Principle of operation
Let's consider what a steering rack is, the structure and principle of operation of the unit. The rack and pinion design is a common way to control the angle of rotation of the wheels of a car. The principle of operation of the steering rack is simple and consists in transmitting the torque of the steering wheel through the driveshaft and gear shaft to a horizontal rack and pinion mechanism, the translational movement of which through special tips with levers ensures rotation of the wheels around their imaginary axis (castor).
To implement this idea, a rack and pinion gear is used. Regardless of which automaker produced the steering rack, its design and principle are the same for all cars. Essentially, these are two gears connected to each other, the rim of one of which is straightened. The second gear - the pinion - is connected through the drive shaft to the steering wheel to transmit torque from the driver through the rack to the wheels. This design combines two important advantages in one unit:
- Reduction of the force required to turn the steering wheel.
- Converting circular motion to linear motion.
Translational motion is limited by the range of wheel shift when turning, which is inherent in the design of the car. On most cars, moving the rack from left to right dead center requires 2.5 to 4 full turns of the steering wheel.
To understand the relationship between the rotation of the steering wheel and the displacement of the wheels relative to the axis of motion, there is the concept of a transmission coefficient, numerically equal to the ratio of their angles of rotation (in degrees). For example, if a full rotation of the steering wheel (360°) initiates a wheel shift of 20°, then the gear ratio is 360°/20°=18. In general, for light and sports class cars, the figures characterizing the transmission coefficient will be lower than for more massive cars - buses and trucks.
Dismantling
If the steering rod is faulty, you need to unscrew the tip from the shock absorber strut. But if the problem is not hidden in the rods, then you need to remove the steering rack. Next, after removing the rack, you need to remove all the rubber boots.
If the problem is wear of the plastic bushing, it must be replaced. The bushing is made of plastic material, which means it wears out quickly. The replacement method is as follows: it is necessary to clean the area where the steering column is mounted from fuel oil and dirt with a rag. According to the technical documentation of the car, the removal method is described there. After the bushing has been replaced, it is necessary to fasten the rail in the reverse order. If the steering rods or ends are faulty, they must be replaced, but after that, be sure to adjust the camber and toe of the tires. To avoid uneven tire wear. Happy replacement!
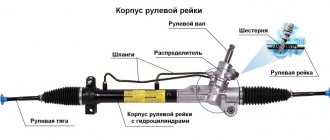
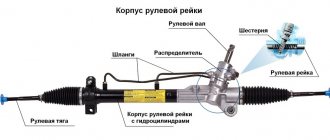
Steering rack device
We realized that this is a mechanism for transmitting to the wheels the turning force applied by the driver to the steering wheel of the car. Due to its simplicity and convenience, this design is widely used to set the course of movement of cars, small trucks and SUVs.
The design diagram separately from the wheels is shown in a simplified form in the picture.
As you can see, the steering rack is built on the interaction of the gearing of the teeth with the gear shaft. It is worth highlighting 4 main components that make up the steering rack:
- vehicle steering wheel;
- a shaft for transmitting torque to the drive gear;
- a rack that moves linearly under the influence of gearing;
- steering tips that transmit translational motion through the hinge to the steering arms of the wheels.
Depending on the type, the mechanism can be equipped with devices to facilitate steering rotation - hydraulic or electric booster. In addition, the design ensures that the wheels move at different angles, which corresponds to the geometry of the outer and inner turning radii, as can be seen from the figure.
Each element of the rack and pinion control system performs a specific function, which is worth considering in more detail.
Steering wheel (or steering wheel)
A car steering wheel is a device for controlling the movement of a car in a given direction. It is rigidly engaged through a toothed seat with the steering column shaft, which transmits rotational forces to the rack.
Modern car steering wheels also have additional functions:
- control on-board systems using built-in buttons (so-called multimedia or multi-steering wheels);
- reduction of injuries due to the introduction of an airbag into the central part of the steering wheel.
According to the requirements of technical regulations, the steering wheel must be firmly fixed on the shaft without play and free movement in the horizontal and vertical plane and along the offset.
Steering shaft
The rotational movement of the steering wheel is transmitted through a shaft, which can consist of several parts oriented in different directions, which is determined by the geometry of the car's design.
They are interfaced with each other through cardan mechanisms. A rigid circuit is used to connect to the steering wheel.
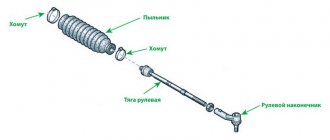
Steering rack
The horizontally moving rack (green in the figure below) is made in the form of a single rigid element with a notch for engagement with a toothed shaft (blue-orange part), which is driven into rotation synchronously with the rotation of the steering wheel.
At both ends of the assembly there are sockets for a swivel or threaded connection with special tips connected to the wheel steering arms.
Steering rods
Direct transmission of force to the wheels is carried out by traction rods connected to the hub block (shown in blue in the figure).
The design takes into account the need to ensure a difference in the rotation angles of the inner and outer wheels. A feature of the rods is the ability to transmit both translational and rotational movements.
Steering end
Since the rack is fixed in such a way that it can only make a linear horizontal displacement, and the wheels change their position in three planes, steering tips (in the figure below are colored purple) are used to transmit the turning force to them.
The tips are made in the form of hinges with fingers for threaded connections and length adjustment to correct rotation angles.
Damper
The damper is a double-acting shock absorber installed on the steering rack between the linkages and the body. It is traditionally used on SUVs and rear-wheel drive premium cars. The damper increases the vehicle's directional stability, minimizes steering wheel wobble when driving on uneven surfaces, and extends the service life of the rack.
There is also a steering shaft damper installed on the column of cars with ESD.
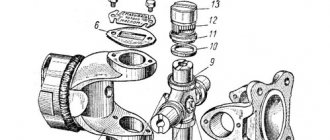
Structure
The design of a mechanical steering rack is as follows. Inside the crankcase, which has the shape of a hollow cylinder in cross-section, there is a protective corrugated cover. A drive gear is mounted on bearings in the crankcase, to which the steering rack is pressed by a spring. A spring is required to eliminate the gap in the gear-rack pair. The travel of the rack is limited on one side by a restrictive ring, and on the other by the steering rod joint bushing. This steering rack design is extremely simple and reliable.
Types of steering racks
The operation of the simplest worm-rack and pinion pair can be realized without the use of additional devices that help rotate the steering wheel. The desire to ease the driver’s efforts led to the equipment of the mechanism with special blocks that relieve the need to strain to carry out the maneuver. As it developed, the scheme was consistently improved, going through three stages of improvements, and is implemented in the following types:
- Mechanical (manual).
- With power steering (power steering).
- With electric power steering (EPS).
Since there are cars on the automotive market that use all of the above rack and pinion control options, we should consider them in more detail.
Mechanical steering rack
This is the simplest type of design, representing a direct drive of torque from the steering wheel through a matching driveshaft and a gear shaft. The mechanical steering rack is shown schematically in the figure.
The obvious disadvantages of such a solution will be the need to apply significant force to the steering wheel (which may limit the circle of people capable of driving such a car) and the transmission of road unevenness, potholes, shocks and blows to the driver’s hands, which are transmitted to the car body vibrations.
The desire to reduce the driver's effort to control movement has led to the emergence of hydraulic and electrical devices that enhance torque.
Hydraulic steering rack
The most common scheme with power steering is shown in the figure. The hydraulic steering rack operates according to a scheme that consists of moving synchronously with the driver’s steering wheel rotation under the influence of a pressure difference in the piston fluid. The principle of operation of a power steering rack is shown in the figure.
The connection between the pinion and the rack is normal, but at the point where it mates with the steering column shaft, there are special rotary valves that regulate the direction of fluid flow (colored in orange in the diagram) under pressure from the pump. When, for example, the steering wheel is turned to the right, pressure is transmitted through the valve along the lower (according to the diagram) fluid line to the part of the cylinder to the right of the piston. At the same time, it (piston), rigidly connected to the rack, helps it move to the left (according to the diagram) and squeezes out excess liquid, which is directed by a rotary valve into the expansion tank (to reservoir). When the steering wheel is rotated in the other direction, the direction of oil circulation changes to the opposite.
The hydraulic steering rack requires the additional installation of a power steering pump on the engine, which takes a certain amount of power from the engine. In addition, the design of the power steering rack implies that the power steering operates only when the engine is running, when the nominal pressure of the hydraulic fluid in a closed circuit is reached.
Electric steering rack
An electric steering rack is an option to relieve the driver's effort on the steering wheel using an electric motor connected by a worm gear to a gear mounted on the steering shaft.
The operating principle of the electric steering rack is simple: the engine controller synchronizes the direction of its rotation with the movements of the driver’s hands. This solution makes steering movement easy, requiring almost no effort.
However, a simple worm-gear pair has one feature, which is that torque transmission is possible only in one direction - from the worm to the driven rim of the gear. In reverse order the mechanism is blocked. Therefore, the use of a simple gear does not solve the problem, and it is necessary to complicate the worm gear, supplementing it with a planetary unit with three satellites to connect the torque amplifier with the gear shaft drive.
The figure above shows an electric steering rack: the structure and operating principle of this unit. The arrows show the effect of additional force through the worm gear and satellites on the displacement drive shaft. In the event of an electric motor failure, this design provides the ability to manually control the movement, as illustrated in the figure below.
So, if a problem occurs in the worm gear and it is blocked, torque is freely transmitted directly from the driver’s hands through the rack and pinion turning mechanism to the wheels (shown by blue arrows). In this case, you will only need to apply more force due to the failure of the electric power steering, but the vehicle's handling will not be affected.
Signs of trouble
The safety of a motorist driving his vehicle directly depends on the good condition of the steering system. Therefore, at the first signs of steering rack malfunctions, you should immediately take measures to eliminate them.
First of all, car owners must understand exactly how to determine faulty steering racks. This is not so difficult to do if you know about the characteristic symptoms and signs of an impending breakdown of the steering rack installed on the car.
Yes, it is possible to accurately confirm or refute a faulty steering rack through diagnostics and dismantling work. But sometimes even indirect signs are enough to confirm the diagnosis.
To begin with, remember that the steering rack does not break out of the blue, unless we are talking about getting into a hole or an accident. There are certain signs that indicate wear and tear and impending serious failure. Therefore, before checking the steering rack, listen to the behavior of your car. She herself will tell you that some problems have arisen, which could soon turn into expensive and dangerous breakdowns.
Depending on the type of steering rack, certain symptoms may appear. Let's consider the main ones:
- if it is a hydraulic steering rack, then the malfunction can be determined by a constant drop in the fluid level in a special tank;
- also in the case of power steering, traces of hydraulic fluid may appear that accumulate in the rod boots;
- control has become noticeably more sensitive. Even when you make a small turn of the steering wheel, the car practically throws from side to side;
- the steering wheel turn does not correspond to the angle at which the front wheels of the vehicle turn;
- the steering wheel may also not return to its original central or neutral position, or it may not do so well when the car completes the maneuver and returns to straight-line motion;
- When the steering wheel is in the center position, the effort may be lost. This indicates a malfunction in the system;
- Sometimes motorists are faced with the fact that the steering wheel literally begins to rotate spontaneously. A bad sign indicating the need for urgent repairs;
- When the steering wheel rotates, there is no effort at all. This potentially indicates hydraulic or electric motor failure;
- When driving in small uneven conditions, a strong knock is created and transmitted to the steering wheel. But it can decrease when the steering wheel is turned to its extreme positions;
- the steering wheel is completely jammed and cannot be turned in any direction;
- it becomes almost impossible to control the car, since any maneuver requires enormous effort.
The appearance of at least one of the listed signs indicates that there are problems with the steering. The malfunction can persist in the form of barely noticeable symptoms for a long time, or at one point lead to a serious breakdown, which is most dangerous precisely while the car is moving.
This suggests that even mild signs of problems with the steering rack cannot be ignored under any circumstances. In such situations, you should contact a car service, or go to your own garage to independently solve the problem. Sometimes you can do the repairs yourself. It's not that difficult if you follow the instructions, follow the car manufacturer's recommendations, and don't forget about safety precautions.
Advantages and disadvantages
Using gears to move the rack that turns the wheels has both pros and cons. They must be taken into account when choosing a car, since reliable handling is the most important principle of traffic safety. Here a lot depends not only on what kind of rail, what type of amplification device is used and how it is implemented. The originality of the unit plays a significant role in the reliability of the mechanism. It is for this reason that contract racks are much more reliable and durable than new duplicates produced in third world countries without control by the automaker.
Pros of rack and pinion steering
When comparing rack and pinion steering with others, there are a number of obvious advantages to consider:
- due to the smaller number of elements involved and their interface points, the rack and pinion mechanism responds faster to impact and is easier to control;
- lower weight of the structure helps to improve the performance and speed characteristics of the car;
- rack and pinion steering provides a better “steering feel”, which significantly increases safety when driving in wet and slippery areas;
- repair and restoration are simpler for two reasons - the smaller number of elements that make up the assembly and the widespread distribution of the mechanism.
The mentioned considerations contribute to the widespread introduction and improvement of various rack and pinion control options in the automotive industry.
Disadvantages of rack and pinion steering
The popularity of using this technical solution on many cars outweighs the disadvantages, of which the following can be listed.
For mechanical and hydraulic systems:
- accelerated wear of elements due to increased load, which is the price to pay for the simplicity of the control unit, consisting of a small number of parts;
- the sensitivity of the rack and pinion mechanism to the quality of the road surface, especially noticeable on all-wheel drive SUVs when driving into terrain unprepared for movement, when the difficulty of control increases sharply;
- susceptibility to vibrations transmitted through the steering wheel to the driver;
- process fluid leaks.
Additional devices that use electricity to power power steering have the following disadvantages:
- higher price;
- the need for special equipment for diagnosing the electronic control unit;
- the difficulty of self-repair.
Whatever the steering rack, the principle of operation of the mechanism is similar, and all the differences lie only in the choice of the scheme for increasing the force transmitted by the driver by turning the steering wheel.
avtoexperts.ru
This is a kind of mechanism capable of transferring forces from the steering wheel to the rods. Roughly speaking, a device that allows the wheels to turn synchronously in the direction specified by the steering wheel. The mechanism works quite simply. It is necessary to understand the relationship: the rotating device rotates the shaft, from it the rotations are transmitted to the gear, and from the latter the movements are transmitted to the rack. Thus, depending on the rotation of the steering wheel, it moves left or right, and with it the rotation of the steering rods, which are attached to the steering knuckles, also changes.
Recently, it is the steering rack that has been attributed primacy among all control systems.
Device
Like any mechanism, this part consists of several elements. So:
• Cylinder, also known as crankcase. The part that houses the rack itself. As a rule, modern cars use light alloys such as aluminum.
• Gear, part of the shaft “coming” from the steering column.
• The rack, which has a spring for reliable engagement with the gear.
• Various seals and clamps at the edges to limit travel.
• Don't forget about the bearings, they prevent the occurrence of play and provide easy “maneuvers” of the rack itself along the body.
Keep in mind that depending on the modification of the car, the device may be supplemented with some additional elements. For example, these could be hydraulic cylinders, electric motors with their own set of parts.
One of the additional elements, a planetary mechanism may act. It allows you to change the gear ratio, that is, while driving, depending on the speed, the “planetary gear” regulates the gear ratio. Handling improves, especially at high speeds, when sharp turns of the steering wheel are not desirable. BMW manufacturers began to use it for the first time.
Nowadays there are three types of such management. You will learn about their differences below. So here are the types:
1. “Naked”, that is, a mechanical rack.
What is rack and pinion steering - in simple words
Rack and pinion steering , or rack and pinion steering as it is also called, is an incredibly common front-wheel steering system on modern passenger cars. Even if you are not an automotive technology guru, you have most likely heard of such a mechanism. But how does it work? Let us explain the principle of operation for beginners, as they say, on the fingers.
Most likely, your car has rack and pinion steering. This incredibly popular engineering choice is due to the progressive operation of the system as a whole (ideal for modern dynamic, fast and powerful cars), good feedback to the front wheels (you understand exactly at what angle the wheels are turned and how quickly they turn) and the ability to install controls for vehicles with front independent suspension.