Shock absorber malfunction: symptoms and what affects
Shock absorber malfunctions greatly affect the car's behavior on the road.
In particular, the car body “dives” during acceleration and braking, the braking distance increases, rolls heavily during maneuvering and sways when driving over uneven surfaces. There are obvious and hidden signs of faulty shock absorbers. Obvious ones include the appearance of oil leaks (wear of the oil seal and/or rod), but there are more hidden ones, for example, aging of the oil, deformation of the valve mechanism plates, wear of the piston seal and the inner walls of the working cylinder. To avoid unpleasant consequences, you need to identify the faulty shock absorbers in time.
Recommendations for diagnosing shock absorbers on a vibration stand
It is not always possible to check the shock absorber yourself, however, there is a method by which the shock absorber does not even have to be removed from the car. To do this, contact a service center equipped with a vibration stand.
The essence of its work is that the device simulates road irregularities and allows you to accurately determine the malfunction of a particular mechanism, however, given that this method is not free, it is worth considering several rather important aspects:
- Find out if the computer allows you to check your car.
- The life expectancy of the car is also taken into account; a ten-year-old vehicle already has far from the best body rigidity, which will accordingly distort the vibration stand readings.
- Before starting the inspection, be sure to check the wheel alignment and air pressure level in the tires.
Signs of faulty shock absorbers
There are two types of signs that a shock absorber has completely or partially failed. The first type is visual. In particular, they can be identified by visual inspection of the shock absorber. The second type of signs includes changes in the behavior of the car in motion. Let us first list the signs related to the second type, since first of all it is necessary to pay attention to how the behavior of the machine has changed, in particular:
Please note that signs such as long braking distances, uneven tire wear and constant need to steer may indicate other problems in the vehicle, such as worn brake pads, low brake fluid levels, uneven tire pressures, problems with the ball joint or other components. pendants. Therefore, it is advisable to perform a comprehensive diagnosis. Visual symptoms of shock absorber wear include:
That is, if there is a malfunction of the shock absorbers, then expect failure of other suspension elements, because they are all interconnected and can be influenced by each other.
Checking the car on a vibration stand
For the reason that it is not always possible to identify a malfunction on your own or without removing the element, you can contact the service. Here, trained craftsmen will perform it with high professionalism.
How are shock absorber struts checked without removing them from the vehicle?
To do this, you should drive the car onto a special vibration stand. The price of this diagnostic is a thousand or more rubles. This service is also good because not only the strut/shock absorber, but also other elements of the chassis and the brake system are subject to professional inspection. On the vibration stand, road irregularities are simulated, which will allow you to correctly determine the breakdown of a specific mechanism. In addition, this makes it possible to determine the serviceability of bearings (ball and wheel) by checking the lateral rolling of the machine.
The stand has a huge number of sensors that transmit information every second to the main computer.
Advantages of testing with a vibration stand
- the highest accuracy in identifying the slightest faults;
- minimum amount of time.
In addition, owners of freight transport cannot do without this service. Because it is impossible to rock a large car. On a vibration stand it will be possible to establish the problem in its entirety. The only downside is the low prevalence of auto repair shops with similar equipment, even in big cities. In addition, the cost of the service for some car owners can be quite high.
So, we have given several ways to check shock absorbers for malfunctions; you just have to choose the most relevant one for you.
And in order to make driving safe and get by with low repair costs, regularly check not only the shock absorbers, but also other components of your car!
There are several fairly simple ways to independently check the shock absorbers on a car without dismantling them. To check, you can rock the car, conduct a visual inspection of the struts, or determine by touch the degree of their heating - each of these methods allows you to more or less accurately check the performance of the shock absorbers in the car.
An experienced driver can determine whether shock absorbers are faulty even by the car’s behavior on the road. For example, large rolls in corners, longitudinal and lateral sway of the body clearly indicate problems with the suspension and the need for repairs.
Below we will talk in detail about how to check the shock absorbers on a car yourself, and which testing method is most effective. And at the end of the article, watch the video , which shows everything very clearly.
We would also like to draw your attention to our material on the repair of shock absorber struts, which also contains quite detailed video instructions.
How to determine if shock absorbers are faulty
Car owners are not without reason concerned about the question of how to check an oil or gas-oil shock absorber. This is due to the fact that modern shock-absorbing devices often have a more complex design than older models, which makes diagnostic measures more complicated. Therefore, ideally, they should be checked in a car service center on a special stand. However, there are a number of “garage” verification methods.
Body rocking
The simplest, “old-fashioned” method is to rock the car body. In particular, they rock its front or rear part, or the shock absorbers separately. You need to swing it strongly, but do not bend the body elements (in practice, such cases occur!). In theory, you need to achieve the maximum possible swing amplitude, then release the body and look at its further vibrations.
If the shock absorber is working properly, the body will make one swing (or one and a half), after which it will calm down and remain in its original position. If the shock absorber has a malfunction, the body will make two or more oscillations. In this case, it must be replaced.
It is worth noting, however, that the rocking method is suitable for cars with a simple suspension system, for example, the VAZ “classic” (models from VAZ-2101 to VAZ-2107). Modern cars often use complex (often multi-link) suspension, so it will dampen the resulting vibrations even with faulty shock absorbers. Therefore, with the help of body rocking, by and large, it is possible to determine two borderline states - the damper is completely out of order, or it jams during operation. It is not easy to identify the “average” states of the shock absorber using swinging.
Visual inspection
When diagnosing a problem shock absorber, be sure to perform a visual inspection. To do this, you need to drive the car into a viewing hole or lift it on a lift. You can, of course, dismantle the shock absorber, but this can take a lot of time and effort. During the inspection, be sure to check for oil smudges on the shock absorber body. You can wipe off traces of oil with a rag and leave it like that for several days. After this period, the test should be repeated.
If the car is raised on a lift, it is advisable to check the condition of the shock absorber rods. They should not show any signs of rust or damage. If they are present, then the device is at least partially faulty and additional diagnostics need to be performed.
When inspecting, be sure to pay attention to the wear pattern of the tires. Often, when shock absorbers are broken, they wear unevenly; as a rule, the main wear occurs on the inside of the tire. There may also be isolated bald spots of wear on the rubber. However, tread wear may also indicate other failures in the suspension elements, so additional diagnostics are also needed here.
If faults in the front shock absorber (strut) are checked, a mandatory inspection of the springs and upper supports must be performed. Shock-absorbing springs must be intact and free of cracks and mechanical damage.
Machine control check
If the shock absorber/shock absorbers are faulty, then while driving the driver will feel that the car is “scouring” along the road, that is, it will be necessary to constantly steer in order to keep it in the rut. When accelerating and braking, the car will sway. The situation is similar with lateral body tilts. In this case, it is not necessary to accelerate to a significant speed; the city speed limit is quite suitable for testing. In particular, at a speed of 50...60 km/h you can do sharp acceleration, braking, and snake.
Shock absorbers in a car should be checked regularly
According to experts, in our country, due to the old age of the vehicle fleet, as well as due to the poor well-being of the population, a huge number of cars on our roads are operated with worn out or broken shock absorbers (dampers). A particularly sharp increase in the poor technical condition of vehicles has been observed since the simplification of the technical inspection procedure. By the way, not many experienced car enthusiasts know that it is advisable to check the condition of the shock absorbers if the car’s mileage has exceeded 80,000 km. Further, shock absorbers should be checked every 20,000 km. And not just anywhere, but strictly at a special stand. As you already understand, this can only be done in a specialized technical auto center.
When to change a shock absorber
It is necessary to understand that regardless of the quality of the shock absorber, as well as the operating conditions of the machine, wear of this unit occurs constantly. With more or less speed, but constantly! Accordingly, their condition also needs to be checked constantly. Most shock absorber manufacturers in the mid-price category recommend checking every 20...30 thousand kilometers . As for replacement, usually the shock absorber wears out significantly after approximately 80...100 thousand kilometers . At this stage, you need to check it more thoroughly and, if necessary, replace it.
To ensure that shock absorbers last as long as possible, follow these recommendations:
Thus, if problems arise with the shock absorbers, it is better not to tighten it and replace the problem units with new ones. As for the purchase, it is better to buy licensed shock absorbers from the “officials”. Or choose products in trusted stores based on reviews from car enthusiasts.
Source
Suspension knocks and creaks. How to fix
Extraneous sounds often occur in the suspension and shock absorbers. These are knocks and creaks. Most often this is present in the front part of the suspension. Moreover, the reason does not necessarily lie in the rack itself. Sounds can be made by:
Problems in these units arise more often than in shock absorber struts. Therefore, if extraneous sounds occur, you must first check them. Usually the problem lies in the bearing. Replacing it is not a problem even if you have no experience. A minimal set of tools is enough. The situation is similar with the ball joint.
But sometimes the problem lies precisely in the shock absorber strut. One of the common problems is that the bump stop makes strange sounds. It just falls down the stem. Which leads to squeaking.
The problem may lie in the strut washer: when it does not press the bushing of the support itself well against the bearing. It is necessary to immediately change the washers and supports at the same time. Creaking often occurs in certain situations. For example, on bumps. In this case, the reason in almost 1000% of cases lies in the shock absorber struts. There is only one way to fix this - complete replacement.
Inspect!
Cheap, reliable and practical. A visual inspection when diagnosing shock absorbers is a mandatory procedure. If you find a way to look at the shock absorbers, then at least traces of oil on the shock absorber body can be noticed immediately. To make sure the diagnosis is correct, just wipe the shock absorber with a rag and repeat the inspection after a few days. If the car is on a lift, then at the same time try to assess the condition of the shock absorber rods: they should sparkle! Traces of rust or other unsightliness are a sign of malfunction.
Tires can also tell you about problems with shock absorbers. Uneven wear patterns hint at a problem. It is also worth assessing the condition of the protective kits (anthers) and springs, then the upper supports. Well, ideally, and all other suspension elements. But here you need an experienced eye.
Unfortunately, a faulty shock absorber itself may not show external signs of wear. Its ineffective operation may be caused by wear of internal components and materials: this is impossible to calculate visually. In such cases, you should use other diagnostic methods, and also remember the actual period of its operation.
Rock it!
Not the most accurate, but the most popular and visual diagnostic method. You need to vigorously swing the front/rear part of the car, then remove the load and observe how quickly the body stops swaying. If, after removing the load, it performs more than one swing stroke, it means that the swing was not done in vain: the shock absorber, alas, is crappy... The only trouble is that in this way you can only determine a completely “dead” product, and even then with the proper experience. It’s another matter if the shock absorber is tightly jammed: this will be determined instantly, since it simply won’t be possible to rock the car.
Try not to overdo it when rocking, so as not to damage the body parts - this happens...
Checking damping properties
The steps for this method are as follows:
- The machine must be in a calm state.
- The car must be placed on a level surface.
- One of its sides is vigorously swung by the hands and it is checked at what time interval the car body stops swaying.
This method, for obvious reasons, can only be used on passenger cars.
It is acceptable to do 1-2 swings. If the car continues to “walk”, then the shock absorbers are faulty.
Minus of car rocking
The negative side of the described method is that this way you can only identify a completely unusable shock-absorbing element . Although this is the fastest and cheapest (most likely even free) diagnostic option. The second caveat is that the device does not always “play.” It happens that the rods simply jam. In such a situation, it will not be possible to rock the car.
Manage!
If, while driving, the car suddenly gains some independence - it yaws on uneven surfaces, sways in all directions, and reluctantly responds to the steering wheel, then most likely the shock absorbers are to blame. Contrary to popular belief, this manifests itself not only at high speeds, but even if the speedometer shows quite “urban” numbers. At the same time, there is no need to write a pretzel on the road - in a quiet place, exercises such as acceleration, braking, snaking are quite enough... In any case, if the car’s handling has deteriorated over time, you should contact competent specialists for diagnostics.
For example, you can see in this video how cars with working shock absorbers behave and those without.
Try it on!
The simplest, fairly quick and not so expensive way to get general information about the effectiveness of the suspension is to stop by a diagnostic stand, take measurements and listen to the verdict.
Another question is how precisely the verdict will apply directly to shock absorbers. The fact is that in the case of various kinds of “shaking” (of which there are more and more recently), the presence of at least one faulty element (not necessarily a shock absorber) will significantly affect the final results of the efficiency indicator. In addition, the algorithms by which the performance of the suspension are assessed differ, and diagnostics of one car on different stands can lead to the fact that the data obtained on the condition of the suspension may differ.
Checking without a diagnostic stand
There are quite a lot of ways to do self-checking and each of them has certain features. The greatest efficiency can be achieved if several methods of different tests are used at once.
It’s worth taking a closer look at each of the possible verification options:
- Visual inspection. The most logical and accessible way is a banal visual inspection of the shock absorber. If there are oil stains and smudges on the element, this indicates a significant malfunction. It would also be useful to inspect the condition of the rods; for this you will need to hang up the wheel of interest; in a garage, this can be done using a regular jack. If there are traces of rust on the rod, the element is clearly faulty and must be replaced. Naturally, this rather simple method has significant drawbacks, for example, the malfunction does not always manifest itself visually; sometimes the shock absorber becomes unusable due to simple wear and tear of the internal elements. Another drawback is that visually noticeable consequences appear during long-term operation of faulty elements, which means that all this time the suspension has already experienced increased loads.
- Checking damping properties. Another example of how to independently check the performance of the suspension. To diagnose, you will need to place the car on a level surface and vigorously rock one of the sides to see how long the body will swing until it takes a calm position. On a passenger car, the norm is one or two body rolls, but if the car continues, then this indicates a clear malfunction of the shock absorber. The disadvantage of this method is that in this way it is possible to identify only the completely dead suspension element. Moreover, often during the diagnostic process the car cannot be rocked at all; this symptom indicates that the rod is jammed and the shock absorber, of course, needs to be replaced.
- Determining a malfunction while driving. Another fairly accurate way to determine whether the shock absorber is working correctly is to carefully monitor the car’s behavior on the road. A car with a non-working suspension “scours” the road, has poor steering response at high speeds and reacts painfully to all bumps. In large holes you can hear characteristic dull knocks, which, by the way, can sometimes be associated with a worn-out silent block.
- Removal check. It is the most accurate and effective. The removed rear shock absorber should be firmly fixed so that it is located vertically in relation to the ground. After this, you need to check the rigidity of the rod. To do this, it is pulled out and pressed down. If the shock absorber works quietly under the force of one hand, this indicates a malfunction.
How to check shock absorber struts on a car
Shockabsorber-replacement-14_
There are known cases when, when diagnosing a car on a “shaky ride” with a working suspension and recently replaced shock absorbers, the data obtained indicated low residual effectiveness of the suspension. But during the “test drive” the car behaved perfectly. The reason is that the stand was not designed for more “hard” settings of the tuning series shock absorbers compared to the characteristics of the original products, as a result - a wrong verdict. Well, that happens.
A very important point! The final indicators may be influenced by such parameters as tire pressure, vehicle loading during diagnostics, small deviations from a straight line when driving to the stand (appearance of a deviation angle from the longitudinal axis), accidental installation of the vehicle on the handbrake, uneven loading of the vehicle during diagnostics, etc. .d. It will be a real pleasure for a careless repairman to “cheat” a client out of the cost of new shock absorbers, so that in the meantime, as if by accident, pump up his flat tire...
iMarker › Blog › Signs of shock absorber wear
What are the functions of shock absorbers and upper mounts?
All tasks assigned to the main parts of a car’s suspension can be divided into two categories: those responsible for the safety of the driver and passengers and those providing comfort while driving.
So, when talking about safety, we first of all mean reliable contact of the wheels with the road: minimizing vertical swaying, “jumping” on holes and potholes, and dangerous deviations of the trajectory when turning. Thus, shock absorbers and upper supports create reliable grip on the road surface and allow the wheel to go around the obstacle as efficiently as possible, and then quickly and quietly return to its original position.
The main signs of a malfunctioning car shock absorbers
Many drivers rely on their senses, assuming that with their help they will be able to identify vehicle malfunctions. Shock absorbers and suspension struts are among those parts whose failure is accompanied by numerous manifestations. That is why a test drive is the easiest way to get confirmation of car owners’ complaints.
The following are 4 signs of shock absorber failure that you should pay attention to during a test ride, as they clearly indicate the need to replace suspension components.
Car rocking
Suspension springs and shock absorbers provide smooth damping of vibrations that occur when driving through potholes and uneven roads. The shock absorbers themselves help control the springs, which limits excessive up and down movement of the wheels. If these parts malfunction, the wheels may lose contact with the road. This leads to shaking and reduced ride comfort. The car becomes rolly and sloppy, and when driving over a speed bump it sways for a long time. This is a sure sign that the shock absorbers in the suspension have leaked and are not working.
The easiest way to check the working condition of the shock absorbers is to press hard on the car's fender and try to rock it up and down. Then suddenly release the wing. If the car continues to swing on the springs, then it’s time to change the shock absorbers.
Many car owners are not even aware of the existence of friction, gas, reinforced and twin-tube shock absorbers. All they know is that a worn or faulty shock absorber will reduce the ride quality. Therefore, before changing the shock absorber, study its characteristics based on your preferences for the type of driving, since, for example, gas shock absorbers are fundamentally different from oil shock absorbers. All these nuances affect the quality of movement.
“Dive” of the front axle/sagging of the rear axle
Shock absorbers and struts provide stabilization of the car body during acceleration and braking. If these parts malfunction, the front axle may “dive” when braking, and the rear of the car may sag when accelerating. This occurs because faulty parts are unable to support the weight of the vehicle.
Owners often think that new shock absorbers or struts simply improve the ride quality, but in reality they do much more, providing crisp cornering and effective braking. Reducing the braking distance and improving controllability significantly improves traffic safety.
Body roll
Along with the car diving and sagging during acceleration and braking, body stabilization may also suffer during cornering. If the struts or shock absorbers wear out, the body begins to tilt in the direction of the turn. This phenomenon negatively affects traffic safety, as it impairs the quality of braking and steering. With leaking shock absorbers, you will hardly be able to hold the car when turning sharply, especially in winter.
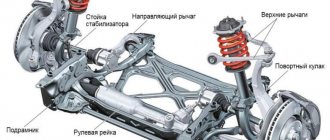
Purpose and principle of operation of shock absorbers
Such a device has a typical passenger car shock absorber
A shock absorber strut is a part of a car's suspension that is designed to dampen the reciprocating movements of the wheel. Always works in conjunction with a spring or leaf spring. To understand the purpose of a shock absorber, let’s imagine for a moment what would happen if it was completely removed. What remains is a wheel capable of moving up and down, and a spring (spring).
The latter is needed to absorb shocks and support the weight of the car. If you remove the shock absorber, then when you hit the slightest hole, the wheel will sharply go down, then up, and due to the spring it will continue to swing back and forth for a very long time. As a result, you won’t get reliable contact between the tire and the road. When hitting bumps and speed bumps, the picture is even worse - an impact will follow, the car will jump, and then continue to sway, remaining uncontrollable.
An equally sad situation would arise when the weight of the car shifts, which occurs during acceleration, braking and maneuvering. In such situations, the body rolls in the direction where the mass shifts. Firstly, it greatly reduces downforce on the opposite side of the chassis. This means that handling and braking distances deteriorate. Secondly, again, due to the action of the spring and its inertia, the car will continue to swing for a long time and tediously.
Now let’s return the shock absorbers to their place and draw the situations described above again. But first, let's take a general look at how the rack works. First of all, it must be said that, roughly speaking, it connects the wheel to the car body. The shock absorber is designed in such a way that the reciprocating movements of the suspension are intentionally damped. That is, a hole, a bump, mass displacement or spring inertia are trying to sharply change the position of the wheel, and the strut is literally holding it.
It doesn't matter whether it moves up or down. But. Firstly, it does not do it as sharply as if there were no shock absorbers. Secondly, after this the body does not continue to swing up and down, since the strut dampens the inertial force of the spring or spring. In some cases, the wheel may not even have time to move. For example, in a small hole and at sufficient speed of the car. If the shock absorber holds the suspension well, the wheel will simply fly over the hole without reaching its bottom, and then without hitting it when leaving it.
Let's summarize. The task of shock absorbers is to prevent the wheels from moving up or down too sharply, and also to dampen the inertial swing of the springs.