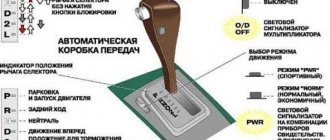
In the list of characteristics taken into account when buying a car, the issue of the engine-transmission combination is one of the fundamental ones. The pros and cons of mechanics, a variator, a robot, a classic automatic transmission are a subject of not only personal sympathy, but also an ongoing dispute in the community of car enthusiasts. Let's figure out which gearbox is better for quiet movement around the city, dynamic driving and off-road driving. Each of the listed transmissions has advantages and disadvantages due to design features,
Operating principle of manual transmission
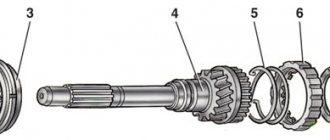
In a manual transmission, torque from the engine is transmitted through the clutch to the input shaft. By means of helical gears, the input shaft is connected to the intermediate and output shafts. For each gear, except reverse, a pair of gears is installed on the output shaft. One of the gears is rigidly fixed to the shaft, and the second meshes with the corresponding gear of the intermediate shaft and has a free fit (rotates on a bearing). When any gear is engaged, only one pair of gears meshes with the intermediate shaft and transmits torque from the engine to the transmission output shaft.
For smooth switching, the design includes synchronizers. By moving the gearshift lever in the passenger compartment, the driver moves the sliding clutch through the fork and rod. It is after the clutch is closed that the pair of gears on the output shaft are rigidly connected and begin to rotate at the same speed. The clutches of the idle gears are open, and the loose-fitting gears rotate idle from the intermediate shaft. The locking ring equalizes the speed of rotation of the shafts, making the closure of the gears smooth. If the synchronizer wears out when switching, you can hear a characteristic crunching sound. Reverse gear in a manual transmission is activated via an intermediate gear and does not require the installation of a synchronizer.
Operation of a manual transmission is impossible without a clutch, which is necessary to temporarily disconnect the driven disk from the engine flywheel. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the torque from the internal combustion engine is not transmitted to the transmission input shaft.
What is the secret of reliability?
From a brief description of the device and operating principle, you can appreciate how simple the manual transmission is. Maximum metal and complete absence of electronics. This is the reason for its main advantages:
- reliability;
- low cost of production. Equipment with a manual transmission will be cheaper than similar models with automatic transmission;
- efficiency when compared with classic automatic transmissions. On average, automatic cars consume 1-2 liters more fuel;
- ease of maintenance and maintainability. The recommended oil change interval is 100 thousand km; the clutch, with proper operation, can last up to 100-150 thousand km. On modern cars, only dual-mass flywheels, which are universally paired with diesel internal combustion engines and many gasoline engines, can cause trouble;
- resistance to loads. Manual transmissions are best suited for off-road driving and cargo transportation.
The most significant drawback is more tiring driving around the city, associated with frequent squeezing of the clutch pedal. People with non-standard equipment are more likely to encounter inconveniences in ergonomics. It is often difficult to combine the correct angle of bend of the arms at the elbows, the distance to the gearshift knob, good visibility and a comfortable position for depressing the clutch pedal.
The difference between an automatic transmission and a robot. Detailed review
- The design features of the automatic transmission include a gearbox and torque converter;
- The torque converter is responsible for smooth gear shifting, which occurs without jerking. To put it in simple language, this module in an automatic machine replaces the clutch;
- The automatic transmission gearbox consists of pairs of gears that are in constant mesh with each other. This module has only three main stages 4, 5, 6. Their capabilities directly depend on the number of gearbox speeds.
- If we talk about the bright sides of the automatic, then this kind of transmission significantly simplifies driving due to the fact that there is no need to constantly operate the clutch and use the gearshift lever. You can fully concentrate on driving and control the car with only two pedals;
- The usual clutch, which is inherent in mechanics, fails very quickly. While the torque converter is highly wear resistant and durable;
- An automatic transmission loads the engine less than a manual transmission, due to the fact that when changing gears there is no significant increase in speed;
- Automatic cars are equipped with a passive safety system, which prevents the car from rolling back when standing on a slope.
- The acceleration dynamics of the car are less than with a manual;
- With low-speed automatic transmissions, significant fuel consumption can be observed;
- Automatic transmission requires a large amount of oil;
- A car with automatic transmission reduces efficiency and dynamics;
- Robotic gearboxes are the most economical when compared with automatic transmissions. The level of efficiency is close to manual transmission;
- The cost of manual transmission is much lower than automatic transmission. This also includes low maintenance and repair costs;
- The car gets more dynamics.
- When compared with an automatic transmission, the robot is inferior in terms of smoothness of gear shifting. When moving, jerks are very noticeable;
- Long delays between transmissions;
- To stop, you need to manually move the lever to the neutral position;
- Robotic boxes do not like slippage when starting to move (their service life decreases);
- When starting to move, the car rolls back.
AutoFlit.ru
Automatic transmission with torque converter
The automatic transmission is based on the operating principle of a planetary gearbox. In a manual transmission, the change in gear ratios occurs due to the different diameters of the meshed gears. In automatic transmissions, a similar effect is achieved by blocking the inputs of planetary mechanisms. In a planetary gear, we can obtain the required output rotation speed by setting different speeds of the ring gear and sun gear. The standard planetary gear can provide 3 different output shaft rotation speeds and reverse. To obtain a larger number of gears, several planetary mechanisms are combined in the automatic transmission.
The elements of the planetary mechanism are blocked by clutch packs. In an unused clutch pack, the discs rotate freely relative to each other. Under the influence of oil pressure coming from the hydraulic unit, the discs are pressed against each other - the drum and gear begin to rotate as one. On older automatic transmission models, the transition from 1st to 2nd gear was carried out by a brake band, and not by a clutch pack.
Similar to the clutch in a manual transmission, a torque converter is used to transmit torque from the engine flywheel to the input shaft. The pump wheel is rigidly connected to the flywheel, and the turbine wheel to the input shaft of the automatic transmission. When the pump wheel rotates, a vortex flow of transmission oil is created in it. The ATF fluid pushed out by centrifugal force causes the turbine wheel to rotate. The reactor is necessary for effective redistribution of fluid and increasing torque on the turbine wheel.
The disadvantage of this design is the hydrodynamic losses due to heating and compression of the transmission oil. Due to mechanical losses, the speed of the turbine wheel will always be less than the rotation speed of the pump part. To minimize torque loss, a lock-up clutch is included in the design. When the friction discs are compressed, the turbine wheel and engine flywheel rotate at the same speed.
The valve body is responsible for redistributing oil along the automatic transmission lines. The spools and valves, with the help of which the fluid is distributed through the channels, are controlled by the automatic transmission ECU.
Everything would be fine, but...
Old-style torque converter automatic transmissions, with timely oil changes, can travel from 200-500 thousand km. At the same time, their repair, due to the simplicity of their design and widespread use, also does not cause problems. But manufacturers of modern cars are forced to gradually abandon automatic transmissions of this type. All due to tightening environmental standards and requirements to reduce harmful emissions.
Even with an increased number of stages and early locking of the torque converter, automatic transmissions are inferior in efficiency to robots and CVTs. At the same time, in terms of switching speed, the newest models are practically in no way inferior to preselective robotic gearboxes, which cannot be said about old automatic transmissions. The automatic transmission switched with long delays, taking away seconds during acceleration and increasing fuel consumption. Features of operation include problems with towing and the inability to start the car from a pusher. When used correctly, automatic transmissions can handle off-road conditions and cargo transportation well.
If you want reliability and smoothness from your transmission, an automatic transmission is still the best choice for civilian driving. Unfortunately, buying a new car with a traditional automatic coupled with a good engine is becoming increasingly difficult.
What is the difference between a robot and a machine gun?
To understand the difference between an automatic transmission and a robot, it is worth understanding the operating principle of each of these transmissions and the design of the system as a whole.
We recommend: Rating of the best compressors for SUVs in 2019
Design and operating principle of automatic transmission
The automation is based on a control system, a torque converter and a planetary type gearbox with specific gears and clutches. Thanks to this design, speeds are switched autonomously without driver intervention. The guideline in this case is such parameters as driving mode, load and engine speed.
Additionally, we recommend reading our specialist’s article on how to properly drive an automatic transmission.
What are the benefits of CVTs?
Continuously variable transmissions (CVT) provide smooth changes in gear ratios. The most widespread are V-belt variators with one belt drive. A V-belt connects two pulleys. By moving and expanding the walls of the conical disks, a change in the diameter of the pulleys is achieved. Due to the smooth change of gear ratios, the driver does not feel the gear change.
The following types of clutch are used in CVT gearboxes:
- electromagnetic;
- multi-disc hydraulic;
- centrifugal automatic;
- torque converter.
The most common are wet multi-plate clutch and torque converter, the operating principle of which we discussed above. CVTs with a torque converter are the most reliable. Before the introduction of the fluid coupling, continuously variable transmissions already suffered from belt stretching and scuffing on the surface of the cones even on short runs. For smooth switching without kicks or delays, the surfaces of the cones must be perfectly smooth. Therefore, CVTs have earned the reputation of being unreliable units.
The addition of a torque converter to the design significantly reduced the load on the belt and cone discs. Until the fluid coupling is blocked, jerks during sudden starts and slipping of the drive wheels are damped due to the slipping of the pump wheel relative to the turbine wheel. ATF fluid absorbs shock loads, which significantly increases the life of belts and cone pulleys.
Is it worth the risk when buying a used car?
Despite all the design improvements, CVTs are still extremely demanding for maintenance and operation in the frosty season. The oil should only be changed to original oil, and the oil aging service counter in the gearbox ECU must be reset to zero. In cold weather, you should drive extremely carefully for the first 15-30 minutes in a car with a CVT. The risk of damage to the cone discs on an unheated gearbox is very high.
CVT transmissions work perfectly in tandem with any engine. When maintaining a low speed, the ECU maintains minimum speed, which ensures fuel efficiency. If you need to accelerate dynamically, the tachometer needle will rise and hover in the zone of maximum engine efficiency. Thanks to the continuously variable transmission, torque is constantly transmitted to the wheels. Improvements in the design of CVT gearboxes have made it possible to use the car more boldly on light off-road conditions. But as before, CVT is an excellent option only for quiet driving around the city and country roads. With proper maintenance, many CVTs run 200-250 thousand km without problems.
Variable speed drive
What is a variator? This is a continuously variable transmission. It is interesting that the chain or belt in such a transmission is thrown between 2 gears. The cones of these gears move apart and shift, thereby influencing the diameter. Compared to a classic automatic transmission, a variator is a much more technically complex mechanism. It is capable of providing an infinite number of transmissions.
The engine of a car equipped with a CVT is capable of periodically operating at high speeds. A control computer interacts with it, which analyzes driving conditions and provides special modes.
A variator is a box that allows you to change speeds manually, like on a manual transmission. There is a special mode called tiptronic.
It’s not for nothing that we first cited the difference between classic boxes above. The fact is that a CVT is more economical than an automatic transmission and the advantage of mechanics in this case is called into question. On the other hand, a mechanic is a mechanic and, whatever one may say, it has less fuel consumption.
In addition, the efficiency of the variator is ensured by periodic operation of the engine at high speeds, which is not only an advantage, but also a big disadvantage. CVTs are almost always very noisy and provide little information to the driver.
Robotic gearbox
The robot's internal structure is closest to a manual gearbox. The only difference is that the clutch fork and gear shift rod are moved not by the driver, but by servos. In automatic mode, the transmission ECU is responsible for powering the electric motors. Based on the vehicle speed, engine load, ABS and ESP system signals, the unit selects the most suitable stage. In manual mode, gears are changed at the command of the driver acting on the steering wheel paddles or selector.
The main problem of robots is sluggishness when changing gears and low reliability. The ECU cannot always adequately assess changing driving modes and wear of gearbox elements, which is why, over time, leisurely shifts are complemented by jerks, dips and jerks.
For auto manufacturers, a robot is the cheapest way to offer customers an automatic transmission. Currently, budget cars are equipped with such gearboxes. The choice of a robot is quite justified if you need a fresh, inexpensive automatic car.
Preselective robots with two clutches
The preselective robot is distinguished from a conventional robotic gearbox by the presence of two clutches. Each is connected to a separate input shaft and is responsible only for changing even or odd stages. We can say that two mechanical gearboxes work in tandem inside the case.
When the car is moving in 3rd gear, the 4th gear moving clutch is already engaged. Therefore, to move to the highest stage, it is enough to disconnect the input shaft of odd speeds from the flywheel and immediately connect the shaft of even speeds. Thanks to this, gears are switched with minimal loss of torque.
To separate the internal combustion engine flywheel from the transmission, two types of structures are used:
- dry combined clutch. Two clutch baskets are connected in one housing. As on a robotic gearbox with one clutch, the release bearing fork is moved by a servo drive;
- wet clutch. The operation of steel and friction discs completely repeats the principle of operation of torque converter-type automatic transmission clutch packs.
Why so much trouble?
At one time, the Power Shift preselective robots surprised us with their short clutch life, sweaty seals, jerking, and complete failure even on short runs. Owners of cars with DSG 6 (DQ250) faced even greater problems. The ECU of boxes with a dry clutch overheated in city mode, and the clutch rarely lasted more than 50 thousand km. With the release of DSG 7 (DQ 200, DQ500), which already has a wet clutch, the situation has improved significantly. But owners are still not immune to problems with clutch wear, kicking and delays when switching.
Preselective gearboxes were created for lightning-fast shifting without loss of acceleration dynamics. Actually, the development migrated to civil transport from auto racing. But the problem is that even a wet clutch is not able to withstand constant pushing in traffic jams. For imperceptible shifts and starting from a standstill without jerking, the friction discs must compress smoothly.
Over time, due to high temperature stress, steel discs become slightly deformed. Therefore, even in the open state, the disks are in contact. In conditions of long slipping of friction discs, frequent starts and stops, and this is what happens in traffic jams, the packages overheat. The dust suspension and adhesive of the friction discs are washed off with oil, after which they circulate through the system, clogging the mechatronics channels. Wear products from friction linings act as an abrasive, damaging the solenoid valves and their seats.
Add to this frequent overheating and rapid aging of the ATF fluid and you will get a whole bunch of problems even on a short mileage. This is the price that owners have to pay for fast and smooth gear shifting.
Automatic or manual: which is better for different operating conditions?
When choosing a car, many potential owners talk for a long time about the need to overpay for an automatic transmission. Each transmission unit has its own pros and cons, which should be understood before purchasing a car. To do this, you can talk with representatives of car repair service centers, and also read reviews about certain equipment options.
With the help of a collective opinion, you can determine the most important shortcomings of the machine, which are usually hidden under its undeniable advantages. And also determine what disadvantages the mechanics have. If you don’t want to collect the opinions of different people due to lack of time, read this publication and make an independent conclusion about the need to purchase a particular gearbox.
The main advantages of a manual transmission
The mechanics are the simplest and most understandable unit that does not require special care. This gearbox works in any frost, under any operating conditions and will not cause any unpleasant moments or unexpected breakdowns. Even if one gear fails, you can easily reach the service center using other steps.
The manual transmission is also more reliable. If you conduct research at different service stations, you will find out that owners of automatic cars are frequent guests of such companies, and most importantly, they pay quite a lot of money for service. Mechanics also has traditional advantages:
- independent adjustment of the type and nature of the trip, the possibility of dynamic sports acceleration;
- saving fuel by keeping speed within a certain range;
- the possibility of easy engine braking when driving along a mountain road or on a long descent;
- ease of operation - it is enough to change the oil once every 60,000 kilometers;
- easy repair of the unit even after serious breakdowns and damage.
A manual transmission is also much cheaper. The design of any automatic or robot, CVT or other type of automatic transmission will cost the buyer on average $1,000 more when purchasing a car. The cost of mechanical maintenance is significantly lower, given the simplicity and high speed of this procedure.
Of course, such advantages cannot go unnoticed in the design of a manual transmission. But do not forget about certain disadvantages, which will be discussed below. The new world of road transport actively continues to abandon manual transmissions and adopts modern complex and expensive technologies.
The main advantages of an automatic transmission
All types of modern automatic transmissions are designed taking into account the requirements of the potential car buyer. A standard automatic is no longer used so often in the design of expensive vehicles due to its tenderness, increased consumption and other disadvantages. Today, robotic gearboxes, which combine the advantages of mechanics and the convenience of an automatic transmission, as well as CVTs, are actively gaining momentum.
Such trends have made the automotive world different and given it new features. The advantages of the robot include fairly low fuel consumption, sometimes lower than a manual transmission, as well as excellent acceleration dynamics. The flexibility of this unit is amazing. The variator is designed for other conditions and provides the following advantages:
- slight increase in fuel consumption compared to a manual transmission;
- high ride comfort - no jerking when changing gears;
- lack of clear modes and restrictions on transmissions;
- a fairly simple design that is not prone to breakage;
- successful technological solutions from modern manufacturers.
Such boxes are gaining momentum today in all sectors of the automotive industry. Manufacturers are mastering new technologies and are beginning to actively use the developments of the world's most successful concerns. The only problem is that the cost of cars increases significantly, because the development of a variator or robot costs quite a lot.
The very design of this type of box involves the use of expensive computer technologies and the highest quality alloys to achieve high-quality and uninterrupted operation. This is the only way to ensure high quality operation of the devices under the hood of your car.
Selecting a gearbox - the main points
You can spend a long time evaluating the pros and cons of different technical solutions for cars, but only a unit that suits your requirements will provide a fairly comfortable ride and will become one of the important safety elements. Many people prefer to drive an automatic car only, while others hate cars with three pedals. And the financial aspect can become a serious obstacle to buying the desired car. Therefore, evaluate the following factors when choosing transport:
- what type of gearbox will be preferable for you;
- are you willing to overpay a certain amount of money for a particular box;
- does it make sense to purchase a certain configuration of a car with an automatic transmission;
- Will you fully use all the advantages of automatic transmission?
Often, when answering these questions, the future owner of the car understands that significant savings in money in the cabin and a certain reduction in receipts at the gas station will be the greatest advantage. This forces us to buy a car with a manual transmission. In other cases, travel conditions may become a determining factor. After all, if you have to drive along a dirt road where you can easily get stuck, the automatic will be a bad help in such a situation. Watch more about the pros and cons of automatic transmission in the video:
Which gearbox is better?
If you want a simple, reliable transmission and don’t mind the extra work with the clutch and gear knob, go for a manual transmission. If you want more comfort for little money, your choice is the simplest robotic gearbox. If you want a durable and at the same time comfortable transmission, take a classic automatic. With careful use in urban areas and short mileage, the variator will also not cause any trouble. Well, if you like to enjoy dynamic driving, are willing to put up with design features, or want a weekend car, buy a car with a preselective robot.
Remember that there is no general concept of the reliability of a CVT, robot or automatic transmission. There are specific successful and unsuccessful examples, and therefore used transmission models working on the same principle can behave differently. Before purchasing, study the experience of car owners with the selected gearbox, and, if possible, examine the service history of the selected used car.
Which is better - CVT or manual? Comparing checkpoints
- Mechanics are always cheaper than CVTs, not only in terms of the cost of the car, but also in terms of servicing the gearbox;
- The manual transmission looks more reliable than the CVT;
- Fuel consumption for manual transmission is lower;
- Acceleration time of the car to 100 km. with a CVT it is much faster than with a manual;
- A CVT is much more comfortable and convenient than a manual transmission, just like an automatic transmission;
- With steering wheel shift paddles, the variator also looks much more interesting than a manual transmission.
AutoFlit.ru