What is an electrolyte and why use it?
This is an acid or alkali based liquid. It works as a current conductor. As the battery charge level increases, the density of the liquid increases.
The chemical solution must be of high quality, made without deviations from manufacturing technology. Otherwise, the battery will not charge.
How to achieve the desired density in a battery
When making a solution yourself, you need not only to know what the electrolyte consists of. The main requirement is to ensure the required density of the liquid so that the charge is well preserved in such an environment. To monitor and check this indicator, a simple and accessible device is used - a hydrometer. It works on the principle of Archimedes' law and shows the density of a liquid. If its level is insufficient, the solution is diluted with acid, and if it is necessary to reduce the density, distilled water is added.
The electrolyte solution ensures the operation of the battery and also determines its performance. With the right approach, this fluid must be periodically tested, topped up, or replaced completely. The operation of the battery is largely influenced by the ambient temperature, so in particularly severe frosts it is worth keeping the battery warm. What electrolyte to fill into the battery in winter, as well as other nuances of the preparation and use of this conductor are discussed in our information.
What types of chemical liquid exist
Since an electrolyte is a mixture either based on an acid or an alkali, there are two types of this mixture: alkaline and acidic.
Acidic - a symbiosis of acid and distilled water. Batteries with this type of electrolyte are needed to start the engine.
The alkaline type of liquid uses a mixture of calcium-lithium base and distilled water.
Such mixtures serve to accumulate electricity in the battery. The scope of application of these batteries is electrical appliances, forklifts, and military vehicles.
Operating rules
The properties of the electrolyte are quite sensitive to changes in environmental temperature conditions, so in areas with a temperate climate it is recommended to check its condition twice a year: at the end of autumn and at the end of spring.
Density measurement
Density is an important characteristic of an acid electrolyte, the composition of which determines its value. The device that measures the density of the electrolyte is called a hydrometer, which can be bought at any auto store. When using it, the ambient temperature and the associated correction factor must be taken into account.
The following table shows the correction factors to the obtained hydrometer readings depending on the temperature (degrees Celsius):
- -40 to -26: -0.04;
- -25 to -11: -0.03;
- -10 to +4: -0.02;
- from +5 to +19: -0.01;
- +20 to +30: 0.00;
- from +31 to +45: +0.01.
In addition to the hydrometer, it is recommended to prepare a blank sheet of paper and a pencil in advance to record the measured results. The check must be carried out in each battery cell separately. The following steps explain the procedure:
- The first step is to open each container in the battery, the density of the electrolyte in which should be measured.
- The part of the hydrometer intended for measurement must be placed in an electrolyte.
- Using the instrument's bulb, you should pick up a certain portion of the electrolyte so that the hydrometer float begins to float.
- At the point of contact between the special rod and the liquid, you should look at the actual readings of the measured value.
- Record the result obtained, and then carry out similar actions for the remaining battery capacities.
We recommend: World ratings of car batteries
Density is a physical quantity , the dimension of which is defined as g/cm3.
In the case of an electrolyte, after the measurements have been taken, you should make sure that its fluctuations in all battery elements do not exceed 0.2-0.3 g/cm3. If the average density value for all battery capacities is below the specified value in the passport, then it is necessary to charge the battery. When caring for the battery and monitoring the density of the electrolyte, it is necessary to keep in mind the temperature regime . Thus, in the cold season, higher values of this value (1.30 g/cm3) should be maintained, since it provides a lower freezing point of the liquid. For example, if the density value is below 1.1 g/cm3, then ice crystals may appear in the electrolyte already at a temperature of -6 °C. In summer, it is better to reduce the density of the charged battery to the level of 1.23 g/cm3, since the lower it is, the longer the device will last.
In winter, at low air temperatures, it is recommended to remove the battery from the car and bring it into a room in which all monitoring measurements of electrolytic parameters should be carried out. In addition, to operate an electrical device in the northern regions of the country, you should purchase a special jacket container, which allows you to retain the heat of the battery case.
Liquid level
Another key battery characteristic that needs to be monitored regularly is the electrolyte level in each cell.
According to general recommendations, it should not be lower than 1-1.5 cm of the upper edge of the plates. Before measuring the electrolyte level in each battery section, place the electrical device on a horizontal surface. After this, it is recommended to take a glass tube 25-30 cm long and 5-6 mm in diameter, lower it to the bottom of the jar being measured, close the free end of the tube with your thumb to prevent the liquid in it from falling when pulled out of the jar, and then pull it out of the electrolyte and Use any ruler to measure the level.
This operation can be carried out using a regular sheet of paper, which should be rolled into a tube and lowered to the bottom of the container being measured. When subsequently measuring a wet print on a sheet with a ruler, the amount of error arising due to the capillary effect should be taken into account.
If during measurements a lack of liquid is detected in any battery capacity, then the required amount of distilled water should be added to it.
This should be done carefully, in small portions, since water entering the acid causes a large release of heat and boiling. It is necessary to add water, not electrolyte, otherwise the electrical appliance may be seriously damaged.
Method for preparing an acid solution
You will need the following:
- Mixing container and spatula designed to resist acid attack.
- Purified (distilled) water.
- Sulfuric acid for batteries.
- Protective clothing (apron, glasses, gloves).
- Baking soda (acid neutralizer).
How to prepare:
- Pour the required amount of water into the bowl and carefully and slowly pour the acid into the water.
- Mix with a spatula.
- Let it sit for at least half a day. For a liter of mixture we take 0.75 water and 0.285 acid.
How to prepare battery electrolyte
If everything becomes clear with the question of how to replace the electrolyte in the battery, then all that remains is to prepare a chemical solution. Today, preparing an electrolyte is not an urgent need. An acid composition with a density of 1.27 g/cm3 is commercially available.
Depending on the size and electrical capacity of the battery, the volume of liquid prepared will differ. Most passenger models will not require more than 2.6-3.7 liters of fluid. It is worth calculating in advance the volume of necessary ingredients, taking into account the final volume with a margin of about 4 liters.
Theoretically, the preparation of electrolyte for batteries with a density of 1.28 units includes the following proportions:
- distilled water – 1 l;
- sulfuric acid – 0.33 l.
When mixing, it is important to remember how to pour the components correctly - acid is poured into the water. There is no need to stir; with gradual addition, the process proceeds successfully on its own. After preparing the solution, leave it for 12 hours, after which the density is measured.
In the case of self-preparation, it should be taken into account that the sulfuric acid must have an excellent degree of purity, which is required by the standard. The permissible impurity content is no more than 7%.
The use of H2SO4 of unknown origin will not successfully replace the electrolyte in a car battery. When using an alkaline battery, the process for replacing the working medium is slightly different. To prepare an alkaline electrolyte, a ready-made dry alkaline electrolyte is used - usually Sodium-Lithium. This composition is mixed in the required proportion with distilled water.
For example, for a traditional concentration of 1.27 g/cm3, the dry mixture/ready solution ratio is 1 to 2 parts. You should read the instructions for the mixture in more detail, and also study the manufacturer’s recommendations for the individual current source model.
Care should be taken when disposing of old composition. It is not environmentally friendly to simply pour it into the sewer or the ground. Contact special acid collection services. The work carried out will not require significant financial and time costs. In return, the car owner will receive a reliable engine start in any season of the year.
Preparing an alkaline solution
We will need dishes that are resistant to chemical alkaline reactions, alkali (caustic potassium or caustic sodium), you can add lithium substances to improve the quality of the solution, water.
Important! We add completely purified water, i.e. distilled!
Cooking method:
- Pour distilled water into the bowl.
- Pour in the lye and stir thoroughly. If the density is unsatisfactory, then add alkali or liquid.
- We insist for three hours.
- Pour the resulting liquid into another vessel without raising the sediment.
Electrolyte parameters under different temperature conditions
For each season or climatic zone, the corresponding electrolyte density parameters are maintained.
You need to know that for winter conditions and colder climatic zones, the density of the electrolyte should be higher, as this will ensure a significant reduction in the freezing point of this liquid.
In hot climates and during warm ambient temperatures, it is desirable to maintain a lower electrolyte density as it provides much longer battery life.
The correct parameters can be maintained thanks to a special table that determines the favorable density for the time of year and climatic conditions. In harsh conditions and with extreme temperature drops, it is recommended to bring the battery into a warm room. There you can also recharge it and check its electrochemical parameters.
Traffic jams in a serviced battery
At a low density of 1.1 g/ml, the liquid is already capable of the appearance of ice crystals even at -6C. Therefore, even when driving in cold weather, motorists in the northern regions use special thermal containers that protect the battery.
Electrolyte with increased density
We may need it to correct the density of what is in the battery. If you have added a lot of water to the battery jars and the density of the chemical mixture has dropped, you can correct it using an electrolyte with a higher density.
To prepare, slightly change the proportions of alkali (acid) and water (0.423 parts per 0.650 water). The sequence of actions is the same as for making the main solution.
The chemical properties of the electrolyte are the same, but the freezing point is lower. The mixture is used only to adjust the main electrolyte.
Electrolyte properties and features
Battery electrolyte is a mixture of distilled water and sulfuric acid.
What is sulfuric acid for a battery?
In appearance, it resembles an oily substance with significant weight. It has no odor and dissolves perfectly in water. During the manufacturing process of electrolyte for lead-acid batteries, you can notice how heat is generated. This effect causes the acid to dissolve.
Drivers use acid for their batteries in accordance with the standard, GOST 667-83 grade A. Also in retail outlets there is high-purity acid GOST 142b2-78. Typically it has the following characteristics:
- Monohydrate 92-94%.
- Density according to standard 1.830 g/cm3.
- Impurities up to 0.03665% (iron 0.012%, nitrogen oxides 0.0001%, manganese up to 0.0001%, chlorine - 0.0005%, arsenic - 0.0001%).
Distilled water for battery
Without this water, it is simply impossible to create a high-quality electrolyte. It is prohibited to take H2O from a river, water supply, or tap as a replacement, or to use technical or drinking water. It is allowed to use condensate from steam. But before use, a chemical analysis must be carried out. The process in which the iron level should be determined, and it should not be more than 0.0004%. In addition, copper should be no more than 0.005%.
To obtain the coveted liquid, pharmacies, factories, hospitals, and laboratories use electronic distillers. These devices are also available to the average consumer. Thus, distilled water can be obtained using such devices as the HR-01 distiller, Wein column, economy primary, etc.
You should test the water produced by your distiller every 6 months. Make sure the solids levels are as follows:
- Calcium – 1.0 mg.
- Ammonia – 5 mg per liter.
- Sulfates – up to 0.5 g/l.
- Ammonium not more than 0.05 mg/l.
- Chloride not higher than 0.02 mg/l.
In addition, you need to check distilled water for the presence of nitrates, iron, and heavy metals. As a result, you should get a table from which you can see whether you can take this water to create an electrolyte or not. It must satisfy the GOST 6709-72 standard.
In regular retail outlets you can buy a 1.5 liter loaf of water for 20-30 rubles.
Preparation of electrolyte for batteries
Battery electrolyte is essentially an aqueous solution of H2SO4. Use water and acid with the parameters written above. For filling and topping up, use an electrolyte with a density of 1.18-1.24 g/cm3. Perhaps you are using a density of 1.83 g/cm3 then divide the process into two approaches:
- First create an electrolyte of 1.4 g/cm3. Wait until its temperature drops to 20 degrees Celsius.
- Next, make the desired one from this electrolyte.
This approach will prevent the sulfuric acid from getting too hot.
The production of electrolyte must be carried out in a specialized container. This can be plastic, earthenware or ebonite dishes. A lead container will also work. But under no circumstances should you use a glass bowl. Due to high temperatures it will burst.
The first step is to add a certain level of distilled H2O. After this, pour in the required volume of sulfuric acid in a thin stream. In this case, this mixture must be constantly stirred with a glass stick. It will be better if you add H2SO4 in portions.
Always pour acid into water. Otherwise, you will end up with a splashing cocktail with drops of dangerous acid flying in all directions. This may result in burns on the body and damage to surrounding objects.
Protective equipment for work:
- Rubber boots.
- Gloves made of the same material.
- Special cloth overalls.
- Glasses for protection.
- Rubberized apron.
Below you will find special tables from which you can understand what proportions should be observed.
Data on the ratios of sulfuric acid and distilled water
To obtain a density of 1.4 g/cm3, you need to adhere to the data from the 2nd table.
To obtain a density of 1.83 g/cm3, use the data presented below.
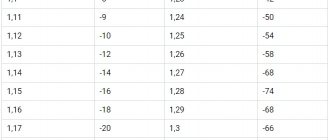
A hydrometer should be used to obtain density information. When measuring temperature, the thermometer should not contain elements of wood or metal. Measurements should be taken when the degree drops to 20.
The density temperature gradient corresponds to a value of 0.0007 g/cm3 per 1C. If t is above 20 degrees, the correction in the calculations is added to the measured density data. Suppose in fact t is at 30 degrees, and ours is 20. Then the difference will be 10 C0. As a result, this is what comes out: 0.0007 x 10 = 0.07 g/cm3. That is, to the obtained density data we add an error of 0.007 g/cm3.
If in fact t is 10 degrees, the difference with the above temperature will be equal to 10 C0. We multiply 0.0007 g/cm3 by ten and get the correction in the form of 0.007 g/cm3. In this version, the correction is subtracted from the measured density index at t equal to 10 C0.
It is prohibited to fill electrolyte at temperatures exceeding 25 C0.
Basic properties of sulfuric acid electrolyte
In addition to the above, one more circumstance should be taken into account. Taking one volume of acid and water at the outlet after mixing, this volume will be significantly less. It turns out that this parameter also needs to be taken into account when preparing the electrolyte. To do this, use the data from the table.
Property viscosity
Affects the functioning of a battery with lead plates. The process in the battery is diffuse. The speed at which this diffusion occurs depends on the viscosity. The rate of flow of electrolyte to the surface and into the pores of the electrodes at the time of discharge depends on it.
If the viscosity increases, diffusion will slow down. When t drops by 25 degrees, the viscosity doubles. At t=50 C0 its increase occurs 30 times when compared with normal t.
As viscosity increases, the battery capacity decreases. In this regard, the functioning of lead-acid batteries decreases in cold weather. This must be taken into account when installing gel batteries.
Electrolyte resistivity
To calculate it you will have to resort to the formula =rS/L. It is relevant when the resistance of the electrolyte occupying a container is limited to a length of 1 centimeter and a cross-section of 1 cm3. The meaning of the letters from the formula:
- L – length.
- r – resistivity in ohms cm.
- S – cross section cm2.
R changes at the moment when the electrolyte t and concentration change. To keep the internal resistance of the battery low, use an electrolyte with the lowest specific R.
The parameters of such resistances are in this table.
R increases when the temperature drops, especially at zero degrees.
In fact, the freezing temperature of the electrolyte is an important indicator. Since during a discharge its density and its freezing t decrease. When it is cold, the volume of liquid increases and this leads to damage to the electrodes and the battery capacity itself.
An electrolyte with a density of 1.29 g/cm3 has the lowest freezing temperature.
Starter batteries that are used in cold conditions have a density of 1.26-1.30 g/cm2. This electrolyte does not freeze even in the coldest weather.
The table below shows the density levels at which freezing occurs.
Which batteries use different types of chemical fluid?
To avoid mistakes, you should study the label on the battery. If the battery is lead-acid type, then we use an acid mixture.
We pour a solution based on potassium or sodium into alkaline batteries. The type of alkali can be recognized by its combustion. Potassium burns violet-red and sodium burns yellow.
So, if suddenly the need arises to prepare the electrolyte for the battery yourself, then, in principle, this is possible. You should follow safety precautions and be attentive to the proportions of substances - and everything will definitely work out.
Which electrolyte is poured into which battery?
If you fill the battery with the wrong electrolyte, the battery will be completely damaged. The type of battery is usually indicated on the product body, so it is absolutely easy to determine whether the power source belongs to a certain category.
If there is no label, you can take a small amount of electrolyte and use tests to determine its composition. Lead-acid batteries are filled with sulfuric acid-based electrolytes. For alkaline power supplies, KOH and NaOH solutions can be used.
When adding electrolyte to alkaline devices, you must also accurately determine the chemical formula of the base used. You can distinguish one alkali from another by the color of the flame. If you add KOH to the fire, the color of the fire will change to red-violet, NaOH will burn with a yellow glow.
Still have questions or have something to add? Then write to us about it in the comments, this will make the material more complete and accurate.
What acid is in a car battery? Question for chemists
I was asked this question several times in letters to the blog; many novice drivers who are just learning about driving are interested. Many people have heard about lead-acid batteries, but have no idea how they work and why there is acid inside in principle. Others know that it is there, but they have no idea what it is! Still others generally believe that there is only distilled water inside and there is no acid there! Today I decided to answer all these questions. It will be interesting, so read on...
CONTENTS OF THE ARTICLE
I would like to immediately answer this question - there is still acid in a car battery, and it contains one of the most powerful ones, namely “sulfuric” acid, if you remember the formula from the chemistry of H2SO4. So all the talk that only water is flooded is, to put it mildly, unfounded. After all, that’s why they get the name lead-acid batteries.
Refilling electrolyte
You need to pour the prepared liquid very carefully. This is done using a glass funnel or other chemically neutral material. A glass mug with a special bent spout will also work.
We carry out the operation until the liquid rises above the plates in the jars by 10-15 mm. Next, leave the entire system alone for 2-3 hours. After this time, the density of the medium may drop slightly, which is an acceptable phenomenon.
Charging the battery
A charged battery must be charged to operating mode. For this operation, a current is used that is 10 times less than the value indicated as the capacity on the battery case. This means that a current reading of 60 A*h on the outside of the battery will require a current of 6 A. Charging must be continued for 4 hours. After this, the density and level of the liquid are measured again. The electrical appliance is ready for use.
Battery electrolyte testing
This operation must be carried out at least twice a year: with the onset of cold weather and when warm summer weather sets in. It is the change in temperature that should be decisive at the beginning of the test.
The work is carried out in the presence of the following auxiliary set:
- hydrometer - a device used to check the density of liquids (it is easy to find in almost any car store);
- glass tube with an internal diameter of 5-7 mm (in some cases it will be replaced by a blank sheet of paper).
Preparation of electrolyte for batteries begins with checking the current state of the liquid in all banks. To do this, you can use a simple algorithm:
- in serviced batteries, unscrew the cap from the tested jar;
- shallowly immerse the working part of the hydrometer in a container with electrolyte;
- Using a rubber bulb on a hydrometer, we draw in a small volume of liquid so that the float becomes raised and floats without touching the walls of the vessel;
- on the line of contact between the electrolyte and the rod there will be real density data;
- write down the result on a piece of paper.
We carry out the measurement procedure for each container separately.
You need to know that the density values in all jars must be as close as possible to each other and must differ from each other by more than 0.2-0.3 g/cm 3 .
The lack of density can be compensated for by a higher charge level. This will provide a higher density and, accordingly, a lower freezing point of the liquid.
In addition to density, the driver is required to maintain a sufficient fluid level in the battery while operating the vehicle. It is not recommended to lower it lower than 10-15 mm above the upper level of the plates.
Battery fluid level
Level measurements can be easily carried out using a glass tube on a battery levelly positioned horizontally. To do this, lower it into the selected jar so that its lower end touches the top of the plates. After this, close the tightly open end of the tube with your finger so that liquid does not leak from the cavity of the tube. We measure the resulting level using any ruler.
If an insufficient amount of liquid is detected, it is necessary to add distillate into the problematic jar in several passes. During the procedure there will be a slight release of heat or boiling.
You need to know that under no circumstances should you top up the battery with electrolyte to bring the fluid to the required level. This action can damage the battery.
Checking the electrolyte using a glass tube
Checking the level in the absence of a glass tube can be carried out using a clean paper sheet rolled into a small tube. The procedure will be the same, however, it should be noted that in this case, getting wet will show a slightly higher electrolyte level due to measurement error.
Electrolyte neutralization
If the battery is completely damaged, it must be disposed of properly. But also in the event of an electrolyte leak from the battery, you need to find out how to neutralize it.
There are situations when, if the battery breaks down, a separate part at its location may be flooded. To do this, you need to remove the battery and clean it. Neutralization of this substance from a battery is usually carried out using special equipment and technology. This is important from an economic and environmental point of view. If neutralization is carried out in an unorganized manner, significant harm to the environment can be caused.
There are currently two industrially produced acid neutralizing options. The first involves the elimination of acid discharge into wastewater by a filter method, passing through magnesite, limestone and other materials, and the second method is the regeneration of acid by special treatment with the subsequent production of a marketable product. But in practice, many drivers recommend using an alkaline solution made from baking soda and water in case of a spill of a dangerous substance.
By regularly checking the battery, including monitoring the density and electrolyte level, you can avoid many problems and extend the life of the battery and prevent mechanical damage. It is always necessary to pay close attention to devices during operation, especially in winter, when at low temperatures and reduced density of the electrolyte, it may freeze or destroy the plates.
Replacement instructions
The electrolyte is replaced in the following cases:
- The electrolyte in the jars changed color and became cloudy. The reason for this may be the use of non-distilled water for the additive, but usually. It may contain impurities that react chemically with the electrolyte and form solid compounds that precipitate
- After charging the battery, it is impossible to achieve the desired density
- Electrolyte leaked due to negligence
- The new battery drains quickly. The reason for this may be freezing of the solution
Replacing the electrolyte, regardless of whether it is alkaline or acidic, is carried out in several steps:
- Removing the battery from the vehicle
- Cleaning the battery from contamination
- Pumping out existing fluid using a bulb or syringe
- Rinsing jars with distilled water
- Filling electrolyte using a bulb or similar devices
The fill level is determined by marks inside the cans. If they are missing, you need to follow the rule - the electrolyte should be 5-7 millimeters above the plates. At the same time, at least two centimeters should remain from its level to the lids of the cans.
When draining the electrolyte, it is very important not to tilt it to the side, much less turn it over. There may be solid particles at the bottom of the vessels that will get stuck in the plates, completely rendering them inoperable. It is allowed to gently rock the water from side to side when washing; the same actions can be performed after filling the electrolyte into the battery.
We recommend: Design and principle of operation of the injector
After this, the battery is installed for charging, after which the resulting density should be checked. Measurements should be taken no sooner than a couple of hours after removing the device from charging, as there is a risk of getting inflated readings. If the density is not high enough or, on the contrary, has excessive values, it should be adjusted by adding acid, alkali or distilled water.