Repost and the information will always be at hand ✅
ESP - what is it in a car? This is a very popular abbreviation that many car enthusiasts know. It stands for dynamic electronic vehicle stability control system. In English it sounds like this - Electronic Stability Program, and in German - Elektronisches Stabilitätsprogramm.
In simple words, this is to prevent the car from skidding or sliding sideways on a vertical axis in emergency situations. And this is very important for the safety of the driver and passengers, since few people have extreme driving skills. Here, the system helps the driver cope with dangerous situations in which one can get into an accident, for example, at high speed or on bad roads. Also, some car owners call this system anti-skid.
The ESP system may be called by other abbreviations, depending on the manufacturer, such as ESC, CST, DSTC, PSM or RSC. The essence of the operation of the exchange rate stability system is based on the fact that the system receives signals from different sensors. If the values approach dangerous values, the ESP is automatically turned on.
To understand how ESP works, you need to find out what it is, its operating principle, and familiarize yourself with real examples. I will tell you all this in detail in this article. I promise it will be interesting!
What it is?
Let's go back to history. The prototype of ESP was first invented in 1959 by Daimler-Benz. It was called very modestly - “control device”. Since then, testing of this system began. The system was first installed on the premium Mercedes-Benz CL 600 in 1995. The tests were successful and ESP began to be serially installed on other classes of Mercedes.
Mercedes-Benz CL 600 (1995)
Interesting! The ESP system became popular thanks to one incident. The fact is that in 1997 the new Mercedes A-Class had many disadvantages due to an unfinished center of gravity. Because of this, the car leaned heavily when turning, and during sharp maneuvers there was a high probability of the vehicle overturning. Engineers completely redesigned the Mercedes suspension and additionally introduced the latest ESP system. After this, the system became very popular all over the world.
ESP is an anti-skid system that includes measures to reduce the vehicle's displacement from its current trajectory. This is important for the lateral dynamics of the car (its stability). That is, ESP only reduces the likelihood of the car moving off the road. We must always remember that even a very expensive system will not be able to overcome the laws of physics.
The anti-skid system is a logical continuation of such car systems as ABS and ASR. ABS is an anti-lock braking system that increases braking distance. ASR is a traction control system that helps ensure stable and fast acceleration. ESP maintains the vehicle’s trajectory during sharp turns and maneuvers, which is very important when driving on wet or slippery road surfaces.
ESP regulates the car's lack or excess of controllability, which actively prevents skidding. ESP corrects errors of incorrect, inexperienced or aggressive driving style.
You cannot independently install ESP on any car, but only under the manufacturer’s conditions. In the basic configuration, the stability control system is installed in the basic configuration only on premium cars.
The term ESP is the most famous, but I note that this abbreviation sounds differently for different car manufacturers. I will give examples.
- ESC – Hyundai, ŠKODA, Chevrolet and Lada.
- DSC - Land Rover, BMW, Jaguar and Mazda.
- DSTC - Volvo.
- ESP – Dodge, Audi, Bugatti, Lamborghini, Volkswagen, Nissan, Renault, Peugeot, Mercedes Benz, Kia, Hyundai, Chery, SEAT, etc.
- ASC - BMW and Mitsubishi.
- CST - Ferrari.
- MSP - Maserati.
- IVD - Ford.
- PSM - Porsche.
- StabiliTrak – Hummer, Pontiac, Cadillac, GMC Truck, etc.
- VDC – Infiniti, Subaru, Nissan, Alfa Romeo.
- VDIM - Lexus and Toyota.
- VSA - Honda, Hyundai and Acura.
What does this system consist of and how does it work? The answer is below in the article.
ESP device
In order for ESP to function properly in a car, the following parts are installed:
- Sensors on the wheels that read their rotation speed.
- A sensor that monitors the position of the steering wheel.
- A sensor that “sees” how the car moves around its axis.
- Hydraulic mechanism. The control unit controls the pressure in the brake system on all discs.
- G-sensor (accelerometer). Measures the position of the car in space.
- The ECU is an electronic control unit that constantly reads information from sensors to know when to activate ESP.
ESP is not an additional option. This is a single system that works comprehensively together with other safety systems, such as ABS (already included in the anti-skid system by default), as well as ASR (anti-slip system), EBD (precisely distributes braking force on each wheel), EDS (anti-lock braking system, eliminates slipping at the start).
Interesting! In expensive cars, the anti-skid system is directly connected to the cruise control, which maintains the set speed on the highway.
Read more: What is cruise control in a car: why is it needed, principle of operation, types, pros and cons, video.
This leads to the conclusion that budget cars, as a rule, do not have as many built-in systems, so ESP is installed in the basic configuration only on cars in the high price category.
Learn more about how ESP works (required reading).
Electronic stabilization system (ESP/ESP): features, functions, operating principle and designations
Everyone, even experienced drivers, makes mistakes. Unfortunately, mistakes while driving can be catastrophic and also very costly for everyone on the road. Fortunately, vehicle manufacturers work year after year to keep drivers and passengers as safe as possible. Among other things, today technology in the automotive industry has come very far, resulting in a safe solution that helps the driver get out of trouble associated with loss of control
over the car while
driving
.{banner_adsensetext} First, let's dive into history and remember the important fact that in the 80s of the last century, more than half of road accidents were caused by skidding.
Therefore, car manufacturers, including the then leading auto company Mercedes-Benz
, which deserved the greatest merit in the field of improving driving safety, in the late 80s began work on an innovative electronic system that would help the driver cope with the car in the event of an emergency on road.
Subsequently, this system was called the Electronic Stability Program
- an electronic system for stabilizing exchange rate stability, also known to everyone as
ESP
(
ESP
).
What is the working principle of the car electronic ESP system ?
So, the
ESP
(Electronic Stability Program) system is a whole complex of electronic programs with sensors that keeps the car on a given trajectory, while controlling the level of traction and slip on the road.
This assistant works on a relatively simple principle. The system, which is actually a kind of extension of the ABS
, checks whether the car is moving along the trajectory specified by the driver.
When the
ESC
receives conflicting values from the electronic control unit (
ECU
), it immediately reduces engine torque, and if this is not enough, it additionally brakes individual wheels to return the vehicle to the correct trajectory.
ESP
system proves extremely useful on slippery surfaces and when avoiding obstacles at high speed.
However, it is worth knowing that even ESP
will be ineffective at very high speeds, so you should always use common sense when driving.
{banner_reczagyand}
How is the ESP system designated by different car manufacturers?
For reference, we note that for some automakers, the electronic stabilization system, also known as
ESP
, installed on certain models may have a different name, but the principle of operation of the mechanism is almost the same.
Today, the
ESP
is still used by the following car brands:
Mercedes-Benz
,
Opel
,
Audi
,
Bentley
,
Bugatti
,
Seat
,
Skoda
,
Chrysler
,
Smart
,
Citroen
,
Dodge
,
Volkswagen
,
Jeep
,
Lamborghini
.
Peugeot
,
Suzuki
and
Renault
.
In some cases, you can also find a dual nomenclature, that is, a combination of systems working in pairs, depending on the model, as is the case with the following automakers:
Fiat
:
ESP
in combination with Vehicle Dynamic Control -
VDC
;
Ford
: uses AdvanceTrac with Roll Stability Control -
RSC
or
IVD
combined with
ESP
DSC
Dynamic Stability Control (Australia only);
Hyundai
: uses
ESP
in combination with electronic stability control
ESC
or vehicle stability control
VSA
;
Kia
: Uses
ESC
in combination with the
ESP
.
For reference, we note that the
ESP
(electronic stabilization system), which prevents the vehicle from skidding, has become mandatory for installation on cars for manufacturers since November 2014.
At first, this requirement applied only to models of passenger cars and small vans with a total weight of up to 3.5 tons. The rest of the cars fell under this requirement only a year later. Video
:
“How does the electronic stability control system ESP work? “
In conclusion, we note that it cannot be denied that, together with seat belts and airbags, the ESP electronic complex is one of the most important safety systems in a modern car.
For reference, we note that according to independent studies, the ESP system can prevent up to 80 percent of accidents resulting from uncontrolled skidding of a car. THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION
.
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWS
.
SHARE WITH YOUR FRIENDS
.
Principle of operation
The ESP system is an active vehicle safety system that automatically turns on when the vehicle skids or loses control. The system computer receives data from several sensors (lateral acceleration, wheel rotation, steering wheel position, gas and brake pedal positions, brake system condition and angular speed).
ESP works so quickly that in 20 milliseconds it can determine which wheel needs to be braked, how much to reduce engine speed in order to level the car in a dangerous situation.
The operation of the ESP is based on activating braking and reducing engine torque in order to prevent the car from skidding.
Another good article: Auto set-ups on the roads: TOP 35 new types, what to do, how to behave, how to avoid
What commands can be issued in a given situation on the road:
- Braking one or all wheels. This will help prevent skidding or help increase the turning radius at high speeds. Also, ESP in a certain situation can reduce the braking force, even if the frightened blonde presses all the pedals with all her might.
- Connection to the engine control unit in order to turn off its cylinders in order to reduce its speed (torque), up to completely turning off the gas pedal.
- Adjusting the rotation of the front wheels.
- In cars with adaptive suspension, it affects the performance of the shock absorbers, and they affect the damping of the springs (the degree of shock absorption).
- Adjusting the automatic transmission to change gears.
- If a driving problem occurs as a result of operating cruise control, it will act together with ESP and other systems to smooth out the vehicle's movement.
According to statistics, the use of this smart system has reduced accidents by 30%. After all, electronics think much faster than a person, who may be very tired or inexperienced. The control system polls all sensors up to 30 times per second!
Despite the fact that this is a very advanced safety system, it cannot see the actual width of the roadway, nor can it accurately calculate the trajectory of the car that will be the safest. It follows that the driver himself must direct the car in the desired direction, and ESP will provide stability and controllability.
The anti-skid system can operate at any speed and vehicle operating mode (coasting, braking, acceleration).
When cornering, ESP monitors the trajectory of movement, which should be the position of the steering wheel. If deviations appear, the stabilization system will reduce engine speed and slow down in order to quickly return the vehicle to its previous trajectory. ESP is especially useful on icy or wet roads.
Video: ESP. What it can do and how it works
For example, at a very high speed when turning a car began to skid. If the driver starts to brake, the car may spin out. If he does not press the brake, there is a chance of flying off the road into a ditch. The active anti-skid system will instantly determine which wheels need to be slowed down or by how much the fuel supply needs to be reduced in order to straighten the trajectory. Agree, this is a mega-useful thing in critical situations. You just turn the steering wheel, and the stabilization system itself thinks about how best to fit even into a sharp turn.
What else is useful in the ESP system?
- Differential locking function, which allows you to transfer torque to exactly that wheel in order to level the car. The differential must have electronic filling. This is a device that transmits different torques to each consumer.
- Help the driver keep the steering wheel in the desired position. This is especially useful in a rut.
- Rear wheel steering. The main thing is that this function is already installed on the car.
Let's look at the operation of ESP using real examples.
Operating principle
All of the above components help the electronics understand when the car begins to skid, and also adjust the behavior of the car depending on the manipulations performed by the driver.
Deviation of the position of the vehicle controls from the actual parameters of the vehicle’s movement provokes immediate intervention by the Electronic Stability Program. For example, the angle of rotation of the wheels is small, but the rate of lateral acceleration and the angle of rotation around the axis significantly exceed the indicators that are typical for the safe behavior of a car for given steering parameters. In this simplified way, we can describe the way in which ESP determines the development of a skid.
The stability control system brakes certain wheels or weakens the braking force if the driver, in fear, presses the brake pedal to the floor; affects the operation of the engine, preventing the drive axle from aggravating the situation.
The main purpose of the ESP is to prevent the onset or worsening of a car skidding. All these manipulations help straighten the trajectory and maintain control over the car.
Specific example
Let's look at how the system works, using the example of a situation in which electronic stability control helps stabilize the car.
Parameters for oversteer (skid):
- the rear axle tends to overtake the front wheels. The rear axle slides towards the outer turning arc;
- the sliding speed is high.
Stabilization occurs due to the braking of the front wheel of the outer radius.
Understeer parameters (drift):
- the front axle slides towards the outer turning arc;
- yaw speed is low;
Stabilization occurs due to the braking of the rear wheel passing along the inner radius.
Of course, the described algorithm is too simplified. The electronic control unit receives information from various sensors several tens of times per second and immediately responds with signals to the actuators, constantly focusing on changing driving conditions.
A video of the operation of the car's exchange rate stability system will help you appreciate the full benefits of the assistant.
Homologation
Cars from EU countries produced from the second half of 2014 are required to have ESP as a minimum configuration. Domestic legislation provides for such a rule only in the case of certification of the release of a new car. Extension of homologation does not oblige the introduction of innovations. Therefore, for most cars such a useful assistant is available only for an additional fee.
DIY installation
You can retrofit your car with ESP yourself. Let's look at the necessary components using the example of the Opel Astra J 1.6T 2010.
You will need:
- ABS/ESP control unit, mounting in the form of a bracket for installation in a standard place;
- SIM module;
- yaw sensor (another name for the lateral acceleration and axial rotation controller), fastening element;
- plug
If you know the location of all the elements and know how to bleed the brake system, installing it yourself will not seem like a difficult task. Please note that such changes must be programmed. This requires a scanner and special software. This is perhaps the most difficult point in the entire installation process.
Why is ESP needed in a car?
Let's give a real example of how the anti-skid system works.
For example, you are calmly driving straight along a flat road. And suddenly a large animal or a drunken person runs out onto the road ahead. What will you do?
There isn't much choice here - slam on the brakes and turn the steering wheel sharply in the hope of avoiding an obstacle. If the speed is low, the road grip is acceptable and there are no other cars nearby, then the maneuver will be successful. And in the worst case scenario, the car will skid. And in winter, even with a normal turn, the car will start to spin on the road.
What options are there if a skid begins?
- If the driver is experienced and knows the techniques of extreme driving, he will be able to handle this situation without any electronics or systems. Here it is appropriate to engage a lower gear, brake intermittently, then sharp gas, leveling, a careful turn, and so on. Perhaps you have this skill. Then everything is OK. If you do not have experience, then there is a possibility of a serious accident.
- Press the brake all the way and turn the steering wheel as much as possible to avoid a collision. If you manage to get around the obstacle, then sharply turn the steering wheel in the opposite direction without releasing the brake pedal. If there is no ESP, then no matter what the drive, the car will go into a long drift or an uncontrolled “dance”. All this can also end very badly.
- If the driver is an inexperienced blonde, but the car has an ESP system. Here it will be very difficult to lose complete control over the controls. The most important thing is that the car simply has time to go around the obstacle, and the system itself will correct the movement of the car. Then an accident can be avoided.
How will the algorithm for the anti-skid system work here in the event of a skid when turning left?
- The accelerometer detects the start of a skid and transmits this to the ESP system.
- At the same moment, information is received from other sensors.
- The ESP instantly calculates the direction and speed of the vehicle's lateral displacement.
- A command is transmitted to reduce the fuel supply and brake the left rear wheel.
- As a result, the car drives slower and straightens out when turning, no matter what the driver does at that moment (even if he presses his feet on all the pedals).
Using ESP is easy. It will be enabled by default. But there are also nuances here. About them below.
How to use ESP in a car?
Remember! ESP is always active and can turn on at any speed and movement of the car.
There is an opinion among car enthusiasts that the anti-skid system can prevent experienced drivers from coping with a skid. For example, sometimes you need to increase speed to get out of a skid, and ESP artificially limits fuel injection. But this is applicable for very experienced drivers. Typically, such skills are not required for those who commute from work to home.
For those who love active driving, the stabilization system has special modes when you can drive to your heart's content, and it will only turn on in critical situations.
In most cases, I do not recommend turning off ESP to prevent even the remote possibility of an accident, especially if the driver is distracted or simply unable to react quickly.
Another good article: TOP 50 real tips on how to reduce fuel consumption on any car by 2 times
Despite the fact that ESP ensures safe driving and smoothes out many mistakes of an inexperienced driver, you should not rely entirely on the stabilization system. Just don't put yourself in dangerous situations.
Does it make sense to disable ESP?
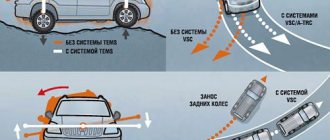
Is VSC always useful?
By the way, despite all its usefulness, VSC technology also has its opponents. It is believed that for experienced drivers it is not only useless, but also an unnecessary burden. There may be some truth to this, which is why many cars equipped with stability control have a button to turn it off.
Sometimes deactivating it allows you to solve a difficult situation in a non-standard way, for example, by adding gas to get out of a skid, or it simply gives active driving enthusiasts the opportunity to tickle their nerves and enjoy a real drive behind the wheel.
I hope you are no longer tormented by the question: “what is vehicle directional stability?” But be that as it may, friends, always be careful on the roads and do not rely on the smart electronics of the car for everything.
I advise you to get acquainted, within the framework of security systems, with the ASR traction control system.
Tags security
How and when to turn off ESP
In almost all cars, it is not possible to disable the stability control system. But on some cars this feature can be disabled. But it’s not so simple here - it can be partially turned off, that is, additional systems (ABS, ASR and others) will remain working. Or ESP will turn off for a while, and after reaching a certain speed or after some time, the stabilization system will turn on automatically.
ESP button in a car indicates that the car has a stability control system installed.
When should ESP be disabled?
- If the car has wheels of different diameters.
- When driving on sand, off-road or ice.
- If there are chains and anti-skid bracelets on the wheels.
- In case of rocking the car to get out of heavy mud.
- While installing the spare wheel.
- When diagnosing a car.
In these cases, there will be a false activation of ESP, in which the system will reduce engine speed and interfere with adequate driving.
Remember! If the car is stuck in a deep rut, then you should not turn off ESP. Many cars have a traction control system that only works when the stability control system is on. Other systems, such as ABS and EDS, also depend on ESP.
How to turn off ESP?
- Press the ESP off button.
- In the on-board computer, disable the ESP system.
What to do if the system behaves inappropriately? I will describe the main problems that car owners face.
1-UBK-20781
Redundant system architecture
The car will soon become much safer; like modern aircraft, it will have various systems that duplicate each other. This is, first of all, necessary to ensure that a sudden failure of one of the systems does not lead to an accident.
Bosch specialists have already developed backup brake system technology. The electromechanical brake booster iBooster and ESP (electronic stability control) allow you to stop the car independently of each other.
Highly accurate map data
Now the positioning accuracy of modern navigation systems is within one meter. For a safe autopilot, the accuracy must be increased at least ten times. In addition, maps should be updated more often. Our habit of installing new signs while the road is being repaired, and then forgetting to remove them, can drive the car’s cybernetic brain crazy. For example, when the video camera detects a “brick” and the navigation determines the road as one-way. Where should we go then? After all, the ban on violating traffic rules will be the main one for artificial intelligence.
We have listed only three problems, while there are dozens of them on the way to creating an autopilot! And yet there is hope that in ten years we will be able to go to the dacha early in the morning in a “smart” car, and on the way sleep peacefully in the driver’s seat.
ESP system: where are we heading?
Reasons for turning on the ESP lamp
The exchange rate stability system has its own ESP indicator on the instrument panel. This indicator lights up from time to time depending on the situation. Why might this happen?
- If the ESP indicator blinks, this means that the system is trying to align the vehicle’s trajectory, or the ASR (traction control) system has been activated.
- If the ESP lamp does not light up on a moving car, this means that the movement is stable and there is no point in interfering with the control of the vehicle.
- If the indicator does not light up when the car is stationary, this means that all electronic systems associated with ESP are operating without errors.
- If the ESP indicator is on all the time, then this indicates an error in the operation of one of the elements (and there may be more than 15 of them). Even simple uneven tire wear or the installation of a new spare tire can affect the constant glow of the indicator. In any case, you need to diagnose the ESP at a service center.
If you do not want to visit service centers, you can check what the problem is with the constant light of the indicator.
- The system itself was turned off. On some cars, ESP will not turn on until it crosses the 50 km/h mark.
- Examine the condition of the wheels and tires.
- Inspect the valve body of the anti-lock braking system.
- Test the car battery voltage. If it is low, the ESP will not work.
Note! The stabilization system may turn on even under strange circumstances, or from time to time. This indicates that the vehicle is running with a continuously running fault scanner.
The system has both advantages and disadvantages. I will talk about this further.
How ESP and ESC work
With so many electronic systems installed in a car, each of which has its own abbreviation, many car owners do not understand at all what the fundamental difference between them is. To further complicate the situation, different names are used to designate similar active safety products, which in most cases are determined by the manufacturer itself.
Thus, ESP (Electronic Stability Program) may be known as ESC (Electronic Stability Control), VSC (Vehicle Stability Control), VSA (Vehicle Stability Assist) or DSC (Dynamic Stability Control). stability). Some automakers use their own "brands" to promote ESP, so you may encounter, for example, Volvo's DSTC (Dynamic Stability and Traction Control) or Porsche's PMS (Porsche Stability Management).
So now we've decided on the possible names, let's take a look at how ESP works.
Advantages and disadvantages
Could there be any downsides to this system, which provides excellent driving safety? It turns out yes.
- The stabilization system cannot cope with the recovery from a skid (in front-wheel drive cars) by increasing the torque on the front wheels. This method is often used by experienced drivers.
- On vehicles with all-wheel drive, when there is ice, the best way is to gently apply the gas. And ESP works here on the principle of braking and reducing torque on the wheels, which is less effective.
- On loose surfaces (snow, sand or mud), the stability control system does not work effectively.
Better to drive in snow without ESP - If the car has different tires, the tire pressure is different, or the tread pattern is worn unevenly, then ESP will have problems.
- Some drivers do not like that the system itself controls the accelerator pedal, preventing it from reaching the desired speed. Therefore, if you need to add gas during drifts, ESP will not allow you to do this. Or you will have to temporarily disable the system.
- The car becomes less sensitive to drive because the electronics constantly check all the driver’s actions.
ESP has advantages due to which you can turn a blind eye to its disadvantages.
- The reaction speed of electronics is many times faster than that of a person. In just a few milliseconds, ESP detects the beginning of a skid and measures against it immediately begin to work.
- More comfortable driving when traveling long distances, which eliminates roll when cornering at high speeds.
- Improving car handling and stability.
- Within just 20 milliseconds, ESP “sees” the loss of controllability and activates braking force on the necessary wheels and eliminates the start of a skid before the driver himself realizes it.
- The stabilization system works invisibly, and only the indicator on the instrument panel indicates that ESP has begun its work.
- More advanced systems include features such as rollover mitigation (RSC) and trailer stability control (TSC).
- ESP can be disabled if desired. And some systems have special modes that allow small slips and maneuvers, turning on only in critical situations.
It is important to understand that ESP is not 100% capable of protecting the car from skidding . Always use your head when driving and performing sudden maneuvers. For example, if you want to drive at a speed of more than 120 km/h on an icy road and make a sharp turn, then even the most advanced ESP system will not help.
Some very useful information that car services and car dealerships won’t tell you about.
Secrets and tips
I'll tell you about what's hidden in the ESP system. It turns out that it includes by default such functions as ABS, ASR, EBD and others. You just need to simply check the box in the on-board computer settings using a diagnostic scanner and the additional options will take effect. To do this, you can go to your car’s forum, where they will tell you everything, or contact local craftsmen.
Another good article: TOP 150 useful tips on how to choose a used car: how to choose a used car, what to look for and what you need to know, how to protect yourself
What other free options do you get with ESP?
XDS function . This is a lightweight version of the differential lock. When turning, there will be no feeling of the front of the car drifting.
Tire pressure measurement . This is provided by special sensors. If the air in a tire deflates, its diameter and rotation speed increase. You should see a warning on your dashboard.
Hill start assist . When driving uphill, if you release the brake pedal, ESP will hold the brake until the car moves forward.
Rain sensor tracking . When you activate the wipers, the rain sensor is activated. ESP “sees” all this and begins to increase the pressure in the brakes in order to destroy the water film from the wheels. The driver will not even feel this, and the system is already ready for unexpected situations.
Steering Assist . If the driver is a novice and turns the wrong way when skidding, then ESP, reading data from the steering wheel position sensor, activates the electric power steering from time to time. You will periodically feel heaviness in it when you turn the steering wheel hard, or lightness when everything goes according to plan. The system can also block gear shifts in the automatic transmission to maintain controllability and stability of the machine.
Braking on different road surfaces . Let's say you brake sharply when the right wheels are on the ground and the left wheels are on the asphalt. If the car does not have ABS, then the car will “drive”, but if this function is present, then it will not.
Trailer Stability Assist (TSA) . ESP can “see” the presence of a trailer. When you connect the towbar socket, the stabilization system will understand that you have hitched a trailer and will rearrange its operation algorithms to ensure confident driving. It is very comfortable!
Off-road assistance . Maybe you've watched SUVs get out of such situations when, when off-road, when hanging diagonally, the suspended wheels spin in the air, but then they stop and the car suddenly twitches and moves forward further. This triggers ESP, which distributes traction to those wheels that have better contact with the ground.
Descent assistance . When HDC (Descent Control) is engaged, the driver simply takes his feet off all pedals and relaxes. ESP, together with HDC, will ensure an independent smooth descent of the car even from a steep mountain. All you can do is sit and listen to the brakes crunch.
It is quite possible to enable all of the above features if ESP is installed in the car. The main thing is to find craftsmen who will “modify” your electronics.
Now I will answer the most popular questions about the anti-skid system.
Does it make sense to overpay for ESP when buying a new car?
In Europe, since 2014, all cars produced already have ESP as standard. Here in Russia, this is not yet a mandatory condition.
If you want to have in your arsenal electronic assistants such as skidding assistance, hill climbing assistance, differential locking and others, then you will have to buy a car with ESP. It is IMPOSSIBLE to install the ESP system (even under the conditions of a branded service and/or at an official dealer, only on the assembly line), but you can only buy a modification of the car with the installed system (and other options).
If you buy a new car with ESP, then the main thing is that it has a switch off button. There are also cars with different ESP modes that can be turned on according to your mood (for example, Dynamic - aggressive driving, Natural - normal driving, All Weather - high safety).
Statistics on the use of ESP on cars
When all modern motorists already know what ESP is, whether it is worth taking a package with this function and overpaying for the car upon purchase, the time has come to talk about the real benefits of this system. The main task of any active or passive vehicle safety function is to prevent possible accidents, which often occur when control control is lost.
This is precisely the task that the creators of the ESP system for cars set for their developments. Using incredibly sensitive sensors, the module reacts within 20 milliseconds and activates all the necessary devices to prevent skidding. This is confirmed by many statistics:
- the number of accidents in winter on cars with ESP has almost halved;
- insurance companies in the USA and Europe have begun the practice of reducing the cost of insurance for cars with such a system;
- Manufacturers are investing more and more money into improving this function;
- Not so long ago, the ESP system successfully migrated to sports cars, although its features contradict sports.
Of course, the most visible benefits from using this technology will be received by novice drivers who do not yet have enough experience and practice to overcome difficult road situations. Previously, the ABS function was considered the exclusive prerogative of novice drivers, but today in some countries the sale of new cars is prohibited without the use of this braking assistant.
Is it possible to install ESP on a car with ABS?
Of course, it sounds very interesting - I bought sensors, installed them on a car with ABS - and you already have an ESP system. Is it really that simple?
Instructions are already freely available on automotive forums. But in terms of money, it’s quite expensive, because you have to buy various parts, and also be able to connect to the electronic control unit and configure it correctly.
However, I believe that you should not modify the car yourself, because there are a lot of pitfalls during installation. The ESP system is a complex thing that should be handled by experienced auto specialists.