What does FSI engine mean: features, repair, maintenance
In the wide range of power units of the German auto giant VAG (Volkswagen AG), FSI, MPI, TSI (TFSI), TDI engines and a number of other units continue to be very popular due to their manufacturability and unique characteristics.
Such engines have been installed previously and continue to be installed on various car models under the Volkswagen, Audi, Skoda, Seat and other brands within the VAG concern. Today, the engine versions listed above can be found on cars of different years of production.
In our articles, we have already told readers about what TSI engines are, which can be seen everywhere under the hood of Volkswagen, Audi and other brands. In this article we intend to talk about another popular motor, which is known as FSI, and also consider in detail the operating principle of the FSI engine. At the same time, the topic of selecting oil for this type of internal combustion engine, common faults and repair of the specified unit will be discussed.
VW designers came up with stratified fuel injection
I am glad to welcome you, my dear readers! If you are the happy owner of a Volkswagen car manufactured after 2000, then with a high degree of probability, when you open the hood and look at the engine cover, you will see the FSI nameplate. So, on the agenda of this article, revealing the secret of the symbols - decoding fsi.
As well as a description of the diagram of the unit hidden under this abbreviation and its main components.
What does this abbreviation mean?
Some will throw up their hands, some have heard of such a system, and others may be well versed in this issue.
Be that as it may, we hope that today’s article will be useful to absolutely everyone. And if you don’t yet have a car or buying a four-wheeled friend is in your plans, then finding out what these mysterious three letters mean will be doubly interesting.
FSI engine: what is it?
First of all, the decoding of “FSI engine” is an abbreviation for Fuel Stratified Injection, which literally means layer-by-layer fuel injection. The main difference between this internal combustion engine and the widely known TSI today is the absence of turbocharging on the FSI version. In other words, this line features naturally aspirated (atmospheric) FSI gasoline engines with direct fuel injection.
The FSI engine is not a “fresh” development, since the finished unit appeared as the first test samples back in 1998. Two years later, this engine began to be serially installed on Volkswagen models. Note that as of 2021, the latest Volkswagen model with FSI remains the Touareg 4 WD off-road vehicle. On other models, the FSI engine has today given way to a TSI (TFSI) or MPI version.
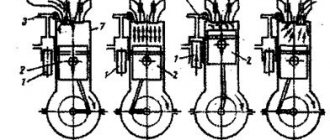
How does a TSI and FSI engine work?
FSI
In order to better understand how a TSI engine works, let's take an example of the operation of its “brother” FSI engine. The abbreviation FSI (Fuel Stratified Injection) denotes engines developed by German specialists with so-called “stratified” fuel injection. The fuel system in this engine is designed similarly to diesel units:
The fuel pump pumps gasoline under high pressure into a fuel rail common to all cylinders. Fuel injection, controlled by a system of electromagnetic valves, is carried out using injectors. By the way, if you want to wash the injectors, this is your place. The opening of each of the nozzles occurs after a command is given by the central control unit. The operating phase depends on both engine speed and load.
FSI engines: disadvantages and main advantages
Let's start with the main advantages and principles of operation. A distinctive feature of the naturally-aspirated internal combustion engines of the FSI line can be considered the implementation of fuel injection and the design of the power system. The fact is that the fuel supply system on such engines structurally has two circuits at once. In the first circuit the pressure is low, in the second circuit it is higher.
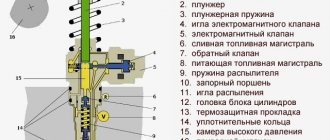
The low pressure circuit in the list of components has:
The design of the high pressure circuit requires the presence of:
The design also includes an adsorber and a special purge valve.
Air is supplied to the cylinders separately via a damper. As a result, it is possible to achieve the best mixture formation and uniformity of the working fuel-air mixture. This mixture burns fully and evenly in the engine, giving maximum energy to the piston in different operating modes of the internal combustion engine.
For this reason, FSI engines provide better acceleration dynamics and are highly environmentally friendly and economical. In some cases, such engines save up to 2.5 liters of fuel per 100 km. paths compared to simple analogues under the same conditions.
Let's get back to the features. As mentioned above, for the smooth operation of a direct injection gasoline engine, engineers separately introduced a high-pressure circuit into the FSI design. This pressure is necessary for the most accurate and economical injection.
In other words, during sharp accelerations and increasing loads, the pressure rises to 0.5 MPa, while during coasting the pressure in the circuit can be as low as 0.05 MPa. A separate electronic control unit, as well as the presence of a low pressure sensor, allows you to achieve such flexible pump control.
The dynamic operation of electronic control systems allows a strictly limited amount of fuel to be supplied to the cylinders in relation to the operating mode. In other words, excessive enrichment or depletion of the fuel-air mixture is eliminated. In parallel with this, the injection is layered, that is, double. This means that fuel is dosed between the injection stroke and the compression stroke.
This solution makes it possible to achieve fuel savings and reduce exhaust toxicity before the engine and catalyst generally warm up, since when a cold unit is started, an enriched mixture is usually supplied to the cylinders.
Disadvantages of the FSI engine
Let's start with the fact that any engine with direct fuel injection is very sensitive to fuel quality. In parallel with this, it is necessary to carefully approach the issue of the quality of fuel filters and strictly adhere to the replacement regulations. The FSI motor we are considering is no exception in this case.
In other words, the unit may simply not start in severe frosts. This phenomenon does not occur on all cars with such an engine, since the manufacturer eliminated the error in later versions by programmatically changing the firmware of the electronic systems.
Using the common 2.0 liter FSI as an example, other inherent problems with this engine become apparent.
Regarding the issue of consumption and which oil is best for the fsi engine, the main condition is to adhere to the VW 504 00/507 00 tolerance. Seasonality must be taken into account individually, since too thin an oil (for example, 0W-30) can be very wasteful. For this reason, many owners of this engine, when selecting a lubricant, choose 5W-30.
Principle of operation
The fuel pump maintains increased pressure in the engine during sudden acceleration. Gasoline is withdrawn from the low pressure zone. The automatic system autonomously regulates very precise fuel delivery, no more, no less. For example, during rapid acceleration a pressure of 0.6 MPa is required, and during quiet driving 0.6 MPa.
Electronic control of the supply allows you to significantly save the combustible mixture. The dual injection system is extremely effective during cold starts, when the mixture itself is enriched until the engine warms up and the catalyst turns on. Double injection is the distribution of gasoline between the injection and compression strokes.
For the information of owners, the FSI engine has repeatedly won the title of “Engine of the Year” since 2006. In addition, thanks to the rotation of the camshaft by 41 degrees, maximum traction is ensured at low speeds when driving in 1.2 gears. Exhaust gases undergo repeated recirculation, which significantly reduces the level of emissions of harmful substances.
As you can see, TSI occupied a leading position until the development of the updated version of TFSI. According to experts, the future of the automotive industry lies with the TFSI. This concludes the discussion of the topic of what an FSI engine is and what it is used with. We hope that the material presented will be useful to many future car owners when purchasing a vehicle. In addition, the cost of vehicles with the TSI system is slightly higher than TFSI, FSI.
What's the result?
As practice shows, with proper care, timely maintenance and maintaining the normal performance of all elements, such an engine can easily exceed the average mark of 200-250 thousand km. without any major repairs, it pleases owners with stable operation, confident acceleration and fuel efficiency.
Motors of the TSI line. Design features, advantages and disadvantages. Modifications with one and two superchargers. Recommendations for use.
TDI diesel engine. Distinctive features of this type of engine. Advantages and disadvantages, resource, features of turbocharging. operating tips.
Line of Hyundai/KIA CRDi diesel engines: strengths and weaknesses of engines of this type, features of operation, repair and maintenance.
Design features of GDI engines with direct injection from engines with distributed fuel injection. Operating modes, GDI malfunctions.
What is the difference between a naturally aspirated engine and a turbo engine? Design features, power, operating features. The main pros and cons of atmospheric engines.
Design and operating diagram of the injector. Pros and cons of an injector compared to a carburetor. Malfunctions of injection power systems are common. Useful tips.
Source
What is FSI?
Fuel Stratified Injection is an abbreviation for stratified direct fuel injection. The entire line of FSI power units is naturally aspirated with direct injection. To this day, these engines, through modernization, are installed on new VAG models, but are gradually being replaced by a more advanced line of TFSI turbo engines.
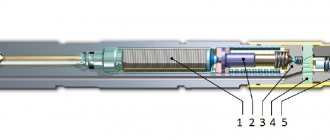
Direct injection means that the fuel system injectors are installed directly in the cylinder head, and the spray nozzle is installed in the combustion chamber (like a diesel engine). Layered injection has two circuits: a low-pressure line and a high-pressure line. To ensure idling, constant speed and coasting modes, the engine does not require a lot of fuel, so the first low pressure circuit will be activated, which includes:
The high pressure circuit comes into play when immediate maximum power is required. The system additionally includes:
When the engine is running, air entering the cylinders through the throttle valve is mixed with fuel directly in the combustion chamber at the beginning of the compression stroke, when the piston moves from bottom dead center (BDC) to top. Such mixture formation is homogeneous, which allows for maximum combustion of the working mixture, which means increasing engine efficiency.
The difference between an FSI engine and a regular gasoline engine
What has changed in a regular gasoline engine that it became known as FSI? There are several such moments that have become distinctive:
- In a conventional engine, fuel enters the pistons through the intake manifold. In a newfangled unit, the fuel mass ends up directly in the combustion chamber.
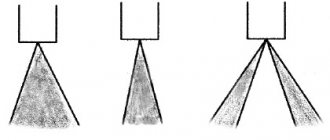
- Improved fuel properties in the cylinders are ensured by the presence of nozzles with six holes, which more efficiently distribute the combustible mass throughout the combustion chamber.
- High acceleration dynamics are characteristic of the new invention.
- Reduced emissions of harmful products, in particular carbon dioxide.
- FSI engines also differ from their progenitor in reduced fuel consumption.
The differences are significant and significant, which explains the popularity and demand for the new model of gasoline units.
Characteristic
The FSI power unit is a German-made motor from the Volkswagen concern. This engine has gained popular popularity due to its high technical characteristics, as well as ease of design, repair and maintenance.
The abbreviation FSI stands for Fuel Stratified Injection, which translated means layer-by-layer fuel injection. Unlike the widely used TSI, the FSI does not have a turbocharger. Speaking in human language, this is a regular naturally aspirated engine, which Skoda used quite often.
The abbreviation TFSI stands for Turbo Fuel Stratified Injection, which means turbocharged stratified fuel injection. Unlike the widely used FSI, the TFSI is turbocharged. Speaking in human language, this is a regular naturally aspirated engine with a turbine, which Audi quite often used on the A4, A6, Q5 models.
Like FSI, TFSI has increased environmental standards and efficiency. Due to the Fuel Stratified Injection system and thanks to the features of the intake manifold, fuel injection and “tamed” turbulence, the engine can operate both on an ultra-lean and on a homogeneous mixture.
Video about FSI engine problems and disadvantages
Advantages of the FSI engine
The advantage of such an engine is that due to strict dosing of fuel injection into the combustion chamber, savings of up to 15% are achieved in comparison with gasoline engines equipped with a classic injection system. In addition, more uniform traction at low and medium speeds is ensured by changing the camshaft phases.
TSI
Unlike the FSI engine, the TSI engine is a gasoline power unit with a dual turbocharging system. The abbreviation TSI (Turbo Stratified Injection) can be translated here as an engine with stratified fuel injection and turbocharging.
This engine inherited the fuel injection system from the FSI engine and received an additional mechanical compression system. Naturally, the design of such an engine is much more complex. However, this disadvantage is fully compensated by its greater reliability, power and efficiency.
TSI engine problems
The main headache for motors in this series is the timing drive. Premature stretching and wear of the chain can cause it to slip through the teeth of the sprockets, resulting in damage to the valves and pistons. The tension regulator does not inspire confidence either, failure of which leads to the same problems.
The new 1.2 liter and 1.4 liter EA211 series engines are free of problems associated with the timing drive. The chains of these motors are replaced by timing belts.
Another problem with TSI is high oil consumption. The manufacturer set the consumption for different versions from 0.5 to 1 liter per 1000 km. Often the result of such consumption of lubricants is clogging of spark plugs.
Video - among the problems, car owners often note the unusual sound of a running TSI engine and increased oil consumption:
Comparison of TSI and TFSI
Car enthusiasts are quite naturally interested in what is the difference between TSI and TFSI series engines, since both options are available on the market and you need to choose the best one among them.
Speaking about the difference between them, it’s worth saying right away that TSI and TFSI are built using completely different technologies.
In the case of the TSI, Volkswagen, or rather its engineers, did not use any old naturally aspirated engine as a basis. In this case, the internal combustion engine was developed from scratch. There is an intake manifold and a pair of turbines. Moreover, one turbine is of an electric type and operates, one might say, on a permanent basis. The mechanical turbine is made according to the classical design. Without going into details, the TSI can even be called a biturbo engine.
There is another important difference that allows us to say that TSI is inferior to TFSI. The latter is supported by the borrowing of the basis in the form of an atmospheric internal combustion engine, as well as its modernization
This made it possible to obtain a more reliable cylinder block design. Unfortunately, TSI does not have such an advantage. Because of this, the latter cannot always overcome the mark of 200 thousand kilometers traveled. Plus the turbines themselves are problematic. They fail and begin to create difficulties in the operation of the internal combustion engine. This becomes especially noticeable when TSI service rules are violated.
I would like to add one more point about how the TSI motor differs from the TFSI. Their development and modernization are carried out by different VAG departments. In the case of TSI, all the work is done by specialists from Volkswagen, Skoda, and Seat. It is on their engines that these internal combustion engines are mainly installed. And the TFSI became the property of the Audi brand, just like the FSI.
It is important to understand that all represented brands work together, sharing their technologies and developments. Therefore, seeing TFSI engines somewhere other than Audi models is more than realistic at present
Understanding the differences between the TSI series engines and the newer TFSI engines, it seems obvious which one to choose. After all, the difference between the internal combustion engine under consideration in terms of reliability, structural strength, efficiency and performance leaves no chance for a conditional competitor. But before you decide to buy such a power unit, it’s worth taking an objective look at its strengths and weaknesses.
Design features
The turbocharger is mounted in the exhaust manifold housing. This is a single module. Exhaust gases are re-fed into the manifold for afterburning. The engineers also had to change the power system a little. Thus, a pump designed for higher pressure is installed in the second pumping circuit.
The fuel pump is fully regulated by an electronic unit. Therefore, the volume of the prepared fuel mixture, which will then be injected into the engine cylinders, will depend on the load on the engine. If this is necessary, the pressure will increase - the unit will give this command if the car is driving uphill in a low gear. This removes serious power from the engine and reduces fuel consumption.
Cars on which the KF engine was installed
There are several cars that have such motors. They are all from Daihatsu. These are the cars:
Most of these cars are compact passenger cars. Compared to typical sedans, they are miniature. However, some of the listed models are minibuses, and the Hidget Truck is a miniature truck.
And on all these machines the KF VE engine performed well. Despite the relatively low traction, it is sufficient for such a small truck as the Hidget Truck. It is also enough for minibuses. Needless to say, the KF engine is also perfect for passenger cars.
Characteristic
Since the invention of gasoline engines, designers and engineers have been trying to solve the issue of high efficiency. In the 20th century, many successful design solutions were made in this area. In the 90s, Japanese automakers introduced direct fuel injection. The peculiarity is that the nozzle is installed directly in the cylinder. But then GDI, as the technology was called, did not become widespread, since operating engines with it was quite expensive, and the increase in power and efficiency was only minimally increased. However, this system was taken as the basis for the invention of new injection systems, and today we are seeing the emergence of new, more efficient power units.
Unlike Japan, Europe came to similar decisions only in the early 2000s. The work on creating effective direct injection was carried out by engineers from the VAG group. During development, experts analyzed the mistakes and experience of Japanese engine builders, after which the FSI engine was born. What it is is already clear from the name. Unlike GDI, FSI uses so-called layer-by-layer injection.
The design is reminiscent of the Japanese GDI, but VAG engineers were able to add an electronic fuel mixture control system. Yes, due to this the engine turned out to be more complex, but in the end the power and efficiency increased to 15%, and this is already a solid figure.
The abbreviation FSI or Fuel Stratified Injection stands for layered fuel injection. One of the main differences from all past technologies is the lack of turbocharging. In this line, the company offers only atmospheric power units.
Using a pump that creates high pressure in the fuel system, gasoline immediately enters the cylinders. Injection is carried out by special nozzles with six calibrated holes. Due to these holes, gasoline is distributed throughout the cylinder as evenly as possible. The fuel mixture is prepared thanks to the presence of electronically controlled air dampers. Due to this, the mixture is more homogeneous and burns with maximum efficiency. This is what environmental friendliness, safety and increased power are built on.
Electronic systems control engine operation so that the most precise amount of fuel enters the combustion chambers. There is also a double injection function - here the mixture can be distributed between strokes. This function is very useful when performing a cold start, for example in winter. The mixture is enriched until the engine and catalyst are completely heated.
Another important nuance is the presence of a fuel injection pump in the FSI engine. What this is, owners of diesel units know well.
FSI engines: pros and cons of FSI engines, what is it
As soon as the gasoline engine was invented, designers constantly addressed the issue of increasing its efficiency. The 20th century, its second half, was marked by many design solutions in this area.
In the 90s of the 20th century, Japanese engineers from the MITSUBISHI company proposed equipping gasoline engines with an innovative GDI injection system (Gasoline Direct Injection - direct injection of gasoline). A design feature of the system is that the fuel injector is located directly in the combustion chamber. However, GDI was not widely used, due to the fact that the cost of operation was quite high, and the increase in power and efficiency was minimal. Subsequently, such systems were taken as the basis for new generations of injection systems; today we can observe a new generation of GDI systems on modern Japanese cars. FSI engines appeared a little later.
What are FSI ? Operating principles of FSI
In Europe, unlike Japan, designers turned to a similar, but note, by no means the same system at the beginning of the 2000s. Volkswagen engineers began to conduct major work on the topic of direct injection. The company's designers took into account the mistakes of Japanese engineers by proposing the FSI direct injection system. The name of the system itself contains its main difference from the GDI system. FSI-Fuel Stratified Injection - “layered” fuel injection.”
Structurally, the system is similar to the aforementioned GDI, but Volkswagen engineers added full electronic control of the air-fuel mixture. This entailed a complication of the system as a whole, but the increase in power and efficiency of such an engine was already a solid 15%.
FSI engines and TSI , GDI and others
Today, almost all leading manufacturers use systems similar to FSI in their engines. Each manufacturer's technology has certain design differences.
Let's say the TSI system implies the joint use of direct injection together with a turbocharger, TOYOTA uses the D4-S system, which combines distributed and direct injection technologies. MAZDA uses SKYACTIV technology, which combines direct injection and a high compression ratio.
A short list of names of automakers and systems using direct injection technology.
Toyota - D4/D4S; Mercedes-benz - CGI; Mitsubishi - GDI; Nissan - NEO DI;
Renault - IDE; Alfa Romeo - JTS; PSA Peugeot Citroën - HPi; Mazda - DISI/ SkyActive; Ford - EcoBoost; Volkswagen, Skoda, Audi - FSI, TSI;
Opel - direct, SIDI (Spark Ignition Direct Injection); Honda - I-CDTI , etc.
Car brands where FSI
FSI technology was developed by VAG engineers, as a result of which FSI technology became widespread on models of this particular manufacturer. Engines equipped with the FSI system were installed in AUDI, SEAT, Škoda, and, of course, Volkswagen.
Advantages (pros) of FSI
The main advantages of engines equipped with FSI are:
- High efficiency compared to standard engines.
- Less fuel consumption.
- Less harmful emissions.
Disadvantages (cons) of FSI
The high design technology of the FSI engine really allows you to get higher power from the engine while reducing fuel consumption. But the use of FSI technology also has the opposite effect.
The fact is that an engine equipped with FSI technology, due to its design features, is very demanding on the quality of service and fuel quality.
The FSI engine requires constant close attention from the car owner.
First of all, due to the location of the fuel injector directly in the cylinder. This design is prone to increased contamination. This, in turn, causes interruptions in engine operation. Such as difficult starting, misfires, adjustments and increased fuel consumption. In critical cases, this can cause irreversible consequences, which in the future will lead to expensive repairs.
This can be avoided by taking preventive measures to clean the injectors. Of course, removing injectors and cleaning them on a bench is a rather expensive process. The manufacturer itself, the VAG concern, strongly recommends the use of special fuel additives to clean the fuel system of FSI engines. Of course, everyone is well aware that the manufacturer itself does not produce additives. And those additives that are sold under his brand are sometimes very expensive. Car owners should pay attention to high-quality products from renowned manufacturers. The market today is oversaturated with various automotive chemicals.
You should choose a truly necessary, and, most importantly, high-quality product, which will give you real results after use.
The German company LIQUI MOLY is a leader in the production of automotive chemicals and additives. The range of fuel additives allows you to choose a product to solve a specific problem. For owners of cars equipped with FSI technology, LIQUI MOLY offers a special fuel additive developed taking into account the design features of the engine. The Direkt Injection Reiniger direct fuel injection system cleaner uses a package of detergent additives that operate at elevated temperatures; it removes all typical contaminants from injector nozzles.
Result of the cleaner
Please note that port injection system cleaners are not effective on direct injection systems.
FSI motor malfunctions
Unfortunately, servicing direct injection injectors is not the only problem with the FSI system. The fact is that the design of the engine is such that the intake valves are also subject to increased contamination. This problem is more serious and requires the intervention of qualified mechanics. The fact is that due to design features, it is impossible to influence deposits using additives. In this case, partial disassembly of the engine is necessary.
Prevention of malfunctions of FSI
In general, prevention helps to significantly reduce the amount of pollution and qualitatively increase the service life of the engine. The use of additives allows you to keep the system clean, reduce the amount of contamination and, thereby, increase the service life. In the case of FSI systems and the like, a whole range of care and maintenance measures must be taken.
To keep the injectors clean, use: Direkt Injection Reiniger.
To clean the intake tract and maintain the performance of the air dampers: Pro-Line Drosselklappen-Reiniger.
To remove moisture from the fuel tank: Fuel Protect
To improve the lubricating properties of fuel and maintain low and high pressure fuel pumps in working condition, it is recommended to use: Langzeit Injection Reiniger
FSI engines?
Cars equipped with the FSI system attract car owners with their dynamics and efficiency. However, on the other hand, there are many negative reviews about the operation of such cars. As practice shows, with proper care and proper use of automotive chemicals, you can avoid expensive investments in repairs.
Bottom line
VAG is a company that looks to the future. Every year it offers car owners new car models equipped with the most modern engines. And the FSI system was replaced by the new TFSI system. It also has its own characteristics in operation. And the project to develop engines equipped with the FSI system has been suspended for now.
FSI engines and their development are one of the revolutions in the automotive industry. They have very specific and tangible advantages. But the downside of using them is expensive repairs (primarily injectors). To avoid large expenses and extend the life of FSI engines and injectors in FSI engines, preventive maintenance of these systems should be carried out. The simplest and most inexpensive way to do this is to use fuel additives.
VW AG: excerpt from self-study material on the 2.0 TFSI engine
History of TSI engines
The story dates back to 2004, when engineers equipped a new, by the standards of that time, naturally aspirated engine with direct injection (FSI) with a turbocharger. At the beginning of production, the line of these engines received the TFSI index, but a little later Volkswagen shortened the name to TSI. But on Audi cars this line of engines has retained its historical name to this day.
The main difference between the TSI series engines and the rest is the presence of both a turbine and a supercharger at the same time. The appearance on the market of the first cars equipped with TSI and TFSI engines gave rise to many myths and many skeptics appeared, claiming that the design was unreliable and inappropriate. It must be said that there is a certain truth in the words of skeptics, because there is a well-known saying that the more complex the design and the more parts it contains, the lower the level of its reliability. The first cars with TSI engines that saw the light of day could not boast of high reliability and had a number of problems associated with the timing mechanism. In addition, TSI engines are very picky about the quality of fuel and lubricants and love to “eat oil”, which is not surprising, because oil consumption in turbocharged cars is a common occurrence.
As inexorable statistics show, the reliability of power units of the TSI (TFSI) line, or rather their accompanying units, in fact, does not occupy the highest position. However, nothing is ideal and the capriciousness of such technologically advanced engines is due to other positive aspects, such as:
TSI engine video
The layout of the TSI engine is different in that the turbocharger and mechanical compression system are located on opposite sides of the engine. A traditional turbocharged engine obtains additional power by using the energy of exhaust gases, which spin the turbine wheel through a drive system, creating compression and air injection. Compared to a classic gasoline engine, this system is more efficient, but the efficiency of the TSI engine with stratified injection and turbocharging system is much more efficient.
Flaws
Now let's look at the disadvantages of the FSI engine. We already know what it is - this is a motor that uses layer-by-layer injection. There are disadvantages, despite the fact that the unit does have higher power with reduced fuel consumption. The thing is that the engine, due to its design features, is very demanding not only in terms of fuel quality, but also requires better maintenance. In order for the power unit to operate without breakdowns, the owner must closely monitor it.
Similarities and differences
The similarity is that both are gasoline-based and have direct injection. The difference: the FSI lacks turbochargers, which means it cannot compete with one and two turbocharged TSIs. Despite its efficiency, environmental friendliness, acceleration dynamics.
- High and low pressure circuits
- The FSI system provides two pressure circuits:
- Increased: fuel pump, gasoline pipelines, main distributor, safety valve, sensor, injectors, adsorber;
- Reduced: fuel tank, fuel pump, fine filter, pressure control valve.