Experienced motorists with extensive experience always closely monitor the exhaust pipe of their car - and for good reason. Sometimes condensation pours out of there, at other times soot particles fly out or a black coating appears on the edges of the pipe. This is a consequence of the processes occurring in the motor. Using these traces, you can determine the quality of the fuel poured, the condition of the catalyst, wear of the piston rings, and even the condition of the engine cooling system gaskets. All this will be useful for cars that have long expired their warranty period and can at any time upset the owners with expensive repairs. The sooner the driver diagnoses the problem, the less hassle he will have in the future.
Periodic table of exhaust gases
Now, thanks to the media, the topic of the ecology of the Planet is under close public attention, namely its saturation and pollution by car exhaust gases. People especially carefully monitor and discuss such a by-product of widespread motorization, which has been widely circulated in the press, as the “greenhouse effect” and the harm of exhaust gases from diesel cars.
However, as we know, exhaust gases are different, despite the fact that they are all dangerous for the human body and other forms of life on Earth. So what makes them dangerous? And what makes them different from each other? Let's look under a microscope to see what the blue smog flying out of the exhaust pipe consists of. Carbon dioxide, soot, nitrogen oxide and some other equally dangerous elements.
Scientists note that the environmental situation in many industrialized and developing countries has improved significantly over the past 25 years. This is mainly due to the gradual but inevitable tightening of environmental standards, as well as the transfer of production to other continents and other countries, including East Asia. In Russia, Ukraine, and other CIS countries, a large number of enterprises were closed due to political and economic turmoil, which on the one hand created an extremely difficult socio-economic situation, but significantly improved the environmental performance of these countries.
However, according to research scientists, cars pose the greatest danger to our green planet. Even with a gradual tightening of standards for emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere, due to the increase in the number of cars, the results of this work, alas, are leveled out.
If we segment the total mass of various vehicles currently present on the planet, diesel engines remain the dirtiest; cars with this type of fuel exceeding nitrogen oxide are especially dangerous. Despite decades of development and assurances from automakers that they can make diesel engines cleaner, nitrogen oxide and fine soot particles are still diesel's biggest enemies.
It is because of these problems associated with the use of diesel engines that large German cities such as Stuttgart and Munich are currently discussing a ban on the use of heavy fuel vehicles.
Here is a comprehensive list of harmful substances contained in exhaust gases and the harm caused to human health when inhaled
Why is there blue smoke coming from the exhaust pipe?
What causes smoke to turn blue? Everything here is quite simple - in addition to gasoline, engine oil also burns in the engine. Most often, oil consumption due to waste reaches up to 0.2% of fuel consumption. In this case, the smoke does not turn blue. But when the engine begins to “eat” oil from 0.5 to 1% of fuel consumption, blue or bluish smoke will come out of the exhaust pipe.
If your car has increased smoke and oil consumption has increased, check the spark plugs first. If their appearance is the same as in this photo, then there is clearly something wrong with the engine, since it provokes severe oil loss.
Carbon deposits on the spark plug
Smoke with a high oil content can range from clear to deep blue. If oil consumption is up to 0.5 liters per 100 km, then blue smoke will only appear when the car accelerates. And if the oil disappears at a rate of 1 liter per 100 km, then smoke will be present in all engine operating modes. By the way, here we must remember that the car’s design contains a neutralizer, which can clean blue exhaust quite well even with severe oil loss.
Blue oil smoke, unlike transparent exhaust, is not able to dissipate in the atmosphere. If you apply a sheet of paper to the exhaust pipe while the engine is running, black oil droplets will appear on the sheet, which are ejected along with the blue exhaust gas. Also, oil may drip from the exhaust pipe instead of water vapor. This is a dangerous breakdown; you need to urgently go to a service station, otherwise the catalyst will very quickly fail.
If there is blue smoke, engine oil may drip from the exhaust pipe.
Ideally, the exhaust consists of 95% oxygen, nitrogen and other products of fuel combustion. These chemicals have no color. And the remaining 5% of the exhaust is water vapor, which is formed during thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) of the fuel. Therefore, blue smoke from the exhaust pipe does not appear when gasoline is burned in the cylinders of the internal combustion engine, but when any excess substances are burned. Oil is used to lubricate the internal parts of the engine, and a cooling system with antifreeze is used to cool the cylinders. If a malfunction occurs in the units, then these substances are mixed with the fuel. The combustion products of such a mixture give a certain color to the exhaust, which can be not only blue, but also white, black, white and even red.
The main symptoms of engine oil getting into the fuel mixture:
- When the engine is running, blue smoke comes out of the exhaust pipe while oil consumption increases . Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to check the engine oil level. If it goes away quickly, then with intense driving the blue smoke becomes thicker.
- When there are initial signs of a malfunction, blue smoke from the exhaust pipe appears only when the engine warms up, that is, “when it’s cold . This is due to the fact that the thermal gaps expand, that is, they come into working condition. When the engine warms up, the smoke disappears. Hence the conclusion - checking compression in cylinders does not always help to identify precise problems.
- When wear on engine parts increases, increased thermal clearances cannot prevent oil from entering the fuel-fuel mixture. As the temperature inside the engine increases, oil loss increases.
- When oil gets on the spark plug, it becomes covered with soot. And this leads to a decrease in the quality of the spark and deterioration of ignition. The engine begins to “trouble”, that is, to work unstably.
- If there is a rupture of the diaphragm on the vacuum sensor of the automatic transmission, then the spark plug located next to the area where the vacuum hose is connected will be turned out and splashed with oil. When the other candles will be fine. As a result, the vacuum in the manifold will “eat” the oil straight from the box.
Another good article: White smoke from the exhaust pipe: causes of gasoline and diesel engine smoke, how to eliminate it
To start searching for the cause of blue smoke, you should start by checking the compression in the cylinders. But this may not give a reliable result, since there are cases that oil seals the gaps. Therefore, they next check the wear of the valve stem seals - this procedure takes less time than disassembling the cylinder-piston group. If the cause cannot be determined, then proceed to disassembling the engine and inspecting the cylinder-piston group. In some cases, it will be cheaper to completely replace the motor with a contract one.
Benzene
Benzene is found in small quantities in gasoline. Colorless, transparent, easily mobile liquid.
As soon as you fill your car's tank with gasoline, the first hazardous substance you will come into contact with is benzene, which evaporates from the tank. But benzene is the most dangerous when burning fuel.
Benzene is one of those substances that can cause cancer in humans. However, a decisive reduction in airborne hazardous benzene was achieved many years ago using a three-pass catalyst.
Features of the diesel engine exhaust system
Motorists need to take into account the fact that power units running on heavy fuel emit more toxic substances into the atmosphere. That is why it is worth highlighting some features of the exhaust system for diesel engines:
- the initial temperature of the exhaust gases in a diesel engine is slightly lower and varies between 500 - 600 degrees Celsius;
- After leaving the cylinders, the exhaust gases are first sent to the turbocharger, which is used to supercharge;
- then the waste passes through the lambda probe and is sent to the particulate filter, where cleaning occurs;
- At the final stage, the exhaust passes through the muffler, after which it enters directly into the atmosphere.
It is worth noting that the evolution of power units, as well as exhaust systems, is carried out regularly, and already, for example, for gasoline and diesel engines with Euro 5 class, the presence of a particulate filter, as well as a catalyst, is a must. However, such components cannot be replaced with a flame arrester in accordance with current legislation.
Fine dust (particulate matter)
This air pollutant is an unidentified substance. It is better to say that this is a complex mixture of substances, which may differ in origin, form and chemical composition.
In cars, ultra-fine abrasive is present in all forms of operation, for example, during wear of tires and brake discs. But the greatest danger is soot from exhaust gases. Previously, only diesel engines suffered from this unpleasant moment in operation. Thanks to the installation of particulate filters, the situation has improved significantly.
Now, a similar problem has emerged in gasoline models as they increasingly use direct fuel injection systems, resulting in the by-product production of even finer particulate matter than diesel engines.
However, according to scientists studying the nature of the problem, only 15% of fine dust deposited in the lungs is produced by cars; the source of the dangerous phenomenon can be any human activity, from agriculture to laser printers, fireplaces and, of course, cigarettes.
Health of residents of megacities
The actual load on the human body from exhaust gases depends on the volume of traffic and weather conditions. Anyone who lives on a busy street is exposed to much greater levels of nitrogen oxides or fine dust.
Exhaust gases are not equally dangerous for all residents. Healthy people will hardly feel the “gas attack” at all, although the intensity of the load will not decrease, but the health of an asthmatic or a person with cardiovascular diseases can significantly worsen due to the presence of exhaust gases.
Rare malfunctions
Bluish smoke near the exhaust pipe appears not only in cars with a worn-out engine. The problem may appear on a car that has just come off the production line. Most often, the pipe begins to smoke immediately after the car is started. As it warms up, the smoke dissipates. The reason for this phenomenon is the gaps between new parts in a cooled state. Gradually they grind in, after heating the tightness is restored and the engine works as it should.
Another good article: The starter turns, but does not turn the engine: reasons for what to do when the starter clicks and does not respond
Blue smoke may be present for some time on a new car or after an engine repair.
For cars with an automatic transmission, thick blue smoke may appear from the exhaust pipe when the membrane of the vacuum corrector (modulator ) breaks. This device reacts to the vacuum that occurs in the manifold. If the modulator is damaged, the oil from the gearbox is drawn into the manifold and burns there, resulting in a smoky exhaust of a characteristic bluish color. This malfunction occurs if a vacuum load cell is installed. Inspecting the spark plugs helps to suspect such a problem. A pronounced soot appears on them.
There are other defects, a sign of which is black-blue smoke:
- destruction of jumpers between rings;
- regular exposure of the engine to high temperatures leads to changes in the design of the lower guide part of the piston (skirt);
- deformation of the connecting rod geometry due to the impact of the piston on the valves or broken belts;
- ignition fault;
- Burning and sticking of rings in the piston grooves occurs when using low-quality motor oil.
Most often, such problems do not occur in all combustion chambers at the same time; 1 or more cylinders are not working correctly.
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Gas, harmful to the entire climate of the planet, inevitably arises from the combustion of fossil fuels such as diesel fuel or gasoline. From a CO2 perspective, diesel engines are slightly cleaner than petrol engines because they generally use less fuel.
CO2 is harmless to humans, but not to nature. The greenhouse gas CO2 is responsible for most of global warming. According to the German Federal Ministry of the Environment, in 2015 the share of carbon dioxide in total greenhouse gas emissions was 87.8 percent.
Conclusion
Modern car enthusiasts need to take into account the fact that a car, at its core, is a complex mechanism that contains a number of structural elements. Among other things, there is a CO2 emission system directly into the atmosphere, which purifies and removes exhaust gases and particles of unburned fuel. Every driver needs to know about these elements, for the simple reason that over time the exhaust system fails, after which toxic substances that do not undergo special cleaning begin to be released into the environment. At this moment, the car owner must immediately begin repairs, because untreated exhaust gases harm not only nature, but also human health. Author: Oleg Mokrov
Carbon monoxide (Co, carbon monoxide)
An extremely dangerous by-product of combustion. Carbon monoxide is a colorless, tasteless and odorless gas. The combination of carbon and oxygen occurs during incomplete combustion of carbon-containing substances and is an extremely dangerous poison. Therefore, high-quality ventilation in garages and underground parking lots is important for the lives of their users.
For the average person, ozone is not some kind of dangerous or toxic gas. However, in reality this is not the case.
With climate change, the risk of high ozone concentrations increases. Scientists believe that by 2050 the ozone load should increase sharply. To solve the problem, nitrogen oxides emitted by transport must be significantly reduced. In addition, there are many factors influencing the spread of ozone; for example, solvents in paints and varnishes also actively contribute to the problem.
Carbon monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide) CO is a colorless and odorless gas. It is a poison for the respiratory system, disrupting the function of the central nervous and cardiovascular systems. In the human body, it binds red blood cells and causes oxygen starvation, which in a short time leads to death from suffocation. Already at a concentration in the air of 0.3% by volume, carbon monoxide kills a person in a very short time. The effect depends on the concentration of CO in the air, on the duration and depth of inhalation. Only in an environment with zero concentration of CO can it be eliminated from the body through the lungs.
Carbon monoxide always occurs when there is a lack of oxygen and incomplete combustion.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
This pollutant is produced when sulfur is burned in fuel. It is one of the classic atmospheric pollutants produced during combustion, power plants and industry. SO2 is one of the most important “ingredients” of the pollutants that form smog, also called “London smog”.
In the atmosphere, sulfur dioxide undergoes a number of transformation processes, which can result in the formation of sulfuric acid, sulfites and sulfates. SO2 acts primarily on the mucous membranes of the eye and upper respiratory tract. On the environmental side, sulfur dioxide can damage plants and cause soil acidification.
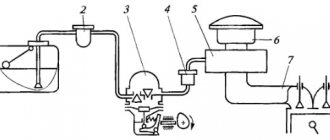
The principle of operation of the exhaust system
In order for the motorist to understand why vehicles have a detrimental effect on the environment, it is worthwhile using a clear example to understand the principle of operation of the exhaust system, namely:
- after fuel combustion, the exhaust valves open and gases and unburned fuel escape through the vacated channels;
- then the gases enter the exhaust manifold, where they gradually combine into one continuous gas stream;
- the processing passes through the pipe to the first oxygen sensor, which transmits data to the control unit, where the composition of the air-fuel mixture is taken into account;
- after this, the waste reaches the catalyst, where the gases react with oxidizing metals, causing them to lose their toxicity;
- further testing passes through the second oxygen sensor, where the quality of gas purification and the performance of the catalyst are determined;
- almost at the very end, the exhaust gases enter the resonator, where flows are redirected, which reduces the noise level;
- After passing through the last muffler, the spent CO2 emissions are directly released into the atmosphere.
It is noteworthy that this exhaust gas system is being improved every year by automobile manufacturers in order to significantly reduce the harm caused to the environment.
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
Nitrogen oxides are formed mainly during the combustion process in internal combustion engines. Diesel vehicles are considered the main source. The introduction of catalysts and particulate filters continues to increase, so emissions will drop markedly, but this will only happen in the future.
NO2 is an irritant gas. This leads to eye irritation and damage to the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. Due to its broncho-constricting characteristics, it is especially problematic for asthmatics and people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Measurement data show that on average the annual amount of NOx was exceeded by 57% of the norm. The main culprits remain a variety of transport. Since 2010, there has been only a slight decrease in the pollution trend. From 1990 to 2015, emissions fell by 59%.
Source
Traffic fumes
Traffic fumes
(exhaust gases) - working fluid spent in the engine. They are products of oxidation and incomplete combustion of hydrocarbon fuels. Exhaust gas emissions are the main reason for exceeding permissible concentrations of toxic substances and carcinogens in the atmosphere of large cities and the formation of smog, which is a common cause of poisoning in confined spaces.
The amount of pollutants released into the atmosphere by cars is determined by the mass emission of gases and the composition of the exhaust gases.
Measures to reduce the concentration of toxic substances in exhaust gases
Currently, the Governments of all countries are introducing certain standards for the concentration of harmful substances in vehicle exhaust gases. Therefore, car manufacturers, in order to enter the market, are forced to modernize internal combustion engine systems in order to reduce the level of toxic substances.
Such systems can include catalytic converters, particulate filters, urea and much more. For example, exhaust gas neutralizers are installed for diesel engines, which reduce toxicity by 80%. In Nin-free engine systems, an antitoxicant is installed in the power system, which also makes it possible to reduce the concentration of harmful substances.
Composition of automobile exhaust gases
| Gasoline engines | Diesels | |
| N2, vol.% | 74—77 | 76—78 |
| O2, vol.% | 0,3—8,0 | 2,0—18,0 |
| H2O (vapour), vol.% | 3,0—5,5 | 0,5—4,0 |
| CO2, vol.% | 0,0—16,0 | 1,0—10,0 |
| CO*, vol.% | 0,1—5,0 | 0,01—0,5 |
| Nitrogen oxides*, vol.% | 0,0—0,8 | 0,0002—0,5 |
| Hydrocarbons*, vol.% | 0,2—3,0 | 0,09—0,5 |
| Aldehydes*, vol.% | 0,0—0,2 | 0,001—0,009 |
| Soot**, g/m 3 | 0,0—0,04 | 0,01—1,10 |
| Benzpyrene-3.4**, g/m 3 | 10—20·10 −6 | 10×10 −6 |
Exhaust gas content. Gasoline combustion analysis
Problems associated with the use of cars have been studied for a long time in Russian science and practice. One of the main problems is the need to study the composition of exhaust gases from vehicle operation in order to reduce their harmful effects.
Issues related to the operation of internal combustion engines were studied by such authors as K. S. Golokhvast, N. K. Khristoforova and others [1], M. S. Assad, V. V. Grushevsky [2], Sufiyanov R. Sh., Moiseev A. E. [3], Smolenskaya N. M., Smolensky V. V. [4], Sadov A. A., Govorukhin I. A. [5].
The purpose of this article is to analyze the composition of exhaust gases generated during the operation of an internal combustion engine and consider ways to reduce their harmful effects on the environment, as well as efficiency.
The relevance of the topic is that exhaust gases pollute the environment. In modern conditions, global warming, as well as high levels of urban pollution, are a common problem. One of the main reasons for this is the growing number of vehicles producing exhaust fumes.
For an individual, the significance of the topic lies in the need to choose the type of engine and the optimal fuel for it in terms of economical fuel consumption, engine maintenance, and the durability of its use.
It is necessary to consider the internal combustion engine itself and the processes occurring in it.
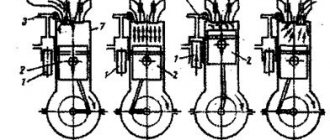
An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine where the chemical energy of the fuel burning in the combustion chamber is converted into mechanical work.
Processes occurring in an internal combustion engine during each of the 4 strokes (cycles are individual processes occurring in the cylinder during one piston stroke and making up the full operating cycle of an internal combustion engine):
− injection - the combustion chamber expands, the valve is open and filled with the fuel mixture;
− compression - the valve is closed, the piston moves up, the volume of the chamber decreases;
− power stroke—the fuel mixture ignites. The mixture expands the combustion chamber, pushing the piston;
− exhaust - the piston goes up, the valve is open, the combustion chamber is cleared of combustion products.
ICEs are classified according to different criteria.
1) by design: gas turbine - the combustion work is perceived by the working blades; reactive - the reactive pressure that occurs when combustion products flow out of the nozzle is used; piston - the work of gaseous combustion products is carried out in a cylinder, or is used in a driven machine. Piston engines are two-stroke and four-stroke.
A two-stroke engine is a piston internal combustion engine in which the working process in each of the cylinders is completed in two strokes of the piston.
A four-stroke engine is a piston internal combustion engine in which the working process in each of the cylinders is completed in four piston strokes.
2) by purpose: transport (automobile, ship, aircraft); stationary - works in one place and is attached to the foundation or to a rigid fixed frame; special - the use of such motors makes it possible to simplify the electric drive and give it some properties that general-purpose motors do not provide.
3) by type of fuel used: heavy fuel (diesel); gas; gasoline.
Diesel fuel is a liquid product used as fuel in a diesel internal combustion engine;
The gas used as fuel in internal combustion engines is propane-butane and methane.
The most common gasoline engines are those used in passenger cars. They are the ones that are of the greatest interest for revealing the topic.
Gasoline is a colorless flammable liquid obtained by refining petroleum. Gasoline is produced in several grades, their characteristics are given in Table 1.
Table 1
Gasoline brands and their characteristics
| Brand | GOST/TU | Octane number (motor method) | Octane number (research method) |
| A-92 | TU38.001165–87 | 83 | 92 |
| AI-93 | GOST 2084–77 | 85 | 93 |
| AI-95 | GOST 2084–77 | 87 | 95 |
| AI-98 | GOST 2084–77 | 89 | 98 |
Octane number is an indicator characterizing the detonation resistance of fuel, which is used in internal combustion engines with external mixture formation.
In Russia, only 2 methods are currently accepted and used to determine the octane level in gasoline. The research method for determining the octane number means conducting tests in strict accordance with GOST 8226–82 [6] and GOST R 32339–2013 [7]. The motor method for determining the octane number is provided for by GOST 511–81 [8] and GOST R 32340–2013 [9]. A comparative analysis of diesel and gasoline engines is presented in Table 2.
table 2
Comparative characteristics of diesel and gasoline engines
| Diesel engine | Gas engine |
| Advantages | |
| - diesel fuel is less susceptible to fire — A diesel unit is more environmentally friendly, as it burns the fuel charge more fully and efficiently. Diesel fuel is also cleaner than gasoline — Diesel fuel consumption is 30–35% less than gasoline engines — The service life of a diesel engine is longer than that of gasoline engines — the absence of an ignition system in the design of a diesel engine eliminates a number of problems that are inherent in gasoline power units | - gasoline engines are more powerful than diesel engines — The noise from a gasoline engine is less than that of a diesel engine - a gasoline engine is quieter than a diesel engine - a gasoline engine is more profitable than a diesel engine in terms of maintenance costs |
| Flaws | |
| - diesel is susceptible to frost — The cost of a diesel car is 25–35% more expensive than its gasoline counterparts. The engine is also more expensive to maintain and repair. Also, owners of diesel cars should change filters and oils more often. — a diesel engine is heavier than a gasoline engine, which affects the vehicle’s weight distribution, its dynamic characteristics and handling | — traction at the bottom is much worse — serious demands on the quality of oils - higher fuel consumption with increasing load — explosion and fire hazard is higher than that of diesel fuel |
From an environmental point of view, it is better to use diesel fuel. The difference in price and fuel consumption also speaks in favor of the diesel engine.
Regardless of the type of fuel, exhaust gases are generated during the operation of the internal combustion engine. Exhaust gases are the main source of toxic substances from two-stroke and four-stroke internal combustion engines that pollute the environment.
The main components of engine exhaust gases are oxides of carbon, nitrogen and hydrocarbons (Table 3).
Table 3
Composition of exhaust gases during operation of different internal combustion engines
| Exhaust gas components | Contents by volume,% | Toxicity | |
| Gas engine | diesel engine | ||
| Nitrogen | 74,0–77,0 | 76,0–78,0 | No |
| Oxygen | 0,3–8,0 | 2,0–18,0 | No |
| Water vapor | 3,0–5,5 | 0,5–4,0 | No |
| Carbon dioxide | 5,0–12,0 | 1,0–10,0 | No |
| Carbon monoxide | 0,1–10,0 | 0,01–5,0 | Yes |
| Hydrocarbons are non-carcinogenic | 0,2–3,0 | 0,009–0,5 | Yes |
| Aldehydes | 0–0,2 | 0,001–0,009 | Yes |
| Sulfur oxide | 0–0,002 | 0–0,03 | Yes |
| Soot, g/m3 | 0–0,04 | 0,01–1,1 | Yes |
| Benzpyrene, mg/m3 | 0,01–0,02 | up to 0.01 | Yes |
Nitrogen - chemical an element of group 15 with atomic number 7. This simple substance is a diatomic gas without taste, smell or color.
Oxygen is a chemical element of group 16 with atomic number 8. A chemically active non-metal and the lightest element from the chalcogen group.
Water vapor is a gaseous state of aggregation of water. There is no taste, smell or color. Water molecules are formed when it evaporates.
Carbon dioxide is a colorless gas, almost odorless, with the chemical formula CO2, density 1.98 kg/m3. Solid carbon dioxide is called dry ice.
Carbon monoxide is a binary chemical compound of carbon and oxygen. In addition to carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide, other carbon oxides are classified as organic compounds.
Aldehydes are a class of organic compounds that contain an aldehyde group.
Sulfur oxide is a compound of sulfur and oxygen with the composition SO2. A colorless gas with a pungent odor, toxic. Under pressure it compresses at room temperature.
Soot is an amorphous carbon, a product of incomplete combustion or thermal decomposition of hydrocarbons under uncontrolled conditions. Used in the rubber and tire industries.
Benzpyrene is an aromatic compound, a substance of the first class of danger. It is formed during the combustion of hydrocarbon liquid, solid and gaseous fuels.
When an engine runs on leaded gasoline, lead is present in the exhaust gases, and for engines running on diesel fuel, soot is present.
Despite the advantages of diesel fuel, gasoline engines are the most common, and therefore gasoline is the most used fuel in passenger cars. During its combustion, 92% of CO emissions occur, of which 63% are hydrocarbons and 46% are nitrogen oxides. When there is a lack of air, fuel burns and a large amount of carbon monoxide is formed.
Conclusions and recommendations
To reduce the harmful effects of exhaust gases on the environment, new environmentally friendly fuels have been developed:
1) biodiesel - based on vegetable oils, used in pure form and as various mixtures with diesel fuel;
2) compressed air - helps small cars reduce fuel consumption to 3 liters per 100 km. The pneumatic hybrid can travel up to 80% of the time on compressed air without creating harmful emissions.
3) solar panels - such cars are equipped with panels that collect solar energy and a battery pack with a capacity of 6 kilowatt-hours. In the absence of sunlight, the battery reserve is enough for 600 km.
4) liquid hydrogen - such cars can run on gasoline and liquid hydrogen. They have a 74-liter gasoline tank and a storage tank for 8 kg of liquid hydrogen. These cars can use both types of fuel during one trip: fuel switching occurs automatically.
5) an electric motor is an element of an electric drive. It consists of a moving part (rotor) and a stationary part (stator). After power is applied, the rotor rotates. Electric motors have recently found widespread use in passenger cars.
Also, in order to improve the environmental situation, it is necessary to implement the following measures:
− construct roads using new technologies, which reduces emissions by reducing the load on the engine and increasing speed;
− reduce the harm from the operation of transport through the use of its environmentally friendly types and public transport;
− improve the quality of fuels and lubricants.
Literature:
- Golokhvast K. S., Khristoforova N. K. et al. Composition of a suspension of automobile exhaust gases // Methods of environmental research. 2013. No. 6. pp. 95–101.
- Assad M. S., Grushevsky V. V. et al. Measurement of the concentration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the combustion products of a gasoline engine // Combustion and explosion. 2021. No. 9..4. pp. 22–27.
- Sufiyanov R. Sh., Moiseev A. E. Measurement of carbon monoxide content in the exhaust gases of automobile transport // XII International Scientific and Practical Conference. ICNS "Science and Education". 2021. pp. 65–68.
- Smolenskaya N. M., Smolensky V. V. Toxicity of exhaust gases in gasoline engines when running on compressed natural gas and gasoline // Bulletin of SUSU. Series "Mechanical Engineering". 2021. T.18. No. 4. pp. 57–65.
- Sadov A. A., Govorukhin I. A. et al. The influence of transport on the environment and events // Youth and Science. 2014. No. 4. P. 28.
- GOST 8226–82 (ST SEV 2183–80) Fuel for engines. Research method for determining octane number.
7. GOST 32339–2013 (ISO 5164:2005) Petroleum products. Determination of detonation characteristics of motor fuels. Research method.
8. GOST 511–2015 Fuel for engines. Motor method for determining octane number.
9. GOST 32340–2013 (ISO 5163:2005) Petroleum products. Determination of detonation characteristics of motor and aviation fuels. Motor method.
The impact of exhaust gases on human health
The greatest danger is posed by nitrogen oxides, about 10 times more dangerous than carbon monoxide.
, the share of
aldehyde
is relatively small and amounts to 4-5% of the total toxicity of exhaust gases.
The toxicity of different hydrocarbons
varies greatly.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons in the presence of nitrogen dioxide are photochemically oxidized, forming toxic oxygen-containing compounds - components of smog
.
The quality of afterburning on modern catalysts is such that the share of CO after the catalyst is usually less than 0.1%.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons found in gases are strong carcinogens. Among them, benzopyrene
, besides it,
anthracene
:
In addition, when using sulfur gasoline, the exhaust gases may contain sulfur oxides; when using leaded gasoline, lead
(
Tetraethyl lead
),
bromine
,
chlorine
, their compounds.
It is believed that aerosols of lead halide compounds can undergo catalytic and photochemical transformations, participating in the formation of smog
.
Prolonged contact with an environment poisoned by car exhaust gases causes a general weakening of the body - immunodeficiency. In addition, gases themselves can cause various diseases. For example, respiratory failure, sinusitis, laryngotracheitis, bronchitis, bronchopneumonia, lung cancer. Exhaust gases also cause atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels. Various disorders of the cardiovascular system can also occur indirectly through pulmonary pathology.
Poisoning in confined spaces
Cases of exhaust gas poisoning are quite common, including deaths of motorists in garages, closed parking lots and inside cars (if leaked into the cabin), with poor ventilation. There have also been cases of poisoning by exhaust gases in apartments located near parking lots (inhalation of exhaust gases leads to the accumulation of toxic substances in the human body). To combat such cases, building standards for ventilation of parking lots and structures related to the operation and maintenance of vehicles are being introduced.
Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide
These substances are considered dangerous and cause serious damage to the environment. In most countries of the world, cars are tested and certified for compliance with international standards for their content in car exhaust gases.
The reason for the high content of carbon dioxide in the air is incomplete combustion of fuel. This most often occurs when the engine warms up. Therefore, it is recommended to warm up the car in a well-ventilated area or in the fresh air.
You can also reduce the amount of these substances in car exhaust by correctly setting the carburetor, replacing the old air filter or adjusting the injection valves.
Hydrocarbons and organic oils
Residues of unburned hydrocarbons and organic oil vapors do not pose a threat to human health. But under the influence of sunlight, they react with other components of the air and form toxic compounds. The resulting substances may cause irritation of the mucous membranes and respiratory tract. In addition, one of the main elements of smog are hydrocarbons and their compounds.
If you monitor the condition of the sealing rings, and also adjust the carburetor and spark plugs in such a way that hydrocarbons burn out completely during engine operation, then harmless substances will be released as a result: carbon dioxide and water vapor.
Formaldehyde
As a result of the interaction of formaldehyde emitted by cars with atmospheric nitrogen and a number of other air components, toxic compounds are formed. When sufficiently concentrated, a fog is formed, which can pose a danger to humans.
Dust and soot
Tiny solid particles contained in vehicle exhaust gases settle on roadsides and various objects along highways. With constant inhalation of such dust and soot, there is a risk of developing diseases of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Due to the small size of soot particles, they easily enter directly into the blood vessels and have a detrimental effect on them from the inside.
It is not yet possible to completely eliminate these substances from exhaust gases. The only way to reduce their number is to use high-quality fuel.
Benzpyrene
Benzpyrene (Benzapyrene) belongs to the group of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). These mutagenic and carcinogenic substances can accumulate in natural objects, water and soil. Benziprene is the most common of a number of hazardous substances in this group. Over time, it accumulates in the human body and, upon reaching a certain critical concentration, has irreversible effects on his health.
Exhaust gas composition
A small educational program for those who like to breathe from the exhaust pipe.
First group. It contains non-toxic substances (natural components of atmospheric air).
A secondary reaction to the effects of nitrogen oxides is manifested in the formation of nitrites in the human body and their absorption into the blood. This causes the conversion of hemoglobin into metahemoglobin, which leads to cardiac dysfunction.
Nitrogen oxides also have a negative effect on vegetation, forming solutions of nitric and nitrous acids on leaf blades. This same property is responsible for the effect of nitrogen oxides on building materials and metal structures. In addition, they participate in the photochemical reaction of smog formation.
Fourth group. This group, the most numerous in composition, includes various hydrocarbons, that is, compounds of the CxHy type. Exhaust gases contain hydrocarbons of various homologous series: paraffin (alkanes), naphthenic (cyclanes) and aromatic (benzene), about 160 components in total. They are formed as a result of incomplete combustion of fuel in the engine.
Unburned hydrocarbons are one of the causes of white or blue smoke. This occurs when the ignition of the working mixture in the engine is delayed or at low temperatures in the combustion chamber.
The aromatic hydrocarbon benzo-a-pyrene C20H12, contained in the exhaust gases of gasoline engines and diesel engines, is particularly carcinogenic. It dissolves well in oils, fats, and human blood serum. Accumulating in the human body to dangerous concentrations, benz-a-pyrene stimulates the formation of malignant tumors.
Exhaust gases contain mainly formaldehyde, acrolein and acetaldehyde. The largest amount of aldehydes is formed at idle and low load modes , when combustion temperatures in the engine are low.
In roadside areas, approximately 50% of lead emissions in the form of microparticles are immediately distributed on the adjacent surface. The remaining amount remains in the air in the form of aerosols for several hours, and then also settles on the ground near roads. The accumulation of lead in roadside areas leads to pollution of ecosystems and makes nearby soils unsuitable for agricultural use. Adding the R-9 additive to gasoline makes it highly toxic. Different brands of gasoline have different percentages of additives. To distinguish between brands of leaded gasoline, they are colored by adding multi-colored dyes to the additive. Unleaded gasoline is supplied without coloring (Table 9).
In developed countries, the use of leaded gasoline is limited or has already been completely phased out. In Russia it is still widely used. However, the task is to abandon its use. Large industrial centers and resort areas are switching to the use of unleaded gasoline.
Not only the considered components of engine exhaust gases, divided into eight groups, but also hydrocarbon fuels, oils and lubricants themselves have a negative impact on ecosystems. Having a high ability to evaporate, especially when the temperature rises, vapors of fuels and oils spread in the air and negatively affect living organisms.
In places where vehicles are refueled with fuel and oil, accidental spills and intentional discharges of used oil occur directly onto the ground or into water bodies. Vegetation does not grow at the site of the oil stain for a long time. Petroleum products entering water bodies have a detrimental effect on their flora and fauna.
Source
Nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2, N2O, N2O3, N2O5, hereinafter NOx)
Nitrogen oxides are among the most toxic components of exhaust gases. Under normal atmospheric conditions, nitrogen is a highly inert gas. At high pressures and especially temperatures, nitrogen actively reacts with oxygen. In engine exhaust gases, more than 90% of the total amount of NOx is nitrogen oxide NO, which is easily oxidized into dioxide (NO2) in the exhaust system and then in the atmosphere. Nitrogen oxides irritate the mucous membranes of the eyes and nose, and destroy human lungs, since when moving through the respiratory tract they interact with the moisture of the upper respiratory tract, forming nitric and nitrous acids. As a rule, NOx poisoning of the human body does not appear immediately, but gradually, and there are no neutralizing agents.
Nitrous oxide (N2O hemioxide, laughing gas) is a gas with a pleasant odor, highly soluble in water. Has a narcotic effect.
NO2 (dioxide) is a pale yellow liquid involved in the formation of smog. Nitrogen dioxide is used as an oxidizer in rocket fuel. It is believed that nitrogen oxides are approximately 10 times more dangerous than CO for the human body, and 40 times more dangerous when secondary transformations are taken into account. Nitrogen oxides pose a danger to plant leaves. It has been established that their direct toxic effect on plants occurs at NOx concentrations in the air in the range of 0.5 - 6.0 mg/m3. Nitric acid is highly corrosive to carbon steels. The amount of nitrogen oxide emissions is significantly influenced by the temperature in the combustion chamber. Thus, when the temperature increases from 2500 to 2700 K, the reaction rate increases by 2.6 times, and when it decreases from 2500 to 2300 K, it decreases by 8 times, i.e. the higher the temperature, the higher the NOx concentration. Early fuel injection or high compression pressures in the combustion chamber also contribute to the formation of NOx. The higher the oxygen concentration, the higher the concentration of nitrogen oxides.
Car exhaust gases
Exhaust gases (or exhaust gases ) - the main source of toxic substances of an internal combustion engine - are a heterogeneous mixture of various gaseous substances with various chemical and physical properties, consisting of products of complete and incomplete combustion of fuel, excess air, aerosols and various microimpurities (both gaseous and and in the form of liquid and solid particles) coming from the engine cylinders into its exhaust system. They contain about 300 substances, most of which are toxic. The main regulated toxic components of engine exhaust gases are oxides of carbon, nitrogen and hydrocarbons. In addition, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, aldehydes, carcinogenic substances, soot and other components enter the atmosphere with exhaust gases. The approximate composition of exhaust gases is presented in Table 1.
Harm to the atmosphere
Exhaust gases often refer to all emissions into the urban atmosphere, including boiler houses, factories and other industrial enterprises. In fact, this term only correctly refers to transport emissions that arise as a result of fuel processing.
Experts call the level of air pollution in Novosibirsk dangerous
Such gases are also called waste gases. Exhaust gases are a product of the work of internal combustion engines, and given the rapid growth in the number of transport over the past 50 years and, in particular, the increase in personal vehicles in cities, exhaust gases in the air of cities have settled seriously and for a long time, and their number is only growing. Nowadays, exhaust gases are the main cause of air pollution in the city. They constantly influence human health.
“As the total volume of the vehicle fleet increases, the level of harmful effects of vehicles on the environment also increases rapidly,” explains ecologist Dmitry Markov . – In the early 70s, hygienist scientists determined that the share of pollution that cars contribute to the atmosphere is on average 13%. Now it has already reached 50% and continues to grow, and for cities and industrial centers the share of emissions from exhaust gases in the total volume of pollution is much higher - up to 70% or more. This creates a serious environmental problem."
All cars emit carcinogens and toxic substances into the air. The composition of car exhaust gases varies depending on the type of engine, gasoline or diesel, but the basic set remains the same. Automotive exhaust gases include both non-toxic (nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, carbon dioxide) and toxic (carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, aldehydes, sulfur dioxide, soot, benzopyrene) chemicals.
The smallest particles of harmful compounds enter the plant's body and poison it. This is why lawns and trees growing near large roads or parking lots often look limp, quickly turn yellow and die.
Air pollution from exhaust gases has significantly affected the composition of precipitation. Because of vehicles, acid rain occurs, colored fogs appear, and dark snow falls. Of course, precipitation cleans the air a little, but all the collected dirt ends up in the soil, which causes general environmental pollution with exhaust gases. The same compounds and heavy metals spread further through the soil: they end up in animal feed and agricultural crops.
This is interesting: Do-it-yourself brake disc repair
Carbon monoxide (CO – carbon monoxide)
A transparent, odorless, poisonous gas, slightly lighter than air, poorly soluble in water. Carbon monoxide is a product of incomplete combustion of fuel; it burns with a blue flame in air to form carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide).
In the combustion chamber of an engine, CO is formed due to poor fuel atomization, as a result of cold-flame reactions, during combustion of fuel with a lack of oxygen, and also due to the dissociation of carbon dioxide at high temperatures. During subsequent combustion after ignition (after top dead center, on the expansion stroke), carbon monoxide may burn in the presence of oxygen to form dioxide. In this case, the process of CO burnout continues in the exhaust pipeline.
It should be noted that when operating diesel engines, the CO concentration in the exhaust gases is low (approximately 0.1 - 0.2%), therefore, as a rule, the CO concentration is determined for gasoline engines.
Atmospheric pollution from exhaust gases: impact on humans and the environment
In the second half of the 20th century, in many countries around the world there was a sharp jump in the development of the automotive industry. The increase in the number of cars has led to increased concern among both scientists and ordinary people about the impact of fuel combustion products on human health and the environment in general.
This problem of air pollution from exhaust gases has not lost its relevance. They contain many toxic components, so exhaust gases are one of the main environmental problems of our time.