Information site about energy storage devices
The purpose of the battery is to start the engine and power the on-board electrics when the engine is stopped and the generator is not producing current. The generator, while moving, supplies energy to the battery, and the battery helps the generator cope with the load. The operation of two energy sources in pairs is the key to stable voltage in the network. If the battery is dead, you can recharge it with a generator. How to return the working capacity? Charge using a network charging station.
When does a car battery need to be charged?
The installed battery is monitored for open circuit voltage, which should be 12.5 V. The operating voltage is measured at the terminals after the battery is charged on the bench or using a booster. The density of the electrolyte in all banks must be the same, corresponding to the operating conditions of the vehicle. Measurements are taken with the engine running at a shaft speed of 1500-2000 rpm and the high beams on. It is normal if the mains voltage is 13.8 - 14.5 V. Both undercharging and overcharging have consequences for the technical condition of the battery.
For low-maintenance and hybrid batteries, periodic monitoring of the density and electrolyte level is mandatory. Maintenance-free batteries have no caps, are sealed, and can be used as long as they hold a charge. What is important for them is the stability of the network voltage and the absence of discharge to zero.
Dependence of battery charge and electrolyte density
Basically, we determine the end of battery charging by the readings of the charger or by the voltage at the battery terminals. But they will not be able to determine the exact state of charge of the battery. To find out how charged the battery is, you need to measure the density of the electrolyte. For this purpose there is such a device as a hydrometer. It is inexpensive and is sold in any car store. We recommend that you definitely have it on your household.
Electrolyte density should be measured in all jars. For more information about measuring density and about electrolyte in general, read the article “What acid is in a car battery.” On a fully charged battery, the electrolyte has a density of 1.28-1.3 g/cm3. A completely discharged battery has a density value of about 1.1 g/cm3. Below you can see a table of the dependence of electrolyte density on the state of charge of the battery:
| Electrolyte density, g/cm. cube (+15 degrees Celsius) | Voltage, V (no load) | Voltage, V (with load 100 A) | Battery charge level, % | Electrolyte freezing temperature, gr. Celsius |
| 1,11 | 11,7 | 8,4 | 0 | -7 |
| 1,12 | 11,76 | 8,54 | 6 | -8 |
| 1,13 | 11,82 | 8,68 | 12,56 | -9 |
| 1,14 | 11,88 | 8,84 | 19 | -11 |
| 1,15 | 11,94 | 9 | 25 | -13 |
| 1,16 | 12 | 9,14 | 31 | -14 |
| 1,17 | 12,06 | 9,3 | 37,5 | -16 |
| 1,18 | 12,12 | 9,46 | 44 | -18 |
| 1,19 | 12,18 | 9,6 | 50 | -24 |
| 1,2 | 12,24 | 9,74 | 56 | -27 |
| 1,21 | 12,3 | 9,9 | 62,5 | -32 |
| 1,22 | 12,36 | 10,06 | 69 | -37 |
| 1,23 | 12,42 | 10,2 | 75 | -42 |
| 1,24 | 12,48 | 10,34 | 81 | -46 |
| 1,25 | 12,54 | 10,5 | 87,5 | -50 |
| 1,26 | 12,6 | 10,66 | 94 | -55 |
| 1,27 | 12,66 | 10,8 | 100 | -60 |
| Electrolyte density, g/cm. cube (+15 degrees Celsius) | Voltage, V (no load) | Voltage, V (with load 100 A) | Battery charge level, % | Electrolyte freezing temperature, gr. Celsius |
Using these values, after measuring the density, you can find out exactly how charged the battery is. In general, that’s all I wanted to say about how to properly charge a car battery. All that remains is to remind you once again about observing safety precautions. Before charging the battery yourself, it makes sense to ask advice from more experienced car enthusiasts. You should have your own charger and hydrometer. They are not that expensive and they will always come in handy when operating a car.
How to properly charge a dead battery
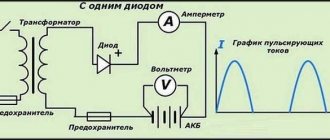
The charger for a car battery is represented by AC rectifiers. These can be devices that allow regulation of the charging current or voltage. How long will it take to charge a completely dead battery?
If the charging station operates at a constant charging current, a battery with a capacity of 60 A/h is fully charged within 20 hours with a constant current of 6 A.
At a constant current value during the charging period, the voltage increases, which leads to abundant gas release from the electrolyte. Therefore, the supplied direct current is reduced stepwise twice, when the voltage reaches 14.4 and 15 V. That is, control of recharging a dead battery needs monitoring and adjustment.
The method of charging batteries at a constant voltage does not require constant monitoring of the process. The target voltage is set, and the current varies from 40 amperes at the beginning to almost zero at the end of recharging. The recharging time for a completely discharged battery will be 24 hours. But maintenance-free batteries will not receive a full charge. 14.5 V corresponds to 90-95% of the battery capacity.
Simple rules for charging batteries
To avoid damaging the battery in your car, you need to follow simple rules. Based on everything said above, we have prepared recommendations that will allow you to most effectively restore a slightly dead battery and bring it back to life. But first, make sure that a deep discharge has not occurred. This will help you prevent unpleasant situations on the road.
The rules are as follows:
- First, make sure that the battery has not been deeply discharged; it can still be restored by charging. Also consider the age of the battery. If it is more than 4-6 years old, restoration may not bring any results.
- If possible, use high-quality and powerful chargers that can be adjusted to a specific battery capacity. This will allow you to professionally and safely restore the battery charge.
- Do not exceed 10% of the rated capacity. For example, a battery with a capacity of 60 Ah can be charged with a direct current of 6A. In this case, the battery will restore its charge in 10 hours.
- Be sure to check the battery in your car before each winter season. This will allow you to go through a dangerous season for your power source much more confidently without problems or troubles.
- Measure the density of the electrolyte and check the fluid level in the battery banks. Otherwise, charging may be the last action with your battery, after which it can be safely sent for recycling.
You should not buy too cheap batteries from unverified companies. Otherwise, you will face rapid equipment failure. But it makes no sense to purchase the most expensive batteries. A sudden generator failure or other circumstances can damage the battery. And here it will not matter how high-quality the battery you bought.
We also suggest watching a video with instructions on charging a car battery:
How long to charge a dead car battery?
The energy spent on starting the car, servicing the alarm system and other on-board systems is replenished by the generator. The voltage in the relay network is regulated by a regulator, which is designed for 13.9 - 14.3 V. The battery is not fully charged and periodically requires recharging. After being idle, the remaining battery charge may not be enough to start the engine. How to determine how long to charge a dead battery?
To charge a dead car battery, you will need to determine the degree of discharge of the battery by the voltage in the open circuit. In a serviced or hybrid battery, the residual charge can be determined by the actual density of the electrolyte.
The charging time is set by dividing the charging capacity by the charging current, which should be less than 10% of the charging capacity. The efficiency of the electrochemical reaction is assumed to be 50%. This means that the calculated time should be doubled.
Before charging, a dead car battery should be prepared for recharging - cleaned of dirt and acid deposits on the terminals. The plugs of low-maintenance batteries need to be unscrewed, the density and level of electrolyte in the banks must be checked.
To quickly charge a dead battery, you can use a mode with a current of 8 A for 3 hours and another hour with a current of 6 A. How long should you charge the battery so as not to harm it? It is optimal to use a current of 2-3 A, eliminate overheating, overcharging, and create the best conditions for long-term operation of the charger.
You can charge a dead car battery locally, but you need to assemble the circuit correctly. You should disconnect the negative wire and break the line so that the increased voltage does not harm the on-board network.
Work related to charging batteries is considered dangerous. An acid battery is filled with a caustic concentrated acid solution. Properly prepare and charge the battery while wearing rubber gloves in a ventilated area. Gases released from cans are explosive. There is no need to bring a lighter or open flame to the hole.
When should you charge the battery? We list the cases
It is important to start charging the battery at the right time. If you charge it every week, after six months there will be nothing left of the lead plates, and the electrolyte will become cloudy. Periodic charging will not save the battery or extend its life. You need to charge the battery only at the moment when it is really necessary. If you do this too often, you will simply shorten the life of the device and speed up the time for replacement.
Here are some indicators that it’s time to charge the battery:
- indicator on the battery itself - some batteries have special indicators that allow you to determine the charge level in time and renew it if necessary;
- readings from the on-board computer - you should sometimes monitor the voltage in the network before starting the engine using various devices; low voltage indicates that the battery is no longer working well under load;
- changes in the nature of engine starting - if the engine starts starting with a stop during rotation, with a changed sound, too slowly, then it’s time for you to look at the health of the battery;
- more than 3-4 years have passed since the first installation of the battery in the car, at this stage it is necessary to check the performance of the device under load and recharge it to its optimal state;
- When measuring, the device shows low voltage, especially at the moment of load - you can measure these parameters even with a regular tester in order to understand the characteristics of the device’s condition.
Batteries last no longer than 5 years in normal mode. Usually after this period they begin to require constant maintenance. In order not to charge the battery every week, at this stage it is better to purchase a new battery. Usually, specialized stores have a stand for testing batteries under load. This makes it as simple and comfortable as possible to check the battery for the integrity of the plates and the normal state of the electrolyte.
The battery is dead, how to charge without charging
If the energy of a dead battery after a long period of inactivity is not enough to set the car in motion, charging from external sources will be required. This could be recharging from the battery of another car or using an external energy source in the form of a battery or booster. You may have to use a pusher. How to apply the first pulse charge, in the future the generator will add energy, but after an emergency drop in charge, it is necessary to take measurements and charge the dead battery with a network station.
A battery that has reached zero is charged with a current of 2-3 A. If the voltage at the terminals does not increase within several hours, the battery needs to be replaced.
How to charge a completely dead car battery
A common cause of deep battery discharge is simple inattention. Often it is enough to leave the car with the lights or headlights, interior lighting or radio on for 6-12 hours, after which the battery is completely discharged. For this reason, many car owners are interested in the question of whether it is possible to restore a completely discharged battery.
As you know, completely discharging a battery greatly affects the battery life, especially when it comes to a maintenance-free battery. Manufacturers of car batteries indicate that even one full discharge is enough to cause the battery to fail. In practice, relatively new batteries can be restored at least 1 or 2 times after they are completely discharged without significant loss of performance properties.
First, you need to determine how much the battery is discharged using one of the above methods. You can also immediately charge the battery. Next, the completely discharged battery must be charged in the mode recommended by the battery manufacturer. The standard is to supply a charge current value at 0.1 of the total battery capacity.
A fully charged battery is charged with this current for at least 14-16 hours. For example, consider charging a battery with a capacity of 60 Amp-hours. In this case, the charge current should be on average from 3 A (slower) to 6 A (faster). A completely discharged car battery should be properly charged with the smallest current, and for as long as possible (about a day).
When the voltage at the battery terminals does not increase any more for 60 minutes. (assuming the same charging current is supplied), then the battery is fully charged. Maintenance-free batteries, when fully charged, assume a voltage value of 16.2±0.1 V. It should be borne in mind that this voltage value is standard, but it also depends on the battery capacity, charging current, electrolyte density in the battery, etc. Any voltmeter is suitable for measurement, regardless of the instrument’s error, since it is necessary to measure a constant, not an exact voltage.
Video
We invite you to watch a video on how to properly charge a car, the devices used, and how to properly prepare the equipment for restoration.
During the operation of any car battery, it is important to know how long the battery needs to be charged. It is also important to remember that the battery must be well prepared and not started in a hurry to avoid unpleasant consequences. It is known that there are potentially dangerous chemicals inside any battery. Careless handling of them can have a sad effect on both the car and its owner. Therefore, when asked about how long to charge a battery, it should be noted that high-quality and complete charging and preparation for it require a certain amount of time.
How to charge a maintenance-free battery
The vast majority of modern car batteries are maintenance-free and there is no way to check the level and density of the electrolyte. The process is not much different from the same procedure with other types of batteries. They charge with both constant current and constant voltage; use a better programmable charger, this will make the task easier for you.
However, when using manual chargers, timing is very important. First you need to find out the degree of discharge. A fully charged battery has a terminal voltage of 12.7 Volts. 11.7 V and below indicates that the battery is completely drained.
For a normal charge, 10% (or 1/10) of the battery capacity is sufficient. Let's take our example of a 70 Ah battery. We take readings with a voltmeter and get a value at the terminals of 12.2 V, which indicates that the battery is 50% low. That is, we need to make up 35 A of the missing current. Divide 35 by the charging current (7 A) and we get 5 hours. This is the required time to fully charge the battery in the example given.
The main thing is not to forget that overcharging is harmful to any type of battery. And if instead of 5 hours from the example above, you leave the battery on charge for 10 hours, then in this case the voltage level will not become higher and the capacity will not increase. But the electrolyte will boil perfectly and begin to evaporate. And in the case of serviced ones, the loss of electrolyte can be compensated for by simple topping up, but in unattended ones this cannot be done. This type of battery does not explode when boiling, as some car enthusiasts believe; it is equipped with a safety release valve for such cases. However, part of the working surface of the plates not covered with electrolyte will reduce the working capacity of the battery and reduce its overall service life. Manufacturers do not recommend recharging for longer than 30 minutes.
How to prepare the battery for charging
Wherever the car battery is charged, the main thing is that the room for this is as safe as possible. When the battery begins to charge, it begins to release toxic chemical fumes. Therefore, the room should be well ventilated and ventilated. Also, you should not charge the battery where there may be problems with electrical wiring in the form of periodic power surges and power outages. Of course, any operation with a battery is carried out where there are no open sources of fire or flammable substances.
What do you need to charge the battery?
To charge your car battery you will need a charger (charger). This device is also called a rectifier, since the charger converts alternating current into direct current. If you don’t have a charger yet, then read about choosing a charger for a car battery. And here we will only briefly talk about choosing a charger for your battery.
When choosing a charger for a car battery, you need to consider the following points:
- modes for different types of batteries. The most common type are WET batteries with liquid electrolyte. There are also AGM, GEL. In the case of the last two, you need a special charger or a universal charger with a mode for these batteries. All devices are suitable for WET;
- output voltage. This parameter must be selected depending on the rated voltage of your battery. Some device models allow you to charge batteries with different voltages (6/12/24V). For common 12V car batteries, the output voltage must be at least 16 volts. This will be enough to fully charge the battery;
- charging current. This value is selected depending on the nominal capacity of the battery. It must be at least 0.1 of the nominal capacity. It is better if there is a small margin so that the charger does not work at the limit of its capabilities.
As a rule, the charger consists of a rectifier circuit itself in a housing, a plug for connecting to a 220V network and wires with alligator clips for connecting to the battery.
Let's say you purchased a memory card. Now let's talk about how to charge a car battery with a charger. But first, a few words on safety precautions. We also advise you to read the material about how to charge the battery without removing it from the car.
How to do it right
To the question of how long it takes to charge a car battery, you can give a precise answer: on average, this process lasts 10 hours, no less . Experienced motorists recommend increasing the charging time with low currents to 15 hours in order to “pump” the battery properly. Of course, this is quite a long time. But only this charging time ensures full and high-quality battery operation. By the way, to ensure that the time does not drag on for the car owner for too long, you can leave the battery to charge overnight, having previously adjusted all the necessary indicators.
To do everything as correctly as possible, without consequences, it is best to disconnect the wires from the battery and completely remove it from the hood of the car (the battery is allowed inside the car, but only as a last resort). The charging process must not be interrupted : this will negatively affect the battery capacity level. This is how to properly and safely charge a car battery.
Express battery charging using constant voltage method
In order to understand the essence of the matter as best as possible and understand how long it takes to charge a car battery, it would first be a good idea to remember the fastest and most common charging method, which is called universal for modern battery models classified as maintenance-free.
In this case, the charger controls the charging current automatically, and the process itself is safe due to the fact that the formation of gases and the release of harmful chemicals into the atmosphere is minimal.
When using such simple technology, motorists, as a rule, do not “bother” with the question of how long to charge a car battery. It is known that the charging time in this case is no more than five hours, and the battery capacity is replenished by 50% in just an hour. In the next four hours, the battery will be charged more than 90%.
This is how the battery is charged by motorists who do not have the time or desire to take it out of the car. It is, indeed, almost safe, but it is more suitable for extreme cases. In order to “pump” the battery more efficiently and gradually, thereby ensuring the best performance, you need to use a different type of charger.
Important clarifications and calculations
How long does it take to charge the battery if you want to get a longer service life from it without causing harm? The fact is that any fast charging with high currents can contribute to a decrease in battery capacity , since we are talking about the use of one or another type of charger. It is with them that the confusion occurs. And not only for novice drivers, but also for those who fundamentally do not want to dive into the study of a simple topic related to such concepts as voltage and current.
As you know, there are six “cans” inside the battery. The output voltage of each of them is about 2 V, for a total of 12 V.
However, this indicator is conditional and not entirely accurate:
- the real U of a well-charged battery should be at least 12.6-12.7 V ;
- if it is 12 V or less , the battery is at least 50% discharged;
- if the voltage is 11.6 V or less - a deep discharge, urgent charging is necessary.
Capacity always remains the most important value and depends on how the battery is regularly charged, maintained, and how the battery is operated. The very concept of capacity can be briefly defined as follows: this is the time during which the battery can operate continuously, provided a certain amount of current is supplied.
For example, the most common capacities for car batteries are 55 Ah and 60 Ah. This is followed by batteries with higher ratings of 75 Ah and higher.
The elementary calculations here are as follows (we start from a capacity of 55 Ah, dividing it by the strength of the supplied current):
- When loaded with a current of 55 A, the battery will work for 1 hour ;
- when the load is less (for example, 27 A), the battery works longer, 2 hours ;
- at a load of 13.75 A, the work will already be 4 hours - and so on.
Of course, a strong current load is not applied to the battery under normal conditions. This is important to know in order to understand the concept of safe current. The safe current figure used when charging the battery should be 10 percent of the battery's rated capacity. Thus, you can calculate the battery charging time in the most basic way.
If calculating percentages is difficult, you can use a calculator:
- for a battery with a capacity of 55 Ah, the percentage of safe current will mean 5.5 A ; Read more about what current to charge the battery →
- how many hours will it take to charge the battery - 55÷5 = 10 hours .
It is very easy to calculate these indicators. They will help you understand that a five-hour express charge for car batteries is clearly not enough. In order for the battery to last longer and not have to be changed frequently, you should understand how to charge the battery in such a way as not to “dead” it ahead of time. It is important not only to achieve a real indicator of a charged battery of 12.6-12.7 V. It is important to ensure that this U lasts as long as possible while maintaining optimal capacity.
What current and how long does it take to charge a car battery?
The current is determined by the capacitive characteristics of the battery and is calculated individually. The labels of all batteries indicate the nominal capacity, indicating with what current the battery can be charged. The optimal charging parameter is about 10% of the battery capacity. If the battery is more than 3 years old or is severely discharged, then 0.5-1 Ampere should be added to this value.
If the starting current parameters are 650 Ah, then such a battery needs to be charged at 6 amperes, but on the condition that this is only a recharge.
If you need to quickly charge the battery, in emergency situations, you can select a value of 20 Amperes, while keeping the battery charged for no more than 5-6 hours, otherwise there is a risk of acid boiling over.
Two types of battery charger
There are two types of chargers:
- Direct current.
- Constant voltage .
Constant voltage memory
The so-called express charging of the battery lasting 5 hours is usually carried out with a popular Chinese charger, which uses the principle of constant voltage (14.4 V). When this device is connected to a battery, it provides more than 10 percent of the current rating: 25-30 A in the first hour of charging. The battery will withstand this current and will charge very quickly, but it will also run out much faster. The current drops in the first 3-4 hours, but the voltage remains constant. In five to six hours the battery will be charged to 90-95 percent.
If the battery is not completely dead yet
How long should a lead-acid battery be charged if, for example, the voltage has not yet dropped to critical levels? It is known that U 12 V means that the battery capacity is already 50 percent or less. But in this case it is not necessary to keep the battery charged for 10-12 hours.
Here are a few more short calculations:
- at a voltage of 12 V, charging time can be reduced to 7 hours, but not less ;
- If U is 11.6 V or less , it is better to charge for 12-15 hours .
During the charging process using a DC device, the voltage changes - up to 13.8-14.4 V. The voltage must be greater than the rated charge of 12 V, otherwise the current from the charger will not flow into the battery. If the battery is completely discharged, in 5-6 hours its charge will be 90-95 percent. In any case, you will have to wait up to 10 hours to reach 100 percent, because the current gradually becomes smaller towards the end of charging.
In conclusion, for novice car enthusiasts, it can also be noted that there is no specific time for charging batteries with different capacities. Everything depends only on the current and voltage indicators, the meaning of which should be understood in order to treat your car’s battery as carefully as possible. With the help of simple calculations and logical conclusions, you can understand that 5-6 hours is not enough time to properly charge the battery. It is better to wait the required amount of time in order to maintain the productive performance of the battery for as long as possible.
In winter, topics related to car batteries are especially relevant, because a cold start can quickly discharge it. Many people change old batteries ( simply handing them over to buyers ), buy new ones (the main thing is to choose the correct polarity ) - however, most try to recharge them and use them further. Fortunately, modern batteries last quite a long time (about 4 - 5 years), but this period can be much reduced! If you apply the current incorrectly and calculate the charging time incorrectly, the battery can quickly fail. Therefore, today we have detailed information about how long it takes to charge your battery...
THE CONTENT OF THE ARTICLE
I would like to immediately make a reservation - we will charge the car battery at home with a special charger, at an approximate temperature of 25 degrees Celsius, this is important, because if the temperature exceeds 35 degrees, then it is better not to start the process (here is the dependence of the temperature of the electrolyte and the surrounding air)! The thing is that the electrolyte has different densities at different temperatures (by the way, you can see how much of it is in different batteries ). However, I suggest remembering the principles of charge and discharge.
Is it possible to charge a “full” battery?
Many car enthusiasts are familiar with the phenomenon of battery overcharging. It occurs when, for some reason, the voltage regulator starts to work incorrectly, so the voltage at the generator output exceeds 14.5 Volts. The optimal voltage of a fully charged battery is 14 Volts. When the voltage difference between the generator and the battery exceeds one volt, the latter begins to absorb additional energy, which leads to boiling and evaporation of the electrolyte, as well as destruction of the lead plates. As a result, the electrolyte level first decreases, then the battery capacity decreases. After a short time (depending on the generator voltage), the drop in capacity becomes irreversible and cannot be restored by adding distilled water.
If the generator voltage regulator is working normally, then the voltage is maintained at 14 - 14.5 Volts, due to which the battery avoids overcharging. All this fully applies to stationary battery charging, which is carried out using a special charger. If the voltage at the output of the device does not exceed 14.5 Volts, then the battery will take the amount of electricity that is necessary to change the density of the electrolyte. When the voltage of the generator and the charger are equal, the rate of absorption of electricity will drop so much that further charging becomes meaningless. Even if the battery sits on the charger for two days, its capacity and charge will not change. If the voltage at the charger output exceeds 14.5 - 15 Volts, then overcharging will begin, which will lead to a decrease in battery capacity.
If you are using a charger that displays charging current but not voltage, consider the following. The charging current of a fully charged battery should not exceed 1 percent of its capacity. As soon as the charging current has dropped to 1-2 percent, it is necessary to disconnect the battery from the charger to avoid damaging it. Do not charge the battery from a charger without a voltage indicator if the charging current is less than 5 percent of capacity. This will extend the life of the battery and protect it from premature damage.
A fully charged battery can only be charged using a working charger that regulates and displays the charging voltage. If for some reason the charger does not regulate the charging voltage correctly, then connecting a charged battery to it will lead to boiling off of the electrolyte and a decrease in battery capacity. Therefore, it is advisable to postpone charging until the battery is at least 30 percent discharged.
Battery operating principle
In order to charge it, you need to understand how it works - no, I won’t break it down into its various components now, everyone already knows that inside there are lead plates in a special solution of sulfuric acid . We need to understand what, for example, 55 Ampere hour and 12 Volts are.
- Amps and Hours – Battery capacity is measured in Amps/Hours. That is, if your battery (rechargeable battery) is 60 Ah, then it can deliver 60 Amperes for one hour. Accordingly, if the load drops, for example to 30A, then it can supply for two hours and so on. I think this is understandable.
- Voltage - it is generally accepted that the voltage is 12 Volts, although this is not entirely correct. The normal value of the working version is 12.6 - 12.7V (there are options with more), this is fully charged to 100%.
If the voltage is 12V, then we can state that the battery discharge is approximately 40 - 50%, but with such indicators you can drive. If your car is in good working order and the generator provides normal “charging”, then the voltage will quickly be restored. I would also like to note that an indicator of 11.5 - 11.6V indicates a “ deep discharge ”, this is very “unpleasant” for the battery. The process of “sulfation” of the lead plates inside begins, which simply reduces the capacity of the battery - maybe so much that the car simply won’t start.
That is, we understand that the normal readings are 12.7V (charged), it is with this voltage that 60 Amperes will be delivered for an hour, and then it will drop to 11.6V (discharged). Then charge and re-use.
How to determine the charge and condition of the battery
There are two indicators of battery charge - electrolyte density and terminal voltage. However, these indicators apply only to serviceable batteries in which the lead plates have not crumbled. If the plates are damaged, then the density of the electrolyte and the voltage at the terminals will not say anything about the battery charge. A working battery differs from a damaged one in that it is capable of delivering high current for a long time. Even a weakly charged battery can spin a cold engine for at least one minute. A fully charged battery can spin the engine for at least 3 minutes. Even after the battery has “dead” and is unable to crank the engine, after 3-5 minutes of rest it will again be able to crank the engine without voltage.
The electrolyte density of a fully charged battery must exceed 1.22 grams per cm³. To measure the density of the electrolyte, you need to use a hydrometer, which can be purchased at any auto store. Given the huge number of hydrometer models, it is impossible to give a universal recommendation for their use. Therefore, carefully read the instructions that come with the hydrometer.
The voltage of a charged battery (no load) is 14 volts. When the ignition is turned on, it is 12.5 - 13.5 volts; when the starter is started, the voltage drops to 10 - 11 volts. If the battery voltage is below these values, you need to charge it.
Two battery structures
This is also an important line, the whole point is that you need to charge each type differently, or rather prepare for the charging process. SO:
The first type is the so-called maintenance-free batteries. They have an electrolyte inside and it is, as it were, “sealed” inside, that is, it cannot evaporate. If it turns into steam, it then condenses on the walls and re-precipitates into the main electrolyte. This is the most problem-free type. No need to worry about level replenishment, density, etc.
Battery preparation
Before charging the battery, you need to properly prepare it, because if you remove it, you need to check everything at once. As I wrote above, we will talk specifically about the battery being serviced.
- First you need to remove all condensation, oxide and dirt from the surface and contacts. To do this, simply take an ordinary rag, soak it in a solution of ordinary soda and wipe the upper part - the contacts. This way we achieve cleanliness - this is important! After all, if your battery has screw-on caps on top, then dirt may get into them during dismantling - which is highly undesirable! After all, it can cause battery failure by simply bridging the banks .
- You can unscrew the covers. We check the electrolyte level, if it is extremely low - it does not cover the plates, then it is MANDATORY to add distilled water. Otherwise, you will simply “kill” your battery. The lead plates will heat up and crumble.
- Ideally, you need to measure the density of the electrolyte. Let me remind you that for a working, normal battery it is 1.26 – 1.30 g/cm3.
After the preparatory work, you can proceed to charging. However, it is worth noting that it comes in two options - using direct current and using constant voltage, the time can vary greatly from these parameters. Unless, of course, you have a universal charger, you have minimal settings there.
Safety precautions when charging the battery
The charging procedure should not be carried out in an apartment, especially if you have small children. The battery must be charged in a ventilated area. If this is not possible, then do it on the balcony. The main danger is the release of hydrogen when charging the battery. Together with oxygen it forms an explosive mixture. Therefore, there must be good ventilation in the room so that hydrogen does not accumulate.
Remember that you cannot set anything on fire, smoke, cut metal to create sparks, etc. near a battery that is charging, etc. In addition, it is important to remember that the electrolyte is an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid. This is a caustic substance hazardous to human health. When working with electrolyte, wear gloves and safety glasses to prevent it from coming into contact with your skin or eyes. Ideally, you should keep a 10% baking soda solution nearby to neutralize the acid.
DC charging time
I think there is no need to explain that you connect the negative terminal of the battery to the negative terminal of the “charger” with the positive terminal in exactly the same way. Many people adhere to this option, because the “Amperage” that we supply to the battery is a very important parameter - it should never be exceeded, and if it is greatly underestimated, the battery will take a long time to charge.
I would also like to warn you that the voltage must be higher than the nominal voltage - that is, from the charger we get about 13.8 - 14V, about the same as a car generator gives. Only then will the charge begin; if the voltage is less than 12 (and even more so 11V), then nothing will happen, but will most likely worsen the discharge.
SO : The optimal voltage is considered to be 10% of the total battery capacity, that is, if you have 75 Ah, then you need to charge with a current of 7.5A.
Thus - if your battery is completely discharged (voltage less than 11.7V), then it should charge in 10 hours! However, the time may be reduced depending on the discharge level.
In the version with a serviceable battery, this is quite easy to determine - as soon as bubbles appear from the surface of the electrolyte in the banks, this means that the charge has been fully completed.
I would like to add on my own behalf - in ancient times (about 20 years ago), my father very often charged the battery at home, especially in winter. He set the 60Ah option to a current of 2A and left it overnight, so the battery took the required amount of energy from this small current. It should be noted that the discharge was not deep then. Therefore, if you just want to “feed” your battery, for example, the voltage at the contacts is exactly 12V, set it to a current of 1 - 2A overnight!
However, now there is another method that also requires a minimum of human intervention.
How to charge a calcium battery
Such batteries are designated on the casing Sa-Sa. They appeared on the market relatively recently and are practically maintenance-free. Their main advantages are:
- significant starting currents;
- large capacity;
- the electrolyte does not evaporate.
However, they also have disadvantages. And the main one is that if they are handled incorrectly, after three or four cycles they lose a lot of capacity. Therefore, it is very important to charge these batteries correctly.
In the manufacture of calcium car batteries, special technologies are used, and accordingly, they must be charged in a special way. To do this, you need to have a charger with the ability to output direct current at a voltage of 16.1 - 16.5 V. That is, having a charger with a maximum output voltage of 14.8 V, then the battery will only be charged halfway. In such cases, an excellent solution would be to purchase an Orion Vympel-55 charger; it has a programmable cycle and is excellent for charging calcium batteries.
An interesting point is that the car generator produces up to 15 volts of voltage, which is not enough to fully charge a battery of this type. And given the weather in our latitudes with cold winters and difficult operating conditions, a calcium battery can easily discharge at the most inopportune moment. To avoid this, it is better to periodically charge it - once a month will be enough. And for this you need a device that has programmable modes.
The sequence of actions for this charging:
- Set the voltage on the charger to 16.1 V. Set the current on the charger equal to 10% of the battery capacity.
- Charge until the charging current drops to 0.5 A. This can happen in 10 minutes, or maybe in an hour or five, it all depends on the degree of discharge of the battery and its technical condition.
- Indicate two limits on the charger. The upper limit is with a voltage of 16.1 V and a current of 3 A. and the lower limit: 13.2 volts and 0 A.
- Set up a “swing” for the battery. Their process is simple: at a current of 3 A, the voltage gradually increases to 16.1 V, and the current drops to zero. Upon reaching this level, the voltage begins to gradually drop to 13.1 V, and the current increases to 3 A. And so everything repeats.
During the charging process, the time it takes to complete one such cycle will decrease. At the beginning, it will take 20–30 minutes for the voltage to rise to its maximum value, and the drop will occur much faster. But as loading progresses, the situation will change to the opposite. The fall will be prolonged, and the growth will take place in a few minutes. This is a Signal that the calcium battery is charged.
Constant voltage charging time
This option is gaining increasing popularity - it is this principle that is implemented on many Chinese devices, where there are practically no “VOLTAGE” and “AMPERAGE” indicators, but only glowing “dots” or a scale that indicates the charge. This device is designed specifically for maintenance-free batteries, because you will not be able to watch the boiling of the electrolyte and the release of gas from it, because everything is sealed. Therefore, the first option is not entirely good. Here the voltage and amperage are automatically adjusted.
SO : The voltage can float in the range from 13.8 to 14.5V, the higher the voltage, the faster the charge.
So in the first hour the battery can absorb from 50 to 60% of the nominal capacity. That is, if it is 60A, then 60X60% = 36A
In the second hour - the voltage drops and the charge occurs more slowly, about 15 - 20%
The third hour is even lower, about 7 – 8%
The fourth is almost full capacity at 90 - 96%.
The subsequent hours are not really needed, the current strength can “drop” to 0.2A, charging to 100% will take almost the same 10 hours.
This option is convenient because you don’t need to worry about setting up the device – it will do everything for you.
DETAILED VIDEO - MUST WATCH!
So, how long does it take for batteries 55, 60, 75 - 100 Ah?
Guys, as you understand, everything is quite individual, which device you use. You also need to understand whether the discharge is complete or not.
If you exaggerate and imagine the complete discharge of any of the batteries. THAT:
In the case of a current of 10% of the nominal value - 10 hours until fully charged.
In the case of “regulated” voltage – 4 – 5 hours, up to 90 – 95% (which is quite enough) and again 8 – 10 hours until fully charged.
As you understand this, with a maximum discharge, if you have a partial discharge, then the time is much adjusted.
That's all, I think the information was useful to you. Read our AUTOBLOG.
(
71 votes, average: 3.73 out of 5)
Similar news
How much lead is in the battery. Let's look at car options.
AGM or GEL (gel) battery. Main differences. This is not one.
How to check for current leakage in a car. Multimeter or simply.