A modern automatic transmission is the second most complex unit after the engine, and one of its main components is the planetary gear. But the most interesting thing is that this mechanism has more than 100 years of history - it was first used back in 1908 on a Ford model T.
True, on a manual gearbox. Many people are not aware, but the first automatic transmission appeared even earlier - in 1906. It was three-stage and had a hydraulic drive, which took root and was used everywhere until recently, when the control of the automatic transmission was transferred to electronics.
But the planetary gearbox still remains the most common type among automatic transmissions.
Gearbox - principle of design and operation
The planetary gear design has a set of gears on a rotating axis:
- The main element is the “sun” wheel located in the center.
- An important part of the system is the carrier; it fixes the axes of the remaining gears (satellites).
- Satellites are gears of the same size located around the central wheel.
- Ring gear - it combines all parts of the gearbox and is in contact with the satellites. This is the only part of the gearbox that is stationary.
The rotation of the central wheel sets in motion the satellites, which move around the perimeter of the ring gear. This process rotates the axes of the satellites, and they give movement to the carrier.
How to change gears correctly when riding a bicycle
It is difficult to harm the mechanism of a bicycle gearbox, but it is possible if it is systematically misused. When riding a bicycle with a planetary gear, there is a simple rule: change gears without pedaling.
Strange? Not at all. The planetary mechanism is similar to a manual transmission of a car, and there, too, when switching from one gear to another, the gas is released. And “gas” for a cyclist means pedaling.
You need to switch from one gear to another a little in advance, and this is done like this:
- The bicycle coasts, the effort on the pedals is minimal.
- The gear is changed using the handle.
- After a few rotations of the wheels (about 2 seconds), you can pedal.
Driving uphill is accompanied by a transition to a lower gear, that is, the gear ratio should be less than before the transition. On three-speed planetary gears it's simple: go to first gear. With other options, it is quite normal to switch, for example, from third to second.
You need to go for promotion sequentially, that is, first the first, then the second and so on. When you slow down, you can step over. In monotonous conditions where it is impossible to develop speed (a sidewalk with pedestrians, for example), it is better to use only the main gear without shifting.
Pros and cons of planetary gearbox
The device is popular because it has a number of positive qualities:
- compactness - does not require much space and time for installation;
- has low weight;
- creates less noise during operation than conventional gearboxes;
- the load on the shafts and supports is small, this makes the supporting structure simpler, thereby reducing costs;
- has large gear ratios.
Differential transmission drives folded or unfolded movement in devices, which is used in metallurgical machines.
The planetary gearbox also has a number of disadvantages:
- The requirements for the manufacture of gearboxes are high. Precision is necessary because the teeth must fit tightly but move easily, so they are more difficult to assemble than other types of gears.
- The cost is higher than the price of other gearboxes.
Scope of application of planetary manual transmissions
At the dawn of the automotive industry, planetary transmissions were also present in manual transmissions - for example, in the famous Ford T model. Gears were switched by three pedals, the gas pedal was moved to a steering column switch. The first gear was engaged with the left pedal, the second with the center pedal, and the reverse with the right pedal. In 1928, the model was removed from the assembly line, and the era of planetary manual transmissions faded into oblivion.
In the 30s, the first semi-automatic planetary-type gearboxes appeared, which were later replaced by fully automatic ones.
In semi-automatic machines, the clutch function was performed by a fluid coupling. In automatic transmissions there is a torque converter.
However, planetary manual transmissions are still in use - they are installed in tracked vehicles (tractors, excavators), including military ones (tanks, transporters, tractors). A planetary mechanism is used in metal-cutting machines, and even in aircraft engine turbines, as a gearbox.
Planetary gearboxes are very popular in bicycle transmissions. They are durable, lightweight and easy to operate, being essentially maintenance-free. However, they significantly increase the cost of two-wheeled vehicles, so they are not used in purely sports models, largely due to the increase in vehicle weight by 1.5-2 kg. and poor maintainability when compared with parallelogram-type gear shift devices.
Gear ratio
The gear ratio in a planetary gearbox is difficult to determine visually, since there are different ways to drive the system. In a planetary gear, one part is fixed, and the others act as drive and driven. The gear ratio depends on the teeth of all gears, their number, and the fixed element.
Gear ratios are:
- positive - when both gears are in the same direction;
- negative - if the gears move in different directions.
If the carrier is stationary, then the gear ratio is S/A, where S is the central wheel, A is the number of gear teeth.
When the ring gear is blocked, power is supplied to the carrier, and then the sun gear PO is less than 1 and will look like 1+A/S.
When the ring gear is fixed, and power passes through the central wheel, the software is equal to 1/(1 + A/S). It is the largest number that can be obtained with a planetary gear.
Device, principle of operation
Schematically, an automatic transmission can be represented as a structure consisting of two parts - a planetary mechanism and a torque converter. The torque from the power unit is transmitted to the torque converter - it is this that converts the torque, reacting to changes in the driving mode (or does not transmit rotation at all).
In a manual transmission there are three shafts (drive, intermediate, driven), and their gears are in constant mesh. Changing to another gear is accomplished by connecting the driven shaft to a specific pair of gears. In an automatic transmission, the principle is different: the selection of the required driving mode is carried out by locking the corresponding gears of the planetary mechanism.
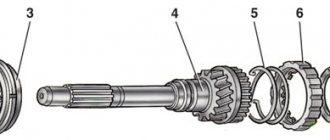
The design of a planetary gearbox, or planetary gearbox, includes a sun gear that receives rotation from a torque converter through an element called a carrier, to which 3 or 4 satellites are connected. The satellites are connected to the ring gear (its second name is ring gear). All of the listed elements of the planetary gear contain a friction-type brake mechanism (in rare cases - band brakes), with the help of which the gears are locked.
To understand the operating principle of a planetary gearbox, consider three simple examples:
- let us need to speed up, that is, switch to a higher gear. In this case, the ring gear is locked, the rotational movement from the torque converter and the secondary gear is supplied to the satellites, the rotation speed of which increases. The carrier, as it were, “sums up” the rotation of the satellites and, as a result, also begins to rotate faster;
- when the speed of movement decreases, the carrier is already fixed, and the satellites continue to rotate, which forces the ring gear to reduce the rotation speed;
- direct transmission is ensured as follows: the carrier is rigidly fixed with the ring gear using a friction clutch, all inactive elements of the planetary gear do not rotate, minimizing friction.
It is important to understand that in each mode certain elements of the planetary gear are blocked.
How is torque transmitted further to the drives (transfer case for cars with PP or driveshaft for rear-wheel drive cars)? It’s simple: rotation is “removed” from those elements that remain unlocked. So, if the carrier is blocked, rotation is transmitted to the wheels from the ring gear. If we talk about direct transmission, here the planetary gearbox is actually “superfluous”, since torque is transmitted to the drive directly from the torque converter.
Improvement of automatic transmissions, aimed at reducing fuel consumption, creating more favorable operating conditions for the engine, and improving vehicle dynamics, occurs in several directions. To do this, the number of planetary gearboxes is increased, while all gearboxes, except the first one, do not contain reduction gears. As a result, the direct transmission on the second and so on gearboxes turns out to be faster than the overdrive gear of the main gearbox. At the same time, additional gearboxes do not seem to need a reduction gear, since the torque is not removed from them in all cases.
Let's take a closer look at the operation of the clutches, which are actually responsible for switching modes. Each planetary gearbox includes a set of friction clutches - thin movable or fixed rings. The moving rings are connected to the rotating gear units. If the electronics, reacting to manipulations with the accelerator pedal, creates the appropriate fluid pressure in the automatic transmission, the stationary discs engage with the movable ones. As a result, certain elements (for example, the steering wheel or carrier) are immobilized. This principle is the essence of the planetary mechanism.
A lot depends on electronics. It is she who monitors the current speed of the vehicle, as well as the speed of rotation of the crankshaft, regulating the operation of the box in such a way as to provide optimal conditions for the engine while minimizing fuel consumption. Modern electronics can even determine the degree of wear of clutches and report this when performing vehicle diagnostics. For those who are planning to buy a used car with an automatic transmission, this is useful to know - this way you can insure yourself against purchasing a car with a faulty transmission.
The planetary gearbox device includes a pump, the function of which is to create the required pressure in the line of movement of the technical fluid; between the lines, the distribution of fluid pressure is regulated by solenoid valves.
Since the amount of pressure created by the pump is quite significant, you cannot push-start a car with an automatic transmission - towing cannot provide the required pressure.
If an automatic transmission with a planetary gear were directly connected to the engine, when stopping the car and changing gears, the engine would stall, because there is no clutch. The problem is solved by a torque converter, which, in fact, performs the clutch functions, but in automatic mode.
It consists of three components:
- a centrifugal pump rigidly connected to the flywheel shaft;
- reactor, if necessary blocking the transmission of rotation;
- a centripetal turbine, the function of which is to transmit the converted torque to the planetary mechanism.
The turbine and pump wheels have some clearance between them. Rotation is transmitted to the turbine through transmission oil, which is directed from the pump wheel blades to the turbine blades. The geometry of the torque converter elements is selected in such a way that, despite the absence of a rigid coupling between the pump and the turbine, the TM moves in a closed circle. Thus, when the car stops, rotation is transmitted without the need to switch off the gear. When the need arises to change the current mode of motion, the reactor begins to “work.”
When you sharply press the accelerator pedal (say, at start), the speed of rotation of the turbine wheel increases, and the reactor stops. This is the so-called torque converter mode. The shape of the reactor blades is such that when the oil returns from the turbine to the pump section, additional resistance is formed, which accelerates the movement of the liquid.
At a certain point in time, the rotation speed of the turbine wheel is compared with the pump wheel, and then the reactor wheel also begins to move, without interfering with the movement of the fluid, increasing the efficiency of the automatic transmission. This mode is fluid coupling.
Types of planetary gearboxes
A distinctive feature of planetary gearboxes is the presence of two or more degrees of freedom. And the speed of a link is directly related to the angular speed of the remaining links.
There are several types of transmissions:
- Single-stage is the simplest option with small dimensions.
- Multi-stage - used to obtain a larger subordinate number.
Planetary gearboxes differ in the location of the shafts: vertical or horizontal.
In addition, planetary gears differ in the meshing of gears, there are:
- Direct (traditional method) - since installation of this design is the simplest. Used at low speeds and low loads.
- Helical - its use can reduce the noise of gearboxes, but axial loads complicate the selection of bearings. The tilt angle is 18 degrees, the stroke is smoother, used at medium and high speeds.
- Chevron - the teeth are directed in different directions. Recommended for transmissions with high loads. The advantages of this type are that there is virtually no axial load on the bearing, this extends the service life of the entire assembly. This type of transmission makes it possible to increase the inclined angle of the teeth up to 40 degrees. The disadvantage of this type is its high cost.
The history of planetary hubs for bicycles
Before being used on bicycles, planetary hubs were used on tricycles. The patent for the planetary bicycle hub dates back to the mid-1880s. The first patent for a compact planetary hub was granted in 1895 by American mechanic Seward Thomas Johnson of Noblesville in the USA. This hub only had two speeds. It was not commercially successful.
In 1896, William Reilly of Salford, England, patented a two-speed hub. It began to be produced in 1898 under the name “bushing”. It became a great achievement in the bicycle industry and was produced for many decades. Many people liked the practicality of the compact planetary hub.
In 1902, Reilly designed a 3-speed planetary hub. He stopped working with and gave them the intellectual rights to the planetary hubs. To get around the patent problem, Reilly's colleague James Archer acquired a patent for a 3-speed hub. Meanwhile, the famous English journalist and inventor Henry Starmay also invented his 3-speed hub. In 1903, Frank Bowden, director of the Raleigh bicycle company, created the Three-Speed Gear Syndicate and acquired the rights to both Reilly/Archer and Sturmey 3-speed hubs. The Reilly hub was released as the first 3-speed Sturmey Archer hub.
Fichtel Sachs Torpedo two-speed planetary hub, produced in 1904 - 1954.
In 1902, Michael Pedersen, who manufactured Dursley Pedersen bicycles, patented a 3-speed hub. It began production in 1903. This hub was based on the "counter-drive" principle, with an unusual planetary gear that used a second sun gear instead of a gear. In 1904, Fichtel & Sachs (Schweinfurt, Germany) released a bushing under the Wanderer license. Thus, until 1909, there were 14 different 3-speed planetary hubs available on the English market.
By 1930, planetary hubs were being used on bicycles all over the world. They were especially popular in the UK, the Netherlands, German-speaking countries and Scandinavia. Beginning in the 1970s, they fell out of favor in English-speaking countries. But in many northern European countries, where bicycles were constantly used as everyday transport, and not just for sport and recreation, planetary hubs were still widely used. Cheaper and more powerful (but less reliable) classic shifters appeared, offering a wide range of gears.
In 1987, Sturmey-Archer only made 3 and 5 speed hubs, Fichtel & Sachs and Shimano only made 2 and 3 speed hubs. That same year, the first book (excluding maintenance instructions) covering 80 years of planetary hub history was published. Since then there has been a slow but steady increase in interest in planetary hubs, which is reflected in the increase in the range of hubs available.
In 1995, Sachs introduced the Elan, the first planetary hub with 12 speeds and a total ratio range of 339%. Three years later, Rohloff came to market with the Speedhub 500/14 14-speed planetary hub, with an overall range of 526% comparable to 27-speed classic shift systems. It was quite reliable and light. This is the only hub that can be mounted on mountain bikes as well as derailers. In 2007, NuVinci launched a continuously variable ∞-speed hub (bicycle CVT) designed for daily commuting, with a total range of approximately 350%.
As of 2008, Sturmey-Archer produced 3, 5 and 8 speed hubs, SRAM (successor of Fichtel & Sachs) produced 3, 5, 7 and 9 speed, Shimano produced 3, 7 and 8 speed . In February 2010, Shimano officially introduced the 11-speed Shimano Alfine 700 model.
Failure
Wear is the main cause of planetary gear failure, which is mainly due to poor lubrication. Worn gears have increased gaps in the gears, which leads to increased noise, vibration and ultimately a decrease in tooth strength.
Jamming – breakdown of high-speed gears. Seizing occurs as the oil film is squeezed out between the teeth at high speeds.
Fracture – caused by bending stress. A fracture can destroy the shaft, bearings and the entire mechanism.
Planetary gearboxes are used where average precision is required and there is no need for a full shaft. The main industry for using planetary gearboxes is mechanical engineering; in addition, they are used in medical technology and measuring equipment.
Advantages of planetary gear
Planetary gears have many advantages and are therefore widely used in industry and mechanical engineering. The advantages include:
- Compact size, light weight.
- Quite quiet in operation.
- Gear ratio (for planetary gears it is larger).
- Uniform load thanks to several satellites in the device.
- Wear-resistant.
The disadvantages of planetary gears, perhaps, include the large number of components involved in the manufacture of the device. And also, due to the large number of parts with teeth, you need to carefully monitor their alignment and accuracy. Perhaps the main disadvantage of such gears is the difficulties that arise during their creation and installation, since this is a rather complex mechanism.
DIY gearbox repair
Repairing a gearbox with your own hands is a very difficult task. So, this mechanism is very complex and consists of many parts. When making repairs with your own hands, you can often even disassemble without knowing that you can easily lose a whole bunch of small parts inside, for example, needles instantly fall apart and get lost. Planetary gearbox repairs are best left to the professionals.
It is worth noting that today the planetary gearbox is very common and is used in most trucks in drive axles, and is also very often found in the role of winches.
Like all gearboxes, it can be either single-stage or multi-stage. If you are going to purchase a mechanism of this type, then it is best to buy it from trusted manufacturers, since repairing it yourself is very difficult, and if it often fails, then a lot of money will be spent on it. In this article we tried to collect general information on planetary-type devices used for the production of cars. It must also be said that this type of device is being very intensively introduced into many areas and industries due to its very significant advantages.
Read also: Homemade sharpener from a washing machine engine
Mechanism malfunctions and repairs
The most common sign of a planetary gear malfunction is the presence of vibrations in the gearbox area. Drivers also note extraneous noises, jolts and twitching. The presence of certain symptoms depends on the nature of the malfunction, for which there may be several reasons:
- Overheating of the mechanism.
- Aggressive driving style with sharp braking and acceleration.
- Lack of oil, low level or insufficient quality.
- Insufficient warming up of the gearbox before driving.
- Slipping on ice.
- The vehicle gets caught in snow or mud.
- Wear of planetary gear elements.
To repair a planetary gearbox, you need to know the specific cause of its failure. To do this, the mechanism is disassembled. Typically the box is held on by bolts inside the drive shaft. It is necessary to remove the speed brackets from one side (depending on the design) and then unscrew the bolt through the hole in the drive shaft. Next, the failed element is cleaned or replaced. As a rule, we are talking about contamination with metal shavings, breakage of teeth, wear of axles and gears.
Who manufactures planetary planets?
Many companies are engaged in the production of planetary bushings. But we will highlight the main manufacturers that are worthy of attention.
Rohloff is a top manufacturer. The company has been able to design the most sophisticated equipment and is also a market leader. Planetary gears from Rohloff can have up to 14 speeds.
Shimano is a very popular company. It produces planetary gears from 3 to 11 speeds. The quality of the products from this manufacturer is high, the mechanisms can last for a long time.
SRAM is somewhat inferior to Rohloff in the production of planetary bikes. The products of this company have up to 12 gears. You can buy products from this company if you are looking for the ideal combination of price and quality.
Sturmey-Archer has concentrated on producing hubs with hybrid cassette-planetary mechanisms. In this direction, the company has been able to achieve significant success and is constantly improving existing models. Additionally, the organization produces other types of bushings for 3, 5 or 7 gears.
When purchasing these mechanisms, give preference to trusted manufacturers. Of course, there is a great temptation to save money and buy a part from some no-name company.
But it is important to consider that these mechanisms are extremely difficult to manufacture. Therefore, the company must have advanced equipment, significant experience and the best specialists
Only then will it be possible to achieve excellent functioning of the planetary hub and a long service life.