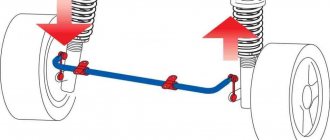
The design of the car contains parts and devices that provide protection against instability and easy rollover in the event of a sharp turn. Stabilizer links are devices designed to create lateral stability of a car. That's why they are called anti-roll bars. These are important elements of the machine’s design, so you need to monitor them and be able to determine from the signs of malfunctions which malfunctions are in which unit.
Design and principle of operation
The stand is a rod with a length of 5 to 20 centimeters. The rod has hinges at both ends for mobility. The following options can be installed as hinge joints:
- two ball joints;
- stabilizer joint and bushing;
- two bushings;
- on one side there is a hinge, and on the other there is a thread.
As a rule, hinge parts are welded to the rod at a right angle (90 degrees). At the point where the tip attaches to the metal rod, it has a neck (thin end). This was done on purpose, that is, they weakened the structures in this particular place, so that if the permissible maximum loads were exceeded, the device stand would break in exactly the thinned place. This method can be called a mechanical fuse. If the strut had broken in any other place, it could have pierced the bottom of the car, causing harm to the driver or passengers.
This thoughtful design of the racks allows you to protect yourself from unnecessary problems. There is no need to complain that the racks often fail; they are specially made not too thick. Non-original racks are often larger in diameter than the original ones. They will last longer, but safety in this case is reduced.
The most popular type of racks are racks with ball joints. A device of this type of rack includes a steel ball pin and a plastic seat with a lubricant that has special temperature and dynamic characteristics. A metal or plastic cap is pressed onto the top of the finger.
To protect against dust getting into the hinge joints, sealed rubber boots with lubricant are always installed. Such a simple part as a boot significantly increases the service life of the device and the moving mechanism protects against loss and contamination of lubricant. The main property of the lubricant for the hinges under the boot is frost resistance so that it does not thicken in severe frosts.
To better understand how stabilizer struts work, you need to understand that the struts are not rigidly connected to the stabilizers, that is, they have some mobility relative to each other. During a turn, the car begins to tilt (natural roll), and at this time only forces act on the car body, and forces act on the suspension, which try to straighten the body. If the roll force is much greater, then there is a risk of breaking the associated parts: the stabilizer and the hub eye. It turns out that the stabilizer link is a damper that equalizes oppositely directed forces. But, since the force that wants to overturn the car (during a sharp turn) and the force that is against it, both put pressure on the stabilizer bar, which is why the hinge joints of the strut are gradually destroyed.
There are manufacturers who make stabilizer struts with self-adjustment. For example, on the Nissan Patrol GR (Nissan Patrol GI ER) an electronic anti-roll bar is installed, that is, the electronics can turn off the stabilizer.
There are also cars, often SUVs, in which the operation of the stabilizers is regulated by an electronic control unit (ECU).
avtoexperts.ru
Very often, novice car owners are faced with the problem of misunderstanding why a stabilizer is needed in principle. To explain what the stand itself is, it is necessary to understand the structure of the entire “bar.” In technical terms, the correct name for it is an anti-roll bar, for example, it is of a different type at the back and front, see the photo for more details. It is necessary in order to reduce the horizontal roll of the car body when driving, especially when cornering. As for the “bar” racks themselves, they serve to install the latter on the frame. This provides a “live” connection of the elements with the hub or steering knuckle.
Stabilizer link (bone) using the example of Skoda Fabia
Types of stabilizer struts
Remember that depending on the suspension configuration, the shape of the struts and even the principle of attachment to the car body change. It is also necessary to distinguish between some features of the front and rear pillars in different car models. In models where the rear suspension is of a multi-link configuration, “bones” are usually used - these are U-shaped figures, with hinges at the edges. There are also “eggs”, as they are popularly called. They are used, for example, on domestic VAZs, for attaching the front and rear stabilizers.
Stabilizer strut (eggs) Lada Kalina
Device
Often, the stand is a rod from 4 cm to 20 cm. At both ends of the “bone” there are special hinges that provide “live” fastening. There are many options and varieties, for example, it can be only two bushings (rubber bands), a hinge with a thread, or a hinge and a bushing. Also, do not forget about “eggs”, where a rubber or polyurethane bushing is used instead of hinges.
Please note that the structure is not solid and is welded to the rod. This is a kind of security element. By the way, the place where the weld seam is located is called the “neck”. That plane is made thinner, so that in the event of serious overloads on the car, the fault occurs there. Otherwise, it is impossible to predict where exactly the break will occur and then, having broken, the “bone” can easily break through the bottom.
This is how a hinged type stand works
In modern cars, you can often find articulated struts. The design is a steel ball with a “finger” and a “socket” where a plastic housing contains lubricant. The “finger” itself, as a rule, is pressed in; different manufacturers have their own peculiarities; some make plastic plugs, while others make metal ones. In our conditions, it is difficult to say exactly what is beneficial. Plastic cannot be corroded, and the metal plug can rot and collapse after winter, rendering the mechanism unusable. Especially if the boot is torn. This is a protective rubber band that protects the hinge from dirt, sand, and moisture.
To understand the principle of operation, you need to remember that the connection is not rigid, that is, movement occurs there, but in a limited “circle”. For example, when a car turns into a corner, a natural roll occurs. It is necessary to distinguish that the effects on the body and suspension are multidirectional. Thus, if this is not compensated for, the risk of damaging the “bone” eye or the hub increases. Simply put, the “bone” plays the role of a kind of damper that “damps” the effects on the suspension.
Almost the same situation is with the “eggs”, which also provide “live” fastening of the strut and stabilizer. For example, in a design where “eggs” are used, the upper bushing allows the stabilizer to take the desired position, “removing” rolls from one side to the other.
By the way, many probably didn’t know, but there are even electrically controlled racks that, thanks to systems and stability complexes, block the “bones” at the right moment. As a rule, I use such mechanisms on premium models.
Main symptoms and malfunctions
So, you can even make a small list of signs that may indicate a failure:
• A knocking sound appears when driving on uneven and bumpy roads, provided that the hinge “bone” is installed. If the mechanism has bushings, it is quite difficult to determine while driving, because in this case, the sound is quiet and it is not possible to hear it in the cabin.
• The need for constant “steering”.
• The car began to roll much more when turning.
• Strong body sway during sudden starts and braking.
Often, malfunctions are associated with hinge mechanisms. One of the first problems is the destruction of the anther. As a result, the hinge becomes clogged and wears out. An equally common problem is also the banal erasing of the tip on the “finger” (ball). As a result, it fights in the “nest”, gradually destroying the “clip” itself.
Failed element
In principle, the repair is not difficult, but taking into account all the costs, buying a completely new part is much cheaper. Therefore, it is easier to replace with a new mechanism.
Much less often, the “plug” fails, which ensures reliable fixation of the ball in the “socket”. From the above we can conclude that the basis for long-term operation of the rack is the correct operation of the machine, as well as periodic diagnostics of the unit. Particular attention should be paid to the protective “cap”, which looks like a boot.
Dirt and rust under the strut boot
With “eggs”, as a rule, problems are associated only with the “eaten” rubber band, which is why the strut itself and the stabilizer interact directly, which is why a characteristic knock appears. Less often, the stand breaks at the welding points.
How to check the functionality and serviceability of a part?
Checking the serviceability of the hinges is not as difficult as it might seem at first glance. In principle, as far as the suspension is concerned, the “bones” are the most diagnosed node. There are several simple ways to check:
1. Try to rock the car, but keep in mind that you need to rock it laterally, away from the movement. If you manage to rock the body without much effort, then the first sign that a problem with the “bones” is just around the corner. Moreover, during swinging, depending on the degree of wear, even a characteristic knock may be heard.
2. The second method is somewhat more technologically advanced; you have to turn the wheels to the side. This way, you have direct access to the rack; you can check the play with your hand. However, you will need an assistant who will pump the car. A small clarification, one person checks with his hand, the other rocks the car.
Look at the condition of the anthers; if they are damaged, then it is likely that the racks will not last long. Theoretically, you can buy anthers and replace them, but in fact, it’s cheaper to buy a ready-made kit. In addition, pay attention to oil drips; if there are any, it means there is a high probability that there is almost no oil left there. These facts are especially helpful when buying a used car; contact us here first when checking this unit.
3. There is another way, but it will take a little work. By the way, this method is useful for those who do not have access to the racks even with the wheels turned out. You will have to remove the wheel and place a reliable ledge under the ball joint in order to “unload” the stabilizer itself. Thus, you have direct access to the fasteners, where you can easily determine whether there is play or not.
If the car has struts of a cheaper class, with bushings, then it is much easier to determine their wear. You literally don’t need to do anything, just look at them; if the tires have become worn out, you can safely change even just the bushings. If neglected, then soon the metal elements will come into “direct” contact.
Bushings and stabilizer struts for Volkswagen Polo Sedan
Malfunctions of the stabilizer struts
Malfunctions can be identified by knowing the symptoms and signs of malfunction. If problems occur in the operation of the stabilizer struts, the following symptoms appear:
- There is a characteristic knocking noise when driving on rough roads. This symptom occurs on machines that have racks with ball joints. For example, the stabilizer knocks when moving over a speed bump (an artificially created unevenness in the road to reduce speed).
- While driving on a flat road, the car pulls to the left and then to the right.
- During a normal turn, the car rolls (tilts) more than it was before.
- There is a lateral swaying of the car body when driving on a flat road.
Causes of breakdowns of stabilizer struts
The most vulnerable element in this assembly is the hinge joints. The reasons may be the following:
- The boot has ruptured, causing dust to get onto the lubricant and into the joint itself.
- The ball pin race has worn out. In this case, the ball pin dangles in the seat.
Repairing racks is a complex process. For this you need good factory equipment. You can simply replace the worn part, ball pin or bushing. The cost of such work is high. Therefore, it is better to buy new stabilizers. It is not necessary to buy original ones, you can buy regular ones, they also work well.
Signs of failure of stabilizer struts
The main sign of wear on the stabilizer link is a metallic knock when driving over uneven surfaces. It can be confused with the knocking of a ball joint, but if the latter fails, it is usually the same one that “drums” (if the left front ball joint starts to play, the knocking will come from there). In the case of stabilizer struts, the failed right “bone” will also tap when the left wheel passes over an uneven surface , but not as loudly as on the “sick” side.
Stabilizer struts, photo dr1ver.ru
Without a trip to a diagnostic station, the best way to check your stabilizer bars is to drive out onto a gravel road. But on highways and in the city with a good asphalt surface, they may not provide comfort (with the exception of speed bumps). Off-road, if it’s really time to change the struts, they will drum properly.
Stabilizer links can also knock due to loose nuts on the pins. In some machines this is a “sore” - the problem is solved with thread lockers or cotter pins. But if you need to dismantle such a “bone” to repair other suspension components, you may not be able to do without an angle grinder.
An inspection in a pit or on a lift will confirm or refute the failure of the “bones” - in advanced cases, the hinges will knock even if you shake the racks by hand. Ball boots with cracks or tears are also a sign of the imminent death of the stabilizer struts (if they are not knocking yet, they will soon start).
How to check stabilizer links
You can find out the condition of the racks with ball joints very simply:
- To do this, you need to stand on the side of the car and rock it. If the car easily rocks sideways, this means that the stabilizer strut joints are out of order. If the strut itself is faulty, a knocking sound will be heard in the wheel area.
- Turn the wheels as far as possible in one direction. Now one rocks the car sideways, the second one touches the stabilizers and feels if there is any play. There should be practically no play.
- Check the condition of the anthers. If it is torn or not at all, you will have to replace it. An unprotected hinge mechanism will not last long.
If the car has stabilizers installed not with balls, but with bushings, then it is even easier to check. It is enough to see if the rubber has worn off on only one side. If the tires are worn out, replacement is required. It is better to check tire wear when the wheels are inflated. See what the tire pressure should be for your specific make and model of car. Basically, for passenger cars, the pressure is set at 1.9-2 Atmospheres.
To save money, you should not immediately go to a service station and carry out paid diagnostics. You can do some easy diagnostic tests yourself. In addition, not all people are honest; they can exaggerate and replace what is not needed.
The influence of stabilizer struts on movement
From all of the above features, we can freely say what the stabilizer struts influence. The driver must first of all understand how to behave when cornering and generally drive correctly.
Stabilizer struts affect the following points:
- movement of the vehicle in general;
- without them it is impossible to operate the machine;
- there is a risk of getting into an accident;
- constant noise.
If the struts are worn out, the car will not be able to protect itself from skidding, since the hinges at the ends will not perform their functions. The driver gradually begins to feel a less smooth movement, there will be a feeling of riding on an ironing board. It will subsequently seem so unstable that the car enthusiast will be afraid to get behind the wheel. Quickly worn-out parts are a sign of careless driving, and when the struts are almost worn out, you need to hold the steering wheel with even more confidence than when the struts were still in good condition.
In addition to all this, do not forget that they also connect the anti-roll bar to the suspension arm, so it’s simply not possible to drive without struts. They have a fairly low price on the market and, as a rule, one of these is enough for six months of driving. In any case, there must be a component that allows you to do what the anti-roll bar does.
Do not forget about the risk borne by the driver. With worn elements both front and rear, you can drive, but not freely. At the same time, the driver is responsible for his own actions. The likelihood that a car will drive into a pole increases many times over, and in winter almost every driver will be able to visit at least one snowdrift.
When any element of the car dies, it lets you know by making a sound. When a driver is asked the question “what is the effect of the stabilizer struts,” everyone freely answers: “the struts make a rattling sound.”
Important: If a person experiences discomfort while driving and often skids and hears a rumble, this element definitely needs to be changed. Moreover, they rattle both front and rear, because the struts most often wear out both at once.
How to change stabilizer links
To learn how to change these racks, it is enough to make the change once as an assistant. Obviously, depending on the make and model of the car, the design and replacement methods are slightly different.
Necessary tools for replacing stabilizer struts:
- jack;
- keys;
- hexagons;
- mount.
The front pillars are longer than the rear ones. You should not change only one strut, you need to change either both front ones or both rear ones.
During replacement, the machine axle must be hung and loaded, that is, after jacking up and removing the wheel, a stand must be placed under the ball joint. In this case, the stand and stabilizer will be in a relaxed state.
During repairs, you need to be careful with the anthers so as not to tear them. If they require replacement, it is better to replace them immediately.
Which racks to choose
Now you can buy plastic stabilizer struts. They have less strength, are destroyed if something happens and do not cause harm to other parts and passengers of the car.
Length plays an important role when choosing racks. You should pay attention to the length. You also need to look at the packaging, it says what cars they are suitable for. Stabilizers and struts are interchangeable for models of the same brand, for example, for Ford Focus, Ford Fiesta, Ford Escort, Ford Ka 1995-2001, these parts are interchangeable and fit together .
Rating of stabilizer struts
Below is a list of stabilizer struts by rating:
- Lemforder (Lemforder). Country: France. Such racks are purchased from them by manufacturers General Motors, Mitsubishi, Toyota, Opel, Volkswagen, Mersedes-Benz, Audi, BMW, Ford, Volvo, Fiat and some other brands. Reputable quality and good resource.
Reviews (+) Reviews (-) Lehforbeck tested it in an Opel Omega B, Opel Vectra C, Huyndai Santa Fe New. Had no problems with them either. Lemforder is not suitable for Japanese cars. I can easily drive more than 35 thousand km. No problem. After 0.5 years of operation, the Lempherder began to knock. - Topran (Topran). Country: Germany, China. The country code will tell you where the part was made.
Positive reviews Negative reviews For the money this is a good option. I haven't found any problems with the Opel Omega B yet. They started knocking after 5 thousand km. The stand is a consumable item. Therefore it is necessary to change often. Over 50 thousand km there are no squeaks or knocks. - Sasic (Sasik). Country: France (Normandy). Renault (Renault), Peugeot (Peugeot), Citroen (Citroen) install them on their cars. The cost is not high, the quality is good.
Good feedback Bad reviews Chinese analogs lasted 10,000 km. We installed Sasik until we drove 15,000. After a short run of 5,000 km, these stabilizers sat down. Not very expensive and they last. They burst within 2 weeks. - GMB. Country: Japan. The main consumers are Japanese and Korean cars: Toyota, Nissan, Mitsubishi, Hyundai, Kia, Renault, Suzuki, GM.
Good feedback Bad reviews GMB for a mileage of 35 t.km showed no problems. No negative reviews found The old Pajero (Pajero) had no problems with stabilizers. - CTR. Country: South Korea. Among the consumers are the following car factories: Ford, Kia, Hyundai, GM, etc.
Positive reviews Negative reviews I've only recently been using it. For 2 months there are no crunches or squeaks. When there is nothing else to bet, it will do. Withstands cornering loads well. After 10 thousand kilometers they began to knock. Perhaps it was a fake. - Sidem (Sidem). Country: Belgium. Popular brand. It has 80 factories around the world.
Positive reviews Negative reviews If you can buy a Belgian-made one, there will be no problems. Nowadays you can find them made in China and they don’t last long. . - Links Master. Country: Russia (Tver). Prices are lower than their counterparts. No reviews have been left yet. If you used it, write in the comments and I’ll add it.
Whether the reviews are real online or not is unknown. But everyone should understand that how long the stabilizers and struts will last depends on the style and manner of driving.
Helpful advice: do not brake on bumps (for example, on a speed bump). You need to brake before the obstacle. This simple action can extend the service life of many parts of the car's chassis.