What is a brake caliper
A brake caliper is a part mounted on the brake disc, which is mounted on the steering knuckle or rear beam. The middle class car has front calipers. Brake drums are installed on the rear wheels.
More expensive cars are equipped with full disc brakes, so they also have calipers on the rear wheels.
The action of the brake caliper is directly related to the driver's efforts when he presses the brake pedal while the car is moving. Depending on the force applied to the brake pedal, the response speed will be different. Drum brakes work on a different principle, but the braking force also depends on the driver's efforts.
How to check the condition and carry out maintenance of front brake calipers?
To carry out the intended work, you will need a lift or inspection pit. All actions must be carried out in the following sequence:
- Jack up the car and remove the corresponding wheel from it. This will make it easier to access the node we are interested in.
- Unscrew the bottom bolt and then lift the caliper body. After this, you can remove the brake pads from their seats.
- Next, you need to unscrew the upper mounting bolt, keeping the brake fluid supply hose connected. We unscrew the bolts securing the bracket to the fist, after which we get the opportunity to remove it along with the fixing parts.
- The next step is to remove the piston. It won't be difficult to do this. Just press the brake pedal, after which the hydraulics will push the piston out. It is for this purpose that the hose needs to be kept connected.
- Disconnect and tightly plug the brake fluid line. For this, it is suitable to use an M12 bolt, or use a tight clamp.
- Remove the boot, seal ring and bracket. In fact, the caliper is completely disassembled and ready for preventive measures. You need to carefully analyze the areas that need cleaning and lubrication. As a rule, these are guides that are subject to severe oxidation. Using a special liquid, we clean all the dirt and inspect all parts for mechanical damage - scratches. They shouldn't exist.
Before carrying out work, be sure to buy a special repair kit, which includes a new sealing ring, piston boots, protective rubber bands for guides, as well as special lubricant. It is not recommended to use old parts, even if they are completely intact.
The calipers must be assembled in the reverse order listed. This must be done very carefully, remembering to generously lubricate the pistons with brake fluid.
Purpose of the brake caliper
As already mentioned, the brake caliper is installed above the brake disc. When the system is activated, the pads clamp the disc tightly, which helps stop the hub, and, as a result, the entire car.
This part is dismountable, so if different elements of the mechanism wear out, you can buy a repair kit and replace the failed spare part.
Basically, the brake caliper structure includes the following elements:
- Frame;
- Guides on the calipers, which allow you to set the uniform impact of the pads on the disc;
- Piston boot to prevent solid particles from entering the brake drive so that it does not jam;
- The brake caliper piston drives the movable pad (most often the pad on the opposite side is mounted on a floating bracket and is installed as close as possible to the disc);
- A bracket that prevents the pads from dangling and touching the disc in a free position, causing a grinding sound;
- A caliper spring that moves the pad away from the disc when the brake pedal is released;
- Brake shoe. Basically there are two of them - one on each side of the disk.
Caliper repair
If the caliper is not damaged by wear or corrosion, it can be repaired and continue driving. As a rule, repairs are made in two cases: when the pads jam or when the repair kit needs to be replaced.
How to fix jammed pads?
The outer metal plates of the pads can rust from constant moisture, salt and other chemicals from the road. Even the paint with which they are covered does not help. When there is a lot of rust, the pads move poorly and can jam.
If the problem does not affect the caliper itself, the pads can be cleaned, lubricated (you need to use high-temperature lubricant and make sure that it does not get on the friction surfaces), and then put in place.
If wear, even a small one, is visible on the adjacent surfaces of the caliper, cleaning the pads will not help. Here you can only replace the part itself. Below is a video on the topic of what to do to prevent the mechanism from jamming.
How to replace the repair kit?
Buying a replacement set of rubber for a caliper is not a difficult task, the principle is the same as when buying the caliper itself (search by car VIN code or make/model/year of manufacture, etc.) When doing your own repairs, you need to prepare a place where you can disassemble caliper so that dust and sand do not get inside the mechanism, then we do everything step by step.
- Removing the caliper.
- Complete disassembly and cleaning.
- Check for corrosion and wear.
- Lubrication of guides.
- Installation of repair kit: guide seals, cylinder seals, bleeder nipple seal, guide boots, piston boots.
- Assembly and installation in place.
- Bleeding the brake system.
The video below clearly shows how to make the replacement. We advise you to turn the volume down, otherwise the music is a little annoying.
Working principle of brake caliper
Regardless of the car model, the braking system in most cases works on a similar principle. When the driver presses the brake pedal, fluid pressure is created in the brake master cylinder. The forces are transmitted along the line to the front or rear caliper.
The fluid drives the brake piston. It pushes the pads towards the disc. The rotating disk is clamped and gradually slows down. During this process, a large amount of heat is generated. For this reason, the car owner needs to pay attention to the quality of the brake pads. No one would like to find themselves in a situation where the brakes fail or are stuck.
If the car has disc brakes on all wheels, then the rear calipers, just like in a drum system, will be connected to the handbrake.
Brake system malfunctions
The brake system requires the closest attention. Operating a vehicle with a faulty brake system is prohibited. Therefore, every motorist should know the main malfunctions of the brake system and identify them by external signs. This article discusses the main malfunctions of the hydraulic service brake system of a passenger car.
According to the design of the brake system, faults can be divided into brake mechanism faults, brake drive faults and brake booster faults.
The following malfunctions of the disc brake mechanism are distinguished:
- wear, damage or contamination (oiling) of brake pads;
- wear, deformation, scuffing on the surface of brake discs;
- weakening of the fastening, deformation of the caliper.
The main malfunctions of the brake drive include:
- jamming of the working cylinder piston;
- brake fluid leak in the working cylinder;
- master cylinder piston jamming;
- brake fluid leak in the master cylinder;
- damage or clogging of hoses and pipelines;
- air leakage in the system due to loosening of the fastening.
The vacuum brake booster may have the following malfunctions:
- insufficient vacuum in the intake manifold;
- damage to the vacuum hose;
- Amplifier follower valve malfunction.
All of the listed malfunctions of the brake system, to a greater or lesser extent, reduce the braking efficiency of the car, and therefore pose a danger to all road users.
The causes of brake system malfunctions are:
- violation of the rules of operation of the brake system (violation of service intervals, use of low-quality brake fluid);
- low quality of components;
- maximum service life of system elements;
- influence of various external factors.
The occurrence of a malfunction in the brake system is indicated by various deviations from normal operation, the so-called. external signs of malfunction, which include:
- deviation from straight-line movement when braking;
- long brake pedal travel;
- grinding noise when braking;
- squealing, whistling when braking;
- reduced pedal effort when braking;
- increased pedal effort when braking;
- pedal vibration when braking (not to be confused with pedal pulsation when the ABS system is operating);
- Low level of brake fluid in the reservoir.
- low brake fluid level;
- brake pad wear;
- ABS system malfunction;
- malfunction of the ESP (ASR) system.
To identify specific malfunctions of active safety systems, computer diagnostics of the vehicle is used.
External signs and corresponding malfunctions of the brake system
| Signs | Malfunctions |
| deviation from straight-line motion when braking |
|
| long brake pedal travel |
|
| grinding noise when braking |
|
| squealing, whistling when braking |
|
| reduction in pedal effort when braking |
|
| increased pedal effort when braking |
|
| pedal vibration when braking |
|
| low level of brake fluid in the reservoir |
|
Types of brake calipers
Although today there are many developments aimed at improving the reliability of the braking system, there are two main types:
- Fixed brake caliper;
- Floating brake caliper.
Although the design of such mechanisms is different, the operating principle is almost identical.
Fixed design
Such supports are installed motionlessly. They have at least two working pistons. Two-piston calipers on both sides clamp the disc, which increases the efficiency of the system. Basically, such brakes are installed on sports cars.
Automotive manufacturers have developed many fixed design caliper options. There are four-, six-, eight- and even twelve-piston modifications.
Floating brake caliper
This type of caliper was created earlier. In the design of such mechanisms there is one piston of the brake cylinder, which drives the pad installed behind it on the inside of the disc.
To ensure that the brake disc is clamped on both sides, there is also a pad on the outside. It is fixedly mounted on a bracket connected to the body of the working piston. When the driver presses the brake pedal, hydraulic force forces the piston toward the disc. The brake pad rests on the disc.
The piston body moves slightly, driving the floating bracket and block. Thanks to this, the brake disc is fixed with pads on both sides.
Budget cars are equipped with such a braking system. Just as in the case of the fixed one, the floating modification of the calipers is collapsible. You can purchase a repair kit for the caliper and replace the broken part.
Caliper Lubricant
Is it possible to lubricate the “fingers” with any available lubricant? Unfortunately no. The reason is that the caliper operates at high temperatures, especially if the car is heavy or the driver likes to drive. In this case, both the caliper, the guides, and the lubricant on them heat up.
For this reason, the most common lubricants are no longer needed: they are based on mineral oils and, when heated, liquefy and flow off the metal.
The second reason why you cannot use lithol, grease, or even higher-quality ceramic and copper lubricants is their interaction with rubber boots. Most lubricants damage the rubber, the boots slip out of their places, and the fingers are left without protection.
What to lubricate with?
Only what the manufacturer calls guide lubricant. Bosch, Liqui Moly and other auto chemical manufacturers have such products. One of the indicators that a lubricant is suitable is high-temperature stability, maintaining properties when heated to at least 200 degrees.
Why can the store offer the wrong thing? Simply because there are other lubricants for calipers, such as ceramic and copper anti-squeak lubricants, which are applied to the metal plate of the pads. Yes, they do their job perfectly, but they are not suitable for fingers!
Malfunctions and repairs of brake calipers
Since the car's braking system takes on a large load when the vehicle slows down (to increase the service life of the brakes and avoid emergency situations, experienced drivers use the engine braking method), some parts need to be replaced. But in addition to routine brake maintenance, the system may fail.
Here are common malfunctions, their causes and solutions:
| Problem | Possible manifestations | How to solve |
| Wedge of the caliper guide (due to wear, dirt or rust, deformation of the bracket) | The car smoothly moves to the side, “grabs” the brakes (braking continues even when the pedal is released), great efforts are required to brake, the brakes jam when the pedal is pressed hard | Caliper overhaul, replacement of worn parts. Change the anthers. You can clean elements damaged by corrosion, but if there is wear, the problem will not be eliminated. |
| Piston wedge (most often due to natural wear or dirt, sometimes due to a worn boot, corrosion forms on the surface of the piston) | Identical | Some people try to grind the piston mirror, but replacing the part will have more effect. Cleaning will only help with minor corrosion. |
| Broken mounting plate (holds the pad in place) | Identical | Replace at every service |
| Pad wedge or uneven wear | Identical | Check the caliper guide bolt and pistons |
| Brake fluid leaking through the fitting | Soft pedal | Check where the fluid is leaking and change the seals or tighten the hose onto the fitting. |
When repairing a caliper, it is important to choose the right repair kit that matches the model of the mechanism. Most brake caliper problems are caused by failed boots, seals, and guides.
Depending on the car model and the calipers used in the brake system, the service life of this part can be about 200 thousand kilometers. However, this is a relative figure, since it is primarily influenced by the driver’s driving style and the quality of materials.
To repair the caliper, it must be completely removed and cleaned. Next, all channels are cleaned and anthers and seals are changed. The rear caliper connected to the handbrake requires special care. Often, mechanics at service stations incorrectly assemble the parking system, which accelerates the wear of some of its parts.
If the caliper is severely damaged by corrosion, there is no point in repairing it. In addition to scheduled maintenance, you need to pay attention to the brake system if the problems listed in the table are observed, as well as if the calipers rattle or knock.
How to tell if your calipers are knocking
Knocking calipers is a common problem for many cars, and in some car models it can be called a “birth disease.” For example, in a number of Chevrolet cars, the calipers begin to knock up to 30 thousand kilometers, and this malfunction is associated with the guides.
Determining that the calipers are knocking is quite simple. The tapping sound of the caliper is best heard when the car is moving at low speed, and especially when passing obstacles. That is, in order to hear it, it is recommended to listen to the car’s suspension when driving over a speed bump or when driving on a dirt road. When you press the brake the knocking noise disappears.
It is worth noting that in most cases, caliper knocking is not a problem that is covered by the vehicle manufacturer's warranty. Accordingly, the driver has to solve the problem for a fee at a service center or independently.
How to choose a brake caliper
It is very important that the caliper is selected to match the technical characteristics of the car, namely, its power. If you install a low-performance option on a powerful car, then at best the brakes will simply wear out quickly.
As for installing more efficient calipers on a budget car, this is already a matter of the financial capabilities of the car owner.
This device is selected according to the following parameters:
- By car make. The technical documentation must include all important information. At specialized retail outlets, specialists already have this data, so if the car was purchased on the secondary market without technical documentation, they will tell you which option is suitable for a particular car;
- By VIN code. This method will allow you to find the original spare part. However, budget analogues are selected according to this parameter with no less efficiency. The main thing is that the owners of the resource where the device is being looked for enter the data correctly;
- Caliper code. To use this method, you need to know this information yourself.
You should not immediately purchase budget analogues, as some manufacturers of auto parts are dishonest in the manufacture of their products. More guarantees - from purchasing a device from trusted manufacturers, such as Meyle, Frenkit, NK, ABS.
Disc brake caliper, description, diagram
- Articles and reviews
- Brake system
- Disc brake caliper
The efficient, trouble-free operation of a disc brake directly depends on the serviceability and correct functioning of its main component - the caliper.
A disc brake caliper is a device that provides braking to a vehicle by pressing pads coated with a friction compound against a disc rigidly connected to the wheel. A caliper is a kind of hydraulic vice that compresses the pads during braking and opens them (retracting them from the disc) when releasing the brakes.
Caliper device
In automotive practice, calipers of two significantly different types are used:
- floating;
- fixed.
Fixed caliper
This type of caliper body is rigidly mounted on the suspension elements. In a metal housing, cylinders are located symmetrically on both sides of the brake disc.
When the brake is applied by pressing the pedal, the pads clamp the disc on both sides simultaneously, slowing down its rotation. In the position removed from the disc, the pads are held by special springs.
Synchronization of the pistons is carried out by simultaneously supplying brake fluid to the cylinders.
Several cylinders are installed in a fixed caliper. This design makes the brake very effective. These are the brakes that are installed on heavy trucks, sports cars and motorcycles.
The advantage of a fixed caliper is the absence of guide pins in its design. Therefore, they cause less trouble during operation, their maintenance is simpler and cheaper.
The disadvantage is that this type of caliper is heavier and bulkier.
Floating caliper
This caliper is attached to the suspension elements using guide pins. It is equipped with working pistons on one side only.
The operation of a floating caliper has its own characteristics. When you press the brake pedal, the piston moves the inner pad and presses it against the disc. The piston, continuing to move, moves the entire caliper along with the outer pad until it rests against the disc.
The advantages of a floating caliper are light weight, simplicity of design, and low cost compared to fixed ones.
The disadvantage is that the force created by a floating caliper is much less compared to a fixed one.
Most passenger cars and light commercial vehicles are equipped with floating calipers. Due to the simplicity of the device, ease and low cost of maintenance, lower metal consumption compared to fixed ones, reliability and durability, they have practically replaced drum-type brakes.
Cars of different models have calipers of a similar design. They are built according to the same scheme. The difference may be in the number and shape of the pads, and methods of attachment to the hub. The most popular scheme is two brake pads per wheel, two-point mounting.
Depending on the amount of braking force required, the caliper can be equipped with one or more cylinders. In a floating one there are one or two cylinders, in a fixed one their number can reach six or even eight.
Floating brake caliper device
Components:
- frame;
— brake hose;
- piston with components (boot, rings - fastening and sealing);
- bracket;
— guides with anthers and fasteners.
The presence of a bracket in the design ensures uniform pressing of the pads from the outside and inside.
Requirements for calipers
The temperature conditions in which brake calipers operate, especially during the break-in period (grinding in) of new pads, forces manufacturers to take a very responsible approach to their performance characteristics.
Main requirements:
- strength;
— high heat transfer;
- resistance to high temperatures.
Increased heating of the caliper parts, which can occur, for example, when driving along a long descent on a mountain serpentine, or when the brakes jam, can lead to overheating of the parts and irreversible thermal deformation (warping).
Advantages and disadvantages of disc caliper
Advantages:
— high braking efficiency;
— good resource indicators;
- relatively simple device;
- low operating costs.
The main advantage of floating calipers is their low weight. This circumstance turns out to be especially important in light of modern trends aimed at reducing the weight of cars to improve their fuel efficiency.
A significant disadvantage of calipers is their openness and exposure to external influences. Water entering the caliper from the road surface significantly reduces braking efficiency.
On the other hand, it is the openness and accessibility of the caliper to the oncoming air flow when the car is moving that allows for effective cooling of parts exposed to heat.
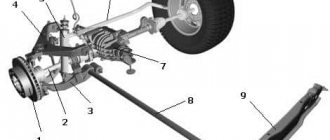
Rear brake caliper
The rear wheel caliper differs from the front caliper not only in size. Its peculiarity is the presence in the design of elements of a parking brake, the so-called “handbrake”.
On vehicles with disc brakes on all wheels, various parking brake drive designs are used:
- with screw drive;
— with cam transmission;
- drum.
Screw and cam mechanisms are installed in single-piston designs.
The drum mechanism is used in a multi-piston caliper. In terms of design, this is an independent shoe brake. The role of the drum is played by the inner (hub) surface of the brake disc.
Some models of modern passenger cars use an electric parking brake.
Typical caliper malfunctions
The need for repair of floating and fixed calipers is approximately the same. The impact of water, dirt and sand on the piston seals leads to their destruction, resulting in jamming of the piston and complete loss of brake functionality.
It should be noted that there are more problems with a floating caliper - in places of friction, the guides wear out, which can cause them to skew and jam the brake.
The most common malfunctions inherent in both types of calipers are the following:
- swelling or cracking of the sealing collars, wear of their working edges and loss of elasticity, associated with a violation of the tightness of the hydraulic system;
— air suction into the hydraulic system;
- so-called souring of the guides (only for floating calipers) with loss of mobility of the bracket relative to the caliper (the caliper “wedges”, that is, it does not release the brakes).
Swelling of sealing cuffs made of special rubber can occur for various reasons:
— installation of cuffs made of low quality rubber;
— using brake fluid of inadequate quality, mixing fluid of different brands.
These faults are eliminated by replacing the cuffs with new ones from a trusted seller or by replacing the entire volume of brake fluid with flushing and blowing with compressed air the entire brake hydraulic system.
Cracking and wear of sealing cuffs can occur due to the natural aging of rubber, which for original products can occur after 8-10 years of operation or a mileage of no more than 150 thousand km. Other reasons are parking the car for a long time without moving or using cuffs of poor quality. The consequence of such a malfunction is loss of tightness of the hydraulic system with the entry of air and leakage of brake fluid.
In addition, wear of the edges of the sealing collars prevents the free return of the piston to its original position when braking stops and the release of the wheel. If there are edges on the cuff, the piston returns due to the elasticity of the cuff. A worn-out part ceases to perform this function.
Air entering the hydraulic system (airing) is manifested by sluggish braking, indicating a decrease in the efficiency of the system. Actions:
— replacement of worn parts;
— topping up or replacing brake fluid;
— bleeding the brakes to remove air.
Souring - loss of mobility of the guides in floating calipers leads to a decrease in braking efficiency. This happens because only one pad (on the cylinder side) is in contact with the disc.
The cause of the malfunction is cracking, destruction or damage to the guide boot. At the same time, moisture, dust and dirt particles, wear and oxidation products of parts penetrate into the friction zone. The mobility of the guide decreases, or even jams.
Troubleshooting - replacing seals, cleaning parts from old grease and contaminants, filling boots with new grease.
Souring of the piston in the caliper cylinder occurs for the same banal reason - a violation of the integrity of parts designed to protect the piston from the penetration of moisture and contaminants. This malfunction is manifested by an increase in the length of the braking distance.
Troubleshooting - replacing parts, eliminating the effects of corrosion and abrasive wear of metal parts, restoring the mobility of parts.
Uneven pad wear. As a rule, increased wear on the upper part of the pad occurs more often. The reason is the jamming of the lower guide, since it is on it that dirt flows when the car is moving. The guide loses its mobility, the pad is pressed against the disc only with its upper part.
Brake caliper: repair or replace
If the caliper on a car sticks, you can hear the question from car owners: what is better, repair or replace the caliper. Naturally, there is no definite answer. It all depends on the condition of the caliper components. To determine the possibility of restoring the caliper's functionality, it must be disassembled, thoroughly cleaned of dirt and rust, and diagnosed. In what cases should this be done?
The main symptoms indicating a caliper malfunction are:
— The car pulls to the side when braking;
— The need to apply more force than before to completely stop the machine;
— Pulsating brake pedal;
— Excessively flexible pedal with dips;
— Blocking the rear brakes during sudden braking;
— Sticking, jamming of brakes.
There may be several malfunctions.
Pads jamming. If, after dismantling the caliper, which is done very simply - just unscrew two bolts - it turns out that the pads have lost free play, most often the reason is corrosion of the parts. It is enough to remove traces of corrosion mechanically or chemically, thoroughly clean and rinse the surfaces, and apply a special lubricant during assembly, and the problem will be solved. If there are pronounced signs of wear on the working surfaces of the caliper (pits, grooves, grooves) that prevent its normal operation, then it should be replaced.
Guide jamming. It is necessary to remove the pads, install the caliper in place, and try to move it along the guides. If movement is difficult, you need to check whether the guides have any deformations or kinks. Then you need to thoroughly clean and lubricate the elements. If free movement cannot be achieved in this way, it is necessary to replace the corresponding repair kit.
Rusted piston. This indicates insufficient care of the caliper. Also, a similar defect can result from long-term parking of the car or rupture of the boot. The caliper must be disassembled, thoroughly cleaned and the rusted piston polished using a special paste.
If the piston has burrs, holes, or chips, it should be replaced.
Similar damage, as well as annular grooves and irremovable traces of corrosion on the working surface of the cylinder are evidence of the need to replace the caliper.
Often the caliper piston jams due to extreme wear of the pads. Naturally, if the pads are really worn out, they need to be replaced. Moreover, if even one pad is badly worn, the entire set is replaced.
Buying a brake caliper is not a cheap pleasure. Therefore, if repairing the caliper is possible, it needs to be repaired. Various repair kits, brake cleaning products and special lubricants are designed for this. All this can be bought in the Avtozapas online store.
Caliper lubrication
The caliper is a complex and responsible unit. In modern cars, it is made of high-tech materials, operates in difficult conditions, and highly specialized lubricants must be used to lubricate it. Traffic safety and people's lives may depend on this.
It is strictly not recommended to use traditional lubricants to lubricate the caliper: nigrol, Litol-24 or solid oil-based graphite lubricants.
To lubricate calipers, highly specialized materials are used, the selection of which we will consider separately in one of the subsequent publications.
Painting brake calipers
The calipers are painted in order to create an individual image of the car, as well as to protect the mechanism from the influence of adverse factors. When choosing a color, two approaches are used:
- choose bright, saturated colors, playing with contrast;
— select the color to match the rims.
If the color of the paint used is a matter of taste for the motorist, then its performance must meet certain requirements. The main thing is high heat resistance, as well as resistance to the influence of negative factors and aggressive environments. For this purpose, special decorative and protective paints are used for calipers and brake drums.
Before painting, the caliper must be thoroughly cleaned of dirt, sanded and degreased. The paint is applied in 2 or 3 layers, with drying intervals of 30-40 minutes.
In addition to a purely aesthetic effect, the coating provides:
— protection of caliper elements from the destructive effects of aggressive chemical compounds coming from the road surface;
— reliable protection against corrosion;
- increased heat transfer.
In addition, on the brightly painted surface, leaks of brake fluid and lubricant that appear over time, as well as accumulated wear products of parts, are clearly visible, which can serve as a signal about the need for maintenance of the unit.
To enhance the effect, painting the calipers is combined with painting the wheel disks, brake drums and the hub part of the brake disks.
Is it necessary to paint the calipers?
Not at all necessary. Still, this is more tuning than a technical necessity. No amount of coloring of the caliper can replace regular care of it, checking its technical condition and maintaining its serviceability.
Procedure for replacing the brake caliper
To replace the front or rear caliper, it does not require any special skills. First, the machine must be on a level surface. Part replacement should always be done as a set.
The wheel rims are loosened, the car is jacked up (you can start from any side, but in this description the procedure occurs starting from the driver's side). When changing the rear gear, you need to lower the handbrake, put the front-wheel drive car in gear and install wheel chocks under the wheels.
In this case (the caliper on the driver's side is changed), the shoes are installed under the wheels on the passengers' side. The machine should not swing forward/backward during work.
The brake system bleeder screw is unscrewed and the hose is lowered into an empty container. To remove remaining fluid from the caliper cavity, use a clamp to press the piston so that it is hidden in the body.
The next step is to unscrew the caliper mounting bolt. In each model this element has its own location. If the handbrake is raised, you will not be able to remove the caliper. At this point, the appropriate mechanism for the desired side is selected. The brake hose mounting thread must be at the top. Otherwise, an incorrectly installed caliper will suck air into the system.
When changing a caliper, you immediately need to pay attention to the discs. If there are uneven surfaces, the surface must be sanded. The new caliper is connected in the reverse order.
In order for the brake system to work correctly, you need to bleed the brakes (after replacing all the calipers). Read about how to do this in a separate article .
Replacing the rear caliper
· lift the vehicle completely, or the wheel itself when using the jack;
· then remove the wheel;
· Next, remove all the tubes and drain the brake fluid from the base of the caliper;
· we remove the broken caliper;
· then we clean and process all the mounting holes on which the new caliper will be put on in the future;
· we assemble and secure the brake system into one unit;
· we fill the brake substance without exceeding the permissible level;
·Next, as stated above, we carry out a test check, and if the brakes work, then the repair has been made, right.
Most motorists do not repair calipers themselves, and this is bad. So, it doesn’t take much time to disassemble and assemble, and there is nothing complicated in this process. But going to a service station with such a problem will be expensive, since repairing brake equipment now costs a lot of money. And in order to protect yourself from repairs, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics of brake equipment more often. Thus, if while driving a vehicle you hear whistling or squeaking brakes, then you immediately need to make repairs and eliminate the malfunctions. But if you doubt that you cannot cope with this repair yourself, then it is better to contact brake equipment specialists at a service station.
About the need for caliper maintenance
Car enthusiasts often complain that the front brake caliper (Niva or another car, it doesn’t matter) is ineffective, gets hot and often jams. At a certain point, the brakes, which previously delighted their owner with precision and reliability, suddenly became capricious. Such problems arise due to the lack of servicing of these nodes. Restoration work begins only when the car no longer slows down.
If you carry out maintenance more often, then repairing the front brake caliper will not be necessary. Let's look at the reasons why a caliper may fail, how to maintain and replace it.
Rear and front calipers
The car's braking system has one feature: it is equipped with different calipers at the rear and front. Simply put, the front caliper cannot be placed at the rear.
The front caliper is an open, well-cooled unit. It works in tandem with a disc that is mounted on the wheel hub. Cylinders are placed in special sockets, and inside the cylinders there are pistons with sealing materials. In addition, the caliper guides are protected from external irritants such as dust and water by a high-strength boot. As soon as the reverse release process begins, the pistons in the braking system are returned to their normal position by elastic rings.
Unlike the front caliper, the technically more complex rear caliper is adapted to work also with the handbrake mechanism. Otherwise, the principle of its operation is no different. However, the rear caliper is more expensive due to its greater design complexity. There can be two drive systems for the rear wheel brake system: hydraulic, mechanical.