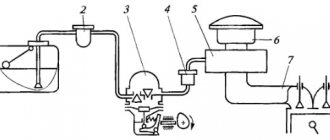
Current cut-off
Relay protection ensures reliable and safe operation of electrical networks.
Among the many protective means, current cutoff is widely used, the operating principle of which is based on a sharp increase in current strength in any part of the protected circuit. These devices are fast-acting devices.
They have selectivity and the ability to be adjusted depending on the maximum value of short-circuit currents. To ensure proper operation, you need to know how current cutoff works.
Operating principle of current cut-offs
When electric current flows in the network, its elements begin to heat up. This is the so-called operating temperature, which allows it to function for a long time as usual.
When there is a short circuit in the network, a significant increase in current occurs. As a rule, this leads to fires, destruction and other negative consequences. Elements that can withstand a short circuit for a long time are not economically profitable to produce.
A person simply does not have time to react to a short circuit due to the high rate of current increase. This function is taken over by automation, including current cut-off. It is used to control the amount of current in a section of the circuit. If the current increases and begins to exceed the set value, the protection is activated and the section is switched off.
The amount of current that triggers the protection is called the setting. Its value should ensure that the circuit is turned off before damage begins. There are various ways to create a current cutoff.
Most often, this procedure is carried out using electromagnetic relays. The closure of contacts in these devices occurs under the influence of electromagnetic force. Thus, the device sends a signal that turns off the protected element.
The same principle is applied in various designs of circuit breakers.
Fuses are an effective means of protection. Here the leading role is played by temperature, which increases under the influence of current and exerts its effect. When its value reaches a certain limit, the fuse link is destroyed and the electrical circuit breaks.
Features and types of current cut-offs
When a short circuit occurs, the amount of current passing through the circuit depends on where it occurs. Its value increases as it approaches the current source. Based on this property, selectivity of current cut-offs is ensured.
The protection must operate in the area for which it is intended. Therefore, its setting exceeds the fault current that occurred in another section. In this situation, the protection will not operate in the event of a short circuit outside its area.
In some cases, selectivity is not necessary. Here, protection is provided not for a single section, but for the entire line using additional differential protection devices.
Depending on the response time, all current cutoffs are divided:
- Instant. Their action depends entirely on their own response time. The main starting element is a current relay. Relays are used as intermediate elements, supplying a tripping signal directly to the circuit breaker release. The operation of such devices begins in the range from 0.04 to 0.06 s.
- With time delay. Their design includes an element that allows you to set a given time. The cutoff response range is from 0.25 to 0.6 seconds. Such devices are called automatic selective switches.
Thus, current cutoff allows protection to be performed in a variety of ways. As a result, reliable protection is provided not only for individual sections, but also for complete electrical circuits.
Rev limiting with Valvetrain
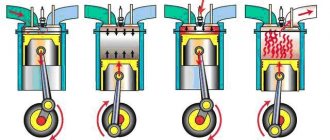
One example of work systems is Valvetrain technology. Most of these designs use metal springs to actuate the valves and return them to their designed, correct position, even when used harshly. But if the engine revs too quickly, the amplitude of the valve springs can exceed their limits, effectively leaving the valves open.
This phenomenon is called “incomplete valve closure,” which is not good. Unsynchronization in operation can lead to reduced compression, misfire, or even the collision of pistons with valves. After excessive "out of sync" ordering of fresh parts for the engine will be very likely.
The second problem of failure has already been described above - a broken connecting rod. Unfortunately, if the speed is exceeded, it can also happen on gasoline engines, but on diesel engines it happens more often.
When is high revs appropriate?
It is worth telling about one more interesting point. So, despite the fact that it is recommended to stick to medium speeds, experts have one interesting piece of advice. High speeds will benefit the engine if you start them once every 4-5 thousand kilometers, on a flat road, with a warmed-up unit. You don’t need to do this for a long time; 10-15 km of travel will be enough. This normalizes oil exchange, ensures uniform wear on the cylinder walls, and provides other significant benefits.
Complain
Types of cutoffs
It must be taken into account that there are different types that differ in their operating principle, but have the purpose of protecting against increased loads.
- Speed – the cut-off type is activated when a certain speed is reached, which is the maximum. Thanks to this function, manufacturers have created a limit on the peak speed of the machine. Due to the given system, the car cannot accelerate faster than the specified parameters.
- Turbine - this type can be activated by the speed of the turbocharger or the gas pressure in the turbocharger. This type is used on turbocharged engines.
- The crankshaft is the most common. It controls rotation and, due to certain limits, the function does not allow the shaft to rise. Not only foreign cars, but also domestic cars are equipped with these types of cutoffs.
It is recommended to use high-quality lubricants at high speeds to protect wear of parts and various breakdowns
It is very important to promptly replace the lubricant and control its quantity. It is not advisable to operate the machine at high speeds, this can lead to high fuel and oil consumption
Driving at low speeds and early shifting
It happens that driving school teachers and experienced drivers tell beginners that it is better to shift to a higher gear when the crankshaft reaches 1500–2000 rpm. V. min. Driving instructors give such recommendations to improve driving safety, and old drivers with experience, simply out of habit, because... Previously, low-speed engines were installed on cars.
Today, this mode can only be useful for a diesel car, the maximum torque of which has a wider rev range than that of a gasoline car. Not every car has a tachometer, for this reason drivers with little experience in this type of driving need to focus on the speed of the car. A mode involving early switching can be represented as follows - first gear, then the start of movement, after which the driver switches to 2nd: 10 km per hour, then to 3rd: 30 km per hour, after which he uses 4- y.: 40 km per hour, and then 5th gear: 50 km per hour.
This shifting method indicates a calm driving nature, which ensures safe driving on the road. However, there is also a drawback, which is that engine parts will wear out much faster, and there are reasons for this.
Adjusting the carburetor of a 4t scooter
One of the most important parts of any scooter is the carburetor; it is responsible for the correct supply of fuel, and therefore you should have a properly configured carburetor. Initially, the manufacturer makes scooters that would be suitable for a certain climatic situation, and the fuel system may not be able to cope with our weather changes, as a result of which the carburetor does not work correctly and most often does not maintain speed. That is why modern scooters are equipped with various adjusting bolts so that the vehicle owner can adjust the engine to the desired parameters, and adjusting the scooter’s carburetor does not cause difficulties.
A carburetor is a specific part of a scooter that is responsible for preparing the fuel mixture, mixing gasoline with air. The standard ratio of gasoline to air is 1 to 15, so any carburetor should produce these figures. Also, depending on this ratio, the mixture may be different; in the above parameters it will be optimal. But if you want to get a mixture that does not stall the engine at idle, use a ratio of 1 to 13.
After this, you can call the mixture “rich.” And finally, the last type is a lean mixture. This is the worst option, where the ratio of fuel to air is 1 to 17. With a lean mixture, there is a risk of carbon formation in the piston and its complete breakdown, so next we will talk about how the carburetor is adjusted on a 4t scooter.
Speed and revolutions: fuel savings and engine life
So, you can often hear from drivers that as soon as the car accelerates to 60 km/h, you can engage, for example, 5th gear (if the gearbox is 5-speed). In this case, the speed will drop to 1900-2000 thousand rpm and in this mode fuel consumption will be minimal. In other words, the most economical option is to drive when the highest gear is engaged and the speed is low.
If you study the theoretical part a little, accelerating to a certain speed will require energy expenditure. The more intense the acceleration occurs, the more energy is consumed. After reaching a constant speed (cruising), fuel consumption becomes less, but it must be taken into account that the car also overcomes air resistance.
It turns out that to maintain a speed of about 50 km/h, you need about 30-35 hp, while when accelerating to 120-130 km/h, 80-90 “horses” are needed to overcome resistance to air flows. To this you need to add the mass of the car itself, which is different for each vehicle, make allowances for road conditions, etc.
What is cutoff
It is a function in modern vehicles that provides protection against high loads and unsafe operating conditions. Its job is to stop the supply of fuel to the cylinders if critical values are reached during engine operation.
This term can be explained in simple language as follows: as a result of reaching maximum load values in the engine operation, the protection function is triggered. This allows the engine to spin up less, since the motor already has an increased load. At such moments, car drivers may feel that the engine does not pull, and at the same time there are jerks and pauses in traction.
Optimal engine speed.
Every driver should know what speed is optimal for the engine of his car, this knowledge will not only help save some money on fuel and repairs, but possibly also save a life, because without knowing the capabilities of your car, without knowing how to use its engine, you can put yourself in danger and its passengers.
Let's start with the fact that there are no universal speeds for all operating modes
. To warm up the engine, certain revolutions are required, for overtaking others, and for measured movement around the city, others.
Let's start with, of course, starting the engine, immediately after turning the key, the engine starts running at higher speeds (compared to idling). In this situation, this is the optimal speed for warming up the engine.
(usually 1100-1200 rpm), to supply frozen oil and thermal expansion of the connecting rod and piston group to the working size (you can read more here). If you want to extend the service life of your engine, you should not try to get rid of them, reflash the ECU, apply gas to warm up faster, but it is not recommended to start driving at warm-up speeds.
When the ShPG reaches operating temperature, the engine goes to idle speed
(600-800 rpm)
- this is the optimal speed for a stationary car
. The engine runs in light mode, just to avoid stalling and ensure minimal fuel consumption. The shafts rotate almost in a free state, they are not loaded and there is practically no wear in them, if not for one BUT: the oil pump also operates at minimum modes, if the oil is fresh and of high quality, then there will be no problems, the pump will drive it through all channels and throw it into the most inaccessible places, thereby lubricating them and cooling them. If the oil does not have the required qualities, the oil pump cannot cope, the engine begins to overheat little by little, deteriorating the oil even more and little by little oil starvation occurs and, as a result, increased engine wear.
So, we put the car in gear and started driving. Optimal speed for uniform straight-line movement on a flat surface
usually in the range from 1800 to 2000 rpm. In this mode of operation, the engine produces exactly as much as is necessary to maintain movement at a given speed with minimal fuel consumption. Usually the engine and gearbox are selected so that at these speeds the maximum permitted speed on the road is ensured. For example, 60 km/h in fourth speed at 2000 rpm or 90 km/h in fifth speed at 2000 rpm. Perhaps this is the ideal operating mode of the engine in terms of durability and fuel consumption, the engine is practically not loaded, the oil is evenly distributed and lubricates everything, but there is one caveat - an engine that has been running for a long time at such speeds can fail at the most inopportune moment.
Situations on the road are different, sometimes you just need to accelerate at a traffic light in order to change lanes in time, and sometimes you need to quickly overtake a truck, in this case, the optimal speed for fast acceleration will be the speed that creates maximum torque
. At these revolutions, the car is given the greatest acceleration, and the engine experiences enormous loads, and it is at this moment that the engine, which has run in at 2000 revolutions, can fail. When the engine is running, the engine connecting rods, under the influence of the inertia of the piston, are slightly extended; the higher the speed, the stronger the deformation (the connecting rod is longer). During long-term operation in gentle modes, a groove forms on the cylinder walls; it is only a few hundredths of a millimeter deep, but this is quite enough so that when switching to high speeds, the wear of the piston rings increases, and there is a possibility of damage and destruction of the rings.
Tips and tricks
Note that on many types of cars several types of engine cut-off are used at once, and simultaneously. As a rule, we are talking about vehicles that are equipped with highly accelerated naturally aspirated and turbocharged internal combustion engines.
Although constant driving at high speeds reduces the life of the internal combustion engine due to significant loads, it is possible to spin the engine up to the cutoff, without the risk of engine damage. As a rule, on many units, the engine reaches maximum power precisely when the speed rises in the range of 90-95% or more before the cutoff is triggered.
As for engine tuning and modifications, the cutoff speed is often shifted to obtain maximum performance from the internal combustion engine. There is also a scheme where the protective function is completely disabled by software. As a result, the full power of the unit becomes available, the car can be accelerated to high speeds, etc.
So-called tuning and sports control units allow you to push back the cutoff speed
It is important to understand that abnormal loads on the motor can lead to accelerated wear or even rapid failure. Usually the cut-off is shifted or disabled on specially prepared cars, the engines of which have more durable parts installed.
If we talk about the service life of a conventional engine, turning off the cutoff can easily be considered the reason for the rapid breakdown of the power unit. For this reason, the maximum that you can count on after such manipulations is the same 5% of the reserve. In this case, you can shift the speed without significant risk. In other situations, without additional changes to the engine design, it is highly not recommended to move the cutoff by more than 5%.
Finally, we note that the habit of turning the engine to high speeds means that the engine will naturally increase oil consumption. For this reason, it is necessary to select the correct lubricant and constantly monitor its level. Otherwise, operating the machine at maximum loads and high speeds may result in significant engine wear or serious damage.
- What engine speed is best to drive at?
Engine speed and service life. Disadvantages of driving at low and high speeds. At what engine speed is it best to drive? Tips and tricks. Read more
- How to increase engine power: basic methods
Increased power of naturally aspirated and turbocharged engines. Deep or superficial tuning of internal combustion engines. Modification of the intake and exhaust system. ECU firmware. Read more
- Cons and consequences of engine chip tuning
Is it worth doing chip tuning of a production car engine: the advantages and disadvantages of such modifications. Engine life and maintenance after chipping, tips. Read more
- Chip tuning and fuel cards
Fuel cards, chip tuning and tuning box. The influence of the ECU on the composition of the working mixture. Dependence of the AFR indicator on various engine operating modes, detonation. Read more
- Tuning the engine fuel system
Tuning the fuel system of atmospheric and turbo engines. Performance and energy consumption of the fuel pump, choice of fuel injectors, pressure regulators. Read more
- Power increase unit: chip box for diesel internal combustion engine
Diesel engine power increase module. Types of chip boxes, features of connection and operation of these blocks. Advantages and disadvantages of a tuning box. Read more
Optimal engine speeds at which wear and fuel consumption are minimal.
Many people wonder at what speed they should drive so that fuel consumption and engine wear are minimal.
In order to answer this question, you need to understand what processes occur in engines and at what speeds the lubrication and cooling system operates more efficiently. Fuel consumption greatly depends on driving style and engine speed. At higher speeds, consumption increases. This happens because the number of clock cycles per unit of time increases. That is, you need to inject fuel into the cylinder more often. The most optimal speed is considered to be 30% of the speed at which maximum engine power is achieved.
Driving style also has a strong influence on fuel consumption. Driving at a steady speed of 90-100 kilometers is considered the most economical. At the same time, any sudden acceleration and braking increase consumption like an avalanche. When the throttle is sharply opened on a carburetor engine, the accelerator pump starts working. It injects additional fuel into the diffuser. This is necessary in order to enrich the mixture entering the cylinders. In an injection engine, the mixture enrichment mode during acceleration is set by software, while the software transition to the power mode of operation depends on the throttle position. For example, when the throttle opening reaches 70% or more, the controller begins to calculate the composition of the enriched mixture. This is necessary so that the engine can deliver the necessary power. Therefore, for more economical driving, you need to avoid large throttle opening angles and sharp accelerations, while the speed should be kept at the same 30% of maximum power, that is, in most cases it is 2000-2500.
As for the optimal speeds at which engine wear is minimal, it is impossible to specifically say about one established figure. The golden rule applies here: the greater the load on the engine, the higher the speed it needs to be given. The problem is in the lubrication system. In order for the crankshaft bearings and the cylinder-piston group to be lubricated most effectively, it is necessary that the oil completely separates the friction pairs. That is, a so-called oil wedge was formed. This is when the gap between the parts is completely filled with oil, and there is not even the slightest contact. At low speeds and high loads, the oil pressure and volume are not enough for its formation, and with increasing loads the oil can be squeezed out. This will lead to contact between moving pairs and the formation of scoring on surfaces. Therefore, the more load, the higher the speed. But increasing them for a long time by more than 85 percent of the maximum is also not recommended. Because the cooling and lubrication system will work at the maximum of its capabilities without reserve. If any malfunctions occur in them, for example, clogged channels in the lubrication system or a clogged cooling radiator, the engine may overheat or scuff marks may form on the friction pairs. The oil may also be of poor quality and at high speeds its efficiency will be lower.
It is periodically recommended to increase the speed above 4000. There are two reasons for this.
The design of the timing valve mechanism is such that the valves can rotate when the engine is running. This is necessary so that their wear is even. But they can only rotate at high speeds. Around 4000-4500 thousand. And if you do not periodically turn the engine up to these speeds, a notch appears at the end of the valve because the pusher presses on it. If the valve rotates, then the wear on the end, rod and plate is uniform. If this recess has formed, then when higher speeds are reached, the valve will no longer rotate, for the reason that the protrusion on the pusher fits into the recess at the end of the valve and does not allow it to rotate.
The speed must also be increased periodically so that the engine can clean itself. At low speeds the temperature and turbulence of the mixture are lower than at high speeds. Therefore, increased soot formation is possible in the combustion chamber. If you drive at high speeds for a short distance, part of the soot will burn out, and the other part will break away from the vibration and fly away with the exhaust gases to the outlet. You can read more about engine self-cleaning at high speeds here.
You can also read the following articles.
Source
AMG195 Bio Sonic
- Complete skin cleansing without damage
- Wireless charger
- Protection of the case from moisture
- Has a soft attachment for sensitive skin
- 3 operating modes
- Comfortable procedures
- Efficiency can be compared to salon cleaning
- Good combination of price and quality
Not very convenient to change attachments
Many users believe that AMG195 Bio Sonic is the best facial massager. You can use it every day without taking breaks. The timer notifies you when you can move on to processing the next zone. The set includes 3 brushes, and the waterproof design allows you to use it directly in the shower.
In addition to age-related changes, the device fights various imperfections: acne, blackheads, age spots, oily sheen, flaking.
The presented rating will help you choose the most effective facial massager that is suitable for use at home.
What is engine speed cut-off in modern cars?
Quite often in the slang of professional drivers you can hear the following phrases: “the engine has reached the cutoff” or “the cutoff has worked.” So what do these phrases mean? Let's try to figure it out.
On new machines, the cut-off serves as a fuse against extra-heavy loads and dangerous operating conditions. The principle of operation is quite simple. When the critical point of the sensor in the power unit is reached, the cutoff stops the supply of fuel to the cylinders.
To put it into simpler terms, the moment the engine reaches its limit, the protection is triggered. After reaching critical levels, the engine speed decreases accordingly.
There are three types of fuse in total. All of them are different from each other, but they have the same goal - to preserve the engine in case of danger. Main types of cutoffs:
- The first type is activated when critical speed indicators are reached. At this moment, the number of revolutions decreases, and acceleration will be impossible;
- The second type runs on turbocharged engines. Such cut-offs are capable of responding to the speed of revolutions in the turbocharger or measuring the pressure in the compressor;
- The third type is the most famous. This cut-off controls the number of engine revolutions and, if necessary, prevents the crankshaft from rising above critical values.
- We are in social networks:
Discuss
Select it and press Ctrl + Enter
Thanks for the information, I'll let you know.
Ferrari announced a gradual reduction in the pricing policy of new sports cars.
The Ferrari car brand is going to start producing a more budget sports car, the Ferrari Roma, which will be available to almost all categories of citizens. Unfortunately, it is not reported how much the pricing policy of new sports cars will change.
Many experts believe that such actions by the brand may be caused by deteriorating sales figures in the global car market
Thus, the company wants to attract attention to its products from less wealthy motorists who want a Ferrari, but cannot afford it due to its high cost.
“When we created the Ferrari Roma, we focused on accessibility, quality and comfort. We wanted any driver to be able to drive our car without sacrificing anything. Including big money,” the brand’s press service reports.
It was also mentioned that in the future the company will consider creating more affordable sports car models.
It is worth noting that despite Ferrari’s adamance in creating exclusively sports cars, the brand intends to release its first crossover by 2022.
The auto mechanic claims that the domestic “Vesta” from below turned out to be a rusty “Logan” and it’s not clear what else.
Everyone knows that LADA cars came out not so long ago. Although a video appeared on the YouTube channel of one mechanic, where after three years of use, the car received an impressive malfunction.
The breakdown turned out to be a leaky muffler corrugation, which is why the car makes unusual sounds.
“The car, although it has a short lifespan, is only a couple of years old, has a mileage of 30-40 thousand km, and after the warranty expired, the car rusted,” the observer emphasized.
He claims that this problem has spread to the LADA Vesta from Renault
The observer also drew attention to the fact that on the bottom of the car he found a part not from AvtoVAZ, but from a piece of Logan and some other unknown model.
Finally, the upset mechanic gave his verdict: in order to repair the car, he would have to dismantle the section with the corrugation and the pipe adjacent to it, as well as part of the engine compartment.
Sales of electric trucks from DAF have started in European countries.
Representatives of the brand shared information that the first buyers of the vehicles were HVC and ROVA. Their main activity is waste collection and subsequent disposal.
It is also known that one truck with an electric motor was purchased by Cure from Rotterdam. A garbage truck with a crane will be used for its operation.
It is noteworthy that the vehicle has three axles, and its permissible gross weight is 28 tons.
The cars provided to the companies have a VDL E-Power power unit, its power is 210 kW, with a fairly high torque of 2000 Nm.
DAF said that the power unit is powered by several “batteries” that have a total capacity of 170 kWh.
It will take only half an hour to charge the installed batteries.
There is no word yet on when trucks with an electric motor will hit the markets of other countries.
Vehicle speed, engine speed and engine load: what you need to know
Let's start with the fact that many drivers are often faced with the fact that fuel consumption during the operation of a car differs markedly from the data declared by the manufacturer itself. More precisely, the engine is fully operational, but in terms of fuel, the “appetite” of this or that internal combustion engine is noticeably greater than according to the passport.
Let us add that there is a lot of controversy around various techniques and methods that help save fuel when driving. Some drivers believe that whenever possible they need to coast in neutral gear, others always try to engage a higher gear as early as possible and regardless of the speed of the car, others monitor the speed, not allowing the needle on the tachometer to rise above a certain threshold and etc.
Next, we will talk about the relationship between engine speed and speed, at what speed and in what gear you can drive with maximum fuel efficiency, and also what modes can be considered the most gentle for the engine itself.
Overcurrent protection
Purpose:
Maximum current protection (MCP) is a type of relay protection, the action of which is associated with an increase in current strength in the protected circuit when a short circuit occurs in a section of this circuit. This type of protection is used almost everywhere and is the most common in electrical networks.
Operating principle:
The principle of operation of the MTZ is similar to the principle of operation of the current cut-off. If the current in the protected network increases, the protection begins to work. However, if the current cut-off acts instantly, then the maximum current protection gives a signal to turn off only after a certain period of time, called the time delay. The time delay depends on where the protected area is located. The shortest time delay is set at the area furthest from the source. The MTZ of the neighboring (closer to the energy source) section operates with a longer time delay, differing by an amount called the selectivity level. The selectivity level is determined by the duration of the protection from which this time delay is applied. In the event of a short circuit in the area, its protection is triggered. If for some reason the protection does not work, then after a certain time (equal to the selectivity level) after the onset of the short circuit, the overcurrent protection of the section closer to the source will operate and turn off both the damaged and its own section
For this reason, it is important that the selectivity stage is greater than the protection response time, otherwise the protection of the adjacent area will turn off both the damaged and the working area before the damaged area’s own protection has time to operate. However, it is also important to make the selectivity level small enough so that the protection can operate before the short circuit current causes serious damage to the electrical network
The setting (or the current value at which the protection is triggered) is selected based on the lowest value of the short circuit current in the protected network (short circuit currents differ for different faults). However, when choosing a setting, you should also take into account the nature of the protected network. For example, when electric motors self-start after a power outage, the current in the network may be higher than the rated current, and the protection should not turn it off.
Implementation
MTZ is implemented, as a rule, using a current relay. Current relays can be either instantaneous or triggered with a time delay determined by the magnitude of the current. In the first case, a time relay is additionally used to provide the required time delay. In modern relay protection and automation schemes, microprocessor protection units are most often used, which combine the properties of these relays.
Literature
1. “Relay protection and automation of power supply systems” Andreev V. A. M. “Higher School” 2007 ISBN 978-5-06-004826-1 2. “Relay protection of power systems” Chernobrovov N. V., Semenov V. A M. Energoatomizdat 1998 ISBN 5-283-010031-7 3. “Maximum current protection” Shabad M. A. Leningrad. Energoatomizdat. 1991
What engine speed should you keep?
Almost every driver is well aware that the life of the engine and other components of the car directly depends on the individual driving style. For this reason, many car owners, especially beginners, often think about what speed is best to drive at. Next, we will look at what engine speed should be maintained, taking into account different road conditions during vehicle operation.
What is engine cut-off: what is it for and how does it work
As already mentioned, the engine cut-off performs a protective function. The scheme of operation of this solution on modern internal combustion engines with an injector is as follows: when the limit of preset values is reached during the use of the engine, the electronic engine control unit blocks the supply of fuel to the cylinders, thereby reducing the crankshaft speed.
As for the values themselves, the engine cut-off is triggered taking into account the following parameters:
- vehicle speed;
- crankshaft revolutions;
- exhaust gas pressure in an internal combustion engine with a turbocharger;
Speed-based cut-off (maximum speed limit) is a solution that is usually used in conjunction with rev-based cut-off. In the first case, the cutoff is needed to ensure that the car does not accelerate above a certain threshold, while in the second we are talking about protecting the engine itself when driving in different gears.
The speed cutoff is triggered in such a way that after reaching the “maximum speed,” the ECU turns off the fuel supply to the cylinders. The fuel supply is resumed after the vehicle speed decreases to the required value.
In practice, if the car is accelerated to 250 km/h, then the cut-off will work; when the speed drops to a conditional 240 km/h, the control unit will supply fuel again, but when the speed increases to 250 km/h, the software engine cut-off will work again. It turns out that the car simply will not go faster than the cut-off speed.
A cut-off based on the exhaust gas pressure in the turbocharger and the turbine rotation speed is present on turbo engines. The fact is that even if the crankshaft speed has not yet reached critical levels for the internal combustion engine itself, the consequences for the turbine can already be serious and damage an expensive element.
In simple words, after the turbocharger has spun up to an average of 110-115 thousand rpm. and more, it is necessary to limit the flow and pressure of the exhaust gases so that the turbine does not collapse. This can be done by cutting off the engine.
As for the cut-off based on crankshaft rotation speed (engine speed), this option is the most common and is used everywhere. Most engines in foreign and domestic cars have the specified protection scheme.
Currently reading
For example, the stock gasoline engine in both the Kia Rio or Hyundai Solaris and the domestic VAZ Kalina has a cut-off that operates at 6.5 thousand rpm. This is a conditional established standard for many engines. At the same time, there are many units that have different cut-off speeds. Car engines that typically spin higher (up to 7-7.5 or even 8 thousand rpm) are already considered high-speed. On sports cars, this figure is far from the maximum.
The speed cut occurs at the command of the control unit and prevents a further increase in speed. As a rule, the specified cutoff assumes that the protection is activated when the engine spins up to 95 or 100% of the maximum possible operating speed.
To put it differently, designers leave 5-7% of the maximum speed at which a particular type of internal combustion engine operates without significant loss of life or destruction. For example, if the cutoff operates at 6.5 thousand rpm, then the maximum speed for such an engine can be considered almost 7 thousand rpm, and the internal combustion engine will operate without breakdowns.
The cutoff speed on the tachometer is highlighted by the well-known red zone. After reaching such speeds, the cut-off occurs when the ECU turns off the fuel supply to the cylinders. Further resumption of fuel supply will occur when the speed drops to the limit that is registered in the memory of the control unit.
How to drive?
What speeds can be considered optimal? Listening to the opinions of experts, drivers come to the conclusion that the best operating mode of the power unit is from 0.3 to 0.8 of the maximum performance. Anyone who prefers to drive this way does not have to worry about the life of the engine. Major repairs will not be needed in the near future.
If the iron horse was purchased relatively recently, in other words, if it is being run-in, you should not constantly press on the gas. It is best not to gain speed more than 0.65 from the maximum. This also plays an important role in extending the period of use.
Most likely the article will be able to help people. It will enable drivers who are worried about their iron horse to find out how to significantly extend the operating time of the engine. Plus, it became clear which mode of operation would be best for him.
In the end, it should be noted that regular driving at too low and very high speeds provokes processes that at some point lead to engine failure. If you do not listen to recommendations regarding what speeds are best to drive at, you will need a major overhaul. Everything would be fine, but its cost is quite high. And you will have to spend a lot of time so that the iron horse can please its owner again!
Source