depressed) will go down a little.
If this does not happen after starting the power unit, it means that there is no vacuum in the brake system. And, this means that there are malfunctions that impede this process.
Option 3
This vacuum brake test helps determine if there are air leaks.
- Start the engine.
- Depress the brake pedal all the way and immediately turn off the engine.
The depressed pedal should remain in this position for approximately 30 seconds. This shows that there are no problems . But if it begins to move to its original position, it means that the pressure in the working chamber increases. This indicates problems with the mechanism.
Checking the vacuum booster
What if it is not replaced in time?
Very often, when an amplifier breaks down, air begins to enter the system. Typically this happens due to a faulty control valve. As a result, the pressure in the circuit drops. The pedal becomes too soft. Often drivers think that the system is simply airy and bleed the brakes. But after the first trip, the pedal becomes soft again. The response time of the system also increases. This can lead to accidents on the road.
In the worst case scenario, the valve fails completely. Because of this, the system is not able to work at all. In this case, driving out onto the road is extremely dangerous. Therefore, if there are any signs, you should carefully inspect the system and replace the faulty element.
The brakes stopped working
In the worst case scenario, the brake booster control valve fails completely, resulting in complete inoperability of the brake system. Fortunately, such an outcome is unlikely. But if suddenly it does occur, carefully stop the car, tow it home and contact a qualified specialist in the diagnosis and repair of brake systems. Depending on the severity of the case, the matter may be limited to only replacing the valve, but serious repairs of the entire brake system may be required.
The brake booster control valve is an important element of the braking system, ensuring driving safety. That is why the presence of the described symptoms should not be ignored or postponed “for later”. Contact a qualified mechanic who can professionally diagnose and repair your vehicle's brake system.
The vacuum booster is one of the integral elements of the car's braking system. Its main purpose is to increase the force transmitted from the pedal to the master cylinder. Due to this, driving becomes easier and more comfortable, and braking is more effective. In the article we will analyze how an amplifier works, find out what elements it consists of, and also find out whether it is possible to do without it.
Let's get started
Work should be carried out during daylight hours or in a garage with good lighting. So, put the car in gear and raise the hood. The amplifier is located on the left, driver's side and is screwed to the engine bulkhead. At the first stage, we need to disconnect the clamp of the rubber tube that is connected to the body. This can be done with a flat or Phillips screwdriver. At the next stage, remove the brake fluid level sensor chip. then move the driver's seat as far back as possible. This is necessary in order to conveniently perform work under the steering column. So, lowered into the pedal assembly. It can be dark here, so a portable lamp will not be superfluous. Next, using pliers, remove the stopper from the bushing that connects the pedal to the vacuum rod. The rod connector itself is easy to identify. It is a U-shaped plate with several holes.
Next, remove the rod and lower it to the floor. We return under the hood to the amplifier. To remove it, you will first need to remove the brake master cylinder. It is dismantled along with the iron tubes. Do not unscrew them separately under any circumstances. Otherwise, air will get into the system, some of the fluid will spill out and you will have to fill it in, followed by pumping all four brake mechanisms.
Then we clean the threaded connection on the master cylinder bushings with a metal brush. If necessary, you can use a liquid key lubricant. Please note: the nuts must be unscrewed carefully without damaging the threads. If the nut does not “go”, tighten it one turn, and then unscrew it back. This should help. Also, together with the nuts, remove the washers that are in a compressed state. If they are stuck and difficult to remove, use a flat-head screwdriver. By walking slightly along the cylinder body, you can get these washers out.
What's next?
At the next stage, you can proceed to dismantling the master brake cylinder. It is important not to damage its tubes. The element is removed forward, without distortions to the side. Now you can unscrew the vacuum booster. As we have already said, it is located on the partition and mounted on brackets. The latter is secured on two studs. They often rust. Therefore, it is recommended to first apply lubricant or soda solution here. After this, unscrew the nuts and remove the amplifier along with the bracket. Next, unscrew the two “blind” bolts from the vacuum seal. We screw the new amplifier to the bracket and install it in the reverse order.
Is it necessary to carry out additional work on the brake system? If the tubes were not damaged and the fluid level did not drop, there is no need to bleed or do anything else.
Cost and how to spot a fake
If we talk about the VAZ-2109, a vacuum brake booster costs from 1.2 to 1.5 thousand rubles. You can buy it in any store or online. A VAZ-2110 vacuum brake booster will cost exactly the same. The exception is the yellow “Sport” amplifier. It is sold for 2.3 thousand rubles. We also note that the amplifiers are interchangeable on VAZs. For example, the vacuum seal from the “eight” is ideally installed on the “nine”, 13, 14 and 99 models. The amplifier for the “ten” is also suitable for “Lada” 11th and 12th models. If we talk about manufacturers, Pekar and DAAZ have proven themselves well. The so-called sports amplifier works in the same way as regular factory ones. Therefore, there is no point in overpaying money for it.
When purchasing, it is important to pay attention to the packaging. It should be made of corrugated cardboard. There is always a label on the box that says:
Let's sum it up
So, we found out what a vacuum brake booster is. This is a very important element in any car. In general, a vacuum brake booster rarely fails. This is a fairly reliable and simple mechanism. Sometimes it is not changed for 10 years. It does not have a specific resource. And malfunctions most often relate to air leaks due to the hose through which the vacuum flows from the engine to the amplifier. But if during diagnostics the pedal does not behave as it should, it is worth making an urgent replacement. Indeed, in emergency situations, you simply may not have enough distance to stop the car.
Failure of the “vacuum seal” is a rather rare failure, but unpleasant - to slow down and stop the car, the driver has to press the brake pedal hard. A sudden failure of the mechanism while driving can provoke an accident - the driver does not have time to change lanes and apply the required force at the right time. To identify signs of critical wear of an element, it is proposed to consider the operating principle of a vacuum brake booster (VBR) and diagnostic methods in a regular garage.
Lack of lubricating oil due to improper installation
Why can a vacuum pump fail? What is the reason for the decrease in braking power and deterioration in the performance of the vacuum brake booster? Is the cause due to lack of lubricating oil? This is possible when using vacuum pumps that are driven by the camshaft. You can find out why a vacuum pump can break down and how you can prevent it from failing here.
| Automobile | Engine identification code | Vacuum pump |
| Pierburg Nr. | ||
| Citroën, Fiat, Peugeot with 1.8/1.9 l diesel engine | XUD7, XUD9A, XUD9AU, XUD9TE, XUD9Y, D9B | 7.24808.11.0 |
Vacuum pump mounted on the cylinder head
Possible claims:
- retained braking force
- loss of braking force
- complete failure of the vacuum pump.
Design and operating algorithm
The first passenger cars produced in the last century were not equipped with “vacuum seals”. To sharply slow down the car in case of emergency braking, the pedal had to be pressed with a force of about 80 kg. The device of the vacuum brake booster installed on modern vehicles makes it possible to reduce the mentioned force to a light press.
To diagnose malfunctions of this unit, you need to know its design and operating principle. The amplifier is a cylindrical metal housing, inside of which the following elements are located:
In fact, the body of the “vacuum generator” is divided by a membrane into 2 separate chambers. The first is supplied with vacuum from the power unit, while in the second the air pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure. The chambers communicate with each other through the channels of the air valve, which alternately open when the driver presses and releases the pedal.
The classic vacuum brake booster works according to the following algorithm:
Reference. In diesel and some gasoline cars, the vacuum is created not by the intake manifold, but by a separate vacuum pump in the brake system. Such a scheme operates reliably in high altitude conditions with low atmospheric pressure, where a conventional membrane amplifier loses its functionality.
If the brake pedal is held down by the driver, the diaphragm also stops and exerts a constant force on the rod. Thanks to the described operating principle of the VUT, the driver’s work is greatly facilitated, and the system responds to the pedal much faster.
Design and principle of operation of the vacuum amplifier
A vacuum booster (or VUT) is the most common type of mechanism for boosting brakes. It operates on the principle of reducing pressure or simply vacuuming. Structurally, it forms a single whole with the main cylinder and includes several important components:
- body, divided by a diaphragm into 2 parts - vacuum and atmospheric chambers;
- a valve that closes the bridge between the parts of the vacuum chamber;
- a mechanical (or electric) pump necessary to ensure uninterrupted operation as the main or additional source of vacuum (may not be present on some gasoline cars);
- return type spring - needed to move the diaphragm to its initial position after pressing the brake pedal.
Signs and causes of malfunctions
A breakdown of the booster does not lead to a complete failure of the braking system, but much more physical effort is required to slow down the car. The first and main symptom of VUT failure is a sharp decrease in braking efficiency and a feeling of “hardness” in the pedal. Other signs also appear:
Note. The amplifier is unable to function normally without supplying vacuum from the motor. Therefore, symptoms of problems should only be checked with the engine running.
The above symptoms of a faulty vacuum brake booster occur for the following reasons:
The first reason can be easily eliminated in your own garage; the main thing is to check the “vacuum unit” for functionality. Sealing connections or replacing the pipe will not be a big problem. Another issue is when the amplifier breaks down; usually the entire mechanism has to be replaced.
What are the signs to identify a faulty VUT?
During the operation of a vehicle in which a vacuum brake booster is installed, one should not ignore the tightness of the structure of the booster itself and the hoses leading to it. Here are some signs of a malfunction that will help the driver always keep the situation under control:
- the driver has a need to apply more effort when braking in order to achieve the same efficiency;
- reducing the brake pedal travel;
- the car continues to brake even after the brake pedal is returned to its original position;
- there is a “suction” in the vacuum hose, and therefore there is unevenness in the speed of the power unit;
- when braking, extraneous sounds like hissing are heard;
- VUT completely “refuses” to work;
- fuel consumption increases when operating the vehicle in normal mode;
- the car suddenly begins to “tweak”;
- Candles don't work.
VUT
Sometimes a brake booster malfunction may manifest itself in a slightly different way, but if you feel one of the mentioned symptoms, then this becomes a reason to check the brake system.