Greetings friends! In today's article, we will analyze in detail and answer such an interesting question as: is it necessary to change the rollers and pump when replacing the timing belt?
A timing belt is a connecting element that allows all parts of the equipment to operate other structural elements by their movement. Thanks to the latest developments, it is made of particularly durable polymer, which makes its operation silent and the safety margin is quite high. However, due to constant friction, certain incidents may occur, for example, its rupture. If this happens, the driver will most likely remain standing on the road until the problem is corrected.
Therefore, the answer to the question of whether the timing belt needs to be changed is obvious. According to the advice of the experts, it is best to replace it at 100 thousand kilometers , but if defects were discovered on it at an earlier date, then you should not hesitate. In this case, it is appropriate to make a replacement, even if the mileage is small.
Many car enthusiasts are interested in whether it is necessary to change the rollers and pump when replacing the timing belt? This action is optional, but if additional means are available it is best to do so, as this will affect the operation of the new belt. In addition, in order to perform the replacement, you will have to disassemble all the components of this equipment, including the rollers with the pump.
This is what locked camshafts look like when replacing the timing belt and pump
Thus, replacing all consumables will not greatly increase the cost of this procedure. Therefore, the reformatted answer to the question whether it is necessary to change the rollers when replacing the timing belt will sound like “not necessary, but recommended.” This is due to the convenience of complex replacement and increasing the service life of the replaced unit.
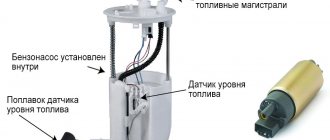
The car pump is a pump responsible for ensuring the circulation of fluid in the circuit of the car's cooling system. There is an opinion that the pump needs to be changed every time a new timing belt is installed. This article will tell you whether it is worth changing the pump when replacing the timing belt and how often to do it.
What is a pump in a car
Engineers know how to extract thermal energy from an internal combustion engine in several ways:
- air;
- liquid;
- combined.
Systems developed on the basis of air cooling are usually called open. They involve directed air flows that bypass the engine body from the outside. This design is becoming less and less common in modern cars, but is in demand in small motor vehicles.
Representatives of closed systems are liquid analogues. Heat is removed due to the circulation of antifreeze through the channels of the covering jacket of the cylinder block. The combined scheme involves the introduction of both air and liquid cooling for the car.
In the last two types of designs, a pump is a mandatory attribute; this is what a water pump is usually correctly called, as an integral part of the forced circulation of coolant in a car.
Important! Liquid-cooled systems are much quieter than their counterparts that use air to dissipate heat.
Location and purpose of the element
Cars most often have two cooling circuits:
- small;
- big.
Various elements included in the cooling system are also provided. Each of them performs its own function. Why a pump is needed is obvious to many experienced motorists, since it works to forcibly pump fluid in the cavities and channels designated for this purpose.
The impeller built into the pump body is responsible for pumping antifreeze. The rotation of this wheel is transmitted via a belt drive. The transmission pulleys are located on the pump shaft and on the output shank of the vehicle's crankshaft.
The water pump is located where the engineers placed it. In most models of modern cars, you can find the pump in the following areas:
- if you look in the direction of travel, then in cars with front-wheel drive, the pumping device is located on the right end of the cylinder block (since the pump is rigidly connected to the timing drive, it is located where the drive is protected by a cover);
- rear-wheel drive cars are equipped with a water pump fixed to the front wall of the cylinder block, and the rotation of the impeller is provided by a timing belt or from the generator drive.
The pump distills antifreeze through channels and two radiators, one of which serves to remove heat into the atmosphere, and the second is capable of transferring heat to the cabin. In this way, it is possible to quickly cool the power plant.
Where does the pump go?
The pump always pumps away from itself, that is, it pushes, but does not suck. This is ensured by the fact that the rotating impeller creates a centrifugal force, which pushes the antifreeze further. The purpose of the pump is to ensure the movement and pressure of the fluid from the radiator to the engine, so it pumps coolant into the engine. Structurally, the impeller can rotate both clockwise and counterclockwise.
When should you change your pump?
The pump replacement intervals are clearly stated in your vehicle's owner's manual. The most common option is every second replacement of the timing belt or when symptoms of its failure appear (bearing noise, leakage, play).
Replacement frequency
As for the planned replacement of a car pump, the frequency of its replacement for many cars is simply not indicated in the technical documentation. Therefore, most car enthusiasts carry out a planned replacement every 60...90 thousand kilometers, which corresponds to a planned replacement of the timing belt. Accordingly, you can change them in pairs.
In the second case, if a higher quality pump and a lower quality belt are used, then the replacement can be carried out as follows - one pump replacement for two timing belt replacements (after approximately 120...180 thousand kilometers). However, it is necessary to carefully study the state of one and the other node. Along with replacing the strap and pump, it also makes sense to replace the guide rollers (if you buy them as a set, it will be cheaper).
Water pump service life
The service life of the water pump is significantly reduced when operating in extreme temperatures. The component is subject to greater wear during extreme heat or severe frost.
The water pump is replaced together with the timing belt (every 60,000 - 90,000 km). Higher quality auto parts are replaced after 120,000 - 180,000 km.
Replacing the cooling pump yourself
A car enthusiast can easily change the water pump on his own. Let us illustrate this process using the example of a Peugeot 307 car. But before that, let’s decide on the tools and consumables. To work we need the following things:
- new water pump;
- open-end wrenches, set;
- socket wrenches and wrench included;
- coolant, 5 liters;
- jack.
The sequence of replacing a pump using the example of a Peugeot 307
- The car is driven into the inspection hole, the wheels are secured with shoes. The front right wheel is lifted with a jack and removed with a socket wrench.
The right front wheel of the Peugeot 307 is jacked up and removed - Through the drain hole under the radiator, the old antifreeze is drained into a substitute container (this can be either a ten-liter bucket or an ordinary basin).
- The next step is to remove the timing belt to gain access to the pump. Next to the camshaft pulley there is a belt retainer and a timing belt tensioner bolt. Using a 10-mm open-end wrench, first loosen the clamp, and then the tensioner bolt.
To loosen the timing belt on a Peugeot 307, you need to loosen the tension roller - Once these bolts are loosened, the timing belt tension will also be released and it can be removed manually.
A loose timing belt on a Peugeot 307 can be removed manually - Access to the pump is available. It is held on by five 12mm bolts, which can be easily unscrewed with a regular open-end wrench.
Access to the Peugeot 307 water pump is open, you can remove it - The pump is removed, a new one is put in its place and the cooling system is assembled in the reverse order.
This is interesting: Types of carburetors
The principle of operation of the pump and its design
Cars have a fairly simple pump design. Its body simultaneously serves as a mounting flange. It is equipped with several holes through which the unit is fixed to the BC.
Due to the fact that the body is made of aluminum, it is possible to minimize the influence of corrosion processes, and the weight of the finished product is also reduced. The design also includes:
- the main shaft with rolling bearings is pressed into the central hole of the housing;
- at the cantilever end of the shaft there is a rigidly fixed plastic or aluminum impeller;
- the outer shaft shank is equipped with a pulley (grooved or gear models are used);
- The sealing gland helps prevent antifreeze leakage and ensure the tightness of the structure.
The pump flange can be screwed either directly to the block or through an adapter to ensure alignment of the belt drive without removing the impeller from the antifreeze flow. Manufacturers install a gasket under the flange.
Based on the device and method of fastening, the operating principle of the antifreeze pumping unit becomes clear. Rotation is transmitted to the shaft and then to the impeller via a belt drive. As the crankshaft speed increases, the impeller speed increases, which promotes intense circulation through the channels.
Manufacturers guarantee uninterrupted operation of the pump for 40-140 thousand kilometers. The resource depends on the brand and model of the vehicle. Domestic cars are located closer to the lower value of the interval.
Important! Certain brands of cars are equipped with pumps powered by a personal electric drive.
Autonomous electrical equipment for pumps is not widely used among cooling system designs. This is due to an additional increase in the cost of the finished product and a slight decrease in the degree of reliability.
Technical features
First, let's look at the main technical characteristics and features of the water pump; this will allow us not only to make a correct diagnosis, but also to understand why the breakdown occurred. Antifreeze is pumped using an impeller, which is mounted on a shaft. The drive is carried out from the crankshaft of the motor; a belt drive is used for this. Here it is worth clarifying that in practice there are 2 drive methods used for the pump:
The pump housing is usually located at the front of the motor. This allows for the most optimal pumping of coolant through the system. It is also precisely this approach that makes it possible to use the crankshaft pulley as a moving element. In addition, placing the part at the front makes it easier to access for repairs. The main malfunctions of the pump are directly related to its technical features; accordingly, this must be taken into account when carrying out diagnostic actions. As a rule, all signs of a malfunction are completely related to the characteristics of the various elements that ensure the operation of your car's cooling system.
Circles of circulation
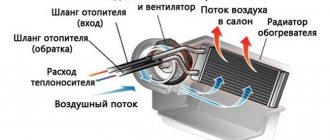
Installation and installation of the oil pump VAZ 2108-2109-21099 The cooling system in the car has two circulation circles: large and small. The small one is considered the main one, since when the unit is started, coolant immediately begins to circulate through it. In the operation of the small circle, only the channels of the cylinder block, the pump, and the interior heating radiator are involved. Circulation takes place in a small circle until the internal combustion engine reaches normal operating temperature, after which the thermostat activates and opens the large circle. Thanks to this system, engine warm-up is significantly reduced, and in winter, the system does not so much cool the unit as maintain its normal temperature regime.
Small and large coolant circulation circles
The operation of the large circle involves a fan, a cooling radiator, inlet and outlet channels, a thermostat, an expansion barrel, as well as those elements that take part in the functioning of the small circle. The outer circle, also known as the large circle, begins to work when the coolant temperature reaches 80-90°C and ensures its cooling.
Car water pump device
Its design is simplified as much as possible. Everything simple is brilliant and less likely to break. It consists of a shaft, which is supported in a housing by two bearings. An impeller is attached to the shaft inside the pump, which causes antifreeze to circulate in the system. It comes in metal or plastic. The first is more reliable, the second is cheaper.
An oil seal is located between the working chamber and the bearings. It prevents coolant from getting into the bearings and leaking out under the hood of the car. The body is made of aluminum or cast iron, which can withstand temperature changes and vibration. It consists of two parts. A rubber gasket is installed between them. Thanks to this design, it is possible to replace the pump without removing it from the engine housing.
On the opposite side of the shaft, on the outside, there is a drive pulley. Which is firmly fixed to the shaft and driven by attachment belts or timing belts (it all depends on the car model). For example, on a VAZ 2107 - an alternator belt, an Opel Cadet - a timing belt. Therefore, the speed of fluid circulation depends on the rotation speed of the engine crankshaft; the higher the speed, the faster the coolant moves through the system.
The weak link in the design is the oil seal and bearing. The first one begins to leak antifreeze, which, entering the working cavity of the bearings, washes out the lubricant from them. The result is increased noise, and then jamming of the pump. There are cases when bearings begin to “howl” before the seal wears out. This low quality of parts makes itself felt. The service life of the mechanism is from 60 to 100 thousand km. In some cases, it requires replacement at 30 thousand, and some specimens lasted 160 thousand km.
Which pump impeller is better?
Most modern pumps have a plastic impeller. Its advantages lie in its lower mass compared to metal, and therefore lower inertia. Accordingly, the engine needs to spend less energy to spin the impeller. Often, so-called turbo pumps have a plastic impeller. Moreover, they have a closed design.
However, plastic impellers also have disadvantages. One of them is that over time, under the influence of high temperatures of antifreeze, the shape of the blades changes, which leads to a deterioration in the efficiency of the impeller (that is, the entire pump). In addition, the blades can simply wear out over time or even fall off the rod and spin. This is especially true for inexpensive water pumps.
As for the iron impeller, its only drawback is that it has great inertia. That is, the engine spends more energy to spin it up, in particular at the time of start-up. But it has a long service life, practically does not wear out over time, and does not change the shape of the blades. In some cases, it is noted that if the pump is cheap/poor quality, then rust or large pockets of corrosion may form on the blades over time. Especially if low-quality antifreeze is used or ordinary water (with a high salt content) is used instead.
Therefore, which pump to choose is up to the car owner to decide. To be fair, it is worth noting that most modern foreign cars have a pump with a plastic impeller. However, they are made with high quality, and over time they do not wear off or change their shape.
When choosing a pump, you also need to pay attention to the height of the impeller. From general considerations, we can say that the smaller the gap between the block and the impeller itself, the better. The lower the impeller, the lower the performance, and vice versa. And if the performance is low, this will not only lead to problems with engine cooling (especially at high engine speeds), but also to problems in the operation of the interior heater.
Also, when choosing a pump, you should always pay attention to the seal and bearing. The first should provide reliable sealing, and the second should work smoothly at any speed and for as long as possible. To extend the service life of the oil seal, it is necessary to use high-quality antifreeze, which includes oil seal lubricant.
Most often, the pump body for passenger cars is made of aluminum. This is due to the fact that it is easier to make parts of complex shapes with complex technological requirements from this material. Water pumps for trucks are often made of cast iron, since they are designed for low speeds, but it is important to ensure a long service life of the device.
Pulley
The rotation speed of the shaft directly depends on the diameter of the pulley. The manufacturer selects the optimal sizes for a particular modification.
There are three types of pulleys:
- Toothed - driven by a timing belt.
- Belt - driven by a regular belt.
- Electromagnetic - a clutch that regulates the rotation speed of the pump using a magnet.
The latest modification does not require sealing with an oil seal, so this pump will never leak. The pulleys are rigidly attached to the axle using bolts or key connections.
Bearing
The most common designs include a double row sealed ball bearing or roller bearing. This element is lubricated with high temperature grease.
Stuffing box
The seal is responsible for the tightness of the pump. To improve the properties of the seal, antifreeze is used with the addition of lubricant. Most modern pumps are equipped with a ceramic seal, consisting of two elements similar to a flat spool.
Checking the pump's health
It should be noted right away that in order to identify many problems with the water pump, this device will have to be removed from the engine and disassembled. This is the only way to see dirt, corrosion and traces of cavitation.
Water pump impeller heavily damaged by corrosion
But there are a number of signs by which you can determine if the pump is faulty without removing it. Here they are:
- a thin continuous whistle coming from under the engine camshaft pulley. This whistle indicates a faulty bearing.
- coolant leaks, which are visible both on the engine itself and on the asphalt under the car;
- play in the pump, which can be detected by simply holding the pulley and moving the pump up and down with your hand.
Let's look at these faults in more detail.
Pump whistle
The reason for the pump whistling is a partially or completely destroyed ball bearing on the main shaft of the device. Moreover, the pump bearing, as a rule, produces a very high-pitched, piercing whistle, while the whistle of a faulty generator is significantly lower and sometimes turns into a grinding sound. This is affected by the difference in the size of the bearings: the ball bearing on the pump is small, so it whistles very thinly. The generator bearing is twice as large, so the sound comes from it accordingly. So it is almost impossible to confuse the sound of a broken pump and a broken generator.
The central ball bearing of the pump has completely collapsed
The problem is solved by replacing the central bearing of the pump. However, there is one caveat: these bearings are practically not sold separately anywhere. And they can only be purchased in conjunction with a new pump. Therefore, the driver, having heard a characteristic thin whistle coming from under the hood, must be prepared to fork out the cash: a new water pump can cost from 2 to 10 thousand rubles (depending on the make of the car).
This is interesting: Ford Focus has acquired a new turbocharged 1.0 liter EcoBoost engine
Coolant leak
Liquid begins to flow from under the pump in two cases:
- the mounting bolts have become loose;
- The sealing gasket under the pump is damaged.
The first problem can be solved by simply tightening the bolts. But a damaged sealing gasket will have to be replaced. Fortunately, it is easier to find a gasket for a pump on sale than a central bearing (and in especially difficult cases, car enthusiasts even order seals via the Internet, from the Chinese on Aliexpress, for example).
Water pump is leaking due to over-tightening
It should be noted here that even a new gasket can easily be cut by a pump if the mounting bolts are not tightened correctly. The pump is one of those devices where it is very important not to over tighten it. It is necessary to tighten the bolts in a cross pattern: first tighten the upper right, then the lower left, then the upper left, lower left, etc. Only this tightening pattern can guarantee maximum tightness and tightness of the connection.
Finally, we must not forget about sealants. There are situations when neither a new gasket nor the correct tightening pattern helps get rid of a leak. Then there is only one option left: to use a sealant, and its composition must be very resistant to high temperatures.
The sealant is applied to the pump gasket in a very thin layer.
The best option here is a professional sealant from ABRO, which has proven itself on all brands of cars.
ABRO professional sealant, resistant to high temperatures
Coolant leak after replacing heat exchanger
In the vast majority of cases, after replacing the heat exchanger, antifreeze begins to flow not from under the pump, but from under the clamps of the pipe connected to the pump. On most modern cars, pump pipes are made of plastic, and very fragile plastic. Any careless movement when replacing the heat exchanger, if it does not break such a pipe, will at least break the tightness of its connection to the pump. After this, the antifreeze will definitely begin to leak. There are two options to solve this problem:
- if there are no cracks in the pipe, then you can simply tighten its clamps with a flat screwdriver, then let the engine idle for a few minutes, and then check the connection for leaks;
- If the pipe is broken after replacing the heat exchanger, there is only one way out: going to the nearest auto store and replacing it. This part cannot be restored.
The pipes on water pumps are made of very fragile plastic.
Purpose of pumps: fluid dependence
There are quite a few models of water pumps, but all devices are distinguished by one more characteristic - the ability to work without problems with a particular liquid medium.
- Clean or slightly polluted water. Such equipment has a chance to pump almost uncontaminated liquid without damage to working units. It may contain solid inclusions up to 0.5-0.8 mm in size.
- The water is moderately polluted. Pumps designed to work with it are more powerful. In this case, the partings are able to cope with pumping liquid, the size of solid particles of which is a maximum of 15 mm. The first example is fire motor pumps, which are used not only for their intended purpose, but also for transporting water over long distances.
- Heavily contaminated liquid. This pumping equipment is characterized by high performance, the ability to create pressure, the maximum of which is 35 m of water column. Such pumps easily cope with inclusions whose diameter does not exceed 25 mm.
The most serious problem is sewage wastewater, which requires “professionals”. Such pump pumps are called fecal pumps. Their purpose is to pump wastewater containing large, fibrous, insoluble inclusions. The difference between fecal aggregates and all previous types is the presence of a special device - a cutting mechanism. Its task is to grind the solid inorganic components of the liquid.
Types of cooling system pumps
Types of cooling system pumps Coolant pumps used in the modern automotive industry do not have any fundamental design differences. But they can be divided depending on the type of drive, purpose and housing design. The pump can be driven in two ways:
- Mechanical - the pump shaft is connected via a belt drive to the crankshaft or camshaft of the engine. In this case, it is set in motion synchronously with the engine starting.
- Electric - in this scheme, the pump shaft is driven by an additional electric motor, the operation of which is controlled by the electronic engine control unit (ECU).
According to its intended purpose, a car engine pump can be:
- Basic. Such a pump directly pumps liquid in the cooling system.
- Additional. It is not installed on all cars and can be intended for auxiliary cooling in regions with very hot climates, reducing exhaust gas temperatures, cooling the turbocharger in turbocharged engines, and additional cooling of the engine after stopping. Unlike the main pump, the additional one is driven by an individual electric motor.
The service life of a coolant pump depends on the type of construction of its housing. This parameter distinguishes between:
- Collapsible. This type is used in old and domestic cars. This design allows you to repair and flush the pump.
- Non-separable. In most countries, an engine pump is considered an inexpensive consumable spare part, and therefore many manufacturers have switched to producing non-separable pumps. They must be completely replaced every 60 thousand kilometers of the car. When installing a new pump, the drive belt must be replaced.
In addition to the designs described above, there are also switchable pumps. They allow you to turn off the flow of coolant until it warms up to a temperature of 30°C. This allows for faster engine warm-up and improved fuel consumption.
Liquid pump
Multipliers or booster compressors are sometimes used as liquid pumps, for example, the ultra-high pressure compressor of the High Pressure Institute (Fig. 65) works well at a pressure of 5000 atm and, as a liquid pump, with a capacity of up to 60 l/hour. Although the amount of harmful space in this compressor is very small (5 - 6%), its performance nevertheless increases when working on liquids that are less compressed than gases.
If you have a liquid pump or multiplier, it is more advisable to replace the bomb / with them, the cooling and heating of which (even one-time) requires time and coolant consumption. If a mercury seal is installed in front of the reactor / / (Fig. 89), and the reactor itself and part of the seal are filled with gas from a cylinder or compressor, then experiments with gases can be carried out at the installation.
When the liquid pump operates, oxygen or nitrogen leaks (through the gap between the plunger and the cylinder liner), which returns back to the column, passing along the way through a filter 15 made of porous metal to remove graphite particles.
Note that piston liquid pumps allow suction of gas with the same success as a compressor.
Unlike liquid pumps, air and other gas compressors (except low pressure compressors) are cooled by water or other means (surface cooling) to remove the heat that the compressor generates.
Surface pumps
Surface units are located in an area that is located in close proximity to a water source. A hose is connected to the suction pipe of the pump, its other end is immersed in the liquid. Such devices are:
- garden pumps: they are used only for watering the garden or vegetable garden;
- pressure devices: these devices become an element of the engineering system, their task is to provide the necessary water pressure;
- pumping stations, which in addition to the pump include a hydraulic accumulator - a device that accumulates water and also regulates the pressure in the system.
The advantage of surface structures is ease of maintenance and operation. The downside is the impossibility of extracting water from deep sources.
Pumps located at the source
Submersible pumps operate directly in the water column. The liquid rises up through a hose or intake pipe. Since this equipment does not suck, but creates a constant pressure, they are used for sources whose depth is already significant - from 100 meters or more. Submersible equipment is divided into several types.
- Wells. These pumps can work with sources whose depth is 10 meters. Their features are better cooling, less sensitivity to solid, large inclusions, and low noise levels.
- Borehole pump pumps. Such elongated cylindrical equipment has maximum power. It is designed for pumping liquid from deep, narrow sources with a large flow rate.
- Drainage Their purpose is to combat flooding in basements, pits, ditches or trenches. Drainage devices are recommended if the diameter of particles in the liquid does not exceed 30 mm.
- Fecal. This equipment does the most thankless job. Its task is to pump out highly contaminated water, which has various impurities.
As you can see, the choice of device depends entirely on the quality of the liquid, the type and depth of the source. Since many of them are threatened by water loss, the best option for a well or well in any case remains a submersible device. In addition, this equipment can be used to drain pits, empty tanks and other reservoirs.
Signs of a pump malfunction
In a machine, during operation, natural wear and tear occurs on all mechanical elements. The sealing collar and bearing are subject to significant load, which is why they fail more often than other parts. Less often, breakdowns occur with a pulley or impeller.
Signs of pump failure can be seen by the following factors:
- Without removing the pump, you need to test for the presence of antifreeze stains under the car in long-term parking areas.
- During operation, both on the side walls and below, the space is splashed with antifreeze. When the design includes a protective casing, symptoms appear in the form of drips in the lower area of the casing.
- Malfunctions or damage can be heard while the motor is running. Extraneous noise appears in the form of a crackling or hum in the area where the pump is installed.
- On the instrument scale, the thermometer displays values higher than the maximum permissible values. After this, the engine may often stall.
The driver should always be wary of stains that form under the car in the engine compartment after parking. To better examine the potential leak area, we recommend unscrewing the fasteners of the protective timing cover. If excess humidity is detected, we recommend carrying out simple diagnostic measures:
- turn off the engine completely and put the car on the handbrake;
- remove the timing cover;
- loosen the tension on the belt drive on the pump pulley;
- We try to apply a little force to the shaft, rocking it in the seat to the right/left.
Perceived shaft play is one of the main signs, after the appearance of which it is necessary to attend to replacing the water pump in the car. If you can hear obvious noises from the pump, then it is also necessary to diagnose the shaft.
Negative fears may be confirmed when the engine stalls while driving, and at this time there is a critical temperature on the sensor, for example, above 1200C. This is evidence of a jammed pump shaft, a loose belt, or a broken timing belt. In the worst case scenario, the valves will additionally be bent from the pistons.
If the alternator belt breaks, the driver will be able to recognize this by the indicator light on the dashboard lighting up, indicating that the battery is not charging, and at the same time the temperature will begin to rise noticeably. We recommend that the driver turn off the engine as quickly as possible and evacuate the car to a service station.
What tools are needed for replacement
To replace a part taking into account the need to remove the timing belt, the following keys are required:
- by 8;
- on 10;
- at 13;
- at 18.
You also need a slotted screwdriver.
Service stations also have expensive special tools. An experienced auto mechanic can do without them. However, they significantly facilitate the procedure and reduce the risk of damage to vehicle components to almost zero. Therefore, if you do not have experience and expensive professional tools, it is better to contact a service station to change the pump.
If a failure occurs
We recommend that you monitor possible negative symptoms that appear when the car water pump is operating. Its breakdown carries great risks for the performance of the engine. The extent of the consequences is influenced by the installation area and the method of connecting the pump.
The list of potential problems includes factors:
- A failed shaft bearing can jam the rotation of the pump. Accordingly, the pulley mounted on the shank will stop rotating, and the drive belt will fly off or break.
- Problems with sealing occur due to a worn oil seal or gasket, as a result of which the coolant level decreases. A lack of antifreeze leads to overheating of the internal combustion engine.
- Leaking antifreeze from under the seal ends up on the rotating pulleys, which distribute coolant to surrounding objects, including belts. After getting wet, the belts slip and wear out faster.
Often the root cause of loss of tightness and a decrease in antifreeze level is a worn-out bearing, and not an oil seal. The main shaft dangles and warps due to the force of the drive belt on the pulley. This causes the seal to deform and become unable to hold antifreeze, causing a leak to occur.
The most negative development of events is the rupture of the timing belt due to bearing jamming. Most cars then require expensive engine repairs. This is due to the impact of the pistons on the caps of the open valves, which results in an instant bending of the latter.
After a belt failure, it is highly likely that the car will have to remove the cylinder head and also replace the valves. Worst case scenario, the pistons and potentially cracked cylinder head will need replacing.
In a structure where the generator drive belt falls off, significant damage does not occur quickly. Such a malfunction can be identified by possible symptoms:
- the on-board power supply system will switch to discharging the battery;
- the battery will begin to lose voltage;
- the motor begins to overheat.
An increase in temperature leads to rapid depletion of the cylinder-piston group.
Consequences of breakdown
A pump that has become unusable can cause a lot of trouble. The amount of damage depends on how the pump in the car is activated - from the timing belt or the generator drive. Emergency situations look like this:
- A leaky oil seal or gasket begins to leak. The level of antifreeze in the system decreases, which can lead to overheating of the engine if the problem is not noticed in time.
- Due to a broken bearing, the pump shaft jams. The jerk causes the drive belt to fly off or break.
- When the pump seal leaks, the rotating pulleys throw fluid in all directions. Wet belts slip and wear out faster.
Note. The root cause of an antifreeze leak is often a worn bearing, not a seal. The shaft with the pulley and impeller begins to dangle and warp under the pressure of the drive belt. Under such conditions, the oil seal is not able to hold the antifreeze, causing the water pump to leak liquid out.
The worst case scenario is a timing belt drive rupture due to bearing jamming. For many cars, this leads to expensive repairs to the power unit, since the piston heads hit the open valve plates and bend their tappets. In the best case, you will have to remove the cylinder head and change the valve group; in the worst case, you will have to throw away the broken pistons and a cylinder head cracked from the impact.
A broken alternator drive belt will not cause any damage, unless the power supply to the on-board network disappears and the battery begins to discharge. But in parallel, the engine will overheat, leading to accelerated wear of the cylinder-piston group.
Main reasons
Before talking about the signs of a dying pump that needs replacement or repair, you need to say a few words regarding the reasons for the failure of this device.
In total, there are several main factors that cause this to happen:
In most cases, it is the car owner himself who is to blame. Drivers are required to monitor the condition of the cooling system, periodically check the pump, and change the coolant on time.
We cannot exclude the problem of manufacturing defects, as well as simply low-quality and cheap pumps that are installed on budget cars or as part of repairs, thereby deceiving the client.
It is not surprising that the timing belt may then fail, the tension roller may rupture, the cylinder head gasket may break through, and other troubles that can cost a lot of money during repairs.
Problems with the water pump can occur on various cars:
Don’t think that this is a problem exclusively with cheap and budget cars, as well as simple engines like ZMZ 406.
The pump can also be used on more expensive cars. It all depends on how the owner monitors and maintains the car with his own hands, or in a car service center.