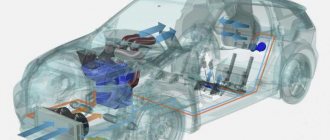
How does the air conditioning system work in a car?
The compressor is driven by a belt from the crankshaft.
The compressor compresses the refrigerant entering it in a gaseous state. When refrigerant is compressed, a lot of heat is released. The refrigerant, compressed and heated to approximately 100°, enters the radiator-condenser . Passing through the condenser, the refrigerant is cooled to approximately 45° and changes from a gaseous state to a liquid state. Those. condenses. The receiver-dryer located on the condenser accumulates liquid refrigerant. In its flask there is a desiccant substance that absorbs moisture after assembling and vacuuming the entire system. The same flask may also contain a filter that retains compressor wear products.
On our YouTube channel you can watch a video review about car air conditioners.
You can select and buy an air conditioning compressor for your car in our used spare parts catalog.
From the condenser, liquid refrigerant is directed at a fairly high pressure of about 17 bar to the evaporator. On its way to the evaporator, it passes through an expansion valve or expansion valve . This valve has 2 functions: to reduce the refrigerant pressure and to regulate its supply to the evaporator. Passing through the expansion valve, the refrigerant pressure drops to 4 bar. In this case, the refrigerant evaporates and absorbs heat from the environment, cooling to 10°. At this temperature it enters the evaporator.
Instead of a thermal valve, an expansion throttling insert can be used, which continuously meters the supply of freon to the evaporator. In this case, liquid refrigerant collects in the evaporator. In this condition, it should not get into the compressor, which will cause water hammer. Therefore, on the way to the compressor, the freon enters a separate battery, in which it is simply evaporated.
The evaporator belongs to the interior ventilation system. The fan directs the air entering the cabin to it. In the evaporator, the refrigerant evaporates, removing heat from the environment. Those. it cools and dries the air passing through the evaporator. The refrigerant evaporated in the evaporator is again sent to the compressor.
You can select and buy an air conditioning evaporator for your car in our catalog of used spare parts.
The accumulator-drier is used in an air conditioning system with a throttling insert instead of a thermal valve.
In general, during operation of the entire air conditioning system, the evaporator temperature is maintained at a certain level, about 10°. Regulation is carried out in the same expansion valve, but in a different circuit with a thermostat. It goes like this. The more the refrigerant heats up in the evaporator, the higher its pressure will be. This pressure pushes on the thermostat membrane. Thus, the warmer the refrigerant leaving the evaporator, the more it presses on the membrane, which through the rod opens the ball valve more strongly, which releases more refrigerant to the evaporator.
Causes of unpleasant odor
The stench that appears when the air conditioning system is turned on is the result of dust, bacteria and mold entering the evaporator of the car's air conditioner along with the air. After it is turned off (usually when the car is stopped), the temperature of the air inside the evaporator and the freon in the tubes is leveled, dust and dirt adhere to the surface of the radiator, and in conditions of high humidity and comfortable temperature conditions, ideal conditions are created for the rapid decomposition of organic residues contained in dust. And they, in turn, are a breeding ground for microbes.
The products of rotting organic matter, together with the waste products of microflora, lead to the appearance of unpleasant odors. When the air conditioning is turned off, the stench does not spread beyond the evaporator, but as soon as you start the engine, stagnant air rushes into the cabin through the air duct system. The appearance of odors just indicates that it is time to clean the car air conditioner evaporator.
Types of air conditioning compressor in cars
There are 3 types of air conditioning compressors used on cars. The most common type: piston. There are options with variable and fixed displacement. Accordingly, the compressor design can have from 5 to 7 pistons or 10 pistons. Piston compressors can have either variable or permanent drive.
Rotary type compressors are less common. The rotor can have blades or be a movable spiral immersed in the same fixed spiral. Both types of rotary compressors are common on Japanese cars.
Since 2012, air conditioning compressors with an electric drive and a spiral rotor have been increasingly used.
Insufficient lubrication of parts
Sometimes car enthusiasts use too little oil to lubricate elements or do it irregularly. In such cases, it will be necessary to overhaul the air conditioning compressor in the car. Otherwise, insufficient lubrication in the future will result in:
- Breakage of the bearing that occupies space in the constant rotation pulley. Strong heating of the bearing during operation leads to distortion of the pressure disk or burnout of the varnish on the electromagnetic clutch.
- Abrasion of the walls inside the case. As a result of strong friction of unlubricated parts, metal dust appears, which settles on rubber hoses, aluminum tubes, in the evaporator and other parts of the system, leading to jamming.
Sometimes low-quality lubricants containing large sediments are poured into the system. Then, during operation of the air conditioner, this sediment inevitably clogs the thermostatic valve and the receiver. To correct the situation, you will have to replace them with new ones, having first cleaned other parts of the air conditioning system.
How does an air conditioning compressor work?
The only function of the air conditioning compressor is to take the refrigerant evaporated in the evaporator, compress it to a higher pressure and send it to the condenser to cool and turn into a liquid state. The entire air conditioning system can be self-regulating or controlled by external commands. In both cases a corresponding control valve is used.
A little about oil in refrigerant
Any repair of the compressor is fraught with an imbalance of the oil added to the freon to ensure lubrication of the car air conditioner parts. Since you find yourself forced to restore the compressor’s performance, it would be useful to take into account several recommendations based on experience in repairing climate control systems.
If you are doing work that requires complete dismantling of the compressor, keep in mind that there is still oil in the system, albeit in small quantities - unlike volatile freon, it does not have time to drain either from the lines or from other air conditioner components. To drain these residues, you will have to flush the system. It's expensive, but necessary.
When charging with freon, the required amount of oil has already been added to it, so flushing allows you to achieve the ideal ratio of refrigerant to lubricant. The algorithm for determining the required amount of oil in the system is as follows:
- determine its quantity in the removed compressor;
- Find out from the documentation how much oil there should be;
- subtract the first digit from the last digit and remember the difference;
- When you drain oil from the lines, make sure that its volume is less than or equal to the saved calculated value. If there is excess oil in the system, there is no need to drain it.
Typically, after repairing a compressor, oil needs to be added. How much to add is important, since its excess will cause jamming of the compressor and its complete replacement. If you know how much oil has drained, fill in the same amount plus 40 grams, and it is recommended to use the same type of lubricant. It is also necessary to know that topping up should be carried out exclusively through the high-pressure port - otherwise there is a possibility of creating insufficient vacuum inside the line.
How does the displacement of a compressor change?
When high compressor performance is required, gaseous refrigerant under high pressure enters its inlet. As we know, his blood pressure increases because... too much refrigerant has evaporated in the evaporator.
This pressure pushes on the compressor pistons. In this case, the control valve relieves gas pressure from the crankcase into the suction line. In this case, the suction pressure above the pistons will be higher than the pressure that “props” them out of the crankcase. Consequently, this pressure will force the pistons to increase their stroke. Thus, the working volume of the compressor cylinders also increases.
When less refrigerant evaporates in the evaporator, the suction line pressure will be lower. To reduce the working volume of the cylinders, part of the gas (refrigerant) compressed by the pistons is directed into the crankcase. This pressure puts pressure on the pistons from behind, causing them to reduce their stroke.
Thus, the change in the working volume of the compressor occurs due to the balance of forces on the pistons and below them - in the crankcase.
Main unit of the climate system
Any air conditioner is essentially a refrigerator. And since both devices can be considered “close relatives,” then their internal structure is relatively the same and assumes that a car air conditioner has a compressor - a heart that accelerates the refrigerant through the system lines. Today, two types of compressors are mainly installed: piston and rotary vane.
Automotive air conditioning compressor
For the piston type, as the name suggests, the main part of the unit will be the piston. Such parts may be present inside the compressor in varying quantities - from one to several. This is where the way the engineering worked plays a role. The location of the pistons can also vary. They can be placed in a V-shape, crosswise and in one plane. The main thing is the ability to compress the coolant element in order to force it to circulate along the car air conditioner line from a high pressure zone (discharge area) to a low pressure zone (suction area).
The design of a rotary vane air conditioning compressor for a car is very similar to an electric pump for an air bed. When the rotor rotates, its blades create cavities that forcefully draw in the refrigerant on one side, and on the other, push it into the main line under pressure, forcing it to circulate through the evaporator pipes.
Design of a rotor-blade unit
The remaining types of automobile compressors number more than 40 modifications, and therefore we will not try to provide information in one article that is unlikely to be useful later. Let us only say that there is a variety of piston-type units with the scientific name “axial-piston superchargers”, which are based on a rotating inclined disk that forcibly pumps a coolant-forming mixture.
Compressor oil
In addition to the refrigerant, the air conditioning system contains a special oil. It lubricates all friction pairs. Oil circulates throughout the entire circuit and is also present in the compressor crankcase. Depending on the type of compressor and the refrigerant used, different types of oils are used, which absolutely cannot be mixed with each other, because Paraffin may form and clog the system.
Compressor oil is completely transparent and almost colorless. It may have a bright green color if it contains dye.
Malfunctions and breakdowns of the compressor and air conditioning system
The most common failure of an air conditioning system is refrigerant leaking through leaking seals or cracks. If there is a lack of freon, the performance of the air conditioning system decreases. When the freon level is very low, the system can completely turn off the compressor to avoid its breakdown. A low level of freon is determined when refilling it by the quantity and pressure drops in the system. Compressor oil leaks indicate a large hole. Although in most cases it is necessary to add a special dye to the system, visible in ultraviolet light.
The enemies of the cylinder-piston group or compressor rotor are increased friction due to lack of oil or increased refrigerant pressure. Also, increased pressure leads to overheating of the compressor and the oil, which becomes too liquid. These factors lead to friction pairs rubbing against each other, and the entire system becomes clogged with aluminum powder.
Why does refrigerant overpressure occur? The first reason is factors that prevent normal condensation. This is a dirty condenser or a non-working fan on it. Also, excess pressure can be caused by an excess amount of refrigerant charged.
If metal shavings get into the air conditioning system, it must be washed out and even the evaporator and condenser must be replaced. Otherwise, the chips will very quickly finish off the newly installed compressor.
Failures of other mechanical and electronic components such as expansion valve and control valve are quite rare. They manifest themselves in the fact that the air conditioner does not cool as it should, but there is enough freon in the system and there are no leaks.
Efficiency of an autonomous air conditioner
Now let's discuss the key question: which air conditioner is better - standard or portable? The ideal option is an autonomous climate control system. It can operate independently of the power unit. The only thing is that they require a more powerful battery. With a standard battery, the device will have little or no power.
Evaporative-type analogs are less demanding on electricity, so they can be used in any passenger car. True, the coolness of the evaporated water may not be enough for a comfortable trip. Fungus or mold are constant companions of moisture, which lingers in the air ducts of the car ventilation system.
All other portable so-called air conditioners are simply fans that are installed in a plastic case, and sometimes may have elements that absorb moisture. Such devices do not cool the air, but simply provide improved circulation throughout the cabin. The quality of temperature reduction compared to standard cooling systems is much lower, but their cost is lower.
Homemade options
If a standard compressor-type air conditioner requires a decent investment, then a homemade option can have a minimal cost. The simplest type can be made almost from available materials. To do this you will need:
- Plastic tray with lid;
- Fan (its dimensions depend on material capabilities, as well as on the required efficiency);
- Plastic pipe (you can take a sewer pipe with an elbow).
Two holes are made in the tray cover: one for air injection (a fan will be connected to it), and the other for cool air outlet (a plastic pipe is inserted into it).
The maximum efficiency of such a homemade installation is achieved by using ice as a refrigerant. The disadvantage of this product is that the ice in the container melts quickly. An improved option is a cooler bag, in which solid water will not melt so quickly. In any case, such an installation requires a lot of space in the cabin, and when the ice melts, the water in the container can splash while the car is moving.
Compressor units remain the most efficient today. They remove heat, which they themselves generate, and also effectively cool the interior of the car.
Constant drive clutch
Air conditioning piston compressors are often permanently driven. Those. their shaft constantly rotates when the engine is running, there is no electromagnet in the pulley, and no wires are connected to the clutch.
Permanent drive clutches can be plastic or metal and can be belt driven or shaft driven. Inside such a coupling there are always simple rubber dampers. The dampers are located between the pulley and the drive plate, which is mounted directly on the compressor shaft. The drive plate is also called a "stall" or "safety" plate.
This means that if the compressor shaft is jammed or there is excess pressure in its housing, the drive plate is literally destroyed: a break occurs in a special safety element or section of the plate. This breaks the connection between the shaft and the compressor pulley. Also, breakage of the safety plate occurs due to runout of the drive belt, a malfunction of the tension roller, or jamming of the generator overrunning clutch.
Other drive plate failures are also possible. A permanent drive clutch that has served for a long time may begin to knock while the engine is running. The knocking occurs due to the destruction of rubber dampers and the appearance of play. Those. The drive plate connecting pins will click against the grooves in the pulley. After some time, ignoring the knock leads to all the pins being cut off, i.e. again, the connection between the pulley and the compressor shaft is destroyed.
Some cars use permanent drive compressors, the coupling of which does not have an elastic damper, but uses a shock-absorbing weight. Such couplings are destroyed due to problems with the tension of the drive belt.
The permanent drive clutch rotates on a bearing mounted on the neck of the front cover of the air conditioner. If there is play in the bearing, in most cases it can be replaced with a new one. But at the same time, the seating plane on the neck should not be worn out.
When installing a new drive plate on many VAG compressors, it is extremely important to remember to install a shim on the compressor shaft. Without it, when screwing, the plate will simply break as intended by the manufacturer in the event of a jammed compressor shaft.
Basic air conditioner malfunctions and their symptoms
- Refrigerant leak. Freon is characterized by high volatility, and therefore gradually disappears from the system at the slightest leak. Even on a sealed system, the air conditioner needs to be recharged every 3-5 years. Most often, a leak occurs when the condenser honeycomb is damaged, due to the natural loss of elasticity of rubber seals (rings on tubes, hose crimps, compressor shaft seal).
- Broken condenser clutch. The normal resistance of a working winding is 4-6 Ohms.
- Faulty wiring, air conditioning relay. The most common occurrence is a banal fuse blown and the formation of oxides on the contacts.
- Condenser clogged. The main sign of a malfunction is low compressor performance, increased pressure in the high-pressure circuit.
- Malfunction of the high/low pressure switch in the system. All modern systems use a combined pressure sensor. Thanks to the PWM signal, the control unit constantly monitors the actual pressure in the system.
- Evaporator clogged. Through a clogged evaporator, less air enters the cabin. Naturally, the air conditioner will not blow cold from the deflectors.
- Sticking thermostatic valve.
- Compressor failure. This happens due to natural wear or operation without oil.
Often the compressor does not turn on after a long period of inactivity. Therefore, if you are wondering whether it is possible to turn on the air conditioner in your car in winter, the answer is definitely yes. Periodic activation allows the oil to disperse throughout the system and lubricate the compressor elements. It is a well-known fact that air conditioning dries the air, and therefore helps prevent windows from fogging up in winter.
Electromagnetic clutch
The second option for driving the air conditioning compressor is using an electromagnetic clutch. In this case, the pulley and compressor shaft are not in permanent connection. The pulley is mounted on a bearing mounted on the neck of the front cover of the compressor housing and rotates freely from the attachment belt. A drive plate with a rubber or spring damper is connected to the compressor shaft. There is an electromagnetic coil inside the pulley. When voltage is applied to it, a magnetic field is created that attracts and presses the drive plate to the pulley. In this case, the pulley and compressor shaft rotate together as one unit. When the voltage is removed from the coil, the drive plate disengages from the pulley: a gap is created between them.
Most often, the electromagnetic clutch begins to slip. Namely, the drive plate slips relative to the pulley. Not in all cases, slippage begins due to wear of the mating surfaces of the coupling. Usually, excessive refrigerant pressure appears in the compressor itself, which puts a lot of stress on the clutch and causes it to slip.
Well, then the destruction process goes very quickly: the rubbing drive plate and pulley destroy the mating surfaces, and a lot of heat is released, which bakes the rubber components and can burn the electromagnetic coil.
The clutch is protected from overheating as a result of slipping by a thermal fuse, which opens the power supply circuit of the electromagnet.
Some types of couplings have a rubber drive plate damper, which is destroyed if the compressor shaft rotates with increased force or is jammed.
Play in the entire coupling occurs due to wear of the bearing and journal of the front cover of the compressor housing. If the journal is worn out, then even after installing a new bearing the pulley will rotate with play and runout.
The history of automobile air conditioners
Increasing comfort when driving a car is a task that was already facing their first designers. Many areas that were considered a priority developed quite actively, but the designers had trouble ensuring a normal microclimate for a long time. Although there were plenty of ideas, they all turned out to be either insufficiently effective or technically unrealizable. You can recall attempts to cool the temperature in the cabin using ice, the cubes of which were stored on a special tray, the installation of additional forced air intakes or hidden fans, the installation of complex air duct systems and other technical solutions that ultimately did not take root for one reason or another.
One of the first more or less successful systems was the solution that was used on Packard machines in 1939. It was at that time that compressor-type cooling systems were invented, which formed the basis of the new cooling system. Structurally, it turned out to be very complex, and therefore unreliable. To put it into action, you first had to stop, connect a prototype of the air conditioner with the engine turned off, start the engine, manipulate the strength and direction of the air flow, wait until the car cools down, turn off the cooling system and only then continue driving.
The idea was borrowed, and as technology improved, the air conditioner became more and more similar to the modern one. In 1941, the American company Cadillac produced the first small batch of cars equipped with an air conditioning system that worked according to the same scheme as now. In the 60s, the number of air conditioners installed on passenger cars was already in the thousands, and in the 80s the number went into the millions.
Clutch bearing
If the clutch bearing falls apart, the clutch rattles and plays during engine operation. If you neglect these symptoms and do not rush to service, the bearing may rotate and lift up the neck of the compressor front cover. In this case, even after installing a new bearing or coupling, the pulley play will not go away. For a complete repair, you will have to buy either a new front cover or a used compressor. There are also options with neck restoration.
Also, a loose clutch quickly wears out the drive belt and its tension roller.
Why might it work poorly?
There is an opinion among Russian motorists that the car air conditioning compressor is almost a prototype of a perpetual motion machine, and therefore does not require maintenance at all. We don’t like to read instructions and only remember them at the moment when almost the entire interior cooling system needs to be changed. Specifically, over time, the compressor suddenly begins to hum, and the design of the car air conditioner is such that it is not immediately clear where the hum comes from. The reasons may be different, but the first thing that comes to mind is a faulty pulley bearing or worn out belt drive. Such problems can be solved by the car enthusiast himself; replacement will not cause difficulties if you have the skills to communicate with hardware.
Worn belt drive
The situation may be much more serious if the piston is jammed inside the unit itself. There’s hardly anything that can be done about this, since the broken part probably damaged the valves and walls. If you are not too lazy, then the replacement will wait; it is not forbidden to try to repair the car air conditioning compressor. But, as practice shows, such measures lead only to temporary improvements and after some period the breakdown will recur. The best option for a car air conditioner in this case is a complete replacement of the compressor.
Car air conditioning compressor repair
More often than other breakdowns, seal failure occurs. This happens either due to damage to the oil seal, or due to loosening of the places where the main pipelines are attached to the device itself. In the case of the oil seal, the matter is complicated, because it needs to be replaced. If you have never had to press it out, it is better not to try. This requires a specialist and the availability of appropriate equipment. It is not difficult to eliminate looseness with your own hands.
Troubleshooting yourself
Once the cause of the malfunction has been determined, you can repair the car air conditioning compressors yourself. To do this, you will need to remove the refrigerant from the cooling system and open the compressor. The further algorithm of actions will depend on which part needs repair or replacement:
- Stuffing box . Dismantle the coupling hub, remove the locking element securing the gasket. In place of the old oil seal, install a new one using a special mandrel, and reassemble in the reverse order.
- Shaft bearing . Dismantle the electric coupling, remove the worn bearing, replace it with a new one.
- Electro coupling . Disassemble the supercharger. Remove the failed part - coil, shaft or pressure plate. Insert a new element and assemble the supercharger.
- Pump . In most cases, problems can be resolved by simply adding oil to the system. If the pump stops working due to large amounts of sediment or aluminum dust, the mechanism should be thoroughly flushed.
When the compressor housing has minor damage in the form of cracks, holes or chips, they can be easily repaired without dismantling the compressor. You just need to turn it off and seal the holes and cracks using argon-arc welding.
This is interesting: Oil for car air conditioners - a choice according to all the rules