VEHICLE ANTI-THEFT SYSTEM (APS)
The car is equipped with an APS-4 car anti-theft system (immobilizer), consisting of a control unit, a system status indicator and code keys.
The immobilizer is an electronic unit that prevents unauthorized engine starting, opening the necessary electrical circuits and works in conjunction with the electronic engine control system.
The immobilizer goes into security mode automatically when the ignition is turned off.
Checking the activity of the anti-theft system
First of all, make sure that the anti-theft system is connected and inactive. To do this, close all the car doors except the driver's door, get into the car and close the driver's door. The interior lamp should continue to light after closing the driver's door for another 12 seconds, and then go out smoothly. Turn on the ignition, the system status indicator LED should light up and stay lit while the ignition is on. In this case, you can proceed to the procedure for transferring the anti-theft system to the active state, i.e. carry out the so-called “training” of the system with code keys, which then become individual for each anti-theft system.
If, when the ignition is turned on, the system status indicator LED blinks at a frequency of 2 times per second, this means that the anti-theft system of your car has already been switched to an active state.
Disarming the immobilizer
To disarm the anti-theft system and start the engine, do the following.
1. Open and close the driver's door or turn on the ignition. In this case, the system goes into the “reading” mode of the key code, and the system status indicator LED on the instrument panel begins to blink at a frequency of 2 times per second. If the transition to the “reading” mode is carried out by turning on the ignition, the buzzer will emit a short sound signal.
2. In the “reading” mode, which lasts 1.5 minutes if the door was manipulated, or 10 seconds if the ignition was turned on, you should bring “your” working key to the indicator. After the system reads and recognizes the key code, the LED goes out and the buzzer emits a double beep. When the LED turns off, the engine can be started.
3. Turn on the ignition, the LED will light up briefly and go out, the engine should start.
The anti-theft system switches to security mode automatically after turning off the ignition and depends on the situation and the actions of the driver. If the driver’s door did not open or was open and not closed, then arming occurs after 5 minutes; If the driver's door was opened and closed, then arming occurs 30 seconds from the moment the door is closed.
In all cases, 15 seconds before arming the system, the buzzer starts beeping at an accelerating pace. If arming is not desired, then you must turn the key to the “ignition” position.
If, when you turn on the ignition, the system status indicator LED does not light up, but flashes at a frequency of 1 time per second for 20 seconds, this means the following:
1) there is no electrical connection between the engine control controller and the immobilizer unit. Check the connection in the engine control system harness;
2) the engine control controller was previously “trained” with code keys from another immobilizer unit. The engine will not start. Contact a service station;
3) if, when the ignition is turned on, the LED does not light up and blinks at a frequency of 5 times per second for 20 s, this means an error in the immobilizer unit. If this flashing does not stop even when the ignition is turned on again, you must contact a service station.
Immobilizer “learning” procedure
If you are convinced that the anti-theft system is in an inactive state, you can proceed to the procedure for “learning” (coding) code keys. To do this, follow these steps:
1. Turn on the ignition. The LED of the system status indicator should light up with a steady, non-flashing light no later than 5 s.
2. Bring the red code key marked “APS-4” to the indicator.
3. Hold the red code key near the indicator and turn off the ignition. The LED should remain lit and the control unit buzzer will emit a short beep.
4. Remove the red code key from the indicator. No later than 5 seconds after turning off the ignition, the LED should start flashing at a frequency of 10 times per second. If this does not happen, without turning on the ignition, wait at least 15 seconds and repeat operation step 1.
5. No later than 20 s after the LED starts blinking, bring the first black code key marked “APS-4” to the indicator. The buzzer should sound for about 1 second and the LED will turn off during this time.
6. Remove the “trained” black key. No later than 20 seconds after the LED resumes blinking, bring another black key to the indicator. The buzzer should sound for about 1 second, and the LED will go off during this time.
The anti-theft system allows you to “train” up to four black coded keys. Repeat the procedure for training them in accordance with paragraph 6.
7. Remove the second “trained” black key and no later than 20 s, bring the red key to the indicator. The LED will light up and the buzzer will beep. Remove the red key from the indicator.
8. No later than 15 seconds after the LED turns on, turn on the ignition.
If your car has an M1.5.4 or “January-5” controller installed, then no later than 3 seconds later the LED will go out and the buzzer will beep. After this, the ignition can be turned off. If the MP7.0 controller is installed, then after 3 seconds after turning on the ignition, the LED will continue to light. No later than 10 seconds later, while the LED is on, turn off the ignition. The LED will go out and a buzzer will sound.
9. Wait with the ignition off for at least 6 seconds.
10. Check the quality of immobilizer “learning”. To do this, turn on the ignition, a sound signal should sound, and the indicator LED should blink at a frequency of 2 times per second. Do a test start of the engine - the engine should not start for 3-5 seconds. Turn off the ignition, wait at least 6 seconds and repeat the test start of the engine - the engine should not start.
If the engine starts, this means that the “learning” procedure was performed incorrectly or the waiting time was exceeded in any interval and the anti-theft system automatically returned to its original inactive state. In this case, the “learning” procedure should be repeated, but before each repetition it is necessary to turn off the ignition for at least 15 seconds.
11. Turn off the ignition and no later than 10 seconds after turning off the ignition, bring one of the “trained” black keys to the indicator - the buzzer should sound 2 beeps and the LED should go out.
Turn on the ignition and test run the engine, the engine should start.
12. Turn off the ignition, open and close the driver's door. After 15 s, the buzzer should sound a sound signal at an accelerating pace for another 15 s, and the indicator LED should light up with a flickering light, which indicates that the automatic immobilization mode (engine start blocking) is in progress.
After this time, the buzzer should stop sounding and the LED should go into flashing mode with a frequency of 1 time every 2.5 s.
Possible emergency situations arising during operation of the immobilizer
1. Lost working black key.
In this case, it is recommended to “retrain” the second remaining working key so that the lost key cannot be used to steal a car.
Then you can purchase a second key and “retrain” the system again with two keys. Carry out “retraining” in the manner described in the subsection “Procedure for “training” the immobilizer.” The only difference is that when the ignition is turned on at the beginning of the procedure, the system status indicator begins to blink at a frequency of 2 times per second.
What is traction control system (ATS)?
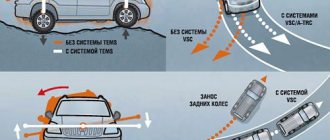
APS is a set of useful active safety functions of the car, designed to ensure optimal traction of the wheels with the road surface. It simplifies vehicle control when starting, accelerating, braking and cornering. In addition, APS significantly helps the driver cope with control in slippery road conditions.
The first traction control system was invented by American engineers and used in 1971 on Buick cars. In 1987, she developed an APS for Mercedes-Benz cars.
But these were just mechanical prototypes of modern security features. And already in the 1990s, the ASR (Anti-Slip Regulation) traction control system appeared. This was already a full-fledged APS, consisting of a set of hydraulic mechanisms controlled by electronics.
How does traction control work?
Most modern cars have electro-hydraulic APS. It is controlled by a central control system and prevents slipping of the drive wheels, regardless of the speed of the vehicle.
Its main functions are:
- in reading and analyzing information from wheel sensors;
- in controlling the amount of torque transmitted from the engine to the wheels;
- in monitoring and managing the braking system of the driving wheels.
Information from angular velocity sensors located on the drive wheels is transmitted to the main computer. If the traction control system detects that one wheel is slipping, it immediately reduces engine speed or applies the brakes to that wheel using solenoid valves in the brake system.
The choice of option depends on the speed of the vehicle. If it is less than 80 km/h, the APS uses braking of the drive wheels. If the car moves at a higher speed, the traction control system sends a signal to the central computer, which instantly reduces engine speed.
ARMING
The anti-theft system switches to security mode automatically after the ignition is turned off and depends on the situation and the actions of the driver. If the driver's door was not opened or was open and not closed, then arming occurs after 5 minutes; if the driver's door was open and closed, then arming occurs 30 seconds from the moment the door is closed.
In all cases, 15 seconds before arming the system, the buzzer starts beeping at an accelerating pace. If arming is not desired, then you must turn the key to the “ignition” position.
Types of modern APS
Each automaker installs its own security systems on its cars. Because of this, for example, only APS has several names with different abbreviations:
- ASR – installed on Mercedes, Audi, Volkswagen cars;
- DSA - used exclusively for Opel cars;
- ASC - used on all BMW cars;
- TRC – installed on Toyotas;
- TCS is our own development.
What is the ESP system?
In parallel with APS, other vehicle safety systems were developed. For example, the ESP traction control system was announced back in 1959, but only in 1995 was it first tested and installed on Mercedes-Benz cars. The abbreviation stands for electronic exchange rate stabilization (stability) system. Its main function is to control the lateral dynamics of the chassis during skidding and lateral sliding when entering a turn.
ESP is also controlled by the main computer and is activated immediately when the ignition is turned on. It constantly cooperates with other safety systems, such as ABS and ASR, and receives information from their sensors. In addition, the stability control system reads information from controllers located on the steering wheel. In other words, she always knows at what speed the car is moving, at what speed the engine is running and how many degrees the steering wheel is turned.
General principles of APS operation
Simply put, the principle of operation of the program is based on listening to these same ports described in the database. The database contains a brief description of each port - the brief descriptions contain either the names of viruses that use the port, or the name of the standard service to which this port corresponds.
When an attempt to connect to the listening port is detected, the program records the fact of connection in the protocol, analyzes the data received after connection, and for some services transmits a so-called banner - a certain set of text or binary data transmitted by the real service after connection, i.e. simulates a response and thus protects your computer and prevents a real attack. Let's look at the simulation in more detail.
How ESP works
When these sensors send alarms to the central computer, the system processes them and decides how to properly correct the situation. In the event of a skid, roll, or loss of the correct trajectory of the vehicle, the exchange rate stability system sends a signal to the ABS hydraulic modulator, which, in turn, begins to brake the desired wheel or wheels. At the same time, the engine speed decreases or increases. On cars with an automatic transmission, the speed is additionally switched in one direction or another.
Some modifications of the ESP system, in order not to interfere with the driver making a timely and correct decision, may be activated with some delay.
Often, one too strong press on the brake pedal or careless turn of the steering wheel can lead to dire consequences - from skidding to flying into the oncoming lane. To minimize the risk of such situations, engineers from leading automobile corporations equip cars with useful systems that provide real assistance to the driver and make driving extremely comfortable and simple.
ASR operating principle:
— The sensor informs about changes in the control unit, which in turn processes the received signal. — The control unit compares the wheel speeds and then transmits the command to the actuator. — The mechanism reduces the rotation speed of the wheel that is slipping and coordinates it with the performance of other wheels. Result:
The differential is not locked; as a result, when the car moves along an indirect trajectory, the wheels of the drive axle rotate in the normal mode, but at the same time have different speeds.
DISARMING
To disarm the anti-theft system and start the engine:
1. Open or close the driver's door, or turn the ignition on and off. In this case, the system goes into the “reading” mode of the key code, and the system status indicator LED blinks at a frequency of 2 times per second. If you switch to the “reading” mode by turning on the ignition, the buzzer will emit a short sound signal.
2. In the “reading” mode, which lasts 1.5 minutes if the door was manipulated or 10 seconds if the ignition was turned off, you should bring “your” working key to the indicator. After the system reads and recognizes the key code, the LED goes out and the buzzer emits a double beep. When the LED turns off, the engine can start.
3. Turn on the ignition, the LED will light up briefly and go out, the engine should start.
How does ASR work?
The drive wheels are influenced in two ways:
When the car moves at a speed of, say, 60 km/h (each brand has its own indicator), the wheel that is slipping is slowed down by the brake system. Why does this happen? The brake fluid pump, which is part of the ASR, creates the necessary pressure, the solenoids actuate the valves, which supply fluid to the brake cylinders. If the set speed limit is exceeded, the traction control control unit signals this to the engine, which in turn reduces the torque. If the car is equipped with an automatic transmission, then overdrive is activated, which leads to a “weakening” of the car’s traction characteristics.
Is it possible to disable ASR?
If necessary, you can deactivate the system. Typically, this option is useful for beginners who want to practice their driving skills on an empty road.
ASR OFF button
, which allows you to disable the option, in most cars is located near the gearshift lever or on the dashboard. When you press a key, the corresponding light will light up.
Detailed instructions for deactivating the system in your car are presented in the car's operating manual.
ALTERNATIVE ENGINE STARTING PROCEDURE
This procedure allows you to start the engine for one trip without reading the code from the working (black) key in case of its loss or malfunction of the anti-theft system. The procedure becomes possible only when the car owner himself allows it, by programming a “bypass password” consisting of six digits.
Depending on which controller is installed on your car, learning the “bypass password” and the method of bypassing immobilization is performed in two different ways.
"Doubles" of the system
Cars of different brands are equipped with similar systems that have different names. Yes, A.S.R.
- This is the prerogative of cars from the German brands
Mercedes , Audi
and
Volkswagen
.
DSA
Opel cars .
TCS
Toyota
vehicles .
ASR, like other twin systems, is part of the stability control system known as ESP
.
APS classification
Automatic fire alarm installations and warning systems are presented in different types, which are recorded in GOST under the number R53325-2012. The photo below graphically shows this classification.
Automatic alarm classification
The figure shows that two more subsections have been added to the types of information transmission: information content and information capacity.
What does information content mean? Essentially, this is the number of modes (or notifications) issued: fire, malfunction, normal, etc. There are three positions here:
- low information content – up to 3 notices;
- average – from 3 to 5;
- high – over 5.
Information capacity is an indicator that determines the number of connected loops and sensors. There are also three positions here:
- small capacity – up to 5 loops;
- average – from 5 to 20;
- large – more than 20.
What is ESP in a car?
Electronic
Stability Program ,
or
ESP
, is an electronic stability control system, also called stability control. The main purpose of ESP is to control the torque of the wheels, which allows you to eliminate lateral movement and level the position of the car.
Like ASR, the system has several analogs that are used in specific brands of cars:
- ESC
is installed on KIA, Hyundai and Honda cars . - Rover, BMW and Jaguar are equipped with DSC
. - A distinctive feature of Volvo is the DTSC
. - VSA
in Acura cars . - Toyota models are equipped with VSC
. - Subaru, Nissan and Infiniti cars use the VDC
.
Aps4 - immobilizer for cars, instructions, positive qualities in terms of appearance and operation
ATTENTION! A completely simple way to reduce fuel consumption has been found! Don't believe me? An auto mechanic with 15 years of experience also didn’t believe it until he tried it. And now he saves 35,000 rubles a year on gasoline! Read more"
Each immobilizer has its own distinctive features and operating features. The aps4 model is designed to work with domestic transport - VAZ cars. This immobilizer is a small, electronic device that must be connected to the vehicle systems by connecting wires. The efficiency of the immobilizer is high, the quality indicators are at the highest level. To install and use the immobilizer, you need to replenish the supply of important information about this model, and those who wish to do so will do this right now.
What does ESP consist of?
The system includes a control unit, measuring instruments that monitor various parameters, and a hydraulic unit.
ABS anti-lock braking system
.
— Anti-slip system ASR.
— EBD brake force distribution system
.
— Electronic differential locking system
EDS
.
How does ESP work?
External sensors analyze various parameters - the functioning of the braking system, the characteristics of the vehicle's movement, the position of the accelerator, and changes in the steering angle. This data is transmitted to the control unit. He compares the information received with the actual movement of the car. If ESP decides that the driver has lost control of the car, it intervenes in the control, that is, it uses mechanisms that are associated with other active safety systems.
Correcting the trajectory of the machine is carried out in several ways:
- By braking specific wheels. The system itself decides which wheels will brake. So, when skidding, braking is carried out by the outer front wheel.
- Thanks to changes in engine speed.
The ESP control unit also interacts with the engine and automatic gearbox of the car. This allows the system to adjust their operation in force majeure circumstances.
What is an automatic fire alarm in fire safety
An automatic fire alarm, abbreviated as APS, is a complex device that is responsible for detecting fires and notifying about their detection. Moreover, many models are associated with automatic fire extinguishing systems. That is, when an alarm is triggered, its control panel transmits a signal to the pumping units, which immediately turn on automatically.
APS is installed in all premises, regardless of their purpose, which is enshrined in legislative acts and instructions of the Ministry of Emergency Situations. Moreover, a building cannot be put into operation if it does not have a fire alarm system. Therefore, at the construction stage, a project is developed that displays the entire distribution diagram of sensors connected to each other by loops (sections of cable routes).
The main requirement for automatic fire alarm installations is timely detection of a fire and notification of people about the outbreak of a fire. And the faster the automation works, the faster the evacuation will occur with minimal human and material losses.
It must be noted that the fire extinguishing system itself is not a fire extinguishing system. It is part of the fire safety system. Today, with the introduction of security video surveillance systems, manufacturers are offering an integrated approach to solving two problems at once. To do this, the APS is connected to video surveillance channels. And such a network is called a security and fire alarm system - OPS.
Security and fire alarm
What does ABS consist of and what is its operating principle?
The design of the system implies the presence of a control unit, speed control sensors and a hydraulic modulator.
The functioning of the anti-lock braking system involves three stages: releasing pressure in the brake system cylinder, maintaining it and increasing it to the required level. In reality it looks like this:
- When braking, speed sensors transmit data to the control unit.
- The control unit smoothly reduces the speed of the car.
If one of the wheels begins to slip or has completely stopped, the sensor informs the control unit about this, which activates the exhaust valve. It blocks fluid from entering the wheel brake cylinder - the pump immediately begins returning it to the hydraulic accumulator. The result is that the blocking is removed. When the wheel speed has returned to normal, the control unit closes the exhaust valve and opens the intake valve. As a result, the pump starts working again, but now it performs the actions “in the reverse order”: it pumps pressure into the brake cylinder, which allows the wheel to be braked. All these operations are carried out very quickly. They are repeated until the vehicle comes to a complete stop.
What does this give?
During emergency braking, cars equipped with ABS slow down smoothly rather than skidding. Consequently, even in difficult road conditions the car remains controllable. The driver only needs to monitor the direction of movement of the car until it comes to a complete stop. In other words, the anti-lock braking system provides controlled braking, which helps avoid an accident.
When emergency braking a vehicle not equipped with ABS, pressing the brake pedal hard means that no matter how much you twist the steering wheel, the car will not change its trajectory. This is because locked wheels will slip and prevent the driver from maneuvering. As a result, the car will drive in a straight line, which can lead to serious consequences.
Distinctive features of the aps4 immobilizer
Immobilizer aps4 is designed for cars from the VAZ model range. This device has a number of features by which it can be recognized among a large number of other immobilizer models. These include the following:
- the possibility of contactless code reading and quick authorization of the vehicle owner;
- availability of a special code key for using the system;
- the code reader is built directly into the vehicle panel, which is located inside the cabin;
- There is a key fob for personal use;
- possibility of automatic arming;
- the presence of a maintenance mode for which a special key is prescribed;
- operation at low and high temperature conditions and minimal energy consumption by the device.
The appearance of the immobilizer makes it easy to disguise it inside the car, and the connection diagram that comes with it can help even a novice install the aps4 immobilizer on their own.
The operation of the immobilizer is no different from the functionality and capabilities of other systems in this series. The basic operating principle of almost all immobilizers is the same, but a number of additional features will depend on the model of the security device.
Nuances worth knowing about
The effectiveness of the anti-lock braking system depends on the condition of the road. If you are driving on an uneven road surface with bumps and potholes, then the car’s braking distance will be much longer than usual. This is explained very simply. When a car slows down, its wheels “bounce” for a moment. This leads to loss of traction and, as a result, the cessation of rotation. ABS perceives this as a blockage and stops braking. When adhesion to the coating is restored, the system has to rebuild. This takes time - hence the increase in braking distance. To make the ABS work optimally in this situation, simply reducing the speed of the car will help.
It should be remembered that active safety systems help the driver in a difficult situation, and do not take control of the car, so the car enthusiast should not relax - he must be prepared for anything.
Composition and types of APS
An automatic fire alarm system is a complex consisting of several technical elements:
- sensors,
- cable,
- control panel, also known as control panel,
- sirens of various types.
Several types of sensors are used for signaling:
- thermal, responding to changes in indoor air temperature;
- smoke, triggered by smoke in the premises;
- light, react to fluctuations in light flux (daylight or artificial);
- combined, often smoke and heat in one sensor.
As for sirens, these are either sound or light devices. They are often used in combination.
Types of fire alarms
Today, manufacturers and installers offer three types of fire alarm systems:
- non-addressed, they are also threshold,
- targeted or address-threshold,
- addressable analog.
Threshold
It is necessary to immediately indicate that sensors in an automatic fire network of this type can only be in two physical states: normal or fire. To move from the first to the second, there must be a change in resistance in the sensor design. This is how the signal is generated from the sensor to the control panel. The signal passes through the loop into which the sensor was installed during installation.
But there is one caveat. Up to 20 fire detectors are installed on one loop of the threshold system, so it is impossible to determine which of them worked. The control panel can indicate the loop number, nothing more.
To increase the quality of threshold APS automation, additional resistance is installed in sensor devices. Plus, a resistor is mounted at the end of the cable route. This solves two problems:
- conditions appear for the creation of two additional operating modes: “attention” (this is when the preconditions for a fire appear) and “probability of fire”;
- it becomes possible to reduce the formation of false alarms.
That is, the alarm starts the fire hazard and fire extinguishing mode only if at least two sensors are triggered simultaneously.
The advantage of threshold systems: ease of installation, plus the low price of the equipment. Disadvantages - difficulty of maintenance, high probability of false alarms, which are influenced by a considerable number of different factors: dust, condensation, etc.
Threshold APS
Address-threshold
This type of automatic fire alarm and warning system is more advanced. The thing is that the installed control panel is programmed with a different sensor polling algorithm. The latter (each) is assigned its own unique address. Therefore, the control and receiving device distinguishes each device and will not confuse it with any other.
In this case, the remote control constantly polls the sensors not only for their fire status, but also for malfunctions (specific causes). This is convenient in the sense that maintenance is minimized, because the control panel itself shows which sensor is not working and for what specific reason. But these are not all the modes in which the sensors can be located. In addition to “normal”, “fire” and “malfunction” there are other modes, for example, “attention”, “dusty” and so on. It should be added that sensory devices themselves move from state to state. This makes it easier to determine the exact location where the fire started, or which of them is currently out of order.
In SP5 (set of rules) under number 13130 there are conditions under which only one automatic addressable threshold fire alarm sensor is installed.
- If buildings or structures belong to the fifth fire safety category.
- If the process equipment may cause a fire during startup.
- If the fire area (planned) is not larger than the sensor coverage area. The last parameter is indicated by the manufacturer in the device passport.
Address-threshold APS
Analog addressable
In essence, this is an address-threshold automatic alarm. Only it contains a better algorithm for processing the data that comes from the sensors to the control panel. At the same time, the control panel records various factors that can change the sensor readings, filtering them out. And this creates conditions to avoid almost completely false inclusions.
The positive aspects of the operation of addressable analogue automatic systems include the ability to work when the loop breaks. And the latter have a variety of shapes and configurations for connection and distribution throughout the premises. Most often, installers use ring, star or bus configurations.
For example, if there is a break in the ring circuit, the system is immediately automatically divided into two separate sections in the form of straight buses. The same goes for the star scheme. By the way, insulators are installed in loop-type loops that are triggered by a cable short circuit. They indicate exactly where the break or short circuit occurred. That is why the advantages of this type of APS include ease of maintenance.
Addressable analog signaling
Generalization
When choosing an APS (automatic fire alarm), the design organization proceeds from the requirements that the customer places on the fire safety of the facility. In this case, the main attention is paid to the reliability of the purchased system, its cost, as well as the cost of installation activities, plus the regulations for maintenance are taken into account. And if during the calculations the reliability of the system decreases, then the designers choose an alarm system with a higher level of reliability.
Sometimes facilities encounter conditions that are simply impossible to overcome. For example, architectural structures do not allow for cable laying. Or their installation is not economically viable. In this case, designers solve complex problems and often choose radical measures, which both in terms of execution and in terms of future maintenance of the automatic fire system become complex and sometimes unprofitable. One of these options is to use not wired current from an alternating voltage network to power the alarm, but direct current with the installation of batteries. One of the difficulties is that power supplies will have to be replaced as they wear out.