The pleasure of driving a particular car is difficult to describe in words, but you can try to explain it by its design features. If we talk about the information content of the steering, then in addition to the architecture of the car’s chassis as a whole, the type of its amplifier plays an important role.
An uninformative or “wobbly” steering wheel, its poor self-return, weak feedback from the road, and so on - all these points depend primarily on the design of the steering system. Friction losses and parasitic moment of inertia play a fundamental role here.
Which is better, electric power steering or hydraulic power steering?
Those who learned to drive in their father’s “penny” remember the unforgettable sensations with every turn of the steering wheel. Control in those days was completely devoid of auxiliary elements that could significantly simplify driving a car. Today the situation has changed and now driving a car, a truck or a bus does not require physical training and nerves of steel, since auxiliary units such as hydraulic (power steering) and electric power steering (EPS), which are equipped with almost all modern cars, have come to the aid of motorists . Thanks to these systems, the steering wheel can be turned with one finger.
How to determine power steering or electric power steering installed in a car
You can determine which unit is installed on the selected brand of car without the help of the seller. To do this, you need to look under the hood of the car. If you find a tank there with a corresponding pictogram depicting a steering wheel, it means that in front of you is a car with power steering. It is into this tank that the power steering fluid is poured. If there is no reservoir, and the steering wheel turns freely, then this means that the car has an ESD installed.
Healthy! In some cars, the power steering fluid reservoir is located in the bumper and the device is a hybrid of electric and hydraulic power steering. But such cars can be counted on one hand. For example, several Opel Zafira models are equipped with just such “hidden” power steering units.
To figure out whether electric power steering or hydraulic power steering is better, it’s first worth talking about the features and differences of each of these systems separately.
Power steering
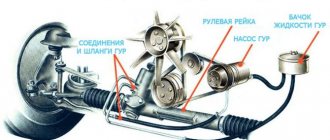
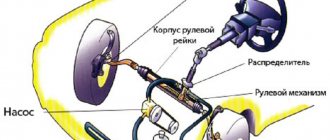
Power steering is more common today, unlike the electrical system, which is just gaining momentum. The hydraulic booster consists of complex components - low and high pressure pipelines, belts and other elements through which fluid circulates, poured into a special tank connected to pumping equipment. As soon as the driver turns the steering wheel, a number of processes occur. First, high-pressure fluid is supplied through the distributor into the steering mechanism, after which it is pumped into the hydraulic cylinder, thereby creating pressure that affects the piston. As a result of the displacement of the latter, the degree of effort that the driver applies to turn the steering wheel is reduced. When moving along a straight path, the power steering fluid flows back into the reservoir. As you can see, this is a rather complex closed fluid circulation system, in which many elements are involved, each of which can fail over time.
If we talk about the features of power steering, it is worth mentioning the following disadvantages:
In addition to these shortcomings, many car enthusiasts often complain that the power steering hums when turning. This problem may be due to a breakdown in the steering rack, problems with the pump, belt or poor quality oil. As a result of the fact that the system, designed to simplify the life of motorists, began to bring a lot of trouble, a simpler and more convenient mechanism was developed - an electric booster.
Electric power steering
The design of the electric power steering is much simpler than that of a hydraulic booster. By and large, this is a small electric motor, a control unit and two sensors: torque and angle of rotation. A device mounted on the steering rack or column itself reads information about which driver is transmitting the steering angle. In this case, torque is transmitted using a torsion shaft, which is built into the steering unit.
If we talk about how power steering differs from electric power steering, then in the first case, the force applied to the steering wheel is reduced due to pressure and circulating fluid, in the second, the information is converted thanks to electrics, as a result of which the wheels turn slightly. In this case, the electronic power steering unit analyzes the data and, based on it, calculates how much current the electric motor will require. Thanks to this, when parking or sharp maneuvers, the greatest effort is produced from the EUR. During slow turns, the electric power steering reduces torque and is practically not used.
If we talk about the advantages of electric power steering over power steering, then it is worth noting the following advantages of the electric amplifier:
However, electric boosters have their own characteristics that confuse some drivers. Therefore, let’s try to figure out which system performs better in management.
Types of EUR
Like everything in car design, the EUR has evolved, and now there are several varieties of it, each of which has found its application in different types of cars. And if its basic principle remains unchanged, some details seriously affect the quality and convenience of work. Depending on the installation location, there are 3 main types.
- Electric power steering integrated into the steering column.
- Twin-shaft EUR built into the steering rack.
- EUR with a screw-ball connection.
These types are distinguished by the connection diagram of the electric motor and the type of drive, and each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. Let's look at them all.
Electric power steering integrated into the steering column with worm gear
ESD device built into the steering column with a worm gear.
The simplest and cheapest type of electric power steering. The motor and worm gear are mounted directly on the steering column and control it. At the same time, the remaining steering elements (in particular, the rack) do not change. This design is convenient because the electric motor is located inside the car, which means it is easy to dismantle and maintain, and at the same time it suffers less from cold and moisture. In addition, the simple design of the steering rack simplifies and reduces the cost of repairs. However, such a system cannot cope with heavy loads, so it is installed on small class cars. The video below clearly shows the principle of operation of such an electric amplifier.
Electric power steering integrated into the steering rack
EUR built into the steering rack: 1 – torque sensor on the steering wheel;
2 – drive gear 1; 3 – drive gear 2; 4 – amplifier electric motor; 5 – amplifier electronic unit; 6 – steering angle sensor; 7 – steering shaft torsion bar A more difficult to maintain design, which is used in middle-class cars. As the name implies, the electric motor is installed in the steering rack at the junction between it and the intermediate shaft. Here a gear is used, which transmits force to the rack itself.
The main disadvantage of this type of electric power steering is that it is placed on a rail, which means it suffers more from external factors. And although the device has a protective casing, it still gradually deteriorates from moisture and temperature changes. And the location in the engine compartment complicates dismantling and repair.
A complex design in which the electric motor is placed on the rack not from the side of the steering column, but from the opposite end. Two gears are used for control: one is connected to the intermediate shaft and rotates directly from the force applied by the driver. The second gear is installed on the other side of the rack and is controlled by an electric motor. This dual design greatly increases the cost of purchasing or repairing a steering rack. On the other hand, due to its features, the reliability of this mechanism is quite high.
EUR with screw-ball nut
EUR device with a screw-ball nut
This is the newest and most successful version of the electric amplifier. First of all, it uses a different motor design that has virtually no inertia when stopping or starting. And there is no worm gear, which takes away part of the electric motor’s effort. Thanks to these changes, the accuracy and information content of the steering wheel reaches maximum levels.
Operation of the EUR with a ball screw nut
For control, a ball nut is used, connected directly to the electric motor. During operation, the motor rotates the nut in one direction or the other, and it, in turn, moves the steering rack, as shown in the animation above.
Which system is more convenient to manage?
When developing car control system amplifiers, designers faced a difficult task. On the one hand, it is necessary to ensure ease of turning the wheels, on the other hand, the driver should not lose “contact” with the road; for this it was necessary to provide feedback.
In fact, many drivers are convinced that when using an electric steering system they will not always be able to feel the road. In reality this is absolutely not the case. The fact is that the electric booster, on the contrary, most accurately senses and analyzes the situation on the road surface, so it clearly conveys the angle of rotation, and when the car accelerates, the steering wheel becomes “heavier”. The power steering loses in this matter, since although it provides reliable feedback, it cannot protect against the steering wheel turning out at high speed. The electric amplifier will not allow such a situation.
Among the really real shortcomings of the ESD, it is worth mentioning the careful calibration that such a system requires. In fact, all these settings can be made on foreign cars; the offspring of the domestic automobile industry will be much more capricious in this matter. Also, the electric motor needs additional protection - a damper, which will dampen vibrations and vibrations that affect the integrity of the electric power steering.
What is the difference between hydraulic power steering (power steering) or electric power steering (EPS)?
Automakers do everything to make driving a car comfortable and enjoyable. This applies to literally everything in the car, including the steering. The steering wheel should turn easily, without effort, and not with difficulty, as it was in the old days on older vehicles.
Currently, it is difficult to imagine a car without power steering, that is, a special device that helps turn the wheels of the car. Many people know that there are two types of such amplifiers: hydraulic, that is, driven by hydraulics (power steering), and electric, operated by an electric motor (EUR). Let's see what is the difference between power steering or electric power steering?
Power steering operating principle
Hydraulic power steering column rotation appeared in the last century and was initially installed only on trucks. It's clear. Driving a multi-ton vehicle is much more difficult than driving a passenger car. However, over time, automakers began to use power steering, including on passenger cars, thereby increasing their attractiveness compared to other brands. Currently, approximately 60% of new machines are equipped with hydraulics.
Power steering is a rather complex mechanism consisting of several elements: - a pump connected by a belt drive to the engine crankshaft; — reservoir for hydraulic fluid; — a piston installed in the steering rack; — a hydraulic distributor that sets the direction of movement of the piston.
All these elements are connected to each other by metal tubes containing hydraulic fluid. Its task is to transfer the pressure created by the pump to the piston, which then pushes the rack shaft and in this way helps to turn the wheels of the car. In general, power steering works as follows.
After the car engine starts, a pump rotated by the crankshaft builds up pressure in the system. As long as the driver does not turn the steering wheel, excess pressure is released into the expansion tank. When you try to turn the steering wheel of a car, the distributor opens the desired line and directs the fluid into one of the chambers located on the right or left side of the piston.
Under pressure, the piston moves and pushes the steering rack shaft simultaneously with the rod attached to the front wheel steering knuckle. This significantly reduces the amount of effort required by the driver to turn the steering wheel.
If the steering wheel of the car is turned in the other direction, the distributor will close the first line and open the second, pressure will arise in the other chamber and the piston will move in the opposite direction.
Operating principle of the EUR
Electric power steering was introduced later than hydraulic power steering and began to be widely used only after 2000, gradually conquering the world automobile market.
Both of these mechanisms perform the same function - they make it easier for the car owner to steer the car. However, the difference between them is that the power steering moves the rack shaft using a special electric motor, and the power steering using a pump and hydraulic fluid.
In this case, the engine in the electric power steering is controlled by a separate electronic unit (ECU). The operating principle is as follows:
After starting the engine, voltage is supplied to the control unit, but the EUR is not yet active at this time. After the slightest turn of the steering wheel, this movement is detected by a special sensor, which transmits an impulse to the ECU. Based on the sensor signal, the controller commands the electric motor to rotate the steering shaft in one direction or another through a gear transmission.
Pros and cons of power steering
Power steering has a number of advantages, thanks to which it was once widely used in the automotive market. Here are the most important ones:
- lower production costs, which in turn affects the final price of the new car; — thanks to the use of power steering, you can get more power, which is necessary when operating heavy trucks and minibuses; — reliable design of the hydraulic booster, which has been tested over years of use.
However, power steering also has disadvantages. The main one is the need to control the fluid level in the system and the frequency of maintenance. It is necessary to ensure that the seals of the piston mechanism, distributor and pump do not leak, change and tighten the belt in time, and lubricate the bearings.
Among other disadvantages, which are less significant, is a slight increase in fuel consumption due to the fact that the power steering pump works constantly while the engine is on.
Advantages and disadvantages of electric power steering
Compared to power steering, an electric amplifier has a number of advantages:
— such a system, including an electric motor and a control unit with a sensor, does not require regular inspections and maintenance; — smaller dimensions of the mechanism, that is, it does not take up much space; — The electric power steering does not consume electricity unnecessarily and, it turns out, does not consume additional fuel.
Electric power steering also has other advantages, for example, those related to changing its operation settings depending on driving conditions. In addition, the ESD is used in modern premium cars because it can be controlled by an on-board computer.
The main disadvantage of an electric amplifier is its high price. The higher the cost of the mechanism and its elements, the more expensive the repair will be. Often a failed EUR has to be completely replaced. In addition, the electric booster has less power, making it difficult to use for trucks and heavy vehicles.
Which power steering is better?
Experience shows that both amplifiers are quite reliable in operation. Although breakdowns occur with both. When choosing between power steering or electric steering, it is necessary to consider each situation separately: what kind of car, what budget does the driver have, etc. It's up to you to decide, and the characteristics of each are given above.
It is only worth noting that electric power steering is constantly being improved and is displacing hydraulics from the market thanks to a more modern and simpler design. Perhaps over time their cost will be reduced and their power will increase.
Source
Electric power steering
Electric power steering circuit
In electric power steering (EPS), additional force when turning the steering wheel is created by an electric motor.
Design and principle of operation of electric power steering
The main elements of the electric amplifier include:
- electric motor;
- torsion bar and steering column shaft;
- steering mechanism (gearbox);
- steering wheel position sensor;
- torque sensor;
- electronic control unit.
When the driver turns the steering wheel, the torsion bar begins to twist. The torque sensor measures this twisting, determines the torque value from it and transmits this information to the control unit. The latter processes data from the power steering sensors and correlates them with the readings of other vehicle sensors (speed, crankshaft revolutions, etc.).
The control unit calculates the force that must be applied to help the driver turn the steering wheel and gives the appropriate command to the electric motor. The latter acts on the steering column shaft or steering rack, thereby facilitating rotation of the steering wheel.
Advantages and disadvantages of EUR
Electric power steering rack
The main advantages of an electric amplifier include:
- fuel efficiency - the EUR does not take power from the engine and turns on only when the steering wheel is turned;
- reliability associated with the absence of a hydraulic system;
- compactness and ease of maintenance;
- ability to adjust steering characteristics and settings;
- the possibility of implementing automatic vehicle control.
Despite numerous advantages, EUR also has some disadvantages. These include:
- low power while maintaining minimal overall dimensions and cost;
- possibility of overheating and temporary failure under unfavorable driving conditions;
- expensive repairs.
Power steering or power steering
Behind the abbreviation power steering lies a hydraulic system or simply power steering. It is noteworthy that it was hydraulic systems that were first used to solve the problem of a heavy steering wheel - and hydraulic drives still do not lose their positions. At the same time, modern power steering systems are strikingly different from their predecessors, which appeared in the second half of the last century.
A modern hydraulic booster has the following components in its design:
The operating principle of the power steering system is quite simple and reliable. The pump receives energy from the engine through a belt drive and forces fluid from the reservoir into the distributor. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the distributor is commanded to direct fluid to one or another part of the cylinder. It creates pressure inside it, under the influence of which the piston moves. And the movement of the piston already helps to turn the wheels in one direction or another. When the steering wheel returns to a straight position, the fluid returns to the reservoir.
What is power steering (power steering)?
The hydraulic booster appeared first and significantly simplified driving, while its main task was not only to remove the power load from the driver’s hands, one of the tasks that the designers set for themselves was safety. After damaging the front wheel at speed with power steering, the driver did not lose control of the car, and also felt less vibrations that came from the wheels while driving over uneven surfaces.
How does power steering work?
The power steering is a set of components, including: a system of high and low pressure oil lines, an oil pump with the help of which the power steering fluid circulates into the reservoir in which the power steering fluid is located, as well as the steering rack and tips. When you turn the steering wheel, a number of events occur in the power steering system that you are not even aware of. You, the driver, turn the steering wheel and set the direction, after which a special fluid (synthetic or semi-synthetic oil, almost the same as in an automatic transmission) is pumped under high pressure through a distributor. Thereby generating a force that, acting on the hydraulic cylinder and piston, shifts the steering rack mechanisms in the direction you need. After this, the power steering fluid is returned through the return flow system to the power steering reservoir.
Electric power steering or EPS
EPS is an electric power steering in which the force necessary to turn the wheels is created by an electric motor. A peculiarity of systems of this type is that they are mounted directly on the steering rack or column. For comparison: power steering is often installed as a separate system.
The main structural elements of the EUR are:
When the driver turns the steering wheel, the torsion bar twists. The torque created in this case is recorded by a corresponding sensor, in which the received information is interpreted into a signal supplied to the electronic control unit. Here, this data is analyzed and compared with information transmitted from other sensors, including the speedometer, tachometer, etc. Based on the results of the analysis, the ECU determines the force required to turn the steering wheel and sends a command to the electric motor. As it rotates, it transmits its rotation to the steering shaft or directly to the steering rack.
Design and principle of operation of electric power steering
Electric power steering operates from an electric motor. A special feature of the EUR is that it does not work constantly, like power steering, but is activated only when the steering wheel is turned. There are two types of EUR. In the first case, it is attached to the steering rack, in the second - to the steering shaft. The first option is more common. The EUR is complemented by a control unit, with which you can set individual settings. This will ensure a smoother ride of the car.
Electric power steering has the following advantages:
- compact dimensions;
- lack of liquid in the system, which eliminates problems due to the pressure created;
- good performance at any speed, including high;
- ease of installation;
- possibility of setting individual settings.
But there are also several disadvantages:
- risk of electric motor overheating;
- high price;
- frequent lack of opportunities for maintenance and repair, which is why it is necessary to completely change the EUR.
The most common breakdowns of the EUR are:
- overheating of the electric motor;
- problems with the control unit;
- sensor problems.
As can be seen from the above, electric power steering is a fairly reliable device. It is usually chosen by car enthusiasts who are willing to overpay but get high quality. Due to the fact that the EUR does not work constantly, like power steering, but is activated only when the steering wheel is rotated, it wears out much more slowly
But it is important to understand that if a breakdown occurs, you will probably have to replace the entire amplifier at once. And this will definitely cost more than repairing the power steering
What is the difference between power steering and electric power steering and which is better?
Now let’s compare these types of amplifiers with each other and try to determine which is better: hydraulics or electricity?
Let's start with the design features. The hydraulic booster is quite simple in structure, it is not afraid of malfunctions in the ECU. However, its anthers and hoses, as well as all kinds of seals, connections and other elements wear out relatively quickly. In addition, you need to monitor the fluid level in the power steering system. The electric amplifier is distinguished by greater durability and independence from consumables. Failures in the car’s electronic system can disrupt its operation, but they happen quite rarely. And if such a problem manifests itself, then problems with the EUR will probably be the least of the problems. Both types of mechanisms have an emergency mode of use.
Let's move on to ease of use. As practice shows, hydraulic boosters of even the simplest designs are more informative than electronic systems. They provide better connection with the road surface and make it possible to experience the maximum capabilities of the car when taking sharp turns. The EUR is theoretically also capable of this, but for this it must be carefully calibrated, which is done only on premium cars. In general, the hydraulic booster provides a highly informative and natural driving experience - however, it requires more physical strength than the electrical system.
Next, we will consider amplifiers from the point of view of efficiency and reliability. During operation, power steering consumes the power of the car's engine, which is why its appetite increases and its dynamic characteristics deteriorate. In addition, it is sensitive to high loads: it is not recommended to hold the steering wheel in extreme positions for more than 15 seconds, otherwise the pump may fail. The electric booster is driven by its own motor. Under increased loads, it can also overheat, but the automation in this case will reduce its performance or turn it off until the temperature drops.
The scope of application of the power steering is higher; it can be used both on a city minicar and on a multi-ton truck. The EUR is much weaker and therefore suitable only for passenger cars (and even then not for all).
Therefore, it is impossible to give a clear answer to the question of which is better power steering or electric steering. The latter was developed as a replacement for the hydraulic system, devoid of its inherent disadvantages, so for a number of factors it is definitely better. At the same time, power steering has a significantly wider scope of application and at the same time a lower price. Therefore, preference should be given to one option or another solely taking into account personal preferences and the characteristics of the desired car.
Source
What is the difference between power steering and electric power steering?
Let's move on to the comparative characteristics of the electric power steering and power steering in order to ultimately find out which of them is better.
For comparison, let's take the following parameters: device design, ease of use, reliability and efficiency, scope of application.
Device design
Option for placing the EUR in the car
Power steering is a fairly simple mechanism that does not depend on electronic control and is not subject to software failures. On the other hand, the power steering system consists of many connections and seals that are subject to wear during operation. As a result, the node is considered less reliable and requires regular diagnostics.
The EUR, unlike the power steering, is usually located directly on the steering shaft and takes up less space in the engine compartment. Structurally, the electric amplifier is much simpler than power steering, and does not require the use of additional consumables.
Operating principle of power steering and power steering
Hydraulic power steering column rotation appeared in the last century and was initially installed on trucks. In the 80s, it migrated to passenger cars, where it serves faithfully to this day. At the moment, approximately 60% of new machines are equipped with hydraulics . Electric amplifiers were introduced later and began to be widely used after 2000, gradually conquering the automotive market.
The listed elements are connected by metal tubes with circulating liquid. Its task is to transfer the pressure created by the pump at the right moment to the piston, which pushes the rack shaft and thus helps turn the wheels of the car. In general, power steering works like this:
The sharper and stronger you turn the steering wheel, the more pressure is transferred to one of the chambers and the force applied to turning the wheels increases. The system only reacts to the rotation of the main shaft, and when driving in a straight line or parked with the engine running, it continues to work, but does not affect the rack.
The difference between electric power steering and power steering is that the rack shaft is moved by an electric motor controlled by a separate electronic unit (ECU). The operating algorithm is as follows:
The rotation speed of the electric motor shaft and the amplification power are determined using a second torsion sensor, which twists when the steering wheel is turned sharply.
Pros and cons of different amplifiers
The use of hydraulics to make driving easier is due to the following advantages of power steering:
The main disadvantage of the hydraulic system is the need to control the fluid level and periodic maintenance . It is necessary to ensure that the seals of the piston mechanism, distributor and pump do not leak, change and tighten the belt in time, and lubricate the bearings.
Other disadvantages are not so significant:
As opposed to hydraulics, the electric power steering has the following advantages:
Which amplifier should you choose?
Practice shows that both drives are quite reliable in operation, although supporters of electric amplifiers claim the opposite. Even in budget cars, hydraulics last 100-150 thousand km without problems, and in the event of any breakdown, they can be repaired at any car service center. ESD malfunctions more often lead to replacement of the mechanism, since in most cars the unit cannot be restored.
On the other hand, the electric drive does not interfere with driving after failure, as does the power steering, which can only be “neutralized” by turning off the pump.
Therefore, when choosing a hydraulic booster or electric power steering, be guided by considerations of expediency. For example, it is better to buy an economy class car with a hydraulic booster, and a business and premium class car with an electric one.
Owners of domestic cars note cases when the electric amplifier tried to “steer” instead of the driver due to electronic failures, although such moments are extremely rare. However, the EUR is constantly being improved and is displacing hydraulics from the market thanks to a more successful and simpler design.
Source
Power steering - ZR expert chooses the best
At the dawn of the car's history, there were no power steering. Therefore, to turn the steered wheels of relatively heavy vehicles, a steering mechanism with a large gear ratio was used. The steering wheel could make five or more turns from lock to lock. And, as theory teaches and practice confirms, turning in place is always more difficult than in motion. Engineering minds solved this problem at the beginning of the last century, first patenting and later mastering the industrial production of hydraulic power steering (power steering).
How does power steering work?
Hydraulic power steering reigned on cars a century ago and still does not want to give up its position. Moreover, the hydraulic booster is combined with both modern rack and pinion steering mechanisms and a more classic steering gear with a steering linkage.
In the case of a rack and pinion design, the power steering is integrated into the steering mechanism. The power steering fluid supply is located in a reservoir located in the engine compartment. To control the liquid level, MIN and MAX marks are applied on the translucent body of the tank.
The power steering pump is mounted on the engine cylinder block bracket. The pump pulley is driven by a poly V-belt from the engine crankshaft pulley.
The working fluid is drawn from the reservoir by a pump and supplied under high pressure to a distribution device (distributor) located in the upper part of the steering gear housing and mechanically connected to the steering shaft. The hydraulic cylinder piston is fixed to the steering rack. When the steering wheel is turned, the distributor connects one of the hydraulic cylinder chambers to the pump discharge line, and the other chamber to the drain line. In this case, the piston of the hydraulic cylinder, due to the difference in pressure of the working fluid, moves the rack to the left or right and, through the steering rods and steering knuckles, turns the steered wheels of the car. If the hydraulic booster fails, the ability to drive the vehicle is retained, but the force on the steering wheel increases.
Sometimes a system with variable gain is used depending on the speed of the vehicle. At low speeds, the system provides maximum boost for easier turning and parking maneuvers. At high speeds, the steering assistance is reduced to improve vehicle directional stability. The effect is achieved by changing the fluid flow through the pump. The electronic steering control unit receives signals: about vehicle speed - from the engine control system unit; about the angle of rotation of the steering wheel (to calculate the angular speed of the steering wheel) - from the sensor located at the bottom of the steering shaft. Having processed the signals, the unit issues a control signal to the electromagnetic needle valve of the pump, which regulates the flow of working fluid through the pump. That is - pay attention - they are already trying to equip even the good old power steering with electronic systems that affect the force developed by such an assistant.
Pros of power steering:
Disadvantages of power steering:
Electric power steering
Electric power steering circuit
In electric power steering (EPS), additional force when turning the steering wheel is created by an electric motor.
Design and principle of operation of electric power steering
The main elements of the electric amplifier include:
- electric motor
- torsion bar and steering column shaft
- steering mechanism (gearbox)
- steering wheel position sensor
- torque sensor
- electronic control unit
When the driver turns the steering wheel, the torsion bar begins to twist. The torque sensor measures this twisting, determines the torque value from it and transmits this information to the control unit. The latter processes data from the power steering sensors and correlates them with the readings of other vehicle sensors (speed, crankshaft revolutions, etc.).
The control unit calculates the force that must be applied to help the driver turn the steering wheel and gives the appropriate command to the electric motor. The latter acts on the steering column shaft or steering rack, thereby facilitating rotation of the steering wheel.
We recommend: Rolls-Royce Phantom – a legend that is almost 100 years old
Advantages and disadvantages of EUR
Electric power steering rack
The main advantages of an electric amplifier include:
- fuel efficiency - the EUR does not take power away from the engine and turns on only when the steering wheel is turned
- reliability due to the absence of a hydraulic system
- compactness and ease of maintenance
- ability to adjust steering characteristics and settings
- possibility of implementing automatic vehicle control
Despite numerous advantages, EUR also has some disadvantages. These include:
- low power while maintaining minimal overall dimensions and cost
- possibility of overheating and temporary failure under unfavorable driving conditions
- expensive repairs
However, it should be noted that in the design of modern cars, the electric power steering is gradually taking first place, displacing the power steering.
Today, electric power steering is actively replacing hydraulics, as they have much better characteristics and relieve drivers from such manipulations as replacing power steering fluid. In addition, they perform better on the road and have excellent performance. Therefore, if you are purchasing a new foreign car, then preference should be given to electronics; in the case of a VAZ, you should really evaluate the capabilities of the car; perhaps it is better to use hydraulics.
How does the EUR work?
The use of an electric amplifier became possible relatively recently as a result of the development of automotive electronics. With the advent of fast, capacious and energy-efficient computers, it has become possible to have an electric motor help us turn the steering wheel. Moreover, this electric motor can have different designs, which determines the type of power transmission to the steering mechanism.
Many cars use ordinary DC electric motors, which turn the steering shaft through a reversible worm gear.
Such an amplifier includes an electric motor, a control unit, a torsion bar, a torque sensor and a worm gear connected to the steering shaft. Based on the angle of twist of the torsion bar, the sensor determines the amount of torque on the steering column shaft and sends a corresponding signal to the electric power steering control unit. The control unit, in turn, sends a corresponding signal to the electric motor, regulating the direction of its rotation and power. When the power of the electric motor changes, the additional force on the steering column shaft changes.
The degree of boost depends on the speed of the vehicle, the torque on the steering wheel and the steering angle. As the vehicle speed increases, the torque produced by the electric booster decreases. The electric booster only works when the engine is running. The power steering motor only consumes energy when the steering wheel is turned. If the electric booster fails, the car retains full controllability, while the steering wheel becomes somewhat “heavier” than on a car without an electric booster, since an additional load appears in the form of a freely rotating electric motor rotor.
Some domestic cars are equipped with electric power steering motors with so-called direct drive. This is when the axis of the electric motor is part of the steering shaft. Of course, you have to use a much more powerful engine, and even with high precision in positioning the shaft according to the angle of rotation. But the design of the mechanical part is extremely simple.
An electric amplifier of this type has some design features. For example, the electric booster can be turned off:
Advantages of EUR:
Disadvantages of EUR:
Description of the EUR
Device design
The EUR uses a small electric motor. It creates additional force on the steering shaft when turning. Thanks to this, it was possible to reduce the size of steering wheels in cars. Truck drivers were the first to appreciate this new product; today it is available on almost any passenger car.
The system itself consists of several main elements:
- brushless electric motor;
- steering angle sensors;
- torque;
- control unit;
- servo.
They are the main elements that make up the electric power steering. But the design itself is somewhat broader and will be discussed below, immediately after the functions, as well as the pros and cons of the system.
Features, Pros and Cons
Installing the device in a VAZ 2110
The competitor of this system is the hydraulic booster and electric hydraulic booster. The difference between the ESD and power steering: if the ESD breaks, nothing bad will happen, but if the power steering breaks, you need to remove the belt, and in some cars this is impossible to do. But if you drive without oil, the pump will have to be replaced.
Power steering and electric steering have obvious disadvantages. So, you cannot keep the wheels in the extreme position for more than 5 seconds, otherwise it will overheat. It also requires periodic maintenance. Well, and finally, at high speeds, the information content of the steering wheel decreases.
But the electromechanical amplifier, also known as EUR and EMUR, has the following advantages:
- reliability;
- efficiency;
- compactness;
- change in force depending on driving conditions.
The main disadvantage is that it is practically impossible to replace individual components. If they fail completely, you will have to replace the entire system, and this is quite expensive.
As for the functions, it is essentially the same - to make driving easier by taking on part of the required effort. With such a device, the car becomes much more obedient even in difficult conditions. You will learn more about the device in the video below (the author of the video is Car Sales CAR SHOWROOM First Video AutoMarket).
Design and operating principle
On different types of cars, the electric power steering can be installed in different places.
So, on small cars that do not require particularly strong impact, the system is installed directly in the steering column. The device is located directly in the cabin under the control wheel, where all the sensors are located. This position protects the electric power steering from dirt and other influences.
On middle-class cars, the system is located on the steering rack. The force is transmitted through the gear. This system is somewhat less reliable, but widespread.
SUVs and minibuses require installation of the system on a parallel-axle structure. In this case, force is transmitted from the electric motor using a toothed belt drive, as well as a mechanism of a screw and nut on circulating balls. In this case, the nut rotates with a belt, which transmits the force to the balls, from which it passes to the steering rack.
The basic principle of operation of electric power steering is the transfer of additional influence in order to facilitate vehicle control.