Suspension with swing axles
This is one of the simplest and cheapest types of suspension. Its main element is the axle shafts, which have hinges at the inner ends, through which they are connected to the differential. The outer ends are rigidly connected to the hub. Springs or leaf springs act as elastic elements. The peculiarity of the design is that when hitting any obstacle, the position of the wheel relative to the axle shaft remains invariably perpendicular.
Additionally, the design may contain longitudinal or transverse arms designed to dampen road reaction forces. The rear suspension of many rear-wheel drive cars produced in the middle of the last century had such a device. In the USSR, the suspension of the ZAZ-965 car can be cited as an example.
The disadvantage of such an independent suspension is its kinematic imperfection. This means that when driving on uneven roads, wheel camber and track width change within wide limits, which negatively affects handling. This becomes especially noticeable at speeds above 60 km/h. Among the advantages are a simple device, cheap maintenance and repair.
Concept of suspension
Before talking about the pros and cons, as well as the superiority of one suspension over another, if possible, I propose to understand the essence of the concept of suspension.
A suspension is a component of a car that is part of the chassis. This is an intermediate link located between the road surface and the body part of the vehicle chassis. The work of the suspension is to convert into elastic movement all the impacts that the wheels of the car have to face while driving. And these are all kinds of bumps, holes, unevenness, etc. That is, the suspension absorbs energy from impacts and increases the smoothness of the ride.
In this case, a distinction is made between the design of the front and rear suspension. They can be divided into several categories. At the same time, all structures are subject to the same requirements.
The car suspension must keep the car in a horizontal position, regardless of the acting forces, and dampen vibrations. Plus, the structures must be elastic, strong and as durable as possible. Otherwise, expensive repairs will be required.
The current classification provides for the division of pendants into 3 categories.
- Dependent. It comes with longitudinal and transverse springs, it can use guide arms or a thrust pipe. Also distinguished are the torsion-lever design and the De Dion type system;
- Independent. Such systems differ from each other in the use of oblique and double wishbones located transversely, and may have swinging axle shafts. There are options with double and single trailing arms and transverse ones. But still the most popular option is the MacPherson type suspension;
- Active or semi-dependent. Here the rigidity and position change depending on the command given through the control device. Active systems are divided into pneumohydraulic, hydraulic and pneumatic.
But this is objectively not enough to understand what the difference is between them, what differences exist and which type of suspension travel is preferable in terms of comfort. You can also read useful material about checking shock absorbers for performance.
Dependent constructs
First, let's define what it is and what the concept of car suspension dependence means. In simple terms, this is a pair of opposite wheels (left and right), which are rigidly connected to each other using a single beam. This is one of the key ways to distinguish designs from each other. Just take a look at how the left and right wheels connect to each other.
When the impact on one wheel begins, the position of the second changes. The dependence of one wheel on the other explains the name of the design. Such units are more focused on vehicles that are operated in rather difficult operating conditions. Dependent suspension is extremely rare on ordinary passenger cars designed for city driving. Therefore, finding a car is not so easy if you just need a passenger car. But the system is still in demand and is finding its place in the auto market.
Dependent auto suspension components have strengths and weaknesses.
Let's start with the shortcomings. There are several main points worth highlighting here:
- worse sustainability indicators;
- insufficiently clear controllability;
- reduced level of comfort;
- high requirements for road surfaces when driving at high speeds;
- low information content of management.
All this when compared with cars equipped with an independent type of suspension.
The weaknesses are quite significant, and are more pronounced on ordinary roads. But if you drive into ideal conditions for such a suspension, the car will show its maximum.
It is in the element of the dependent structure that its true advantages are revealed. Namely:
- Low cost of maintenance. Maintenance and repair (maintenance and technical work) are quite cheap, which allows you to significantly save on repairs;
- Resistant to damage. This suspension is not afraid of impacts, active driving on bad roads, etc. The design behaves well under heavy loads;
- High strength. Independent suspension is not a competitor in this regard;
- Constant ground clearance. The clearance does not change, which provides a number of advantages;
- Excellent adaptation to off-road and bad roads;
- A small number of design components, which simplifies maintenance and makes repairs more affordable. This also directly affects reliability.
As you can see, in its element, the dependent system allows you to count on a solid list of advantages. But on regular roads everything is not so perfect.
Independent suspension
Unlike the previous design, here the opposite wheels do not have a direct structural connection with each other. Each of the wheels acts and works independently relative to each other.
Such units perform well when driving on highways, in the city, and behave excellently at high speed. Therefore, independent designs are found mainly on passenger cars, crossovers and SUVs.
We recommend: Is it possible to mix Tosol and antifreeze?
This also has its strengths and weaknesses. Benefits include:
- excellent grip on the road surface;
- excellent level of comfort;
- excellent handling;
- minor deviations along the longitudinal axis.
All this affects comfort, agility and handling. Dependent suspensions are not capable of this.
But don't jump to conclusions about the superiority of the independent system. It also has disadvantages:
- repairs are much more expensive, as is maintenance;
- the lever stroke is short, which may reduce ground clearance;
- the design consists of many components;
- due to the complexity of the layout, the likelihood of breakdowns increases;
- It is almost impossible to carry out repairs in the field.
If we take an initially high-quality independent suspension as a basis, and operate the car in the conditions for which it is intended, all these shortcomings will not be so obvious.
Trailing arm suspension
There are two types of independent trailing arm suspension. In the first, springs are used as elastic elements, and in the second, torsion bars are used. The wheels of the car are attached to the trailing arms, which, in turn, are movably articulated with the frame or body. This type of suspension was used in many French front-wheel drive cars produced in the 70s and 80s, as well as in scooters and motorcycles.
Among the advantages of this design are also simple design, cheap manufacturing, maintenance and repair, as well as the ability to make the floor of the car absolutely flat. It has many more disadvantages: while driving, the wheelbase changes significantly, and when cornering, the car rolls heavily, which means that handling is far from ideal.
Dependent and independent car suspension, which is better?
It is best to consider in advance where and how the car will be used, since the choice of suspension type depends on this.
Dependent suspensions are simpler and cheaper to maintain, but they cannot provide sufficient comfort and high controllability.
Independent suspensions are a little more complex in terms of design, but they are much more comfortable to use.
Naturally, repairs of the first type will be slightly cheaper than servicing independent models
Slanting wishbone suspension
The design of such a suspension is in many ways similar to the previous one, the only difference is that the swing axes of the levers are located at an oblique angle. Thanks to this, the change in the wheelbase of the car is minimized, and body roll has almost no effect on the angle of inclination of the car’s wheels, however, on uneven surfaces, the track width changes, and the toe and camber angles change, which means that handling deteriorates. Twisted springs, torsion bars or pneumatic cylinders were used as elastic elements. This version of independent suspension was more often used for the rear axle of cars, the only exception was the Czech Trabant, the front suspension of which was made according to this design.
There are two types of trailing arm suspensions:
- single-hinged;
- double-hinged.
Article on the topic: We are replacing the cabin filter on an Opel Astra H 1.6.
In the first case, the axle shaft has one hinge, and the swing axis of the lever passes through the hinge and is located at an angle of 45 degrees to the longitudinal axis of the car. This design is cheaper, but also not kinematically perfect, so it was used only on light and slow cars (ZAZ-965, Fiat-133).
In the second case, the axle shafts have two hinges, external and internal, and the swing axis of the lever itself does not pass through the internal hinge. It is located at an angle of 10-25 degrees to the longitudinal axis of the car; this is preferable for suspension kinematics since deviations in the track, wheelbase and camber remain within normal limits. The rear suspension of ZAZ-968, Ford Sierra, Opel Senator and many others had such a device.
Semi-independent suspension
Occupies an intermediate place between independent and dependent systems. Structurally, it consists of a pair of trailing arms fastened by a cross member. The use of this type of suspension is possible only at the rear; it is installed on almost all front-wheel drive cars. Among Russian cars, these are the VAZ2108-VAZ2115 models. The advantages of such a suspension are good kinematics, low weight, and simplicity of design. The downside is that there is a limitation on the possibility of installation - only the rear axle is not driven.
As a result, we can conclude that semi-independent and independent suspensions are used. The first option is ideal for the rear axle of front-wheel drive vehicles. The second type of suspension must be selected in accordance with operating conditions; if these are good roads, then a MacPherson is suitable; if you plan to drive over bumps, then it is better to choose a suspension with wishbones. If you have enough funds, and the trips will be made on high-quality road surfaces, then you can choose a multi-link system.
“Madam, why, may I ask you, didn’t you put on diamond pendants?” After all, you knew that I would be pleased to see them on you.
A. Dumas “The Three Musketeers”
Let us remind you: the car suspension is the entire set of parts and assemblies connecting the body or frame of the car with the wheels.
We list the main elements of the suspension:
- Elements that provide elasticity of the suspension. They perceive and transmit vertical forces that arise when driving over uneven roads.
- Guide elements - they determine the nature of the movement of the wheels. Also, the guide elements transmit longitudinal and lateral forces, and the moments arising from these forces.
- Shock-absorbing elements. Designed to dampen vibrations that occur when exposed to external and internal forces
Suspension on longitudinal and transverse arms
A very complex and therefore rare design. It can be considered a type of MacPherson suspension, but in order to relieve the mudguard of the wing, the springs were located horizontally along the car. The rear end of the spring rests against the partition between the engine compartment and the passenger compartment. In order to transfer the force from the shock absorber to the spring, it was necessary to introduce an additional lever, swinging in a vertical longitudinal plane along each side. One end of the lever is pivotally connected to the top of the shock absorber strut, and the second is also pivotally connected to the bulkhead. In the middle the lever has a stop for the spring.
The front suspension of some Rover models is designed according to this design. It does not have any particular advantages over the McPherson, and has retained all the kinematic disadvantages, but has lost its main advantages, such as compactness, technological simplicity, and a small number of hinge joints.
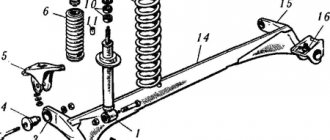
Double wishbone suspension
Its second name is “Porsche system”, after the name of the inventor. In such a suspension, there are two longitudinal arms on each side of the car, and the role of elastic elements is performed by torsion shafts located one above the other. Such a device was used in the front suspension of cars whose engine was located at the rear (models of early Porsche sports cars, Volkswagen Beetle and first generation Volkswagen Transporter).
The independent suspension on trailing arms is compact; in addition, it allows you to move the interior forward, and place the legs of the front passenger and driver between the wheel arches, which means reducing the length of the car. Among the minuses, we can note changes in the wheelbase when hitting obstacles and changes in wheel camber when body rolls. Also, due to the fact that the levers are subject to constant strong bending and torsional loads, they have to be strengthened, increasing their size and weight.
Article on the topic: Used Audi 80 – pros and cons
Double wishbone suspension
The structure of this type of independent suspension is as follows: on both sides of the car there are two levers located transversely, one side of which is movably connected to the body, cross member or frame, and the other to the shock absorber strut. If it is a front suspension, then the strut is rotating, with ball joints having two degrees of freedom; if it is a rear suspension, then the strut is fixed, with cylindrical hinges having one degree of freedom.
Various elastic elements are used:
- coil springs;
- torsion bars;
- springs;
- hydropneumatic elements;
- pneumatic cylinders.
On many cars, suspension elements are attached to a cross member, which is rigidly connected to the body. This means that you can remove the entire structure as a separate unit and carry out repairs in more convenient conditions. In addition, the manufacturer has the opportunity to choose the most optimal way to place the levers, thereby strictly setting the required parameters. This ensures good handling. For this reason, double wishbone suspension is used in racing cars. From a kinematics point of view, this suspension has no disadvantages.
Multi-link suspension
The most complex device has a multi-link suspension. It is similar in structure to double wishbone suspension and is used mainly on the rear axle of cars of class D and higher, although it is sometimes found on cars of class C. Each of the arms is responsible for a certain parameter of the behavior of the wheel on the road.
The multi-link suspension provides the car with the best handling. Thanks to it, you can achieve the effect of steering the rear wheels, which allows you to reduce the turning radius of the car, and better allows you to maintain the trajectory in turns.
The multi-link suspension also has disadvantages, however, they are not of an operational nature - the cost of the design is high, the complexity of design and repair.
Advantages and disadvantages of dependent suspension
Working with a dependent suspension has its advantages:
- constant ground clearance, which is an advantage when driving off-road;
- mechanical resistance to damage;
- simple, fairly cheap maintenance;
- simplicity of design, small number of components.
The disadvantages of dependent suspension include the following characteristics:
- low controllability and stability;
- high demands on road quality when driving at high speed;
- insufficient comfort when moving;
- low information content of the steering wheel.
Dependent suspension is most common on SUVs, pickups, trucks and buses. More specifically, this design is typical for G-class Mercedes, domestic UAZ cars, as well as the rear suspension on the Mitsubishi L200.
Instead of an afterword
In the modern automotive industry, dependent and independent suspension is used. It should not be assumed that one of them is better than the other, since their purpose and scope are different. Under a solid axle, the ground clearance always remains the same, and this is a valuable quality for a car that drives mainly off-road. That is why SUVs use spring or spring rear suspension with a continuous axle. The car’s independent suspension cannot provide this, and the actual ground clearance may be less than stated, but its element is asphalt roads, on which it undoubtedly outperforms the bridge in handling and comfort.
Share with friends on social networks:
Telegram
Technical nuances
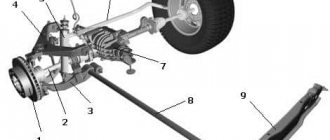
Now let’s move on to the technical side of the issue and understand the design and structure of the dependent system, as well as its varieties. Similar types of pendants include the following:
- on longitudinal springs (spring);
- with guide arms (dependent spring);
- De Dion pendant.
The first option is one of the oldest. This structure consists of a bridge beam connecting two wheels, as well as two longitudinal springs on which it is attached.
The spring in this embodiment acts as a universal elastic element - it takes on loads in the vertical and transverse planes, and also dampens body vibrations. Of course, you cannot achieve high comfort from the operation of the suspension of such a system, and at high speeds, problems with controllability begin to appear.
A design with guide arms can be called more advanced and modern. There are a lot of design options in terms of the number of levers and their configuration - this includes a suspension with a Panhard rod, and with a Watt or Scott-Russell mechanism. Compared to spring systems, these systems have much better handling and cornering behavior. The main elastic element here is the spring, and the shock absorber helps it.
As for the De Dion pendant, there is one nuance. The fact is that this system cannot be called completely dependent due to the tricky arrangement of the elements, which is due to the fact that it was developed for the rear axle of rear-wheel drive cars. In it, the differential and the beam connecting the wheels are separated.
We recommend: Optimal volume of antifreeze in the VAZ-2110 cooling system
The differential is rigidly connected to the car body, and rotation from it to the wheels is transmitted through swinging drive shafts. According to experts, the De Dion suspension is superior in many respects to the best examples of independent designs, and its only significant drawback is the price, which is why you can rarely see it, and even then mainly on sports cars.