What is engine displacement
An internal combustion heat engine is an impressive complex of various mechanisms, systems and additional attachments, forming a complex engineering solution.
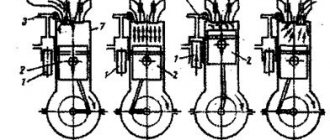
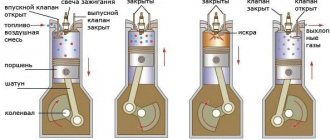
The general principle of operation of an internal combustion engine involves supplying fuel and air to a special closed chamber, where the resulting fuel-air mixture ignites. As a result of fuel combustion, energy is released, which pushes the piston located in the engine cylinder. The piston moves, the crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion, which allows the crankshaft to rotate. Next, the engine torque is transmitted to the transmission and then to the drive wheels of the car.
This process is constantly repeated after starting the engine, that is, the engine is running all the time, provided that the components are supplied and the fuel mixture is efficiently burned in the working chamber. This chamber is called the combustion chamber. The volume of the combustion chamber (also known as the working volume) is the product of the cross-sectional area of the cylinder and the length of the piston stroke from BDC to TDC (top and bottom dead center of the piston stroke). The physical volume of the combustion chamber is the working volume of the engine in gasoline and diesel cars, motorcycles and other types of land, air or water transport, agricultural machinery, as well as other mechanisms and devices using internal combustion engines.
Please note that if the engine has several cylinders, then the volume of the combustion chamber in each of them must be summed up with the others. In other words, the working volume of a multi-cylinder engine is the sum of the volume of the combustion chambers of all cylinders of such an engine. The total volume of all engine cylinders is usually expressed in liters. The working volume of the combustion chamber is indicated in cubic centimeters.
Let's look at this statement using the example of a widely used four-cylinder 2.0-liter internal combustion engine. We will not give exact figures, but simply imagine that each of the combustion chambers has a working volume of 498 cubic centimeters. Since the engine has 4 cylinders, we need to add up the volumes of all cylinders. The result is 1992 cm³. If we talk about internal combustion engines, then to determine the volume, rounding to whole numbers has become the generally accepted standard, and this happens upward. Thus, an engine with the total volume of all combustion chambers, which is actually equal to 1992 cm³, is an engine with a displacement of 2 liters, that is, a two-liter engine.
How does a car engine work?
To begin with, to make it clearer what we are talking about, let’s look at how the working process occurs in a car engine and how the car can move.
Imagine a closed chamber in which one wall is a moving piston. A mixture of fuel (gasoline) and air was placed there through a special pipe, and then it was set on fire using a special device - a spark plug. The mixture flares up and instantly burns, essentially exploding. The hot gas produced by combustion pushes the piston.
On the reverse side, the piston is attached to the crankshaft, through which the pushing force is transmitted to the wheel axle, which sets the car in motion. The more fuel is burned, the stronger the shock will be. Accordingly, a large combustion chamber will provide more engine power than a small one. This is, of course, a very simplified explanation; in practice, power is influenced by many factors.
What depends on the volume
The more mixture of fuel and air enters the engine cylinders and burns there, the more energy is released. Much less fuel will enter the cylinders of a one-and-a-half-liter engine per cycle than a three-liter engine, which means more energy will be released to rotate the crankshaft. A larger motor means better acceleration dynamics, higher top speed and torque. But also higher fuel consumption.
But with power, not everything is so obvious. The use of turbines (forced air injection) made it possible to extract more power from a unit of volume. Thus, the Ford 1.6 liter naturally aspirated engine produces power equal to 115 hp, and the 1-liter Ford Ecoboost with turbocharging produces 125 hp. And the torque of turbocharged internal combustion engines is higher, and its peak value is available from the bottom.
Cars with large engine volumes are more expensive than the same ones with a smaller volume. The fact is that the cost of such an internal combustion engine is more expensive; it needs a different transmission, exhaust and cooling systems, different brakes, etc.
For this reason, budget cars are usually small cars, the engines of which are easy to manufacture and do not have complex systems and electronics. Since the weight of these cars is small, the small engine is enough for comfortable movement around the city and tolerable dynamics. Low cost combined with low fuel consumption makes them popular among car enthusiasts.
Why do model names no longer include engine size?
When turbocharged engines (diesel and gasoline) came onto the market, it became much more difficult to navigate by the “nameplates” hanging on the back of the car. Initially, everything was clear: “BMW 535D” is a diesel BMW of the fifth series with a 3.5-liter engine.
The powerful naturally aspirated five-liter engine, after installing turbocharging, reduces its volume to 4.4 liters, but is still designated as five-liter. This is clearly visible on Mercedes cars, which have already untied the names of their models from their volume. For example, the “AMG63” version no longer carries a 6.2-liter engine. Instead, an internal combustion engine with a volume of five and a half liters is now installed. But the model is still called “AMG-63”.
How to increase the volume of the internal combustion engine
You can physically enlarge the combustion chamber by boring the cylinders. This is called boosting the engine. It will not be possible to significantly increase the volume in this way - the cylinder blocks are designed for their boring limits, which amount to no more than three engine overhauls. During such repairs, cylinders, already elliptical in shape due to wear, are bored to give them a perfectly round shape, and repair pistons with repair rings and other engine parts of an increased size are installed there.
You can buy pistons and other parts for a car engine only in the maximum size corresponding to the third repair. The point of deeper tuning disappears due to its inexpediency, since it is cheaper and easier to buy a larger engine, but it can already be bored out.
Engine capacity
Before talking about compression and compression ratio, let's understand the concept of volume. A cylinder has 3 types of volumes:
- worker;
- combustion chambers;
- full.
The total volume includes the working volume and the volume of the combustion chamber. Each engine has a certain number of cylinders. To find out the total engine volume, you need to add up the parameters of each cylinder.
Engine cylinder volumes
To calculate the working volume of one cylinder, you need to multiply the cross-sectional area of the cylinder by the length of the piston stroke. The piston stroke length is determined by the distance from bottom dead center (BDC) to top dead center (TDC), i.e. from the maximum lower to the maximum upper position of the piston.
According to the formula it looks like this: Vwork. = πr2h , where π = 3.14, r is the radius, h is the length of the piston stroke.
For example, if the volume of one cylinder is 499 cubic centimeters, and there are four cylinders, then you need to multiply 499 by 4 and we get 1996 cubic centimeters. Next, round to 2000 and divide by 1000 to get the value in liters. Thus, the engine displacement will be 2 liters.
Engine volume is a parameter of the internal combustion engine that determines its power.
In most countries, the cost of car tax depends on the engine displacement. The higher it is, the more expensive the tax is. For example, the engine volume of the Japanese Kei Car is only 0.66 cubic centimeters. Owners of these cars do not pay road tax at all.
The displacement of any engine is measured in cubic centimeters or liters. Based on volume, cars are divided into categories:
- minicar (no more than 1.1 liters);
- small-capacity (from 1.2 to 1.7 liters);
- mid-displacement (from 1.8 to 3.5 liters);
- large-capacity (from 3.6 and more).
The larger the volume, the more fuel-air mixture is placed in each combustion chamber. This indicator directly affects fuel consumption, but at the same time the car’s power increases.
Units of measurement: liters or cubic inches
There are various measures of volume. For engines, liters and cm3 are usually used (there are 1000 cm3 in one liter). Quite often in the technical characteristics of cars you can find an indication in cubic inches. This unit of measurement is used by British and American car manufacturers. There are about 61 in3 in one liter.
Engine capacity and fuel consumption
The engine can have a different number of cylinders. Most often there are four, six or eight. On larger vehicles the number can be increased to ten or twelve. Cars with three or five cylinders are much less common.
The more cylinders in the engine, the larger its displacement. Accordingly, to drive the pistons, a larger amount of air-fuel mixture is required. That is, fuel consumption will increase.
Increased crankcase volume and power
- Google+
- LJ
- Blogger
Of course, engine size significantly affects power. But, in fact, engine displacement is not the main indicator that determines its power. The fact is that modern cars implement many technologies that increase power. So, an injection engine will be slightly more powerful than a carburetor engine with the same dimensions. And all because electronics allow for more efficient injection.
The turbine also allows you to increase power without changing the cylinder displacement. The presence of this element increases power to 100 hp. from every liter. Moreover, fuel consumption remains the same. It should be noted that installing this part significantly reduces the life of the motor.
In addition, the turbine is not suitable for installation on SUVs and heavy vehicles. The reason is that it allows you to spin the engine to high speeds. Accordingly, the entire increase in power is carried out at the top. Heavy cars, on the contrary, require the main amount of “horses” at 2000-3000 rpm. Therefore, only large motors are used here (installation of a turbine is acceptable, but it will not be able to show its full potential).
The average car engine volume today does not exceed 1.6 liters. But thanks to the use of modern technologies, the power of the units increases, but fuel consumption remains the same.
Maximum working volume: what will a few cubic cm give?
- Google+
- LJ
- Blogger
Many motorists, when upgrading their engine, increase its volume. This can indeed be done, but only within reasonable limits.
When producing engines, automakers build in a safety margin. This also applies to the crankcase. That is, the engine volume in cm3 can be increased slightly without affecting the service life. This procedure will add several horsepower.
To increase the volume, the cylinders are bored, the pistons and connecting rods are replaced (with ones of a suitable diameter). In order not to harm the motor, it will be enough to grind off 1-2 mm. If you remove more, there is a high probability of failure of the unit. Even when the car owner needs to significantly increase power, you should not try to bore the cylinders too much. It is better to use other methods, or even choose a car engine with suitable characteristics.
Optimal displacement
Almost all manufacturers offer several engines for the same car model, and choosing the optimal engine is not always easy. Conventionally, cars are divided into several classes:
- minicars, with an engine capacity of no more than 1100 cubic meters. cm;
- small-capacity, with a volume of 1200 - 1700 cubic meters. cm;
- mid-displacement, with a volume of 1800 - 3500 cubic meters. cm;
- large-capacity, with a volume of more than 3500 cubic meters. cm.
There is a gradation of power units by car class. For class B cars, engines from 1.0 to 1.6 liters are usually offered, C-class is equipped with engines with a volume of 1.4 to 2 liters, D-class - 1.6 - 2.5 liters, E-class - from 2 liters
When choosing a suitable engine for himself, the future car owner must determine in what conditions the car will be primarily used. For driving in urban conditions, a motor with a smaller displacement (for example, 1.4 liters) is quite suitable if it has good traction at low speeds. If there is insufficient traction at the bottom, the engine will have to be constantly “twisted”, and you can forget about the promised eight liters of fuel per 100 km in the city.
It is also necessary to take into account that the switched on air conditioning system takes up a significant part of the power and increases fuel consumption. In this case, driving a car with a low-power engine becomes unpleasant, since the driver will constantly be forced to engage lower gears.
If the car will primarily be used on the highway, it is better to choose a larger engine.
- Firstly, the difference in consumption will not be so significant;
- secondly, under the hood of the car there will always be a reserve of power, which will allow the driver to overtake more confidently;
- In addition, turning on the air conditioning or climate control system has virtually no effect on the dynamics of the car.
Features of operation of large cars
Compared to small-displacement engines, large-displacement engines are characterized by smoother operation and less noticeable wear, since they are much less likely to have to operate at the power limit. An engine with a large combustion chamber produces its maximum capabilities only when it participates in racing, i.e. in sports competitions. When driving in normal mode, the engine retains a reserve of power, so it does not wear out. Fuel consumption, of course, remains higher than that of small-displacement engines, but it can be reduced by properly adjusting the gearbox.
A powerful engine, which is rarely used in hard conditions, is capable of driving up to a million kilometers without the need for major repairs. Therefore, the costs incurred when purchasing a powerful large car are subsequently recouped by the long-term operation of the car.
What should the displacement be?
Manufacturers are aware of the variability of car owners' priorities, so they produce cars with different types of engines.
Based on this, all vehicles are divided into the following classes:
- Minicars. Such vehicles have an engine capacity of up to 1.1 liters.
- Small cars. The peculiarity of these cars is the installation of 1.2-1.7-liter engines. In our country this is the most popular option.
- Mid-sized cars. This includes vehicles with a displacement of 1.8-3.5 liters.
- Large cars are cars with 3.5 liters or more.
The division discussed above is conditional and applies mostly to gasoline engines.
If the car is equipped with a diesel power unit, the situation will be different.
There is another type of gradation of machines - by class:
- B-class - from 1.0 to 1.6 liters.
- C-class - from 1.4 to 2.0 l.
- D-class - from 1.6 to 2.5 liters.
- E-class - from 2.0 l and more.
When choosing a car, you should pay attention to the operating conditions of the vehicle. If a car is needed to move traffic around the city, a small car would be the best option. The main thing is to have good traction at idle. If this parameter is insufficient, the engine will consume more fuel, so you can’t dream about the promised 7-8 liters.
It is worth considering that when the climate system is turned on, fuel consumption increases and the dynamics of the car decreases. If the car has a low-power engine, you will have to constantly shift the gearshift knob to a lower speed.
If the car will be used for long trips, it is better to give preference to a vehicle with a large displacement.
There are several reasons:
- The difference in consumption is reduced;
- Turning on the climate system has almost no effect on traction;
- Under the hood there will be sufficient power reserves necessary for quick overtaking.
Knowing the considered nuances, it is easier to decide on the appropriate engine size. It is important to focus not only on numbers, but also on real indicators - power, fuel consumption and dynamics.
What is compression ratio
The movement of the piston occurs as a result of the pressure of gases that are formed during the combustion of the fuel-air mixture. Before ignition, the mixture is compressed by a piston in the cylinder. The remaining volume in the cylinder after complete compression of the fuel (the volume above the piston at TDC) is called the combustion chamber.
The compression ratio is the ratio of the volume of the combustion chamber to the total volume of the cylinder. It is calculated by the formula: ξ = (Vр + Vс) : Vс , where Vр is the working volume, Vс is the volume of the combustion chamber.
Compression ratio
For example, the total volume of the cylinder is 500 cubic centimeters, and the volume of the combustion chamber is 50 cubic centimeters. Compression by 10 times. This means the compression ratio will be 10:1.
The compression ratio is a ratio and a relative value.
Compression process in diesel engines
Typically, diesel engines have a much higher compression ratio. If in gasoline engines it averages 10:1 - 12:1, then in diesel engines the value can reach from 15:1 to 22:1. The working process in a diesel engine occurs as follows: first, clean air enters the cylinder, which, due to the high degree of compression, is heated to 700-900 ° C. Diesel fuel is injected under high pressure into the combustion chamber as the piston approaches TDC. And since the air is already very hot, after mixing with it, the fuel ignites. Combustion under pressure (without the need for a complex ignition system) is the main advantage of the diesel engine. But, on the other hand, the requirements for tightness are increasing. A high-pressure pump is also required, which is one of the weak points of this type of power unit.
Briefly about compression
If everything is clear with the degree of compression, then let’s move on to the term compression. This concept refers to the maximum level of pressure that occurs in the combustion chamber at the moment before fuel combustion. If the degree of compression is a conditional value, then compression is an absolute value and is measured in atmospheres, kilograms per cubic centimeter (kg/cm2).
Compression is the pressure in the cylinder; the compression ratio is a dimensionless parameter that describes the geometric characteristics of the cylinder.
There is a close connection between these two concepts, but compression is affected not only by the compression level, but also by the tightness of the compression rings and valves, engine temperature, fuel combustion temperature and much more.
Calculation of cylinder volume
The volume of one engine cylinder is equal to the product of the base area and the height. This formula has been known to everyone since school.
This value is measured in cubic meters or centimeters or in liters. 1000 cm3 equals 1 liter. When specifying engine volume in liters, you must round to one decimal place. For example, if the engine capacity is 1486 cm3, then when converted to liters it should be designated as 1.5 liters; if the volume is 2526 cm3, then it should be written as 2.5 liters. The cylinder displacement of car power units is different.
FAQ
How is engine displacement measured?
Engine displacement is measured in cubic centimeters
(cm3), but in documentation it is often written in liters (l.). 1000 cubic centimeters equals 1 liter. The most accurate unit for measuring volume is cubic centimeters, since when the volume of a car engine is indicated in liters, it is rounded to a whole number after the decimal point. For example, the volume is 2.4 liters. equal to 2429 cm3.
What is the formula for engine cylinder displacement?
The working volume of the engine cylinder is equal to the product of Pi (3.1415) by the square of the radius of the base and the height of the piston stroke in it. The formula itself for the volume of an internal combustion engine cylinder in cubic meters. centimeters looks like this: Vwork = π⋅r²⋅h/1000
How to measure car engine displacement?
Engine volume is the sum of the working volumes of all its cylinders; accordingly, you must first find out what the volume of one cylinder is, and then multiply by their number. The volume of a cylinder is calculated by multiplying the height by the square of the radius and the number “Pi”. But in order to measure exactly the working volume of a cylinder in an engine, you need to take the length of the piston stroke from BDC to TDC as the height, and the radius can also be measured with a ruler, having first found out the diameter of the cylinder. This measurement method is only possible when the head is removed or the parameters are known.
The concept of cylinder displacement
The cylinder displacement is the volume between the extreme positions of the piston movement. It is filled with a combustible warm-air mixture during its intake when the piston moves from the upper extreme position to the lower one. Approaching the top dead position, the piston leaves a free volume - the combustion chamber, or compression. To calculate the full volume of the cylinder, you need to sum up the volume of the chambers and the working volume.
The compression level is a value that is defined as the quotient of the total division in one cylinder and the volume of the combustion chamber. This parameter determines the degree of compression of the combustible mixture in the cylinder. The engine power depends on it, because the higher the compression level, the stronger the burning mixture presses on the piston.
Increasing the compression level is beneficial, since in this case the portion of fuel can do more useful work. However, if the compression level is increased excessively, the mixture may spontaneously ignite or burn too quickly and the fuel may detonate. As a result of rapid combustion of the working mixture, the power unit operates unstably.
Detonation can be identified by a sharp knocking sound, a decrease in engine power and thick black smoke from the exhaust pipe. Automotive designers are constantly looking for ways to eliminate fuel detonation when increasing the compression ratio. The compression level determines the need to use a specific type of fuel.
An increase in engine power is affected by an increase in the number of crankshaft revolutions per minute. But even here there are obstacles. This is a lack of time for the combustible mixture to enter the cylinder, the difficulty of removing exhaust gases, as well as excessive acceleration of the operation of parts and mechanisms, leading to their rapid wear.
To overcome these obstacles, designers increase the number of crankshaft revolutions. For multi-cylinder power units, the cylinder volume is calculated, after which these volumes are summed up to obtain the engine displacement. An increase in engine power is a consequence of an increase in its displacement. And this parameter is determined by the class of the vehicle.
Variable displacement
Providing variable cylinder displacement is an urgent task. To achieve this effect, technology is used to automatically stop some of the cylinders when the engine is not fully loaded. This system is already used in some models of pickup trucks and SUVs, with fuel savings averaging about 20%.
There are also special engines that use mechanical transformation of the piston stroke. However, they are still at the development stage. It is worth noting that internal combustion engines with variable cylinder displacement are used as laboratory equipment, allowing the octane number of gasoline to be determined “by motor method.”
What is affected by engine compression ratio?
It affects the amount of work produced by the engine. The higher the compression ratio, the more energy is released when the fuel-air mixture is burned. Accordingly, this is reflected in the power of the power unit. At the end of the last century, automakers sought to increase power precisely by increasing the compression ratio.
Engine performance and compression ratio
This method has certain limitations. The point is that you cannot compress the mixture indefinitely. There is a certain limit, and if this limit is exceeded, spontaneous ignition of the mixture occurs (detonation). But this rule applies only to gasoline engines.
How to increase engine size
This question is often asked by car owners who have set themselves the goal of increasing the power of their “iron friend” at any cost.
As you know, a car engine consists of several cylinders, they are located in a single block (cylinder block). There is a piston inside each cylinder. And this entire system together is called the combustion chamber and determines the displacement of the power plant.
It is quite simple to independently calculate engine volume; for this there is a formula that was described above.
As a result, how can you increase engine power yourself? Typically, there are several ways to solve this problem. It all depends on how much you want to increase the power output of the engine and of course on the size of your wallet:
- The simplest and cheapest option is simply boring the cylinder block to increase the combustion chamber. In this case, your costs will only be associated with the purchase of new pistons of larger diameter.
- A more expensive option is to replace the “original” crankshaft with a shaft with a larger crank radius. Well, since the diameter of the connecting rods will increase, you will have to change the entire piston group. After this procedure, the stroke of the pistons will increase, and, accordingly, the displacement of the power unit will become larger.
What method to use to increase the power of a car is a personal matter for everyone. But it is worth remembering that boosting the engine at home is simply unrealistic. This requires special equipment, and most importantly, highly qualified specialists. So, if you still decide to take such a step, you have a direct route to a tuning agency.
Classification of cars based on engine size
Since there is no vehicle that would meet the needs of all motorists, manufacturers create engines with different characteristics. Everyone, based on their preferences, selects a certain modification.
Based on engine displacement, all cars are divided into four classes:
This classification applies to gasoline units. Often in the description of characteristics you can find slightly different markings:
In addition to displacement, this classification takes into account such parameters as the target segment (budget model, mid-price or premium), body dimensions, and comfort system equipment. Sometimes manufacturers equip middle and upper class cars with small engines, so it cannot be said that the presented markings have strict boundaries.
When a car model is between segments (for example, according to technical characteristics it is class C, and comfort systems allow the car to be classified as class E), “+” is added to the letter.
In addition to the mentioned classification, there are other markings:
The engines of such cars can have different volumes.
Why are modern model designations not tied to engine size?
After the active introduction of turbo engines into the market in the form of turbodiesel and turbopetrol engines, the situation has changed somewhat, both in the entry-level and middle class, and in the premium segment. Let's start with the fact that it has become more difficult to navigate by the “nameplates” on a car. Initially, many automakers developed such an alphanumeric index that clearly corresponded to the model and engine size. For example, BMW 535 (5-series with a volume of 3.5).
Today, a powerful model with a 5.0-liter naturally-aspirated engine, after installing a turbine, receives a volume of 4.4 liters, but is still designated the same as the previous one. This situation is well illustrated by the fact that the digital designation of a popular Mercedes-Benz model lost its connection to engine size. We are talking about the 63rd AMG. Under the hood of the model has long been installed not a naturally aspirated unit with a volume of 6.2 liters, but a biturbo engine with a displacement of 5.5 liters. However, the car is still called Mercedes 63 AMG.
Let us add that today you can find a highly accelerated engine with a displacement of only 1 liter. (for example, engines of the Ecoboost line on Ford models), which can be installed on a mid-size sedan or hatchback of the “C” / “D” class. The fact is that the installation of turbocharging made it possible to provide such characteristics when the efficiency, power and torque of the engine became possible to significantly increase without the need to increase the physical volume of the combustion chamber.
In other words, the naturally aspirated 1.6 has 115 hp, while the 1.0-liter Ecoboost produces a whopping 125 hp. In parallel with this, the torque of turbo engines is higher and is available from the very bottom, while naturally aspirated engines need to be turned to medium speeds to obtain acceptable dynamics.
We also recommend reading the article about what a boosted engine is. From this article you will learn about ways to increase the power of an atmospheric or turbocharged internal combustion engine.
How to calculate power by engine volume
If you do not know the torque of your car’s engine, then to determine its power in kilowatts you can also use a formula of this type:
Ne = Vh * pe * n/120
(kW), where:
- Vh — engine volume, cm³
- n — rotation speed, rpm
- pe is the average effective pressure, MPa (for conventional gasoline engines it is about 0.82 - 0.85 MPa, for forced ones - 0.9 MPa, and for diesel engines from 0.9 and to 2.5 MPa, respectively).
To obtain engine power in “horses” rather than kilowatts, the result should be divided by 0.735.
Pros and cons of internal combustion engines with large and small volumes
Each type of engine has its own advantages and certain disadvantages, which can significantly affect the choice of a new car.
Advantages of small-displacement internal combustion engines:
- cheaper cost and maintenance of other parts, for example, gearboxes and chassis;
- economical fuel consumption;
- The turbocharged version combines high performance with minimal loads and a small displacement.
Disadvantages of small displacement engines:
- weak power, which is why the car has a small carrying capacity;
- insufficient dynamics;
- low engine life due to frequent driving at high speeds;
- The turbocharged version is very expensive to maintain.
Advantages of displacement engines:
- power is higher than that of economical analogues;
- increased service life (the engine operates at maximum speed less often, so it will last longer);
- excellent dynamics (to overtake less often you need to switch to a lower speed);
- warm up faster in winter;
- atmospheric modifications are not picky about fuel quality.
Disadvantages of volumetric power units:
- maintenance is more expensive than in the case of an economical analogue (you need to fill in more oil and coolant, install a better gearbox, suspension and brakes);
- high taxes upon re-registration (purchase on the secondary market) and customs clearance;
- increased fuel consumption.
As you can see, engine size is closely related to additional waste, both in the case of small cars and more “gluttonous” analogues. In view of this, when selecting a car modification based on displacement, every motorist must proceed from the conditions in which the car will be operated.
What characteristics are affected by displacement?
The main parameter on which the power of the car will depend is the engine size. For example, if a modification of 1.5 liters and 120 hp is installed under the hood, then an analogue with an increased volume of up to two liters will naturally be more powerful.
However, displacement should not be considered the only factor affecting power. The characteristics of the engine can change significantly with the presence of a turbine, changed dimensions of the crank mechanism and a variable valve timing system.
What else does engine size affect?
- Dynamics. The combination of modern gas distribution technologies and a large volume of cylinders allows you to increase the peak speed of the car and reduce acceleration time. These parameters can also change significantly if the manufacturer installs special connecting rods and crankshaft into the engine.
- Cost of the car. Models with a powerful engine will require a more reliable gearbox, improved braking system, suspension, and tires. This is necessary because the driver will try to use the full potential of the vehicle, which means the car will drive fast. The production and maintenance of such vehicles will be more expensive.
- Fuel consumption. Cars with 1.5-liter power units in city mode consume an average of 6-7 liters per 100 km, and medium-displacement cars consume about 9-14 liters per 100 km. The “gluttony” of large-capacity models starts at 15 liters. However, these parameters are relative. So, for dynamic driving in a small car, the driver will often have to “turn” the engine at high speeds, which will certainly lead to excessive fuel consumption. And if the car is equipped with air conditioning, then the small car will be no less voracious than an analogue in a higher class.
The relationship between consumption and volume of an internal combustion engine is described in more detail in the video:
How are fuel consumption and engine size related? Watch this video on YouTube
Pros and cons of large-displacement engines
Flaws:
- original price of the car;
- high fuel consumption;
- high maintenance costs (more oil, more antifreeze, etc.);
- high costs for major repairs;
- high taxes and customs duties (if the car is imported from abroad).
Advantages:
- high vehicle power;
- long service life of the engine itself;
- riding comfort;
- you have to change gears less often with a manual transmission;
- safety when overtaking;
- Such engines warm up faster and better during cold periods.
Large naturally aspirated gasoline power units are less demanding on fuel quality than small-volume turbocharged units.
A few words about turbocharged and naturally aspirated engines
It is worth understanding that a conventional naturally aspirated internal combustion engine is more reliable. A 1.8-2 liter petrol turbo engine with a power of 200 hp, even with the highest quality maintenance, will require a major overhaul at 180-230 thousand km. But a naturally aspirated 3.5-liter internal combustion engine, which has the same power (or slightly higher), easily lasts 350 thousand km before the first major repair.
Classification of cars into classes depending on engine size
Each major automaker has cars of different classes, weights, and sizes in its model line. Regarding passenger cars, they are conventionally divided into:
- Compact and mini-displacement (engine engine working volume up to 1.2 liters).
- Small class cars (volume 1.2-1.8) liters.
- Middle class cars (1.8-3.5 l).
- Powerful sports cars and civilian vehicles with a displacement of more than 3.5 liters.
- Executive cars with engines of various sizes.
Video: Lesson 4 - volume, power, torque, fuel consumption of the engine, small cars, large cars.
Something else useful for you:
Safety of operation of a powerful and voluminous power unit
The current trend towards reducing engine displacement is clear. The more cubic meters the power unit has in its volume, the more gasoline will have to be spent to ensure its operation. But fuel consumption is not the biggest expense for a car owner. After all, it is important that the engine does not require repair, and a large volume can really help with this.
When an engine has a small displacement, it has to work quite hard to achieve a certain acceleration or speed. With a large volume, the operation of the unit always remains soft and measured, parts are not overloaded, and engine wear does not occur too noticeably. In more detail, these factors are as follows:
- the voluminous power unit rarely operates at its maximum capabilities - only during sporty acceleration;
- operation of the piston system occurs gently, the speed increase is quite slow;
- the presence of a large power reserve allows the engine not to strain at high highway speeds;
- if the gearbox is properly configured, the unit does not consume so much fuel;
- Proper operation of the engine means that the power plant can travel more than 1 million kilometers without major overhauls.
These are the features today that large engines with good potential have. They provide not only high operational reliability, but are also the key to a safe trip for the driver, providing high power and power reserve under the driver’s right foot. Also, such units do not require regular repairs.
Of course, the more powerful and voluminous the engine is under the hood of your car, the more careful care it requires. Therefore, it is imperative to buy high-quality oil and replace it in a timely manner. This is where the operating costs for such an engine end. All that remains is to monitor the quality of the fuel and change the lubricant on time.