What is the octane number of gasoline and what does it affect?
Many people do not know the octane number of gasoline - what it is, what effect this fuel indicator has on the functioning of a gasoline internal combustion engine.
The indicator is a measure of the chemical resistance of gasoline to spontaneous combustion. The higher it is, the more resistant the fuel is to detonation. Spontaneous combustion provokes increased wear of the motor and reduces its service life.
During the operation of a gasoline internal combustion engine, at the moment of compression, the piston begins to compress the fuel mixture. When high pressure is reached, it can spontaneously ignite. This phenomenon is problematic if it occurs before the spark plug fires.
The detonating fuel-air mixture provokes the appearance of high-pressure waves that collide with each other. This condition leads to burnout of the pistons in the engine cylinders and increased wear of the entire structure.
To eliminate the occurrence of a negative phenomenon, a warning system is installed on new cars. It provides control over the development of negative processes during engine operation. Such a system consists of special sensors that record changes characteristic of detonation and are controlled by a computer unit.
When changes occur, the engine operating mode changes, which prevents detonation.
General concept
The combustible mixture of fuel and air is compressed in the cylinder before ignition. Moreover, the compression ratio depends on the engine design and is in the range of 7–10. An important point: gasoline must ignite at a certain moment when a spark discharge is applied to the spark plug electrodes.
Reference. It's worth clarifying what engine compression ratio means. This is a figure showing how many times the combustible mixture is compressed before ignition. It is calculated simply: the total displacement of the cylinder is divided by the volume of the combustion chamber. In old engines this figure is 7, in more modern engines it reaches 9–10.
If the air-fuel mixture ignites prematurely during piston compression (as in a diesel engine), the following will happen:
- Self-ignition of gasoline causes a micro-explosion - burning at too high a speed.
- The flash energy propagates in two directions - towards the piston and the combustion chamber.
- Since all the valves are closed, the shock is reflected from the walls and hits the piston, which continues to move upward. There is a loud metallic knocking sound from the piston pin.
The octane number of gasoline characterizes its resistance to detonation and is defined as the percentage ratio of the mixture of two hydrocarbons included in the fuel:
- isooctane, practically incapable of spontaneous combustion at high pressure;
- n-heptane, on the contrary, flares up under slight compression.
The detonation characteristic of isooctane is assumed to be equal to 100 units, n-heptane - zero. The greater the proportion of the first substance, the higher the resistance of the fuel to self-ignition during compression.
The maximum octane number of 98 units in the gasoline marking means the greatest resistance to detonation. This fuel is intended for engines with the highest compression ratio - 10. Accordingly, grade 95 fuel is suitable for engines that compress the mixture 9 times (the vast majority of these). Obsolete versions of power units with a compression ratio of 8 use A-92 gasoline.
The letter “and” in the letter part of the AI-95 gasoline marking means that the octane number was measured using a research method.
Octane number and compression ratio
The engine's high compression ratio produces more power while using less fuel. This value is a measure of how much the air/fuel mixture is compressed in the combustion chamber of an engine cylinder.
In new gasoline internal combustion engines, this figure reaches 10 to 1. Such engines are equipped with direct fuel injection systems. If the engine is equipped with supercharging, then the compression ratio is lower.
The detonation resistance of the fuel mixture has a significant impact on engine performance.
High compression is used in the internal combustion engines of sports cars. Sports car engines require high-octane gasoline. The presence of a high compression ratio in the cylinders requires the fuel to have a high degree of detonation resistance to prevent damage to the engine during operation.
Increase in HP
Drivers are often interested in how to increase the octane number of gasoline or lower this figure. Increasing the OP is considered a simpler process than decreasing it. This may be the addition of a special anti-knock agent or the use of a complex technological process. It is the first option that is usually preferred.
The following substances can be used as anti-knock agents.
- Alcohol additives make it possible to achieve an increase in fuel rating by about 3 units, if we are talking about adding 1/10 of ethyl alcohol to 92 gasoline. As a result, we will get 95 fuel. Exhaust toxicity will also be reduced accordingly, but vapor pressure will quickly increase, which can cause vapor locks to form in the fuel line system. Also, do not forget about the hygroscopicity of alcohol. The fuel obtained in this way must be stored appropriately and the amount of water in the mixture must be controlled. If water gets into the engine, the consequences may require expensive repairs.
- Tetraethyl lead was previously used by manufacturers to increase knock resistance (since 1921). The substance has increased anti-knock properties, but is classified as super toxic and contributes to the failure of oxygen sensors in the exhaust system and catalysts. The chemical formula of the substance is Pb(C2H5)4, it boils at a temperature of 2,000 degrees Celsius, and is distinguished by high viscosity. The octane number increases by 17 units with the help of this additive. Since combustion of the substance leads to the formation of lead oxide and it settles on the internal elements of the engine, causing carbon deposits on pistons and valves, it was not used in its pure form. As an additive to tetraethyl lead, products were used that promote the removal of lead oxide - dibromoethane, dibromopropane or ethyl bromide.
- It is safer to use special additives in the form of paraffin and aromatic hydrocarbons. In most cases, their use requires sealed storage of gasoline due to the high degree of volatility of such components. You can increase the OC yourself using additives. You just need to buy one of them and add it to gasoline. As an option, you can use ASTROhim Octane Plus, which increases the OR by 3 - 5 units, Lavr Next Octane Plus, which increases the OR up to 6 units, "Octane Plus" Octane Plus, which helps increase the OR by 2 - 2.5 units, as well as methyl tert-butyl ether .
How is the octane number of gasoline determined during production?
The required indicator of fuel detonation resistance is achieved during production by shifting the balance between the components of gasoline in one direction or another. The main components of gasoline are isooctane and n-heptane; other components do not have a significant effect on the indicator.
Isooctane is a practically non-explosive compound. It does not respond to increases in pressure and temperature to a certain limit. The resistance of this compound is taken to be 100 units.
N-heptane is the exact opposite of isooctane. This fuel component has virtually no resistance to increased pressure and temperature. This compound is capable of self-detonation, for this reason its durability is taken as 0 units.
A mixture of the main components in different ratios allows you to adjust the indicator, obtaining fuel with values of 80, 92, 95, 98.
There is fuel with an index of more than 100 units; to obtain it, various additives are added to pure isooctane.
Is it possible to mix 92 and 95 gasoline? What consequences?
Modern oil distillation technology allows you to immediately obtain 92-grade gasoline. 95 differs from it in the presence of light ether additives. Accordingly, gasoline with a higher octane number has a lower specific gravity. When two types are mixed, fuel is formed with a certain average indicator of detonation resistance. However, if you leave the car parked, the gasoline will separate. At the bottom of the tank, near the intake pipe of the fuel pump, there will be a heavy 92, and at the top - a 95. As a result, the engine will first produce low-octane fuel and then high-octane fuel. In the situation with 92 and 95, this will not cause much harm to the engine.
It’s worse when motorists try to “reach” the octane number of 80 to 92 in this way. In this case, after separating the fractions, the engine has to run at 80.
Given the small difference in the cost of fuel with different octane numbers, attempts to mix them are not economically justified.
Measurement of RON and NMR
2 methods have been developed for determining OC:
- research;
- motor.
The first method involves testing the fuel for its degree of resistance to detonation by placing a moderate load on the gasoline engine.
Fuel studies are carried out on an equipped stand. In this case, a single-cylinder internal combustion engine is used with a variable load on it and holding 600 rpm. The temperature of the air supplied to obtain the air-fuel mixture should be +52°C with an ignition timing of 13°.
The engine is started using the fuel being tested. After detonation changes appear, the engine is switched to standard mixtures of isooctane and n-heptane in different ratios. After detecting the occurrence of detonation on the reference mixture, the tests are stopped. The volume of isooctane in the gasoline sample under study represents the octane value of this type of fuel.
If the fuel labeling contains the letter “I”, then the indicator was obtained using a research method.
The motor method involves determining detonation resistance under driving conditions with increased engine load. The number of revolutions during the determination should be 900 per minute, the temperature of the air-fuel mixture should be +49°C, and the ignition timing should be variable.
The process of determining the fuel stability indicator is similar to that used in the research method.
Using devices
To determine the isooctane content in fuel, you can use a specialized device - a digital octanometer. The device is simple and easy to use.
The principle of its operation is based on comparing the gasoline under study with reference samples. For this purpose, the dielectric properties of the fuel are used at different ratios of isooctane and n-heptane in it.
This technique is not certified in Russia, and for this reason the device cannot be officially used for research.
When using different research methods, the detonation resistance indicator of the same type of fuel may differ slightly.
Gasoline labeling
At gas stations you can find a variety of names, not excluding those that are most familiar to most motorists. Typically, gasoline is marked with the letters “A” and “AI”. Their decoding:
- “A” - this designation indicates that the gasoline is for automobile use;
- “AI” - the letter “I” means the method by which the octane number was determined.
There are 2 ways to determine the octane number - research (AI) and motor (AM).
Research method - it is determined by testing the fuel on a single-cylinder power plant, subject to a variable compression ratio, crankshaft speed of 600 rpm, ignition timing of 13° and air (intake) temperature of 52 ° C. These conditions are similar to light and medium loads.
Motor method - its determination is carried out on a similar installation, but other conditions are different. The air (intake) temperature is 149 °C, the crankshaft speed is 900 rpm, and the ignition timing is variable. This mode is similar to high loads - driving uphill, running the engine under load, etc.
Consequently, the number of AM is always lower than AI, and the difference in readings indicates the sensitivity of the fuel to the operation of the power unit in different modes. It is noteworthy that in some countries in the West, the octane number is defined as the average between the “AM” and “AI” values. In the Russian Federation, only a higher “AI” value is indicated, which can be seen at all gas stations.
The effect of gasoline with an octane rating higher or lower than that recommended by the manufacturer on the engine
Each brand of car must be operated on the fuel specified by the manufacturer. When refueling your car with the wrong type of gasoline, you should listen to the engine.
If its functionality is stable, but there is a loss of power, then nothing bad happens; you need to remove all the filled gasoline and fill the car with fuel with the desired detonation resistance value. During operation on unsuitable fuel, dynamic driving should be avoided; this will prevent the occurrence of detonation and overloads.
If, when the engine is running on inappropriate fuel, ringing sounds appear, which inexperienced car owners confuse with the knocking of valves, then operating the car is undesirable.
The propagation of the detonation wave leads to engine wear and can cause pistons to burn out. Long-term operation of the engine, even under conditions of natural detonation, is unacceptable.
When using high-octane fuel in an engine designed to run on low-octane gasoline, a complete reconfiguration of the intake-exhaust system is required; in some cases, replacement of components may be required.
When using high-octane fuel, the explosion time of the air-fuel mixture is prolonged, which requires reconfiguring the operation of the valves and ignition system. Operating the engine in an untuned state provokes an increase in its wear and loss of power, which is associated with delayed fuel combustion.
The influence of the engine rating on the characteristics of the power unit
The relationship between the combustion rate of gasoline and the OS is linear. The lower the octane number, the less time it takes to ignite the fuel assembly, which directly affects fuel consumption - if it burns faster than it should, then it enters the combustion chamber at a speed increased by the corresponding value. But this does not mean that by simply increasing the engine speed, we can save: if combustion occurs more slowly than it should, this is also bad, since the engine efficiency decreases, which leads to a loss of engine throttle response and a deterioration in dynamic characteristics. By filling an engine running on 95-octane gasoline with fuel with an octane rating of 92, you will get an increase in consumption. If the situation is the opposite (instead of the working 92 we fill in the 95), the consumption will remain the same, but the engine power will decrease. So using the wrong gasoline is possible, but not advisable. It is recommended to do this only under force majeure circumstances, but not on a regular basis.
Increasing and decreasing the octane number of gasoline
Gas stations do not sell fuel containing AI-76 and AI-80, but there is a large amount of equipment that operates using low-octane fuel.
When operating devices designed to operate on 76 gasoline or 92 gasoline, uneven functionality of the equipment is observed. Engines using the wrong gasoline either start poorly or stall immediately after starting. For this reason, before using 92 gasoline for such equipment, its detonation resistance should be reduced to the required level.
There are several ways to carry out this procedure:
- you can leave the fuel canister open for several days;
- use kerosene as a fuel additive.
Using the first method, you can achieve a reduction in detonation resistance by 0.5 units. per day. The second method is more complicated, because it is difficult to find the required proportions.
Both methods require an initial measurement of the existing knock resistance value.
If there is a need to increase the fuel's resistance to detonation, various additives are added to it, which are paraffin and aromatic hydrocarbons. It is important that the components of such additives have a branched chemical structure. The stronger the smell of gasoline, the higher its durability. For this reason, storing fuel in open containers is not recommended. This method leads to a decrease in the resistance of gasoline to detonation.
Determination of the knock resistance of gasoline
The knock resistance of gasoline is expressed in its octane number.
The octane number of gasoline indicates that this type of fuel has the same knock resistance as the reference comparative mixture of hydrocarbons - isooctane and normal heptane. Since isooctane has an octane number of 100, and normal heptane has an octane number of 0, an octane number of 80 means that the knock resistance of gasoline is equal to the knock resistance of a mixture of 80% (parts by volume) isooctane and 20% (parts by volume) normal heptane. Knock resistance increases with increasing octane number.
The octane rating is determined on an appropriate test bench using a reference engine to evaluate the knock resistance of different fuels. The reference in this case is a single-cylinder, four-stroke benzoin engine with a thermosyphon liquid cooling system, in which there is no pump, and the coolant evaporates and low-pressure steam condenses in the radiator, and then returns to the cooling jacket as condensate. The engine compression ratio during testing can vary between 4 and 18.
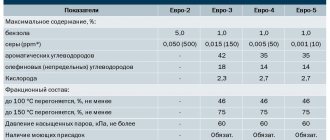
There are two standardized testing methods: the exploratory method and the motor method. Accordingly, the results are the research octane number of gasoline (ROZ) and the motor octane number of gasoline (MOZ). The differences in the main parameters of both methods are shown in the table.
Table. Differences in parameters of exploratory and motor methods
In the motor method, the mixture of air and gasoline is heated behind the carburetor, and in the research method, the air is heated in front of the carburetor.
The reference motor is started and connected to a large electrical generator, in which the torque from the reference motor excites an electrical current that produces a braking torque. The octane number is always measured in the strong detonation mode during combustion of the working mixture. In this case, the excess air coefficient is adjusted so as to obtain detonation of maximum intensity. An inductive sensor and an electronic signal amplifier measure the level of detonation and display the readings on the display of a special device - a detonometer. The engine compression is adjusted so that the detonometer readings of the gasoline being tested are in the middle of the instrument scale. Then two comparative mixtures are introduced into the power system, whose octane numbers differ by only two units. One comparison mixture should cause stronger and the other weaker detonation than gasoline. Using linear interpolation, the octane number of gasoline is determined and rounded to tenths.
The same gasoline tested using the motor method has a lower octane number than that detected using the research method. The octane number determined by the motor method in modern gasoline is approximately 10 units less than the octane number determined by the research method. This difference is due to the fact that the ratio of olefins and aromatic hydrocarbons in the two test methods is different. Today, the research octane number in gasoline is approximately 92, and in premium gasoline it is 95 units. The octane number, determined by the research method, indicates how the fuel behaves during acceleration (detonation during acceleration).
The octane number determined by the motor method, on the contrary, indicates behavior under heavy load (detonation at high crankshaft speed).
Along with research and motor octane numbers, there is also a road octane number (SOZ). It is determined by road testing the vehicle according to the “modified road method”. Various comparative mixtures of isooctane and normal heptane are fed into the warmed-up engine. The car first accelerates to maximum speed in direct gear, allowing smooth movement without jerking. The ignition timing is adjusted until detonation disappears. As a result, the test data forms the base curve shown in the figure.
Then, using the same method, the ignition setting at which detonation begins is determined for the gasoline under study. The base curve determines the road octane number of gasoline. This value will have different values for the same gasoline in different engines.
What could this lead to?
I hope you understand that if you constantly fill up with fuel that is not the best, then gradually many components of the unit will say goodbye to you. Spark plugs will very quickly become unusable and if you notice a red coating on them, then everything is bad, quickly take it to service. You may also detect incorrect operation of the catalyst. Since this is fuel, almost all elements of the fuel system, such as the fuel pump, filter and injectors, will very quickly become unusable.
Unfortunately, you don’t always find problems right away, since they form gradually and everything can break down after a few months. But there are times when problems appear after a couple of days. This depends both on the gasoline and on the car itself, as well as on how worn some parts have already been.
Cetane number of diesel fuel
Gearbox ratio: what it means and how to calculate it
It is the main characteristic of the flammability and combustion of diesel fuel in the engine. The higher it is, the calmer and more complete the fuel mixture burns out.
In numerical terms, this indicator is comparable to the volume fraction of cetane in a specially prepared mixture. This mixture consists of hexadecane and α-methylnaphthalene with the same lag period as the test fuel.
For standard engines, diesel fuel is considered optimal, the cetane number of which varies from 40 to 55. Diesel fuel with a cetane number from 51 to 55 units is considered the highest quality. Premium diesel fuel is lighter, it contains flammable fractions that help the engine start quickly at sub-zero temperatures. When using it, the smokiness is noticeably reduced.
The cetane number of diesel fuel depends on what paraffins, aromatics, olefins and naphthenes are included in its composition. For measurements, use a standard Waukesha power unit or IDT-90. An alternative could be a chamber with a constant volume; testing with this method, unlike the first, takes no more than 20 minutes.
FuelEXx Diesel is recognized as an effective way to increase. It increases this indicator by 3–5 units. At the same time, water is removed from the fuel, the piston rings are decarbonized, and the combustion chamber is cleaned. This has been confirmed by bench and road tests.
How to check the brand of gasoline at home
Gasoline may be good, but whether it is the right brand is another question. Often they sell 92 under the guise of 95. By color, smell, setting fire, dripping is useless, only chemical analysis or the simplest knowledge of physics will help here.
The density of different types of fuel is different. To check, you need a simple hydrometer. We dip the device in gasoline and compare the readings with the table:
| Gasoline brand | Density, g/cm3 |
| AI – 80 | 0,700 – 0,750 |
| AI – 92 | 0,715 – 0,760 |
| AI – 95 | 0,720 – 0,775 |
| AI – 98 | 0,730 – 0,780 |
Density readings vary depending on fuel temperature. To more accurately determine the type of gasoline, it is better to take the verification data at the gas station and compare it with your data.
Check directly at the gas station
So, we have found out how to check the quality at home, with this you can find the best station in your city and refuel there. But there are situations when you urgently need to refuel on the highway. What to do in this situation, especially if the nearest gas station is not the most famous of all. Fortunately, the modern world is now and there are many devices that seem simple, but they will help very well.
One of these is Octis 2, it costs about 5 thousand rubles, which is a bit much. But the point is that only 100 milliliters are needed to reveal the exact amount of octane in the fuel. There are also other devices that can also be used to find out about diesel fuel (diesel fuel) and how good it is.
You can also check it after you have refueled, but problems will arise here; if the quality is not the best, you will have to quarrel with the administration and everything else. We have already talked about this in one of the articles, link above.
If the tank is almost empty, add new fuel and start the engine. If the speed jumps, you hear some suspicious engine sounds, and you can also hear that the fuel is burning unevenly. We congratulate you, but what you have in the tank is so-so “food” for the engine. You can also check all this while driving, listen to see if there is so-called detonation of the fingers. Your task is to accelerate to maximum gear, 5th or 6th, depending on the car. Then sharply press the gas pedal to the floor, if there is a sound of detonation of the fingers, then everything is bad, run to fix it.
Also pay attention to the smoke from the exhaust system; if the fuel is bad, it will be black with soot. High-quality fuel produces brown or bluish smoke. Besides all this, you can find out about bad fuel if you notice a sharp increase in consumption, which can be bad or even terrible for the injector.
Here are all the symptoms:
- jumps in idle speed;
- startup problems;
- increase in consumption;
- black smoke and exhaust pipe;
- poor response to the gas pedal;
- dynamics dropped;
- finger detonation.
Is this an attraction of unprecedented generosity? No, just a bad guy!
The error for 92 gasolines was about 2%, for 95 gasoline - about 1%. This is enough to distinguish high-quality gasoline from obvious waste by its detonation resistance. But with 80 gasoline, OKTIS produced as much as 93.9 units of octane number. UIT gave much more realistic values - OCHI 81.3, and OCCH - 79.4! This is usually caused by gasoline that contains something bad in its composition, most often methanol. This is understandable: refineries are already curtailing production of the 80th, and it is becoming scarce. Therefore, it’s easier than ever to run into obvious self-destruction. That's what happened to us!
In a word, here is our opinion. You can trust OKTIS, but you should treat its readings like this: if, for example, it shows 90.5 or 93.4 on 92-octane gasoline, you can take such fuel. Ours is not an exact setting, but an indicator: what it can, it shows. But if the device readings deviate from the expected figures by a dozen or two units, either downward or upward, you should stay away from this gas station.
A few words about calibration in laboratory conditions. We resorted to it only in order to obtain a obviously reliable result. But for evaluation checks, calibration is carried out on site, in three minutes. And the device is intended precisely for them - it is not an arbitration device, but an information device.
For dessert there is a fly in the ointment: experts cannot live without it. Do not try to make claims on the quality of gasoline based on OKTIS readings. This is not an expert method, so neither the court, nor the manufacturer, nor the seller will recognize them. The device information is only for you.
Home inspection
If you wish, you can collect several containers from different gas stations in your city and check them at home in order to find out where it is best to refuel in your city. You don't need to do anything complicated to do this. Impurities are often added to fuel and this is often the main problem.
Your task is to take a regular white sheet of paper and drop a little fuel on it. Ideally, the gasoline should evaporate and leave the sheet the same perfect white. If additives are present, they do not evaporate and various stains remain on the paper; their color may be different, it is impossible to say for sure. If the stain is greasy, then there is oil in the fuel.
Also, the manufacturer can use resins and this is normal, but they need to be added in a certain amount. An experiment was conducted that found that the presence of resins in excess of the norm immediately reduces the life of the power unit by as much as 24%. Agree, it’s a little scary for the engine. Your task is to take a small piece of glass and drop gasoline on it. After which it must be set on fire. If the glass remains clean or small white rings remain, then everything is perfect, there are either no resins, or they are in the right quantity. If any drops remain, this indicates that diesel fuel, the so-called diesel fuel, has been added. If, after combustion, brown or yellow spots remain, then you can immediately mark this fuel as containing high amounts of resins.
You can also study density, but for this you need an additional device, this is the ANT-1 aerometer. Although it is not expensive, we understand perfectly well that we don’t want to spend money. He will help you, because there are very dishonest gas station owners who add additives to AI-76 and sell it as AI-92.
Density indicators for specific fuel brands:
- A-76 from 730;
- A-80 from 775;
- AI-92 from 760;
- AI-95 from 750;
- AI-98 from 780.
You can also check the quality of gasoline through color both at the gas station itself and at home. Manufacturers are required to color their fuel a certain color. AI-92 should have a roughly orange-red tint, and AI-98 blue. This will allow you to understand whether you were deceived or not.
Some people also add water, which also doesn’t have the best effect. Go to the pharmacy and buy the well-known potassium permanganate. Then your task is to find a transparent vessel, pour some fuel into it and throw in a piece of manganese. This substance does not dissolve in gasoline, but if water is present, the fuel will turn purple.
In addition, some also add hydrogen sulfide or liquefied gas. Pour fuel into a container and wave your hand towards you. Your job is to smell it and if you smell rotten eggs, you can be sure that hydrogen sulfide is present.
What should you be wary of?
First, you need to know what “beacon” indicators can tell you that “the sturgeon is not of the first freshness.”
An important, but, we warn you, not indicative factor of high-quality “fuel” is its cost. Any car enthusiast knows approximately what the price of fuel is in a particular region. Therefore, when driving past a gas station and discovering an unprecedented discount on gasoline/diesel, it’s worth thinking: why is the manufacturer so generous?
“The second “beacon” is smell. It seems that the “aroma” of freshly prepared gasoline is difficult to confuse with anything else, but if the manufacturer has gone too far with oils and additives, then the smell of the final product changes and becomes sharper, with hints of burnt rubber and household chemicals.
And finally, the most “intelligible” “beacon” - after refueling, the engine began to work unstably, tripping and stalling, and at the same time the consumption went up. True, you need to be sure that the car is technically in good working order: the fuel pump works as it should, the coils are in good working order, the spark plugs were replaced on time. If everything is fine with the car, but it doesn’t drive, change the gas station.
What will happen to the car if you drive on the wrong fuel?
To put it briefly, what will happen if the car is “treated” to the wrong brand of gasoline - nothing good. However, car owners do this often, and not always due to oversight or deception on the part of the seller. This is especially common among owners of old VAZ models, for whom they prefer to buy 95 instead of the eightieth or ninety-second prescribed for them.
There is another category of drivers who prefer 92 gasoline, despite the recommended 95, citing a low amount of impurities. Sometimes this is justified, but more often it only makes the situation worse. If a machine, in the “menu” of which the ninety-fifth brand is prescribed, consumes the ninety-second, another nuisance arises - shock loads. They damage rings and pistons, this is indicated by a distinct knocking and clinking sound when the engine is running. The gasoline mixture does not burn out completely; the residues burn out in the neutralizer. Engine components are unevenly lubricated with oil due to detonation waves. In such cases, the ignition is often rearranged or the octane corrector is adjusted. Or they do it simpler - they dilute gasoline with others in a 1 to 1 combination.
A different picture occurs if you refuel with fuel with a higher octane rating than what the factory recommended. The duration of combustion increases, as does the heat transfer. The engine overheats and oil consumption increases. The result is engine failure.
Even if it initially seems that changing the octane number to a higher one only made it better and the engine began to produce less noise, the idea should be abandoned. The poured gasoline with a high octane number is drained, the pipes and the gas tank are washed. After this, fill in the desired brand.
Important: the only case where this can be beneficial is the use of the AI-98 brand instead of AI-95. Consumption decreases, the car's throttle response, on the contrary, improves
How is modern gasoline produced anyway?
Gasoline is a petroleum product consisting of hydrocarbons with admixtures of sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen-containing compounds. The most important task in production is to achieve a balance of light and heavy fractions of hydrocarbons, on which the volatility of the fuel depends.
The simplest and most archaic method of producing gasoline is direct distillation. Oil is heated to separate light fractions (light hydrocarbons) from heavy ones - they evaporate and fall out as condensate. Direct distillation from a liter of oil usually produces only 150 ml of gasoline with a low octane rating of up to 65 units. To obtain AI-92 from it, the semi-finished product is diluted with additives that increase the octane number. But even with the addition of additives, the quality of such fuel leaves much to be desired.
Large refineries have switched to multi-stage production. In Kazakhstan, fuel is produced at three main refineries using catalytic cracking and reforming technologies. The octane number and quality of gasoline are significantly higher than in the first case. For example, the reforming process can increase the octane number of a petroleum product to 97-98 units according to the research method. But fuel additives are still needed.