The design feature of the car is that the main components that set it in motion are located separately, and the transmission of torque from the power plant to the drive wheels is carried out through drive shafts.
The number, length and design of these shafts directly depend on the design features and layout of the car. Shafts not only provide rotation transmission. It is impossible to constructively place the units connected by the drive coaxially, so the drive shafts compensate for angular discrepancies in the positions of the component parts. And this is done thanks to the presence of a cardan joint in the shaft structure. It allows rotation to be transmitted between several parts of the shaft, located at an angle to each other.
What is a cardan shaft
The cardan is a mechanism that transmits rotation from the gearbox to the rear axle gearbox.
The task is complicated by the fact that these two mechanisms are located in different planes relative to each other. All car models whose rear wheels are driven are equipped with cardans. The transmission driveshaft is installed along the vehicle's exhaust system and looks like a long beam running from the gearbox to the rear axle. It is equipped with at least two cross joints (one on each side), and in units with a slight offset of the axes - one.
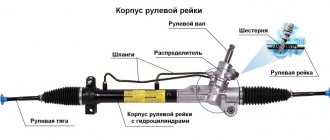
A similar transmission is also used in the steering system of a car. The hinge connects the steering column with the steering mechanism located in a different plane.
In agricultural machinery, such a device is used to connect additional equipment to the tractor power take-off shaft.
A description of the operating principle of a cardan-type transmission was compiled by the Italian engineer and philosopher G. Cardano. In the automotive industry, this scheme was successfully used by the industrialist Louis Renault on a modification of the De Dion-Bouton car (1898).
The design and principle of operation of the cardan transmission
The classic cardan drive has changed a lot and has distinctive features. It is customary to distinguish four main design elements:
- Central pipe - or in technical language “central shaft”. This is a hollow pipe design made of a strong metal alloy.
- Crosses and tips are a special device made in the form of a cross, which is responsible for controlling the rotating elements of the cardan. In simple terms, the cross controls variable tilt angles, which should not be in the range of 0 to 20 degrees.
- The fork is an intermediate connection between the main shaft and the intermediate shaft. The direct function is to compensate for the height distance between the shafts when the car moves over bumps and holes.
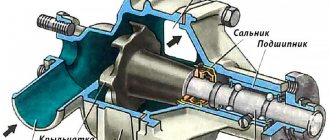
- An intermediate bearing is a very important structural element that supports the main shaft while allowing it to rotate in the required direction. Depending on the type of cardan, there may be two or more intermediate bearings.
Device
The transmission consists of several structural units:
- cardan joints, simple crosspieces and more complex, functionally perfect or cheap elastic ones;
- rigid tubular shafts connecting the hinges;
- additional fastenings in the form of suspended bearings and couplings;
- splined connections that compensate for changes in length.
Simple shafts have inherent disadvantages in the form of vibration loading and uneven rotation.
What is the function of the driveshaft?
HF is capable of performing two important functions.
- Basic. Transmission of torque from the gearbox or transfer case of the car to the rear wheels. The cardan allows you to gently transfer torque from the transmission to the wheels, dampen vibration off-road, and ensure smooth driving.
- Additional. Plays the role of a link between the steering column and the rack. That is, it is already part of the steering mechanism. HF helps improve steering feel.
Thanks to the HF vehicle, good acceleration is ensured even on uneven roads. KV is actually an optimizer of effective unloading of the front wheels and a tool for reducing the risk of slipping.
What is the propeller shaft made of?
Although, at first glance, the driveshaft seems to be a simple element, a pipe and a pipe, in reality its structure is a little more complicated. Let's take a closer look at this issue. The hero of our today’s article consists of the following elements:
- suspension bearing;
- sliding fork;
- fastenings;
- the driveshaft itself;
- crosspiece;
- seals.
It is very difficult to bring all existing types of cardan shafts to any one denominator. The fact is that these devices are used in a huge variety of equipment and, as a result, can have different designs.
For example, the driveshaft can be made up of several sections, or it can be single-section (this is usually found in sports cars). In the second case, the design is elementary - it’s just a steel pipe, both ends of which are crowned with cardan shaft crosspieces and tips.
If there is more than one section, then there are also more crosses - they are needed to interface shafts rotating at different angles.
Another important design detail is the driveshaft outboard bearing. It is a support for the entire structure and holds it in place without interfering with its rotation. The bearing is attached to the car body, and depending on the number of cardan sections there may be several of these parts.
In general, the cardan is a fairly reliable component of the car. It was created taking into account high loads and, as a rule, it copes with its task perfectly. The disadvantages of this unit include its rather large weight and dimensions; in addition, in rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive cars, due to its location under the bottom, it “eats up” part of the useful space of the cabin.
So, fellow car enthusiasts, we briefly went over the main issues related to the driveshaft of a car.
Features of operation
The main feature, which is also a disadvantage of this hinge, is the uneven cyclic transmission of rotation. That is, due to the existing angle between the shafts, the driven part of the drive alternately either overtakes or lags behind the driving part. Because of this feature, the hinge is called “unequal angular velocities”. Therefore, in front-wheel drive, shafts with such a device are not used.
The peculiarity of the operating principle of the cardan transmission is taken into account by the design. To partially compensate for uneven transmission, the drive device uses two or more hinges simultaneously. You can also often find a semi-cardan elastic element on passenger cars.
In order for the existing cardans to compensate for cyclic uneven transmission, they still need to be correctly positioned relative to each other. To do this, the hinges are placed synchronously, and not offset from each other. That is, the internal forks mounted on the tubular shaft and the external ones connected by flanges to the axes of the units are installed in the same plane.
The semi-cardan elastic element is structurally very similar to the unequal velocity joint. It also has two forks, but they are connected into a single structure using an elastic (rubber) insert. There are also designs with a flange connection.
Despite their disadvantage, cardans are widely used. And this is facilitated by the high reliability of the hinge and unpretentiousness to working conditions. This allows the driveline to be left open, without any protective elements.
In general, the cardan drive can operate for a very long time without any maintenance. Failure of the hinge can only be caused by contaminants entering the bearings due to damaged seals. And even then, this will not immediately lead to breakdown. The cardan will become unusable only if the needle rolling elements of the bearings are significantly worn. The hinge itself is irreparable and when worn out it is simply replaced.
Types of cardan drives
In the modern automotive industry, the following types of cardan transmissions can be used:
- Equipped with a unequal velocity joint (classic car driveline);
- Equipped with CV joints (constant velocity joints);
- Equipped with semi-cardan elastic joints;
- Equipped with rigid semi-cardan joints.
The system with the NUS hinge is considered classic. There are forks, crosspieces, and needle bearings. Suitable for most rear wheel drive vehicles.
Modern SUVs often use a system equipped with CV joints. Such devices provide more comfortable driving conditions, almost completely eliminating vibrations.
Elastic hinges are a rubber coupling capable of transmitting torque at bends of no more than 8°. The rubber is quite soft, so a shaft with a similar structure ensures a smooth start of movement and the absence of sudden dynamic loads. In addition, flexible connections require no maintenance. The rigid semi-cardan joint has a complex technical device and transmits torque due to gaps in the spline connection. Due to the complexity of manufacturing, technical shortcomings and rapid wear, it is not used in the automotive industry.
Principle of operation
The design of the cardan spline connection is no less important. The principle of operation is as follows. The gearbox fits tightly onto the inner body and is attached to the edge of one shaft. On the other side there is an axle gearbox, which is connected to the suspension. The gap between the two nodes widens when overcoming uneven areas. Both the rear and front driveshafts need to stretch, an action provided by a splined joint complete with a sealing seal.
Advantages and disadvantages of this transmission
Now that it is clear what a car’s cardan is, it’s worth considering the pros and cons of this type of joint. The design of the cardan has a significant advantage: this mechanism is able to withstand the enormous loads that the transmission endures when driving on paved roads and in rough terrain.
The only negative is the large weight of the cardan, which is displayed on the curb weight. This affects the dynamics of the car and fuel consumption. In addition, the process of installing the universal joint requires a tunnel at the bottom of the car (and this adds inconvenience to passengers). Finally, this hinge creates noise and vibration during rotation.
ADVANTAGES
The advantages of cardan transmission include:
- Work with significant torques.
- Possibility of connecting transmission units installed at large distances from each other.
- Implementation of all-wheel drive on a car.
- Simplicity of design.
- Resistance to loads.
But at the same time, the cardan increases the metal consumption of the transmission and requires significant space for installation, which affects the usable volume of the cabin.
Cardans with unequal velocity joints do not require maintenance and at the same time have a significant service life. Despite the use of bearings in the design, there is no need to lubricate them during operation, since the joint itself is maintenance-free, and the lubricant supplied by the manufacturer is enough for the entire service life.
The cardan is a non-repairable unit. When bent, the cardan requires complete replacement. This is due to the fact that the unit is balanced during manufacturing. Bends lead to imbalance, which increases vibrations and loads in the gearbox and final drive and accelerates wear of the joints.
The hinges are also not repairable, therefore, if increased vibration appears from the cardan side, or third-party sounds (crunches, clicks), the components of the hinge are replaced. Usually the crosspiece and its bearings are subject to replacement, but if the lugs are very worn out, the assembly assembly is replaced.
[custom_ads_shortcode3]
Recommendations for use
Important! In order to extend the service life of the device, you should check the condition of the protective covers when undergoing maintenance at a car service center. At the slightest damage, replace them with new ones, thus protecting the bearings from dirt, which prevents their premature failure. Driving methods also affect the longevity of the system.
Slipping when driving off-road, sudden acceleration, prolonged driving on deep snow or a dirt road with a high rut.
Checking the condition of the cardan shaft
Even if the car is operated in non-extreme conditions (driving on city roads), checking the condition of the driveshaft is necessary every 5 thousand kilometers. When driving on dirt roads, checking is recommended even more often: every 3 thousand km. Special equipment has its own requirements. It all depends on what objects it is used on. When checking, the greatest attention is paid to the crosspiece, which can begin to roll and jam, as well as the outboard bearing. The appearance of backlashes after a certain mileage is a completely natural phenomenon. The spline connection is also very vulnerable. First of all, because it is a moving mechanism that constantly encounters dynamic loads. It is recommended to check the parts in the following order:
- Connecting elements (nuts, washers) of bearings, couplings, flange forks. It is important that not only all connections are in place, but also the tightening torques meet the requirements of the operating conditions.
- Couplings at the moment of shaft torsion. The presence of cracks, let alone ruptures, on the couplings is unacceptable. If there is such a problem, the part needs to be replaced urgently.
- Spline connection at the moment of shaft rotation. Here it is important to understand whether there are any backlashes. In order for the assessment of the spline condition to be as reliable as possible, it is advisable to rotate in both directions.
- Hinges. A simple visual inspection is not enough here. You need to place a screwdriver between the forks and pump thoroughly. The unpleasant moment is, again, finding a gap. In this case, you will have to install a new cross.
- Bearings. How the verification is carried out is of fundamental importance. Skills are important. In order not to miss the backlash, you need to hold the HF with one hand, and with the other you pull it in different directions.
But if there is a suspicion of HF imbalance, you cannot do without diagnosing the unit on a balancing stand. You can’t do without such a check especially if you feel constant vibrations while driving, and an unpleasant grinding noise regularly occurs when changing gears.
Problems, cardan failures
Not often, but it does happen that the driveshaft knocks. Such knocking noises can occur during a sharp start or when changing gears.
Causes of noise:
- The bolts securing the flanges and the transmission coupling have become loose.
- Increased clearance in the sliding spline connection.
- Large gap in the cross bearings.
Reasons for vibration of the driveshaft when driving:
- the shaft is deformed;
- the cardan is installed incorrectly;
- shafts are unbalanced;
- the bushing of the intermediate coupling flange or the ring of the centering secondary shaft of the gearbox is worn out;
- the outboard bearing has increased clearance;
- the bolted connections of the transverse support have loosened;
- large gap in needle bearings and crosspieces;
- the fork connection has become loose;
- lack of lubrication in the shaft splines.
Why does grease leak?
Connections with lubricant and seals often become depressurized and lubricant leaks out (Litol-24, etc.).
There are only two reasons:
- The spline seal is worn.
- The crosspiece bearing seal is worn.
If you hear a crunching sound in the driveshaft area, it is recommended to go to the nearest service center and carry out diagnostics, or do it yourself.
How to eliminate the causes of cardan problems:
- Tap on the threaded connections, check if they are loose, tighten them.
- If there is a lot of play in the spline joint, then the shaft needs to be disassembled and examined; most likely it will have to be changed.
- If there is a large gap in the crosspiece, replace it.
- Replace deformed parts of the propeller shaft or replace them as an assembly.
- If the driveshaft was not installed according to the marks, disassemble it and install it according to the marks.
- If there is shaft runout, you need to check it for bent. Remove, twist. Of course, for this you need a special stand that will show whether the shaft is bent or not, but you can also see by eye whether the shaft is straight or not.
- Replace seals if grease is leaking.
Frequent malfunctions and their elimination
All malfunctions can be divided according to emerging signs of failure:
- Vibration when moving - the bearings of the cross or the sliding sleeve are worn out, the balancing of the shaft is disrupted;
- Knocks when starting - the sliding joint splines are worn out, the fastening bolts are loose;
- Oil leakage from the bearings means wear of the seals.
To eliminate the problems described above, the “cardans” are dismantled and defective, and faulty parts are replaced. If there is an imbalance, the shaft must be balanced under dynamic conditions. Be sure to readReplacing the driveshaft cross
[custom_ads_shortcode1]
How to change the crosspiece on the cardan
To repair the crosspiece, it is necessary to remove the cardan. Before you disassemble, you need to know some nuances:
- Fill the nuts with waterproofing agent to make the fasteners easier to unscrew.
- Use a chisel to mark the cardan flanges and rear axle flanges. If this is not done, vibration may occur on the cardan.
- To avoid damaging the threads of the nuts, it is advisable to use a curved spanner.
- If the cardan bolts rotate, you need to fix them with a screwdriver.
First, unscrew the four bolts on the propeller shaft, then remove the suspension bearing mount. After these procedures, we remove the cardan; it needs to be removed from the gearbox splined connection. Before removing the crosspiece, it is advisable to wrap the spline part with material to prevent sand from getting in there. Before removing the crosspiece, you need to prepare a tool: a hammer, pliers, a thick screwdriver and a round tube of suitable diameter. Clamping the shaft in a vice will make your work much easier. There are special pullers for removing crosspieces, but they are often not used even at service stations. However, many garage craftsmen are able to make such a device for themselves in 10-15 minutes. Next we get the retaining rings. Often, to remove them, you need to tap them with a hammer using a spacer. After this operation, the stoppers can be easily removed with pliers. Next, the cups are knocked out of the eyes. This is done with a hammer and the same spacer that was used when removing the retaining rings. Sometimes the cups fall out on their own; most often you will have to remove them with improvised objects.
Balancing the driveshaft
High-quality balancing at home is impossible. This requires sophisticated diagnostic and balancing equipment, which can only be found in factories and specialized workshops.
If necessary, you can perform rough balancing at home, which will allow you to operate the car for some time.
To balance the driveshaft, the car is lifted completely, the engine is started and gear is engaged in 4th gear. At the same time, the shaft begins to rotate slowly. To determine the places where balancing is necessary, a piece of chalk is fixed 1 mm from the shaft. An unbalanced shaft will move slightly. In this case, marks will remain in the places of beating. You can balance too light areas with heavy ones by welding a small amount of metal on them. In this case, after adding each gram of weight, sea trials should be carried out, noting the degree of effect achieved. The procedure is stopped when the vibration of the car while driving completely or almost completely disappears. Maintenance
Maintenance of the cardan drive consists of periodically, once every few months, injecting the crosspiece.
The procedure involves introducing lubricant into a part and is performed on UAZ Patriot and foreign-made cars. Domestic “classics” do not require injection of the cardan. For lubrication, high-temperature plastic compositions of viscosity class NLGI-2 are used, which are capable of maintaining their properties for a long time under difficult conditions.
Timely maintenance and diagnostics of the driveshaft and crosspiece allow you to keep the axles and gearbox in good condition. In rear-wheel drive vehicles, failure of these units is often the result of vibration that occurs when the driveshaft malfunctions.
Operating principle of HF
The principle of operation of the cardan transmission is the ability to transport torque when the position of the “cardan” in space changes. This principle is implemented through two mechanisms:
- Sliding fork of the cardan shaft;
- Cross joint.
A sliding fork is necessary to slightly increase the length of the mechanism when driving on uneven roads. Due to the long spline connection, the supply of torque does not stop when the suspension, together with the rear axle, moves up or down. The hinge, in turn, ensures rotation of the wheels when the bending angle of the CV changes. It is believed that the mechanism is capable of working productively at angles of no more than 20°. Then its active wear begins.
[custom_ads_shortcode2]
Prospects for the development of a cardan transmission system
The classic ShNUS has some technological disadvantages. The rotation speed of its shafts changes during movement. In this case, the driven shaft can accelerate and decelerate at a stable speed of the drive shaft. This leads to accelerated wear of the mechanism and also creates excess load on the rear axle. Also, the operation of the hinge is accompanied by vibration. The purpose of the cardan drive can be performed by a shaft equipped with CV joints (front and rear). Similar systems are already used on some SUVs today. Also, the cardan transmission of the VAZ-2107 and other “classics” can be equipped with a CV joint. Repair kits are available for sale.
The use of a constant velocity joint eliminates the disadvantages inherent in the classic cross. The shaft rotation speed is leveled out, vibration disappears, the HF does not require balancing after repair, and the torque transmission angle increases to 17°.
Sources
- https://AvtoTachki.com/chto-takoe-kardannyj-val-klyuchevye-funkczii/
- https://VazNeTaz.ru/kardan
- https://pro-sensys.com/info/articles/obzornye-stati/kardannyy-val/
- https://auto-ru.ru/kardannyj-val.html
- https://ZnanieAvto.ru/uzly/kardannaya-peredacha-avtomobilya.html
- https://www.syl.ru/article/353677/chto-takoe-kardan-v-avtomobile
- https://neva-kardan.ru/stati/krestovina-kardannoj-peredachi.html
- https://autostuk.ru/kardan-v-avtomobile.html
- https://SwapMotor.ru/transmissiya/krestovina-kardana.html
- https://ZnanieAvto.ru/uzly/krestovina-kardannogo-vala.html
Additional items
In addition, the design includes a suspended cardan bearing. It plays the role of an auxiliary support element for the shaft. The bearing prevents the part from rotating and ensures that it is in the required position using a bracket coated with lubricant and supplemented with sealing elements, which is attached to the body part. The number of structural elements of the shaft determines the number of bearings.
The universal joint of the heads is necessary, first of all, to ensure a high-quality connection between the drive axle and the crankshaft. Flexibility and strength of the connection become most important when the bridge moves while the car is moving.