The parking brake, which is commonly called the handbrake, is used in all modern cars. In addition to the fact that the system of this brake allows you to park the car even on sites with a slope, it also acts as an emergency (spare) brake. At the same time, the handbrake is essentially a continuation of the hydraulic brake system existing in a car or motorcycle. Their malfunctions may be similar, but this is only a first impression. Let's figure out how the handbrake works, what components the handbrake system includes, and what breakdowns are typical for such a system.
A little about the functions of the handbrake
The main function of a handbrake is to hold the vehicle in one place for a long time. Second function : providing braking in case of an accident or emergency braking. In fact, the handbrake is also a braking device at the same time. It can not only save the driver and his passengers in an emergency, but also simply helps to park the vehicle normally.
In sports cars, the handbrake can also be used to make particularly sharp turns. On such vehicles, the brake lever is not located in the same way as in urban vehicles. By the way, on some trucks and even SUVs the handbrake may look quite ordinary, but in reality it interacts not with the wheels, but with the car transmission. Here the subtleties are in the details. Let's look at some points.
Handbrake device
Speaking about the design of the parking brake, we will not pay much attention to each of the elements, of which there are at least fifteen in the handbrake. It is enough for a competent car enthusiast to know at least the basic elements of such a brake. These include:
- Drive mechanism – pedal or lever;
- System of cables acting on the brake - one, two or three cables.
The most popular handbrake systems use three cables. Two of them are rear and only one is front. The first ones are connected directly to the brake mechanisms, while the last cable is connected to the lever or pedal. The cables are connected using adjustable ends. Each of the cables has adjusting nuts at the ends, which are needed to adjust the length of the drive. When removing the car from the handbrake, the driver activates the return spring. It is located on the front cable, sometimes on the equalizer, and in some cases directly on the brake mechanism.
Parking brake device: classic design
The classic of the parking brake genre is, of course, the mechanical design. It is familiar to owners of creations from the domestic automobile industry and foreign cars, so let’s look at its structure in more detail. It consists of the following parts:
- a hand lever or, less commonly, a foot pedal;
- cable system;
- rear wheel brakes.
The principle of operation of the system is quite simple. The lever, which in our case will be the usual manual one, is equipped with a ratcheting mechanism that reliably locks it in the raised or lowered position. When we lift it, the force on the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels (only they are connected to the handbrake) is transmitted through metal drive cables, of which there can be from one to three (usually three - the central one and two rear ones, connected through an equalizer, ensuring uniform distribution of forces on both mechanisms).
When stretched, the cables press the brake pads against the discs or drums - the car will not move anywhere. When we lower the lever, the tension of the cables weakens, the pads release the discs or drums and we can go.
Most easily from the point of view of engineering refinements, the above-mentioned scheme is implemented on drum brakes, which is why they have long remained and remain indispensable on the rear wheels of budget cars. All you need to do is equip the drum with an additional lever that transmits force from the handbrake cable.
Things are a little more complicated with disc brakes. The engineers had to work a little with them, and as a result, three options for connecting them to the handbrake appeared:
- screw mechanism;
- cam;
- drum
The first two types are typical for single-piston calipers. Their device is similar. In a screw circuit, the cable is connected through a special lever to a screw screwed into the disc caliper piston. When tensioned, the screw rotates and causes the piston to move, which presses the pad against the disc.
In the cam version, the piston is acted upon by a system of a cam and a pusher, which is connected to a cable through a lever. The drum variety is used in multi-piston disc brakes. Essentially, this is a separate drum-type brake mechanism, mounted on a disc and not connected to the main calipers and pads.
Handbrake in a car with disc brake
Spare parts for Mazda 2
Front bumper
1.3 ZJ-VE
Spare parts for Mazda 3
Steering rack/mechanism oil seal (see sizes) 1.6 Z6
The most common disc brake systems can use one of three handbrake systems. It’s difficult to talk about the advantages and disadvantages here - each system is adapted to specific brakes and interacts best with them. The parking brake is divided into:
- Screw;
- Drums;
- Cam.
The screw system has found application in disc brakes equipped with only one piston. The piston is controlled by a screwed-in screw. The screw rotates due to the lever from which the cable is pulled. In a slightly more complex cam system, the brake system pistons are manipulated using a pushrod driven by a cam. It is also connected to the handbrake lever using a cable. As soon as the cam rotates, the tappet and therefore the piston begin to move. The drum system has found application in brakes equipped with several pistons.
Types of parking brakes
In a separate article, we have already looked at the design of the automobile braking system. Not much attention was paid there to the handbrake, but its fundamental structure was still described. The key element of a handbrake is the actuator . It could be as follows:
- Mechanical;
- Hydraulic;
- Electromechanical , otherwise called EPB.
The simplest drive is mechanical. It is also the most common - a mechanically operated parking brake lever can be seen in most cars. The parking brake is controlled through this lever. Due to the tension of the cables, the wheels are blocked, which allows you to reduce the speed of the car or prevent the wheels from spinning when parked. A more complex hydraulically driven handbrake is much less common. Structurally, the most complex electromechanical parking brake, otherwise called simply EPB , consists of the following elements:
- Brake mechanism;
- Drive device;
- Control system (electronic).
Electric drive . Includes belt drive, electric motor, planetary gearbox and screw drive. As soon as the electric motor is switched on, it transmits rotation through a belt drive to the planetary gearbox. The latter uses a screw drive. The planetary gearbox makes the entire system less noisy and lighter. As is the case with all handbrake mechanisms, the electromechanical parking brake acts on the pistons of the brake system.
How does a handbrake work?
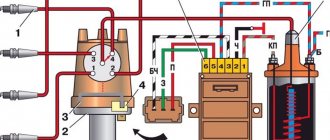
The handbrake has remained virtually unchanged since its inception. By the way, its inventor is the French engineer Louis Renault. His brainchild saw the world back in 1902. Since then, only the adjustment of the mechanism has changed dramatically. A simple and reliable device with a minimum number of vulnerable components is installed in most cars today. The hydraulic brake system includes the following parts:
- main brake cylinder;
- expansion tank;
- brake pressure regulator;
- brake circuits. There are two of them, for the front and rear wheels.
The parking brake device is quite simple. It is for this reason that this mechanism is extremely reliable and can be used for a long period of time without replacing main parts. The pressure generated in the system is transmitted to the cylinders. As a result, they press the pads against the brake discs or drums, depending on the type of braking system. The return mechanism returns the system to its original state and unlocks the brake discs.
More information about the electromechanical handbrake
Continuing the topic of the EPB device, we will also touch on the electronic control unit. It includes the control unit itself, input sensors and an actuator. The transmission of input signals to the unit is controlled by at least three control elements - buttons on the central car console, an integrated slope sensor and a clutch pedal sensor located on the clutch drive. The block itself, having received the signal, gives a command to the operating devices, such as the drive motor.
The nature of EPB operation is cyclical, that is, the device turns off and then turns on again. Switching on can be done using the already mentioned buttons on the car console, but switching off is automated - as soon as the vehicle moves, the handbrake will turn off. However, by pressing the brake pedal, you can turn off EPB by pressing the corresponding button. When releasing the brake, the EPB control unit analyzes the following parameters: the position of the clutch pedal, as well as the speed of its release, the position of the gas pedal, and the inclination of the vehicle. By taking these parameters into account, the system can be turned off in a timely manner - the risk of the car rolling away, for example, on a slope becomes zero.
Electromechanical EPB is the most convenient and at the same time effective on cars with an automatic transmission. It performs well when operating a vehicle in large cities, where alternating starts and stops occurs very often. Advanced systems have a special “ Auto Hold ” control button, by pressing which you can temporarily stop without the risk of the car rolling away. This is useful in the already mentioned city - the driver will only need to press this button instead of constantly holding the brake pedal in the down position.
Of course, the advanced electromechanical parking brake seems futuristic and extremely convenient. In fact, there are at least 3 shortcomings that negatively affect the popularity of EPB. But let’s also touch on the advantages of the system:
- Advantages : compactness, extreme ease of operation, no need for adjustment, automatic shutdown at start, solution to the problem of car rollback;
- Disadvantages : high cost, dependence on the battery charge (if it is completely discharged, you will not be able to remove the car from the handbrake), inability to adjust the braking force.
The main disadvantage of EPB only occurs under certain conditions. If the car is idle for a long time, the battery will have time to discharge - there is no secret in this. For owners of a working city car, this problem is rare, but if the vehicle really needs to be left in the parking lot for some time, you will either have to get a charger or keep the battery charged. As for reliability, practice has shown that EPB is inferior to more familiar handbrake systems in this parameter, but only slightly.
Parking brake, handbrake device and mechanism
Since the moment of time X, when the engine of the first, still experimental, prototype of a car began to roar, design thought has been constantly moving forward, embodied in metal, plastic or silicon wafers. She walked at a snail's pace, flew like a bird, but only forward, giving our pets such a familiar and recognizable appearance.
The hero of today’s article, the parking brake, has also undergone a number of fundamental changes, acquired “intelligence”, and is superior in design complexity to CNC machines that assembled cars in the mid-70s of the twentieth century.
How many brake systems are there in a car?
Three. And all of them provide the functions of changing the speed of the vehicle, stopping and holding in place, using the frictional force and reaction of the support between the wheel and the road surface material. So, the types of braking systems:
Working - provides a controlled reduction in vehicle speed, if necessary, even to a stop. Consists of a drive for transmitting force and a braking mechanism. It is usually of the friction type, installed in the wheel and divided into two types, drum and disc. The drive and force transmission system is also divided into several types:
- Mechanical drive
- Hydraulic
- Electric
- Pneumatic
The first three types of drives will be discussed in detail in further material of the article.
Spare - performs the functions of a working one in case of its complete or partial failure. Structurally, it can be a standalone unit or be part of the main system. Uses working system mechanisms.
Parking brake - better known as a handbrake, it serves to hold the car in place for a long time and prevents it from rolling down an inclined surface. When driving a vehicle, it is used to start moving up an inclined surface. Uses working elements.
How it works
The principle of operation of a parking brake is most easily explained using a mechanically operated system as an example.
A mechanical hand brake is a system of a control lever, connected through rods and a system of cables to the friction mechanisms of the wheels .
The handbrake lever, equipped with a ratchet wheel for locking in the working position, transmits force to a system of one, two or three cables connected to the brake mechanism of the rear wheels of the vehicle. The most popular scheme is using three cables, one central and two lateral. To ensure equal force on the brake mechanisms of the right and left wheels, the central cable is connected to the side ones through a special part of a complex shape, the so-called equalizer.
The parking brake elements are connected to the cables via adjustable ends. This scheme allows you to adjust the system without labor-intensive replacement of the main drive elements.
The levers of the friction mechanisms connected to the cables spread the brake pads, pressing them against the surface of the drum. You can unlock the parking brake, or remove the car from the handbrake, by lowering the mechanical drive lever. The return device will return the pads to their original position and release the brake drum.
Watching a short video will help you understand more clearly how the parking brake works.
Historical reference. Drum brakes were invented by French engineer Louis Renault in 1902. Until the 1930s, a scheme was used in which the pads were moved apart using a system of levers; later, small brake cylinders began to be used. The drum brake design means the pads wear out quickly, and until the invention of the self-adjusting mechanism in the 1950s, the system required constant adjustment. Since 1970, disc brakes have been installed on the front wheels of passenger cars. On the rear ones - as a rule, drum ones, since the parking brake works most effectively with this type of friction mechanisms.
Hydraulic system tuning
Hydraulic drive is used in most modern machines. A simple and reliable device, a minimum of complex and fragile parts, allow it to remain in service even in the age of electronic computing and control units that have replaced many mechanical elements in the design of a car. A simple diagram includes:
- master brake cylinder;
- expansion tank;
- pressure regulator;
- two brake circuits, for the front and rear wheels of vehicles.
When you press the pedal, pressure is created in the system, which is transmitted to the brake cylinders located in the wheels, which press the pads against the surface of the discs or drums. Unlocking when pressure is removed is performed using a return mechanism.
The operation of the hydraulic handbrake will become clearer after watching the next video.
Advantages and disadvantages of EPB compared to a classic parking brake
For clarity, we present the pros and cons of EPB in comparison with the classic handbrake in the form of a table:
| Benefits of EPB | Disadvantages of EPB |
| 1. Compact button instead of a bulky lever | 1. Mechanical parking brake allows you to adjust the braking force, which is not available with EPB |
| 2. There is no need to adjust the EPB during operation | 2. When the battery is completely discharged, it is impossible to “remove it from the manual |
techautoport.ru
Parking brake malfunctions
The fairly simple design of the braking system ultimately became its weakness - many not-so-reliable elements make the entire system unreliable. Of course, a car enthusiast does not encounter a handbrake malfunction very often, but statistics show that during the operation of the car, its owner has studied the issue of parking brake malfunctions at least once. Here's what he might have noticed:
- The travel of the drive lever has increased. With this option, one of the following is observed: the length of the rod has increased or the gap between the drum and the shoes in the corresponding brake systems has increased. In the first and second cases, adjustment is needed, but in the second, optionally, the pads may need to be replaced;
- There is no braking. The options are as follows: jamming of the release mechanism, “oiling” of the pads, everything that is indicated in the paragraph above. This will require disassembling the mechanisms and cleaning them. Adjusting or replacing the pads will help solve the problem;
- There is no disinhibition. Simply put, the brakes get very hot. It is necessary to check whether the brake mechanism is sticking, whether the gaps are set correctly, and also to ensure that the tension springs are in good condition. Disassembly, cleaning and, optionally, replacement of components will solve the problem with brake release.
Single fault: Problem with brake warning light . It may not burn or may not burn in all cases. In this case, the problem most likely lies in the car’s electrical system. If you have to work directly with the handbrake mechanism, then be prepared in advance to buy a handbrake cable. Only the original cable lasts a long time, but most automakers determine that the service life is not the most impressive: about 100 thousand kilometers. Simply put, during the life of the car you will have to replace the cable or adjust its tension at least once.
Checking the parking brake is extremely simple: place the vehicle on an inclined surface, then tighten the lever until it stops. The vehicle should not budge, but the corresponding light on the panel should light up. If any of the above did not happen, you need to repeat the test. If the result does not change, you will have to work on the handbrake again or check the electrical system.
Selecting handbrake elements
Hand brakes are produced by the same companies that specialize in brake consumables, calipers and repair kits. You can search for, say, a handbrake cable using several parameters. Which one to choose is up to the owner of the car or motorcycle. Here are the parameters we are talking about:
- Vehicle data. In particular, the make and model, as well as the year of manufacture;
- Original part code. If the buyer has saved analogue codes, it will not be difficult to find the originals;
- VIN code. A parameter that the vehicle owner knows for sure.
Today, vehicle owners are increasingly looking for the necessary spare parts based on car/motorcycle data . This method would not be accurate if online stores did not create their own cross-databases and did not work on search systems for electronic catalogs. By specifying the brand, model, and selecting the part you are looking for from the list, you can quickly determine the code of the original or analogues, as well as place an order.
A very important factor in choosing handbrake parts is who made it. You should give preference either to original components or to products from companies that have partnerships with automakers. Good hand brake components can be found under the names of the following companies:
- TRW (Germany);
- Cofle (Italy);
- Metzger (Germany);
- ABS (Netherlands);
- LPR (Italy);
- FTE (Germany);
- Valeo (France).
It is important to note that the products of all the above companies are counterfeited, and quite often . Manufacturers from Italy are especially “problematic”. Parking brake components from Bosch (Germany) are also often counterfeited, and much less frequently – from Adriauto (Italy). Carefully inspect each product and its packaging. The slightest discrepancies in design, mechanical damage and sloppy printing indicate that the auto part is a fake.
Conclusion
Despite its simple design, the parking brake does not fail very often. A competent car enthusiast should know how this brake works and what malfunctions are typical for it. In the event of a malfunction, repairs can be carried out even by a non-specialist - all you need are tools, spare parts, a little time and, optionally, cleaning products. Fortunately, all this can be found in a wide range even in small stores. We strongly advise against ignoring handbrake malfunctions, because this brake not only allows you to safely park your car on a slope, but is also responsible for emergency braking.
When to put on the handbrake
the handbrake , even if you decide to leave the car for a short time.
First of all, this will be required when passing practical exams in the traffic police. But the role of the parking brake is the “ handbrake ” not only for parking, but also for assistance: 1) during extreme driving 2) when starting on a slope 3) in case of failure of the “pedal” brake hydraulics 4) other actions where brakes may be required 5) When When passing your driving test, you will be required to show how well you know the basic ways of using the parking brake ( handbrake ). To do this you will need to do the exercise