Torsion bar suspension - what is it?
The torsion bar is a shaft made of special spring steel, thermally treated. The alloy is subject to very stringent requirements. It must withstand prolonged loads without losing its original properties. The reliability and durability of the suspension as a whole depends on this. To reduce the negative impact of the external environment, the torsion bar is coated with an anti-corrosion compound and paint. The shafts that are coated with a rubberized compound are most protected from rust.
When a car overcomes uneven surfaces, the torsion bars work to twist in one direction. Depending on the design features they are:
- round;
- square;
- rectangular;
- assembled from several layers of metal.
The ends of the torsion bar are rigidly attached to:
- support arm;
- car body or frame (depending on the design).
Fixation occurs through slots. Fastening to the body can be realized using a profile other than round. For normal suspension operation, the rotation axis of the lever and the torsion bar axis must lie on the same line.
Torsional resistance is calculated so that the torsion bar supports the weight of the car, but at the same time allows the arm to move, providing an elastic connection between the wheels and the body. The stiffness of the suspension is affected by the shape, elasticity of the alloy, length and other performance characteristics of the torsion bar.
Concept of suspension
Before talking about the pros and cons, as well as the superiority of one suspension over another, if possible, I propose to understand the essence of the concept of suspension.
A suspension is a component of a car that is part of the chassis. This is an intermediate link located between the road surface and the body part of the vehicle chassis. The work of the suspension is to convert into elastic movement all the impacts that the wheels of the car have to face while driving. And these are all kinds of bumps, holes, unevenness, etc. That is, the suspension absorbs energy from impacts and increases the smoothness of the ride.
In this case, a distinction is made between the design of the front and rear suspension. They can be divided into several categories. At the same time, all structures are subject to the same requirements.
The car suspension must keep the car in a horizontal position, regardless of the acting forces, and dampen vibrations. Plus, the structures must be elastic, strong and as durable as possible. Otherwise, expensive repairs will be required.
The current classification provides for the division of pendants into 3 categories.
- Dependent. It comes with longitudinal and transverse springs, it can use guide arms or a thrust pipe. Also distinguished are the torsion-lever design and the De Dion type system;
- Independent. Such systems differ from each other in the use of oblique and double wishbones located transversely, and may have swinging axle shafts. There are options with double and single trailing arms and transverse ones. But still the most popular option is the MacPherson type suspension;
- Active or semi-dependent. Here the rigidity and position change depending on the command given through the control device. Active systems are divided into pneumohydraulic, hydraulic and pneumatic.
But this is objectively not enough to understand what the difference is between them, what differences exist and which type of suspension travel is preferable in terms of comfort. You can also read useful material about checking shock absorbers for performance.
Dependent constructs
First, let's define what it is and what the concept of car suspension dependence means. In simple terms, this is a pair of opposite wheels (left and right), which are rigidly connected to each other using a single beam. This is one of the key ways to distinguish designs from each other. Just take a look at how the left and right wheels connect to each other.
When the impact on one wheel begins, the position of the second changes. The dependence of one wheel on the other explains the name of the design. Such units are more focused on vehicles that are operated in rather difficult operating conditions. Dependent suspension is extremely rare on ordinary passenger cars designed for city driving. Therefore, finding a car is not so easy if you just need a passenger car. But the system is still in demand and is finding its place in the auto market.
Dependent auto suspension components have strengths and weaknesses.
Let's start with the shortcomings. There are several main points worth highlighting here:
- worse sustainability indicators;
- insufficiently clear controllability;
- reduced level of comfort;
- high requirements for road surfaces when driving at high speeds;
- low information content of management.
All this when compared with cars equipped with an independent type of suspension.
The weaknesses are quite significant, and are more pronounced on ordinary roads. But if you drive into ideal conditions for such a suspension, the car will show its maximum.
It is in the element of the dependent structure that its true advantages are revealed. Namely:
- Low cost of maintenance. Maintenance and repair (maintenance and technical work) are quite cheap, which allows you to significantly save on repairs;
- Resistant to damage. This suspension is not afraid of impacts, active driving on bad roads, etc. The design behaves well under heavy loads;
- High strength. Independent suspension is not a competitor in this regard;
- Constant ground clearance. The clearance does not change, which provides a number of advantages;
- Excellent adaptation to off-road and bad roads;
- A small number of design components, which simplifies maintenance and makes repairs more affordable. This also directly affects reliability.
As you can see, in its element, the dependent system allows you to count on a solid list of advantages. But on regular roads everything is not so perfect.
Independent suspension
Unlike the previous design, here the opposite wheels do not have a direct structural connection with each other. Each of the wheels acts and works independently relative to each other.
Such units perform well when driving on highways, in the city, and behave excellently at high speed. Therefore, independent designs are found mainly on passenger cars, crossovers and SUVs.
We recommend: Changing the coolant on the VAZ 2114 model
This also has its strengths and weaknesses. Benefits include:
- excellent grip on the road surface;
- excellent level of comfort;
- excellent handling;
- minor deviations along the longitudinal axis.
All this affects comfort, agility and handling. Dependent suspensions are not capable of this.
But don't jump to conclusions about the superiority of the independent system. It also has disadvantages:
- repairs are much more expensive, as is maintenance;
- the lever stroke is short, which may reduce ground clearance;
- the design consists of many components;
- due to the complexity of the layout, the likelihood of breakdowns increases;
- It is almost impossible to carry out repairs in the field.
If we take an initially high-quality independent suspension as a basis, and operate the car in the conditions for which it is intended, all these shortcomings will not be so obvious.
Design and principle of operation
The figure below shows a torsion bar suspension, the principle of which is to protect the car body from excessive loads transmitted from the wheels by damping them with a spring shaft. As the car overcomes uneven road surfaces, the torsion bar twists, ensuring maximum smoothness. Upon completion of moving through the obstacle, the torsion bar returns to its original position.
The load is evenly distributed throughout the mechanism. According to the principle of operation, it is similar to a spring - but at the same time, the torsion bar demonstrates better efficiency.
The torsion bar suspension design assumes the constant presence of torsional stress on the elastic shaft during the action of lifting and lowering forces on the wheel. Therefore, the absence of deformation changes in the torsion bar is the main requirement for the product.
Multi-link suspension
This type of suspension is a little similar to a double wishbone design, but it is much more complex and advanced. It is not surprising that all the advantages of the previous type migrated to it. This is a set of levers, silent blocks and hinges that are attached to a special subframe. A large number of ball joints and “silents” provide not only an enviable smooth ride, but also perfectly absorb impacts in the event of a sudden collision with any obstacle, and they also reduce the noise level in the cabin from the wheels.
With this scheme, the best adhesion of the tire to the road (any type of surface), refined handling and a smooth ride are achieved.
- small unsprung masses;
- optimal wheel steering;
- independence of each individual wheel from the others;
- separate transverse and longitudinal adjustments;
- good potential with all-wheel drive.
However, the multi-link suspension has one significant drawback - its high cost. Although recently there has been a turning point: if previously this type of suspension was used only on executive cars, now even golf-class cars are equipped with it.
Types of pendants
There are 2 options for the location of torsion bars:
The transverse arrangement of the torsion shaft has found its application in passenger vehicles. Typically, this type of suspension is used in rear-wheel drive vehicles. Its peculiarity is the placement of shafts along the car body.
Longitudinal torsion bars are used on large, heavy trucks. There have been attempts to use them in passenger vehicles, but this practice has not become widespread.
Currently, the automotive industry uses suspensions of 3 main designs:
- The front is independent using transverse shafts.
- The rear is independent with transverse torsion bars.
- Semi-independent rear.
Dependent suspension
Dependent suspension is characterized by the dependence of the movement of one axle wheel on the movement of the other wheel.
Rice. Diagram of dependent wheel suspension
The transfer of forces and moments from the wheels to the body with such a suspension can be carried out directly by metal elastic elements - springs, springs, or using rods - rod suspension.
Metal elastic elements have a linear elastic characteristic and are made of special steels that have high strength under large deformations. Such elastic elements include leaf springs, torsion bars and springs.
Leaf springs are practically not used on modern passenger cars, with the exception of some models of multi-purpose vehicles. It is possible to note models of passenger cars that were previously produced with leaf springs in the suspension, which continue to be used at the present time. Longitudinal leaf springs were installed mainly in the dependent wheel suspension and served as an elastic and guiding device.
On passenger cars and trucks or minibuses, springs are used without springs, on trucks - with springs.
Rice. Springs: a) – without spring; b) – with suspension
Springs as elastic elements are used in the suspension of many passenger cars. In the front and rear suspensions produced by various companies of most passenger cars, helical coil springs with a constant cross-section of the rod and coil pitch are used. Such a spring has a linear elastic characteristic, and the necessary characteristics are provided by additional elastic elements made of polyurethane elastomer and rubber rebound buffers.
On Russian-made passenger cars, cylindrical coil springs with a constant cross-section of the rod and pitch in combination with rubber bumper buffers are used in suspensions. On cars from manufacturers in other countries, for example, the BMW 3 Series, a barrel-shaped (shaped) spring with a progressive characteristic, achieved through the shape of the spring and the use of a variable-section rod, is installed in the rear suspension.
Rice. Spiral springs: a) cylindrical spring; b) barrel spring
On a number of cars, a combination of cylindrical and shaped springs with variable rod thickness is used to provide progressive characteristics. Shaped springs have a progressive elastic characteristic and are called “miniblocks” due to their small height dimensions. Such shaped springs are used, for example, in the rear suspension of Volkswagen, Audi, Opel, etc. shaped springs have different diameters in the middle part of the spring and at the edges, and miniblock springs also have different coiling pitches.
Torsion bars, usually of round cross-section, are used on cars as an elastic element and stabilizer.
Rice. Torsion
Elastic torque is transmitted by a torsion bar through splined or tetrahedral heads located at its ends. Torsion bars on a car can be installed in the longitudinal or transverse direction. The disadvantages of torsion bars include their large length, necessary to create the required rigidity and suspension travel, as well as the high alignment of the splines at the ends of the torsion bar. However, it should be noted that torsion bars have a low weight and good compactness, which allows them to be successfully used on middle and high-class passenger cars.
Front independent
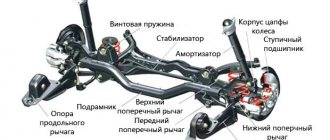
The front independent torsion bar suspension includes the following elements:
- Longitudinal torsion bar. Provides high smoothness.
- Lever arm. Transmits force and causes twisting of the torsion bar.
- Shock absorber. Serves to dampen vibrations that occur in the vehicle's chassis.
- Anti-roll bar. Minimizes car body roll while driving. Improves car handling.
Front independent torsion bar suspension is used on heavy SUVs. This frees up space for powerful wheel drive.
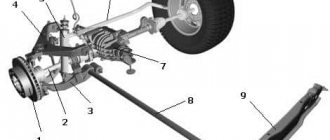
Rear independent
The transverse torsion bars of the rear suspension are installed in tandem with the trailing arms. An example of the design is shown in the image below.
An interesting example of a car with transverse torsion shafts and trailing arms is the Renault 16. The car has a different wheelbase on the right and left. The distance between the front and rear wheels on the right and left differs by several centimeters. The reason for this engineering solution is the sequential arrangement of the shafts one after the other. This slightly worsened the car's handling, but made it possible to increase the luggage compartment.
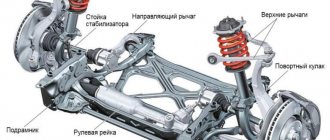
Independent suspension
Independent suspension diagram
First you need to understand what independent suspension is. Simply put, this is a system in which the wheels of one axle are not connected by any rigid connection to each other. When one wheel changes its position, the other, accordingly, may not change its position. But wheel camber and track size can change during compression and rebound. Independent suspension can be on oblique or trailing arms. Independent suspension is used on various cars. When the suspension is on trailing arms, this is when each wheel of one axle is mounted on a lever, which is movably mounted on the frame or body.
The disadvantage of such a system is that the wheelbase changes greatly, but the track remains unchanged. When the car turns, body roll can be more noticeable than with any other system.
The levers absorb very large forces of torsion and bending, so they have to be made very massive and durable. Another disadvantage is the very low ground clearance, which is not very welcome on our roads.
The trailing arm suspension is not very different. Previously, it was called “independent rear axle suspension.” Accordingly, it was used when the rear axle was always the drive one. The difference with the previous version is that there is one hinge on each axis. The first version of such a suspension: the axis of the lever itself passes through the center of the axle shaft hinges, that is, the lever is located at an angle of 45 degrees to the transverse axis. Because of this, such a suspension is cheaper, but the camber and toe change, so you will have to suffer with this.
Second option: previously widely used and they replaced the old conventional dependent types of suspensions. The damping elements were torsion shafts and various coil springs. With the beginning of the spread of front-wheel drive cars, such a torsion bar suspension began to become obsolete, since it had practically no effect on the front axle.
Semi-independent rear
This type of suspension is based on a torsion beam, which has a U-shape. The trailing arms are located one on each side. The beam connects them together. The levers are attached with one side to the body, and the other to the wheel hub.
The beam resists bending well. At the same time, its shape does not prevent it from curling at all. The wheels may move slightly in the vertical plane relative to each other. The location of the torsion beam can be seen in the figure below.
Semi-independent suspension is used in budget cars with front-wheel drive. This is due to the simplicity of the design and low price of such machines.
Technical nuances
Now let’s move on to the technical side of the issue and understand the design and structure of the dependent system, as well as its varieties. Similar types of pendants include the following:
- on longitudinal springs (spring);
- with guide arms (dependent spring);
- De Dion pendant.
The first option is one of the oldest. This structure consists of a bridge beam connecting two wheels, as well as two longitudinal springs on which it is attached.
The spring in this embodiment acts as a universal elastic element - it takes on loads in the vertical and transverse planes, and also dampens body vibrations. Of course, you cannot achieve high comfort from the operation of the suspension of such a system, and at high speeds, problems with controllability begin to appear.
A design with guide arms can be called more advanced and modern. There are a lot of design options in terms of the number of levers and their configuration - this includes a suspension with a Panhard rod, and with a Watt or Scott-Russell mechanism. Compared to spring systems, these systems have much better handling and cornering behavior. The main elastic element here is the spring, and the shock absorber helps it.
As for the De Dion pendant, there is one nuance. The fact is that this system cannot be called completely dependent due to the tricky arrangement of the elements, which is due to the fact that it was developed for the rear axle of rear-wheel drive cars. In it, the differential and the beam connecting the wheels are separated.
We recommend: Rear suspension device
The differential is rigidly connected to the car body, and rotation from it to the wheels is transmitted through swinging drive shafts. According to experts, the De Dion suspension is superior in many respects to the best examples of independent designs, and its only significant drawback is the price, which is why you can rarely see it, and even then mainly on sports cars.
Pros and cons of using torsion bars
Torsion bar suspension has its advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of torsion bar suspension are:
- smooth running of the car;
- the ability to adjust the height, making it easy to change the ground clearance;
- compactness and simplicity;
- good maintainability;
- less load on wheel bearings;
- reliability.
The disadvantages of torsion bar suspension are:
- a large dependence of suspension stiffness on the quality of torsion bars;
- the complexity of manufacturing elastic shafts;
- Driving a car is difficult - turning is too easy.
Elastic element
The main component of the suspension is its elastic part, which absorbs the energy of shocks and vibrations that occur when passing certain road obstacles. The comfort and controllability of the car largely depends on it, so when choosing a specific model you should pay attention to the type of elastic element of the chassis. If we discard the exotic options that are found exclusively in small-scale production, there will be four main types of car suspension.
Springs
Spring suspension was used in horse-drawn carriages and was considered a luxury available only to noble people. Now she is mastering a new profession, represented by cargo transportation. The main advantage of the spring chassis is its enormous endurance, which allows it to carry any load without significant damage. In addition, the spring suspension reduces the load on the shock absorbers, partially performing their function due to friction between the individual leaves.
The downside of springs is their mediocre elasticity and energy intensity. Such suspension cannot make the car comfortable or give it good handling, due to which it is most often found in trucks, passenger vans and pickups. In addition, the spring-based chassis is quite heavy, which is a big disadvantage for a modern car.
Springs
The most popular is the spring suspension, which combines low cost with optimal characteristics and excellent reliability. Cars in which springs act as an elastic element handle well and provide passengers with a good level of comfort. In addition, the spring suspension is easy to repair and does not require high maintenance costs.
The main disadvantage is the small carrying capacity. In trucks, this option is quite rare, since even a spring with a large coil diameter will very quickly lose its characteristics, wearing out under the pressure of a large mass. The spring suspension is also sensitive to shock loads - it is quite possible that after active off-road driving the car will have to wait for the chassis to be repaired.
Torsion bars
On automobile forums, debates still rage on the issue of which suspension is better - torsion bar or spring. Torsion bars are rods that twist under load. Their advantages include:
- Durability;
- Impact resistance;
- Maintainability;
- Compact sizes.
The characteristics of a torsion bar suspension can be compared with a spring suspension. However, while it gains in reliability, it is inferior in comfort. Therefore, the main areas of application for torsion-bar chassis remain large SUVs, for which reliability is important, and compact budget-class cars, for which compact suspension dimensions are higher on the list of priorities than comfort.
Pneumatics
Air suspension can be found on expensive cars of well-known brands - cars and trucks. It can be easily adjusted in height and rigidity, and can also be controlled electronically, automatically adapting the chassis to current road conditions. Pneumatic cylinders provide ideal smoothness and can make overcoming bumps completely invisible to people in the cabin.
The only drawback of the air suspension is that it is not very suitable for Russian roads. We are talking about low reliability, which is due to the use of a large number of complex components. Therefore, if you frequently drive on bad roads, you will have to spend sums comparable to the cost of an inexpensive small car for repairs.