While driving
How to use an automatic transmission correctly in the direction of travel? Modern transmissions allow you to switch from one mode to another without pressing a button on the selector lever (except R). And in order not to prevent the car from arbitrarily starting to move while stopping, you need to press the brake pedal when switching modes.
You also need to know how to properly tow a car with an automatic transmission. You must adhere to the following recommendations:
- check the oil level in the box for compliance with factory standards;
- turn the ignition key, remove the lock from the steering column;
- move the selector to mode N;
- towing is recommended for no more than 50 kilometers, at a speed of 50 kilometers per hour or less. When stopping, it is advisable to cool the box;
- It is forbidden to start the engine when towing.
Switching gear
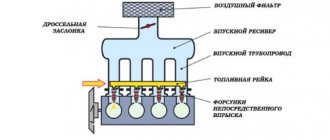
Here we come close to answering the question of what a checkpoint is. The traction force that the crankshaft imparts to the final drive is in a rather limited range. Currently, there are machines and mechanisms that remove transmitted torque directly from the engine, but they are either specially designed for this mode of operation (for example, industrial autoclaves), or are used for operation and maneuvering at low speeds (safety vehicles in large production areas ). However, the bulk of cars and automobiles transmit rotational torque from the engine shaft to their wheel axles through a gearbox. The decoding (what it is and how to read this designation correctly) is quite simple: gearbox. If we consider this unit in a simplified form, then we have two independent shafts with one gear on one of them (it is called the drive, and this gear is the drive), and with five - six, and sometimes more, on the other (the driven shaft and driven gears). We add to all this a device that allows us to move the driven shaft in relation to the drive shaft and engage the gears we need at a given time. This device is called a clutch.
Types of automatic transmission
The structures of various transmissions are similar, but there are certain differences in assembly. They can be divided into several types, differing in the way they are controlled and tested. Some are controlled by a hydraulic device, while others are controlled by an electronic distributor.
Traditional option - hydraulic automatic
The simplest box that eliminates direct communication between the wheels and the engine. Torque is sent by the working fluid through the operation of 2 turbines. Subsequently, the mechanism was improved using an electronic device, which made it possible to add “sport”, “economical driving” and “winter” modes, as well as a “manual mode”, which allows the driver to independently change gears (Tiptronic).
CVT box
It does not have a specific gear ratio. A normally functioning variator gently changes torque, due to which the sound of the engine does not change and remains smooth. This process eliminates the ability to monitor by ear the moment of switching from one gear to another.
Robotic transmission
Otherwise called “DSG robot”, it is most similar to a manual transmission, but the control is similar to an automatic one. Despite this, it weighs much less than a standard automatic transmission, costs less, and most importantly, is much more economical than a manual transmission in terms of fuel consumption.
Like others, these types of boxes have their drawbacks. One of them is increased sensitivity to fast aggressive driving. Unlike other automatic transmissions, when you press the gas pedal hard, the gears switch somehow incorrectly and sharp shocks appear. Such operation leads to damage to parts, and as a result, complete failure of the entire mechanism.
Robotic gearbox
Robotic shift transmissions, or "robots" as they are sometimes called, combine the previous two types of gearboxes. At its core, it is a manual gearbox with two shafts and a clutch controlled by a computer. Thus, the efficiency of such a box is higher, the engine always operates in optimal mode, which allows you to get maximum driving comfort.
The disadvantage of such a box may be that you need to get used to it. With classic manual gear shifting, the driver himself can smooth out the car's ride by smoothly squeezing the clutch and adding speed. When driving with a robotic gearbox, a slight jerk may be felt when the gear is engaged. To compensate for this, manufacturers came up with a manual transmission with two clutches. Its essence is this: at the moment of gear shifting, the computer is simultaneously ready to connect one gear more and one less. Thanks to this, switching occurs almost instantly without jerking.
Catalog numbers and a list of all necessary parts
Catalog numbers of bearings, their cost
| Name | vendor code |
| F-846067-01 (dimensions 56 x 86 x 25) | From 1290.00 |
| F846067-00 | —/— |
| F846067-02 | —/— |
| NA4912NBS | 1706.88 |
| 61912ISB | 1272.96 |
*prices are current as of November 26, 2018.
Before replacing an automatic transmission, always confirm the catalog numbers with service station specialists.
The most unusual boxes
What do we know about gearboxes? The fact that there is an archaic “mechanics”, a convenient “automatic”, a fast-firing, but, according to rumors, unreliable “robot” and a completely incomprehensible variator. It turns out that there are more exotic types of gearboxes.
7-speed manual transmission
Porsche was the first to think of this. In 2011, the legendary 911 (991 body) received a manual transmission with so many gears and an automatic throttle change function when shifting down. For the sake of unification, the 7-speed manual transmission and the PDK preselective robot received a single body. Both versions even had the same number of gear ratios. But the clutch disc of the “mechanics” had a larger diameter - 240 mm (versus the maximum 202 mm for the PDK). A lock prevented me from accidentally shifting to a higher gear. It was possible to turn on the seventh only with the fifth or sixth. Later, other manufacturers followed Porsche. Sports cars were noticed first: the Corvette C7 and Aston Martin Vantage in the limited AMR version received a 7-speed gearbox.
Porsche 911 (991) and Aston Martin Vantage AMR
But what surprised everyone the most was Ford, which donated a seven-speed gearbox to the new Bronco. The revived SUV received a Getrag gearbox. In addition to six forward gears, it has one more forward gear below first. On the gearshift lever it is not indicated by a number, like the others, but by the letter C (Crawler, “crawling”). Its gear ratio is 6.588:1 (for first gear it is 4.283:1).
Ford Bronco
The latest generation 911 is also available with a 7-speed manual transmission. Our colleagues from Car and Driver, who tested the Carrera S with this gearbox, especially noted the familiar shift pattern. In order to maintain this in the PDK robot housing, Porsche engineers developed a mechanically modified MECOSA shift drive. Without it, the driver would have to use an odd gear shift pattern - first gear in place of fourth, fourth in what would normally be sixth.
7-speed Porsche MECOSA
KIA electronic clutch
Soon everything in the car will be done by wire. The brakes and steering are already there, now it’s the clutch’s turn. The recently updated Kia Rio hatchback (has nothing to do with our localized version) with a 48-volt mild hybrid system (MHEV) received an intelligent Manual Transmission (iMT) system: a 6-speed manual transmission, where the clutch is controlled entirely by wire. Pressing the pedal simply sends a signal to the transmission control unit. Thanks to this, the MHEV system is able to disengage the clutch itself, without a command from the driver. With such a clutch, it becomes possible to completely stop the internal combustion engine during a free run at speed, when the battery gives up its energy to the secondary systems of the car. This achieves additional fuel savings and reduced carbon dioxide emissions.
Kia Rio
Not everyone shares Kia's enthusiasm for this innovation. The editor-in-chief of Topspeed believes that “iMT deprives the driver of the main advantages of “mechanics” - the ability to fully control the engine and transmission, use engine braking and have full control over gear selection. If the computer, which is likely to be cautious, does not find your gear selection acceptable, it will not allow the transmission to connect to the engine.”
CVT + “mechanics”
One of the technical innovations applied to the latest generation Toyota Auris is the Direct Shift-CVT gearbox. It combines a classic stage of a pair of gears (the developers call it “starting gear”) and a variator. This first stage is similar to first gear in a conventional manual transmission. It is only activated during acceleration from a standstill, to avoid the sluggish response of a conventional CVT. Afterwards, the electronics turns off this gear and smoothly switches to the variator. This allows it to operate in higher gears, which, for the sake of efficiency, reduces engine speed in cruising mode.
Toyota Auris
CVT + automatic
This is not the first time that Toyota has made a “mix” of two types of transmissions. In 2015, the Multi Stage Hybrid system debuted on the LC 500h coupe. In it, the traditional planetary gear, connecting the internal combustion engine and the main electric motor to the wheels, is complemented by a 4-speed automatic transmission installed behind the hybrid unit. Additional gears enable the internal combustion engine and electric motor to work more actively during acceleration. The coordination between engine speed and accelerator response is more natural. In addition, a manual mode is added. “The gears shift so quickly that the moment of shifting, even in sport mode, is completely unnoticeable. This is simply the best automatic transmission we've ever tested,” The Car Magazine wrote after the test.
Lexus LC 500h
It couldn't be easier
The British company Ariel Motor is known mainly for its countless variations of the lightweight Atom track car. At the same time, the gearbox, interesting in its design, went to another model - the Nomad buggy ("Nomad"), more precisely, its extreme version Nomad R with a power of 340 hp.
The drive to the rear wheels of the lightweight 340-horsepower sports car comes through a Sadev ST82-17 aluminum 6-speed sequential gearbox. This racing box has an integrated oil pump, electronically controlled pneumatic shifter, final drive with limited slip differential. The gearbox is controlled by a single (right) steering column paddle. Pull it towards you and you upshift; push it and you downshift. The speed change itself takes 0.04 seconds (up) and 0.05 seconds (down), respectively. As the English publication Autocar writes, “the gear ratios in the box are so close that you can happily switch to sixth gear at a speed of 40 km/h or engage first at 80.” But the main thing is that this is one of the most compact and lightest gearboxes in the world: it weighs only 38 kg.
Ariel Nomad R
Multi-stage “robots”
It is rare for robotic transmissions to have even nine gears. Recently, a 9-speed “robot” with two clutches 9DCT was declassified by the Chinese Great Wall on the Haval H6 model. But European manufacturers are still making do with fewer gears. For example, Volkswagen, responsible for the fashion for this type of gearbox, uses a 7-speed “robot” in its models.
Haval H6
Honda is aiming to become a leader among mass producers. In 2021, the Japanese patented an 11-speed “robot” with three clutches. This scheme will allow you to change speeds even faster than before, without losing traction on the wheels and choosing the right gear ratios more accurately and quickly. Such a box will be used on small cars aimed at high efficiency. Which ones specifically are still unclear.
Manufacturers of exotic supercars have their own guidelines. For example, the Acura NSX boasts a 9-speed robotic gearbox. But much more interesting is the Koenigsegg Jesko presented last year (1280 hp on gasoline and 1600 hp on an E85 alcohol mixture) with a 9-speed multi-disc Light Speed Transmission (LST). It consists of nine forward gears and seven wet multi-plate clutches in a compact and ultra-light housing (only 90 kg). Unlike conventional sequential gears, which can only change to the next gear, LST is capable of jumping through several steps at once. In fact, all possible gears are always on.
Koenigsegg Jesko
How many steps does an automatic machine need?
Gearboxes with double-digit speeds have long been a reality. It seems that there are CVTs, but continuously variable transmissions are not popular with all manufacturers. One of the first 10-speed automatic transmissions is the result of a collaboration between Ford and GM. The developers managed to ensure that the 10-speed transmission fits into the same form factor as the 6-speed, while weighing only one and a half kilograms more. The crazy Ford F-150 Raptor pickup received the Hydra-Matic 10L80 transmission back in 2015, and a year later the Chevrolet Camaro ZL1 coupe. Subsequently, the “ten-speed” appeared on Mustangs, the new Chevrolet Tahoe and other models.
Chevrolet Tahoe RST
Other examples include the 10-speed automatic Aisin Direct Shift-10A (AGA0E), which is used on the Lexus LS and LC. At one time, this gearbox with a plastic oil pan became the first such gearbox for longitudinal installation. Plus compact dimensions, not exceeding those of an eight-speed, and an enviable switching speed. From second to third in 0.12 seconds in manual mode, in Drive about 0.2 seconds. Honda also has a 10-speed automatic transmission; for example, Accord and a number of Acura models are equipped with it.
Lexus LS 500 AWD
Not all companies support the race for more gear. No wonder the future “king of sedans” Mercedes S-Class is content with a 9-speed automatic transmission. The automatic transmission, which is equipped with domestic Auruses, has a similar number of steps. BMW is also in no hurry to increase the number of steps in its gearboxes. The Bavarians believe that eight speeds on an automatic is the absolute optimum, beyond which the potential benefits do not outweigh the increase in complexity, cost and weight. It’s not for nothing that the latest Bavarian models like the eighth series only have an 8-speed gearbox. And the head of the ZF brand, Stefan Sommer, called nine gears a reasonable limit for an automatic transmission (though this was back in 2012).
What about reliability?
There are a number of complaints about the reliability and maintainability of multi-stage transmissions. This is the conclusion reached by researchers from the American publication Consumer Reports (publishes independent reviews and comparative tests of consumer products and), Jake Fisher, head of the automotive testing department at Consumer Reports, outlines the situation. Older six-speed cars have an order of magnitude fewer such problems.
Another example is the Mercedes 9G-Tronic automatic transmission. For the sake of compact size and light weight, this box received an oil filter built into the pan (replaceable as an assembly) and a single mechatronics module with a printed circuit board, hydraulic valves and sensors. In the event of a breakdown, it is also replaced only as a whole.
Mercedes-AMG G 63
Nevertheless, the project of an “automatic” with 11 gears already exists. Ford registered a patent for this design in 2015. True, the Blue Oval has not officially confirmed the development of such a checkpoint. “Patent materials help protect our ideas but do not necessarily indicate future business development or production plans,” a company spokesperson said.
Strange shapes
Gearboxes are not only strangely designed, but also strangely shaped. Long gone are the days when the transmission selector was a familiar lever on the central tunnel or a steering column “poker”. Today it is primarily a design element. We recall the most unusual solutions.
Rotating washer
For the first time, the first generation Jaguar XF tried on such a scheme. The idea caught on. The lift and turn of the automatic selector became the main feature of all Jaguars, and then Land Rover. But the retractable washer, inconvenient in parking lots and off-road, was criticized not only by journalists, but also by real buyers. As a result, Land Rover left the washers only on the expensive Velar and the large Range Rover. The rest of the SUVs switched to non-locking selectors of the usual shape.
Jaguar XF and Land Rover Discovery
Other manufacturers are also in no hurry to widely implement this original externally, but ergonomically controversial solution. It is found on Fords and Chryslers. Genesis uses a rotary transmission selector only on the flagship GV80 crossover and G80 sedan. The latest new products with such a selector are the Chinese Haval B06 and the fourth generation Kia Sorento, which is localized here.
Buttons
Push-button gear selectors are over 60 years old. Chrysler first used such a scheme in 1956 for its PowerFlite automatic transmission. This design was later copied when creating the Soviet party limousine ZIL-111.
Chrysler (PowerFlite) and ZIL-111
Currently, push-button gearbox selectors are used everywhere. Gone are the days when this was solely a feature of supercars like Aston Martin. The Hyundai Santa Fe crossover and the flagship Palisade received a push-button automatic transmission, although its brother Kia Telluride has a traditional lever installed in the cabin. It's a similar story with the Sonata and Kia K5. The push-button remote control has become a feature of most recent models from Honda, Acura, GMC and Lincoln. In the latest generation of Navigator, automatic transmission buttons are an integral element of the interior decor.
Aston Martin DB9 Volante and Lincoln Navigator
Automatic control buttons can also be on the steering wheel. The first who thought of this were the wizards of the Alpina tuning studio. Subsequently, the scheme became widespread, but in any case it was a duplicate control, in parallel with the traditional gearshift lever.
But technology does not stand still, and all control of the box can be concentrated only on the steering wheel. The corresponding technology was patented by Ford in 2021. Ford thought that all the switches (P, R, N, D, + and -) could be removed from the steering wheel. The patent protects not just the placement of transmission buttons on the steering wheel, but describes the control circuit that links these buttons, the brake pedal, gas pedal and the hybrid powertrain. The switching algorithm is also indicated depending on a number of input signals (whether the brake pedal is pressed or not, the car is moving or standing still). We are waiting for serial implementation.
BMW Alpina B10 and Ford steering wheel patent image
Steering column selector
A modern reincarnation of the “poker” common on classic American dreadnoughts. An old solution in a new way was first proposed by BMW in the still most reviled “seven” E65. Mercedes also did not stand aside - the steering column joystick appeared on the flagship S-Class W221, E-Class and crossovers with a three-pointed star. In modern Benzes, the automatic is controlled in a similar way, while BMW has left this idea in the past.
BMW 745i and Mercedes-Benz GLS 450 4MATIC
And other options
There are a lot of them. There are also various joysticks, like those on the Nissan Leaf or the Lexus CT 200h hybrid. The new Octavia in cars with DSG now has no rigid connection between the selector and the gearbox, so a non-locking “designer” switch has appeared. In BMW, the gear selector handle can be decorated with crystal elements. At least some variety in cars, where the interiors are completely occupied by touch screens and black gloss.
Nissan Leaf and Skoda Octavia
Manual transmission design and operating principle of mechanics
A manual transmission consists of clutches, synchronizers, gears and shafts. The engine and gearbox are connected by a clutch assembly. To disconnect them, you need to depress the clutch pedal. It is at this moment that the required gear should be engaged.
When choosing a gear, a competent driver is guided by the current road situation and vehicle speed. This is quite convenient for those who prefer active, maneuverable driving - for sharp acceleration it is possible to engage a lower gear.
However, there is one significant drawback. Just imagine, you are in the city center, rush hour, you find yourself in another traffic jam and you have to pull the gearshift lever all the time.
Key design advantages of manual transmission:
- Easy to maintain and operate.
- Reliability.
- Light weight.
- High efficiency.
- Compactness.
Interestingly, the design of cars for rally and road racing also includes “mechanics”, but instead of a shift lever, special buttons are used on the steering column - steering column “paddles”, which can significantly reduce the duration of gear shifts.
To achieve maximum smoothness in driving a car with a manual transmission, you need experience. In addition, each car has its own characteristics of the clutch and gearbox, which you need to get used to.
Continuously variable transmission (variator)
CVT or CVT is a continuously variable transmission that allows for maximum smooth driving. Used on cars with small engines.
Basically it consists of two conical pulleys and a steel belt. The variator allows an infinite gear ratio by changing the effective diameter of the pulleys. Those. in essence it is a continuously variable transmission. By adjusting the width of the gap between the cones, the speed change will occur gradually, without jerks. The electronic transmission control unit is responsible for this adjustment.
Disadvantages of the variator:
- severe wear of belts
- high cost of repairs
- It is not advisable to take other vehicles in tow
Pros of a continuously variable transmission:
- low fuel consumption
- high efficiency, saving engine life
Disadvantages of AMT
There are also disadvantages to such a popular and in-demand AMT:
You can’t get used to reprogramming: we put the comma ourselves. If the driver intends to change the dynamics of the car or save the car's resources by reprogramming the AMT, he will be disappointed. It is impossible to reprogram this type of gearbox. There is only one way out: without trying to adjust the AMT to your driving style, adapt yourself to some of the features of its functioning. However, a reservation should be made here. After the car's warranty period expires, our craftsmen still manage to reflash the AMT electronic control unit. It cannot be said that this procedure is guaranteed to lead to improvements in car dynamics, but such attempts are made regularly by domestic car enthusiasts.
Low switching speed. Those who are used to driving with an automatic transmission often complain that the AMT is too “slow.” This drawback is the result of software costs and is inherent in any automatic transmission. Unfortunately, here you have to choose between the presence of an “automatic” and the speed of switching; The modern auto industry, alas, has not yet come up with a third option.
Availability of manual mode. When driving in traffic jams or on rough terrain, switching to manual mode for AMT is mandatory. Otherwise, the AMT will very quickly exhaust its service life and become unusable. This minus can only be called a minus conditionally: some drivers, on the contrary, warmly welcome the ability to manually change gear in the AMT.
Jerks when switching. Sometimes, when changing gears, jerking is felt when the car is moving. The reason is that the gas was not released at the time of switching.
This is not exactly a drawback, but rather a feature of AMT operation: it is important to learn how to not fully press the gas pedal in this situation.
Poor performance on steep climbs. When driving up a steep hill in vehicles equipped with AMT, the clutch may disengage
This happens when it overheats. It is for this reason that a robotic gearbox has the option of manual shifting. Again, this is not a flaw, but a design feature.
Types of gearboxes: types of gearboxes
Having understood the purpose of the box, it should be noted that the gearboxes themselves can be stepped, continuously variable and combined. Let's look at these types of boxes in more detail. First of all, the most common type of transmission is the stepped transmission. In such gearboxes, the torque changes in steps. This type includes manual transmission (mechanics) and manual transmission (robot gearbox).
- The manual transmission is a multi-stage cylindrical gearbox, which allows the driver to manually change gears. Manual transmissions come in four-speed, five-speed, six-speed, etc. The main advantage of such a box is considered to be reliability and simplicity, as well as complete control in all modes.
The downside is the need for constant manual gear shifting and the associated difficulties. For this reason, boxes with automated control have recently greatly pushed back “mechanics”.
- The robotic gearbox (robotic gearbox) is still the same mechanics, however, the clutch release and gear shift functions are fully automated thanks to the use of separate actuators controlled by the gearbox ECU (for example, an AMT box).
The most modern manual transmissions have two clutches and are distinguished by a complex design. At the same time, the double clutch makes the switching process fast and smooth, torque is transmitted without interrupting the power flow from the internal combustion engine to the wheels.
As a result, such a gearbox shifts faster than a professional driver or an experienced racing driver could do. A car with such a “robot” (for example, DSG) is characterized by fast acceleration, as well as maintaining optimal engine speed and at the same time high fuel efficiency. The disadvantage is considered to be the complexity of repairs, reduced service life, low maintainability and the high cost of individual spare parts and elements.
- There are also continuously variable CVT gearboxes. This type should be understood as a variator gearbox (CVT or CVT). The main difference between such transmissions is that they do not have fixed physical stages.
This feature allows you to change the gear ratio in the variator smoothly, compared to step boxes. Also, torque from the engine is transmitted through a hydraulic or mechanical clutch (in this case, the first option in the form of a torque converter is much more common).
We also recommend reading the article on how to distinguish a robot from an automatic machine by appearance and other basic characteristics. From this article you will learn about the main differences between an automatic transmission and a robot, as well as how you can quickly determine the type of automatic transmission in a car.
The CVT gearbox confidently accelerates the car from a standstill, traction is constantly transmitted to the wheels, the gear ratio changes smoothly, and maximum driving comfort is achieved. The main disadvantage of such a gearbox is that the variator is not designed for high torque; it is not paired with powerful engines, as there is a strong decrease in reliability and service life.
- Hydromechanical transmissions, which are sometimes called combined transmissions or simply automatic transmissions, are “classic” automatic transmissions. The design is time-tested and includes a torque converter as a clutch (provides continuously variable torque control), as well as a mechanical planetary gearbox (planetary gearbox).
Automatic machines of this type can have 6, 7 or even 8 steps or speeds (for example, the common 8-speed ZF gearbox). Such gearboxes change gears quite quickly and smoothly, are highly reliable and have a long service life, and can withstand high torque and loads well.
The disadvantages of these automatic transmissions include increased fuel consumption, decreased efficiency due to losses in the gas turbine engine, and worse acceleration dynamics compared to a CVT or a dual-clutch robot. At the same time, the latest versions of hydromechanical automatic transmissions are not much inferior to other types of automatic transmissions.
Let us also add that most automatic transmissions (except for old hydromechanical automatic transmissions), regardless of the type (variator, robot or “classic” automatic transmission), have a Tiptronic mode. This mode is semi-automatic and simulates manual gear shifting by the driver himself. Also, the automatic transmission can be adaptive (separately adjusted to the driving style of a particular driver).
Automatic transmission device
The operating principle is based on the use of a planetary gear. The planetary mechanism consists of a carrier, a satellite and gears - sun and crown. It has 2 inputs and one output. Using the mechanism, you can obtain the desired output speeds by setting the speeds of the gears. In an automatic transmission, the input is connected to the output not directly, but through an intermediate shaft.
Operating principle of an automatic transmission
Also part of the mechanism are friction discs designed to stop and rotate the gears. When the discs close, the sun gear closes the input. After the disks close at the input, the crown gear at the output freezes in a stationary state. In this way the first gear is achieved.
The six-speed gearbox has three planetary gears. The carrier of the second row is connected to the crown gear of the first. In other words, the input of the first is connected to the input of the second.
Planetary automatic transmission
When the second row discs are engaged, the crown gear is stationary. As a result, the gear connected to the first row begins to rotate. The output speed increases. This is how second gear is achieved.
To obtain direct drive or fourth gear, a rotating clutch module is connected to the input shaft. With direct drive, the ring gear and sun gear must rotate at the same speed. That is, the speeds of the input and output shafts must be equal.
In this case, the second row carrier rotates at the speed of the input shaft, but the ring gear does not move. Therefore, the sun gear begins to rotate 3 times faster than the input shaft. The output can be very high speed.
Robotic gearbox (robot)
The robotic gearbox is a combination of mechanics and automatic transmission. Essentially, this is the same manual transmission, only the control is carried out not manually with a shift lever, but with the help of servos or mechatronics. Control occurs through a computer unit, which makes the decision to switch gears.
A characteristic feature of the robot, because of which many car enthusiasts do not like it, is jerking when changing gears. To get rid of this problem, engineers came up with a dual-clutch system. This model is installed in Toyota Corolla. The shifts here are smoother than those of a single-disc robot, but worse than those of other gearboxes. We also note that the robot does not really “like” traffic jams. Therefore, when choosing a car for city driving in heavy traffic, take this factor into account.
Pros of the robot:
- the cost is lower than that of an automatic transmission
- maintainability
Disadvantages of a robotic box:
- jerks when switching
- low reliability of control mechanisms and clutch discs