Everyone knows that the 70s of the last century were marked by an increase in fighters for a clean environment. After all, there are a lot of cars on the roads every year and they all seriously pollute the atmosphere of the planet. As for a gasoline engine, a special catalytic converter was developed to ensure the purity of its exhaust gases, but a diesel engine, which operates on a different principle, needs to be properly cleaned from a large amount of soot. For this purpose, a diesel particulate filter was invented. Let's try to figure out what it is.
What is a particulate filter and how does it work?
The very concept of a filter indicates that the part is involved in the cleaning process. Only unlike the air filter, the particulate filter is installed in the exhaust system. The part is designed to minimize the emission of harmful substances into the atmosphere.
Depending on the quality of the product and filter elements, this part can ensure the removal of up to 90 percent of soot from the exhaust after combustion of diesel fuel. The work of the Federation Council takes place in two stages:
- Soot removal. Filter elements that allow smoke to pass through trap particulate matter. They settle in the cells of the material. This is the main task of the filter.
- Regeneration. This is a procedure for cleaning the cells from accumulated soot. It is performed when, with the accompanying systems working properly, the engine begins to lose power. In other words, regeneration is the restoration of the cleanliness of the cell surface. Different modifications use their own technology for cleaning soot.
Job
The operation of the particulate filter is based on two successive stages: soot filtration and subsequent regeneration. During filtration, soot settles on the walls, and purified exhaust gases are released into the atmosphere. In this case, particles with a size of 0.1-1 microns can pass through the filter. Their share is about 5% of the total. However, they are the ones that are dangerous to humans.
Soot particles accumulated inside can obstruct the passage of exhaust gases, causing engine power to drop. Therefore, the particulate filter is periodically regenerated. Depending on the design provided by the manufacturer, the regeneration process can take place in different ways. Now that we understand that this is a diesel particulate filter, we can consider the issue of regeneration in more detail.
Where is the particulate filter located and why is it needed in a car?
Since SF is involved in exhaust cleaning, it is installed in the exhaust system of a car powered by a diesel internal combustion engine. Each manufacturer equips its cars with a system that may differ from analogues of other brands. For this reason, there is no hard and fast rule about where the filter should be located.
In some cars, soot is used together with a catalyst, which is installed in all modern cars equipped with a gasoline engine. In this case, the filter can be placed either before or after the catalytic converter.
Some manufacturers (for example, Volkswagen) have created combination filters that combine the functions of both a filter and a catalyst. Thanks to this, diesel exhaust does not differ in purity from its gasoline counterpart. Often such parts are installed immediately after the exhaust manifold so that the temperature of the exhaust gases ensures the proper chemical reaction to neutralize harmful substances.
“Eco-castration” with your own hands is not a way out of the situation
Taking care of the environment is, of course, vitally important today. However, a clogged particulate filter causes so much inconvenience to car owners that, willy-nilly, they come to the decision to eliminate this device. And in an effort to save money on fixing the problem, they undertake the “eco-castration” procedure either independently or with the involvement of Uncle Vasya, the “mechanic”, a neighbor in the garage cooperative.
First, you need to understand that no matter what filtration system is installed on the machine, the shutdown process will consist of two complex steps. The first is to programmatically remove the device from the on-board computer, the second is to physically cut out the component. Moreover, the second stage is simpler and requires less time. But taking into account the artisanal conditions in which the procedure will be carried out, it can certainly be assumed that a soldered piece of pipe will take the place of the filter. Regarding the sensors, you can be sure of only one thing: it is unlikely that non-professionals will connect them back. And most likely they will break...
As for correcting the software component of the on-board computer, the matter is much more complicated. Reflashing the “brain” of a car by private mechanics, who usually use simple and therefore cheap software (sometimes even free, from the Internet) always carries an increased risk of a disastrous result. And this result will require significant financial costs in the future, because the mistakes made will have to be corrected.
So, what could be the outcome of an amateur attempt to remove the particulate filter?
Activation of emergency mode, which will limit engine power.
Incorrect motor operation.
The inability to repair the car in the future due to the removal of the error card - even a dealer scanner will not help.
Failure to monitor sensor performance.
The lack of good programming knowledge among private auto repairmen or directly from the car owner is a direct path to additional problems with the car and constant headaches. After all, although it may be possible to return “the way it was,” it will require incredible efforts and financial investments.
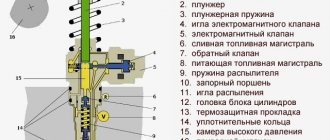
Filter device
In the classic version, the particulate filter device is very similar to the catalyst device. It has the shape of a metal flask, only inside it there is a durable filter element with a cellular structure. Often this element is made of ceramic. The filter body has many cells with a cross section of 1 mm.
In combined versions, the catalyst elements and the filter element are placed in one module. Additionally, such parts are equipped with a lambda probe, pressure and exhaust gas temperature sensors. All these parts ensure the most effective removal of harmful particles from the exhaust.
Replace or remove?
Why is replacing the particulate filter so unpleasant? The main problem with this procedure is the impressive price of a new unit, sometimes reaching 1000 euros or more.
Replace?
It’s clear that not many car owners want to spend that kind of money on a device that is essentially a whim of environmentalists. What to do? Is it possible to remove the particulate filter completely?
Yes, you can do this, but you need to remember:
When this device is removed, the car will begin to comply only with Euro 3 standards.
In our country, this fact is acceptable, but if you suddenly want to travel in your car to Europe, then, when checked, you may be forced to immediately go to a local car service to install a filter.
DPF closed type particulate filters
Modern particulate filters are divided into two types:
- closed type dpf filters;
- fap filters with filter element regeneration function.
The first category includes elements that have a ceramic honeycomb inside, like a catalytic converter. A thin titanium layer is applied to their walls. The effectiveness of such a part depends on the temperature of the exhaust - only in this case will a chemical reaction occur to neutralize carbon monoxide. For this reason, such models are installed as close as possible to the exhaust manifold.
When settling on titanium-coated ceramic honeycombs, soot and carbon monoxide oxidize (the temperature at which the reaction occurs must be several hundred degrees). The presence of sensors allows you to diagnose a filter malfunction in a timely manner, about which the driver will receive a notification from the ECU on the car’s dashboard.
System sensors
To operate the particulate filter in a Mercedes or other cars, entire control systems and sensors are provided:
- Air flow meter.
- Diesel particulate filter pressure sensor.
- Gas temperature sensor before and after the particulate filter.
Based on the results obtained, the computer automatically injects additional volumes of fuel into the combustion chamber, reduces the air supply and even stops exhaust gas recirculation. All this leads to an increase in the exhaust temperature to a value at which regeneration can be carried out.
FAP closed type particulate filters with regeneration function
FAP filters are also of a closed type. They only differ from the previous ones in their self-cleaning function. Soot does not accumulate in such flasks. The cells of these elements are coated with a special reagent that reacts with hot smoke and, at high temperatures, completely removes particles from the exhaust tract.
Some modern cars are equipped with a special flushing system, which injects a reagent at the right moment while the car is moving, so that soot is removed at the early stages of formation.
Sometimes, instead of an additive, an additional portion of fuel is used, which burns out in the filter itself, increasing the temperature inside the flask. As a result of burning, all particles are completely removed from the filter.
How to understand that the filter element needs to be changed
Soot, as we have already figured out, can be burned out. But not only soot accumulates in the filter. There is such a component as ash, which accumulates from the moment the engine is first started and does not go away. It is formed from oil and metallized additives contained in low-grade fuel. That is why it is recommended to use low-ash engine oil in diesel engines with particulate filters.
An impressive mileage (about 200,000 km) and frequent attempts at active regeneration usually indicate that a replacement is approaching. If normally it occurs every 500-1,000 km, then reducing the interval to 150-300 km is considered abnormal.
Attention! You can’t judge a cleaner based on frequent active burning alone! This can also happen due to poor quality fuel poured at the last gas station or a leaking injector.
DPF regeneration
When diesel fuel burns, a large amount of particulate matter is released. Over time, these substances settle on the inside of the soot channels, causing it to become clogged.
If you refuel with bad fuel, there is a high probability that a large amount of sulfur will accumulate in the filter element. It prevents the high-quality combustion of diesel fuel and promotes the oxidation reaction in the exhaust system, which is why its parts will fail faster.
However, rapid contamination of the particulate filter can also occur due to incorrect settings of the diesel engine. Another reason is incomplete combustion of the air-fuel mixture, for example, due to a failed injector.
What is regeneration?
Filter regeneration means cleaning or restoring clogged filter cells. The procedure itself depends on the filter model. And also on how this process was set up by the car manufacturer.
In theory, the soot cannot become completely clogged, since chemical reactions must occur in it. But in practice this often happens (the reasons are indicated a little higher). For this reason, manufacturers have developed a self-cleaning function.
There are two algorithms for performing regeneration:
- Active;
- Passive.
If the car cannot clean the catalyst and filter on its own, you can perform this procedure yourself. It will be required in the following cases:
- The car rarely drives long distances (the exhaust does not have time to warm up to the required temperature);
- The internal combustion engine was shut down during the regeneration process;
- Faulty sensors - the ECU does not receive the necessary impulses, which is why the cleaning procedure does not start;
- When the fuel level is low, regeneration does not occur, since it requires an additional amount of diesel;
- Malfunction of the EGR valve (located in the exhaust gas recirculation system).
A sign of a clogged filter is a sharp decrease in the power of the power unit. In this case, washing the filter element using special chemicals will help solve the problem.
No mechanical means are required to clean the particulate filter. It is enough to remove the part from the exhaust system and close one of the holes. Next, a universal emulator is poured into the container. The product helps remove plaque without having to buy a new part. The liquid should completely cover the contaminated surface. Over the course of 12 hours, the part needs to be shaken periodically so that the soot is better removed.
After using the cleaner, the part is washed under running water.
Passive regeneration
This process is performed while the motor is running under load. When the car drives on the road, the temperature of the exhaust in the filter rises to about 400 degrees. These conditions provoke a chemical reaction to oxidize soot.
During the regeneration process, nitrogen dioxide is formed in such filters. This substance affects the carbon compounds that make up soot. This process produces nitric oxide along with carbon monoxide. Further, due to the presence of oxygen in the cavity, these two substances react with it, resulting in the formation of two other compounds: CO2 and nitrogen dioxide.
It is worth considering that this process does not always occur equally effectively, so periodically it is necessary to carry out forced cleaning of the soot dpf.
Active regeneration
To prevent the particulate filter from breaking down and having to replace it with a new one, it is necessary to periodically clean the active surface of the catalyst. In urban traffic or short-distance travel, it is impossible to ensure passive cleaning of the catalyst.
In this case, it is necessary to launch an active or forced procedure. Its essence boils down to the following. The EGR valve is closed (if necessary, adjustments are automatically made to the operation of the turbine). In addition to the main portion of fuel, a certain amount of air-fuel mixture is formed.
It is fed into a cylinder in which it is partially burned. The remainder of the mixture enters the exhaust manifold and enters the catalyst. There it burns out and the exhaust temperature jumps - the effect of a blast furnace with the blower on is formed. Thanks to this effect, the particles accumulated in the catalyst cells are burned.
This procedure is necessary to ensure that the chemical reaction continues to occur in the catalytic converter. Thanks to this, less soot will enter the filter, and this in turn will increase the resource of the particulate filter.
In addition to cleaning the catalyst, the combustion of an additional portion of VTS outside the engine provides an increase in temperature in the circuit of the filter itself, which partially also contributes to its cleaning.
The driver learns that the electronics perform this procedure to briefly increase idle speed during a long trip. As a result of this self-cleaning, darker smoke will come out of the exhaust pipe (this is normal, as soot is removed from the system).
Automatic regeneration
The Peugeot and Citroen concerns have developed a filter with automatic regeneration. They are installed separately from the catalytic converter. This design uses a regeneration method, which is based on the injection of special additives into the fuel that increase the temperature of the exhaust gases. The same method is implemented in filters from other manufacturers (Ford or Toyota, for example).
Here it works as follows: when the filter is filled to the maximum with soot particles, the system automatically injects a special additive containing cerium into the fuel. This element releases a large amount of heat when burned.
The additive can be injected several times according to a computer signal. The first injection is carried out on the fuel injection stroke. In this case, the exhaust gases are heated to a high temperature and heat the filter matrix to 700 degrees. Then the additives are injected during the exhaust stroke. In this case, the cerium does not burn, but enters the particulate filter along with the gases. When fuel with cerium hits a hot matrix, it ignites and the temperature reaches 1000 degrees. In this case, the soot burns, and thus the filter is regenerated. Note that although the temperature here is very high, destruction of the matrix and the filter itself does not occur.
The cerium additive itself is stored in a separate container. One refill will last on average for several years of operation (about 80,000 mileage). Typically, a diesel particulate filter, the price of which is high and varies in the range of 20-100 thousand rubles (depending on the model), is resistant to the use of low-quality fuel, but in this case the consumption of the additive can be increased due to the large formation of soot.
How to care for the particulate filter
Just like other parts that are subject to stress, the particulate filter also requires periodic maintenance. Of course, if the engine, fuel system and all sensors are properly configured in the car, then less soot will form in the soot, and regeneration will occur as efficiently as possible.
However, there is no need to wait until the engine warning light comes on on the dashboard to check the condition of the particle control element. Car diagnostics will help to identify clogged SF in the early stages.
You can extend its service life if you use a special flush or cleaner that allows you to quickly and safely remove soot deposits from the filter.
Diesel particulate filter clogged: signs and consequences
The role of the soot is such that it only takes power away from the engine. The fact is that soot constantly accumulates inside it, creating resistance to the movement of exhaust gases. You won’t notice this in the city, but on the highway a car with a barely filled filter will accelerate less readily. However, driving on a suburban highway is very useful for a diesel engine, we will explain why later.
One way or another, a slight drop in traction is difficult to notice. It is much easier and more useful to pay attention to the instrument panel, where a special lamp or combination of LEDs will outline the severity of the problem. The exact answer to what this or that icon means can only be found in the instructions for the machine. As an example, we suggest considering the algorithm for signaling problems with DPF on VAG cars:
- DPF icon. The filter is almost full, there have been more than one unsuccessful regeneration, but there is still a chance to burn off the soot using standard means. As soon as the icon lights up, immediately drive onto the highway. We'll tell you what's what and why.
- Check + DPF. A sure sign that the soot hole is clogged. The computer goes into emergency mode, leaving the owner with the only option - to burn off the soot using a special mode.
Instrument alerts duplicate real things, such as fuel consumption, engine oil level, and response to the gas pedal. For example, the following signs help to navigate the impending failure of the particulate filter:
- Average fuel consumption per 100 km suddenly increased by 1-2 liters.
- The oil level in the engine has increased as a result of diesel fuel getting into the crankcase.
There is only one explanation for these events - unsuccessful regeneration (burning off soot using standard means). The purpose of burning is to increase the temperature in the particulate filter so that the soot burns out (converts into carbon dioxide) and the matrix channels become free again. They increase this very temperature mainly due to post-injection of fuel, so that the diesel fuel burns out in the “soot”. If you do not follow the manufacturer's instructions regarding the driving mode during the regenerating event, you will not get a successful result. Attempts at burning will be repeated often, which will ultimately lead to the things mentioned - an increase in diesel fuel consumption and oil level.
We recommend abandoning the idea of letting everything take its course. When the particulate filter is almost clogged, the car does not behave in the best way, because emergency mode means continuous restrictions on speed and current fuel consumption. If this fact does not stop you, then the result of “ignoring” the emergency alert will work in any case: when the purifier is completely clogged, the car stalls and does not start, or starts and immediately stops.
Is it possible to remove the particulate filter?
If you just say it, then it can be done. Only the second question is - what is the point if the car in this case does not meet environmental standards. In addition, the electronic control unit is configured to control the operation of this element. If it is removed from the system, then a permanent software failure will occur in the electronics.
Some take this step and place a decoy for the following reasons:
- There will be no need to maintain additional machine parts;
- A new particulate filter is quite expensive;
- Fuel consumption is slightly reduced since the regeneration process will not be performed;
- Slightly, but still the engine power will increase.
However, this solution has many more disadvantages:
- The very first thing is non-compliance with any environmental standards;
- The color of the exhaust will noticeably change, which will create a problem in a big city, especially in the summer and in traffic jams (there is already not enough air, and then there is a puffing car nearby, which forces you to turn on the air circulation inside the car);
- You can forget about traveling to EU countries, because the car will not be allowed across the border;
- Disabling some sensors will cause a failure in the control unit software. To solve the problem, you will need to reflash the ECU. The cost of firmware is high, and the consequences can be unpredictable. Resetting the data in the control unit will raise a lot of questions that will not make it possible to sell the car at an acceptable price.
These are just some of the negative aspects of cutting out a diesel particulate filter. But they should be enough to discard the idea and start restoring, cleaning or purchasing a new particulate filter.
Symptoms of a problem
Since owners often neglect the proper operation of particulate filters, the devices fail ahead of schedule. This is especially important for Russia, since our fuel is far from being of the best quality.
The main indicator of a problem is a lit icon on the panel. Additionally, the “coil” and “Check Engine” indicators may light up.
Symptoms of problems with the particulate filter:
- Power decreases, especially at low speeds;
- Fuel consumption increases;
- The engine idles rough;
- The oil level is rising. The reason is dilution by fuel due to frequent attempts at regeneration and some of the fuel getting into the crankcase of the internal combustion engine;
- Hissing occurs when the engine is running.
Error codes
- P2002 - low filter capacity;
- P242F - ash accumulation;
- P2452, P2453, P2454 - errors due to pressure sensor A (which is in front of the filter). There may be an electrical circuit malfunction, short circuit or broken wires;
- P2458 - the regeneration process was not completed;
- P2463 - filter clogged;
- P246B - regeneration cannot start;
- P0471, P0472 - problem signal due to exhaust gas pressure sensor
- 00480a, 00481a on BMW - high exhaust back pressure, filter clogged.
Can also be additionally (or separately): P1901, P1958, P2080, P242A, P242B, P246E, P246F.
Reasons that reduce work efficiency
There may be several reasons why it gets clogged. One of the main ones is the quality of the fuel used. Poor quality fuel causes increased soot formation during engine operation, as a result of which the particulate filter will very quickly become clogged with these particles, which will significantly reduce its service life.
Another reason can be considered that the temperature of the exhaust gases is insufficient for complete combustion of soot. The fact is that the particulate filter allows not only to retain soot particles, but also during operation, when the diesel engine provides a sufficient level of exhaust temperature, to burn these particles. But it must be emphasized that this is possible when the exhaust temperature is high and is at least six hundred degrees. At other, lower values, nothing like this happens.
There may be several reasons for a decrease in exhaust temperature, including:
- driving mode (low speed and frequent stops);
- traffic jams while driving;
- disruption of the fuel combustion process.