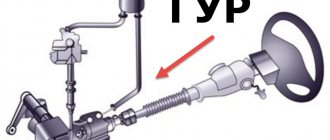
Design and principle of operation of the steering gear
All gearboxes have a housing made of cast iron or welded steel. The housing contains transmission elements - gears, shafts, bearings, etc. Sometimes the gear housing may contain devices for lubricating bearings and gears.
Today, there are many types of gearboxes known. They can be classified: by type of transmission (worm and gear); by type of gears (bevel, cylindrical, bevel-cylindrical); by the number of stages (single-stage, two-stage, etc.); depending on the features of the kinematic scheme (with a deployed coaxial scheme or with a bifurcated stage); depending on the location of the shafts in space (horizontal, vertical).
With all the variety of designs, cars are most often equipped with worm gearboxes. Such gearboxes transmit torque using a worm gear, the main elements of which are a worm screw and a toothed worm wheel. Worm gears are used in all steering gears today.
The worm is a special screw made of durable materials and having a trapezoidal thread profile. A worm wheel is very similar in appearance to a regular gear wheel, but the threads on such a wheel are carefully adjusted to the shape of the threads of the mating worm. Typically, gears for heavy-duty worm gearboxes are made from two different materials. The raw material for the core is any inexpensive and at the same time durable steel (or ordinary cast iron), and the teeth are made of high-strength anti-friction materials. Due to its design, the worm gear is effective in applications that require high torque combined with low angular velocity.
Adjusting the steering gear
It is necessary to make adjustments if there are: jamming when turning the steering wheel; tight turning; spontaneous rotation of the steering wheel when the wheels are level. To adjust, you will need a wrench and a flat-head screwdriver. The location of the steering gear varies from brand to brand. Due to the specific structure of the steering control, it is located in the lower part of the hood on the driver's side, which is quite problematic to get there. Sometimes it's easier to adjust everything from the pit. First, loosen and remove the central locknut. You will need an assistant; to adjust, you need to turn the steering wheel, while locking the central adjustment screw of the gearbox. This adjusts the gap between the gears up or down. To increase the clearance and make it easier to turn the steering mechanism, turn the steering wheel counterclockwise, and to reduce the gap and eliminate free play, turn it clockwise.
If there is no assistant, then adjusting the gearbox will take longer. Align the wheels straight and tighten or loosen the adjusting bolt, checking the play by turning the wheels. It is important to make adjustments without jamming. After completing the adjustment process, you need to secure the screw; to do this, fix it with a flat-head screwdriver and tighten the nut with a wrench. This adjustment is possible until the screw sinks into the steering gear. Then it will no longer be possible to lock it with a nut and only replacing the steering gear will help. For each car there are permissible steering wheel angles. You can orientate 10˚ in each direction.
Adjustment
Unlike repairs, steering gear adjustment can be done on your own. To do this, manufacturers provide an adjusting screw in the design, usually protected by a polymer cap or plug.
This is interesting: Characteristics of motor 21129
Bevel gear adjustment screw
By rotating it, the gap between the transmission parts (roller/worm, sector/worm, bevel gear/bevel gear) increases or decreases, depending on the design of the gearbox being used:
- the protective cap is removed, the lock washer is removed after loosening the nut;
- the steering wheel is quickly turned by an assistant at a small angle of about 15 degrees to the right/left;
- at the same time, the master removes the free play by unscrewing or tightening the screw with a screwdriver;
- the steering force and free play are brought into the optimal ratio in the specified way;
- When tightening the nut, you must hold the screw slot in the adjusted position with a screwdriver.
Adjusting the free play and steering force with a screw
Attention: Play may be present in the axis of the pendulum arm; tightening another nut located on the top of this axis, protected from twisting by a cotter pin, will help get rid of it.
Pulling the nut of the pendulum arm axle
By analogy with this, a knock in the steering gear can be caused by loosening of the intermediate shaft fasteners, swing arm nuts, pendulum arm bracket, or crankcase fasteners. A similar effect is caused by an increase in clearance in worm bearings or in the worm/roller mesh itself.
Classification of steering gears
It must be said that there are a large number of types of gearboxes. Therefore, all of them can be combined into several groups, classified according to the following criteria:
- According to the type of gears, they can be gear, worm or gear-worm.
- According to the number of stages: single-stage, two-stage, and so on.
- By type of gears: cylindrical, bevel, bevel-cylindrical.
- Depending on the location of the shafts in space, gearboxes are divided into horizontal and vertical.
- Depending on the features of the kinematic scheme: they can be with a bifurcated stage, or they can be with a deployed coaxial scheme.
It is worth noting that such a great variety of steering gearboxes is due to the fact that each of them has a different load capacity and, accordingly, a completely different efficiency.
As you know, different types of cars have different weights. And the heavier the car, the greater, in turn, will be the weight that rests on the steering wheels. This means that it will be more difficult to drive this car. That is why, for example, the UAZ steering gear will be completely different from the gazelle steering gear or the VAZ steering gear. That is, the greater the mass of the vehicle, the greater the efficiency of the steering gearbox must be to ensure normal controllability of the vehicle.
For a more complete and detailed acquaintance with the design of the steering gear, you can view the diagram of its structure.
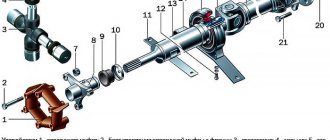
So, this is the steering gearbox of the VAZ 2107. The image shows that its design includes the following parts:
- Sealing cap;
- The nut is low;
- Lock washer;
- Adjustment screw plate;
- Adjustment screw;
- Bipod shaft;
- Ball separator:
- Worm shaft lower bearing ring;
- Adjusting gasket;
- Lower crankcase cover;
- Screw;
- Bipod;
- Spring washer 20;
- Cork mk;
- Upper crankcase cover;
- Top cover gasket;
- Worm seal;
- Steering gear housing:
- Bipod shaft bushing;
- Bipod shaft oil seal;
- Upper bearing ring;
- Worm shaft:
- Nut M20×1.5.
It is clear that this is just one example of a scheme. Based on it, you cannot draw conclusions about which gearbox is in a car of another brand, because they are all different from each other. Although there are analogues, for example, the steering gearbox 2105. The steering gearbox VAZ 2106 and the steering gearbox 2101 are also similar in structure. All these devices differ from each other quite slightly. Therefore, they can even be replaced with each other. So, for example, if the steering gearbox of a Niva is broken, and there is no way to find a new one, you can install a VAZ 2105 steering gearbox. In this case, the price of a VAZ steering gearbox will be significantly lower, and you will only have to take a bipod from the previous steering gearbox 2121.
Gearbox design
In a simplified form, the steering gear design represents a mechanical gear transmission with a gear ratio of 15 - 30. This makes it possible to reduce the torque force that the user must apply to the steering wheel. The main nuances are:
- with an increase in the gear ratio, it is much easier to turn the shaft inside the steering column;
- at the same time, the angle through which you need to turn the steering wheel deviates to a larger direction;
- at high speeds this is dangerous for an accident, since the driver may not be physically able to cope with this task.
Gear ratio
In this regard, in vehicles with hydraulic booster or electric power steering (power steering and electric power steering, respectively), these units duplicate the reduction in torque on the steering wheel. For example:
- in a gearbox with a gear ratio of 30, to turn the wheels by 25 degrees, the steering wheel must be unscrewed by 750 degrees;
- a gear with a ratio of 15 will require a 375 degree rotation of the steering wheel to achieve similar wheel rotation;
- however, in the first case, 6 kN of force must be applied, and in the second, 3 kN, which is half as much.
Gearbox for 2 steering turns
Vehicle designers put a scheme into the gearbox - from a neutral position (wheels in the direction of travel) within 2.5 turns of the steering wheel, they must turn 30 - 45 degrees to the left or right at most. That is, the total stroke of the steering wheel will be 4–5 revolutions, so that the bearing will last longer and the user will have comfortable control at different speeds.
Spatial position
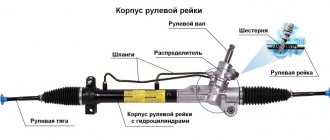
The steering column is located vertically or obliquely, and the rods and levers of the rotary wheels are horizontal, so the simplest option for converting rotation is a horizontally located gearbox - a rack.
In all other cases, that is, when using gearboxes (transmission in a housing), vertical modifications are used:
- the worm, lower bevel gear or screw are located vertically;
- The slide mounted on their shaft rotates in a horizontal plane.
Vertical gearbox
In complex circuits, an angular steering gear usually transmits rotation from cardan to cardan, and then to the control mechanism. Accordingly, each gearbox uses a different bearing design.
Angular reducer
Attention: Power steering and electric steering do not belong to steering gearboxes, as they are independent complex components of the car.
Power steering design
This is interesting: General information
Transmission type
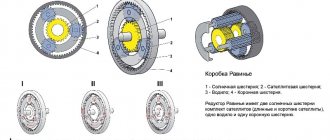
Gear and worm gears are traditionally considered the most effective. However, they can use bevel, spur and combination gears. There are kinematic diagrams of gearboxes of several modifications:
- single-stage, two-stage, multi-stage;
- with split steps;
- with deployed coaxial steps.
Mercedes multi-stage gearbox
The most commonly used schemes are:
- gear – worm (worm);
- bevel gear – bevel gear (angular);
- screw – ball nut – rack – gear (screw).
Screw reducer
Executive-class passenger cars, heavy trucks and buses are equipped with screw mechanisms. Worm modifications are installed on other cars; they are not sensitive to uneven road surfaces; the gear is in constant mesh and provides greater maneuverability.
By default, the worm has a larger contact surface with the shaft, the bearing experiences less load, and is operated in a gentle mode. In helical gearboxes, the shaft and bearing wear out faster.
In practice, the worm can be mated with a two-tooth or multi-tooth crank, a 2-5 tooth sector and a roller with two or three ridges. Most machines use a globoid worm rather than a cylindrical worm (saddle-shaped work surface). This allows you to reduce friction by 15 - 25%.
Regular and globoid worm in gearbox
Gear ratio
This characteristic is strictly tied to the design of a particular vehicle. Cars with steering racks are considered the most maneuverable, but the steering wheel has to be turned with noticeable tension, which is especially noticeable on old VAZs that are not equipped with an electric steering and power steering.
With an average gear ratio U=20, a full turn of the steering wheel corresponds to a wheel turn of 20 degrees. Currently, for trucks and buses the accepted value is U 20 - 25. For example, for LiAZ it is 23.6 according to the passport, and for KamAZ it is exactly 20.
Man Truck Steering Gearbox
For passenger cars, the standard is conventionally considered to be U in the range of 16 - 20. For example, the VAAZ 2105 has a gear ratio of 16.4 units. The main nuances of the steering are:
- As the design becomes more complex, the play in the steering wheel increases, as parts wear out and tightening is not done in a timely manner;
- at low speeds and when taxiing out of a parking lot, more force is required on the steering wheel, which is why mechanisms with variable gear ratios have been created;
- there is feedback - jerking of the steering wheel when moving on uneven road surfaces and rough terrain.
Since the unit is critical and quite complex, the steering gearbox is sold with an instruction manual, which indicates how to adjust the free play and force on the steering wheel for a specific design.
The most common problems, their causes and solutions
Any unit is prone to breakdowns and the steering gearbox is, of course, no exception. It will be much easier for car enthusiasts to understand the cause of the problem and fix it as soon as possible if they are familiar with the main problems.
- The most common breakdown is a leaking steering gear. The presence of such a problem can be detected visually by the presence of oil under the car. The reason may be a leaking oil seal or corrosion of the input shaft. In this case, in the first case, during the repair it is necessary to install new oil seals, cuffs, and gaskets. And in the second case, the shaft should be polished, and then it is mandatory to carry out gas thermal spraying to normal dimensions.
- Feeling of a “tight” steering wheel. It appears due to an increase in the effort to turn the steering wheel. At the same time, in order to be sure whether there are reasons for repairing the steering gearbox, it is necessary to measure the level of steering wheel rotation gain with a special torque wrench. Then compare the obtained result with the data provided by the car manufacturer. If the indicators do not correspond to the established standards, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics on a specialized stand. This will help you find out the pressure, flow rate of the working fluid, as well as the presence of leaks in the gearbox. In this case, you should not try to repair the gearbox yourself. It would be much better, easier and more reliable to simply take it to a workshop. Or, if desired, replace it with a new one.
- Play in the steering wheel. This could be part of a faulty steering column crosspiece, or it could also be play in the gearbox itself. This requires not partial, but complete disassembly of the unit, examination of the condition of parts and replacement of worn elements. After the work has been completed, the device should be correctly adjusted on the stand.
- Knock in the steering gearbox. This type of malfunction can be identified by a noticeable “kickback” in the steering wheel. This problem occurs due to wear of the thrust bearings. It is necessary to replace damaged parts and then adjust the unit on the stand.
These four types of breakdowns are the most common, but sometimes there are other faults.
Pivot table for clarity
| Manifestation | Malfunction | Elimination method |
| Flow | Oil seal leak; shaft corrosion; lack of tightness in the cylinder tubes, in the discharge or discharge tube | Complete overhaul of the unit, precise identification of weak points, and their elimination |
| “Tight steering”, poor self-return, creaking | Bent shaft or crankcase; overtightened adjustment of the crayon stop | Replacement or restoration of the shaft or crankcase |
| Knock | Wear of hinges, crackers, right shaft bushing, silent blocks; free play of the steering shaft; crooked shaft or crankcase | Complete overhaul, replacement of worn parts with new ones, possible replacement of the shaft |
| Backlash | Wear of the crankcase, hinges, silent blocks; crooked shaft or crankcase; free play of the propeller bearing | Gearbox overhaul, replacement of worn parts |
| Knocking and play that is felt on the steering wheel when the engine is not running | The spool stops at the limiters, | These manifestations cannot be called a real breakdown, because Steering diagnostics should be carried out with the engine running |
| Weighting of the steering wheel in repeated positions | Steering shaft drive sticking due to corrosion | This is not a serious problem and can be fixed by repairing the driveshaft. |
| Biting the steering wheel in one or both directions | Crankcase wear; cylinder wear in middle position | Complete gearbox overhaul, replacement of worn parts |
Removing the steering gear
If the adjustment did not help solve the problem or it reappeared after a short period of time, then it is time to repair the steering gear. This is a complex process and first you need to purchase a repair kit, which will include oil seals, bushings, O-rings and other components. Repair is divided into the following stages: dismantling; disassembly, cleaning, replacement; installation back. The main problem and difficulty is removing the steering gear from the engine compartment. Remember, you should not try to remove the bipod from the gearbox while it is under the hood, it is sometimes tightened so that it breaks the keys. It is better to remove it together with the bipod, knocking out the steering rods.
And already at the workbench, punch it with a hammer and easily remove it. To remove the tie rods, you first need to remove the front wheels. Then turn the steering wheel to the extreme left position and knock out the right rod with several blows of a hammer, then turn the steering wheel to the extreme right position and knock out the left bipod. You need to hit not from above, but from the side of the bipod. For easier knocking out, soak everything with WD-40 the day before work. But it’s better to use a puller, it will simplify the task. Don't forget to loosen the nut a little. Next, unscrew the bolt on the steering column so that it comes out of the splines. Now you can unscrew the nuts on the steering gear and pull it out.
Replacing the gearbox
DIY steering rack repair
https://youtube.com/watch?v=—HYiizjMVo
https://youtube.com/watch?v=—HYiizjMVo
When replacing a unit, the labor intensity is lower than when repairing:
- I removed the fastening of the coupled mechanisms, dismantled the gearbox, there is no need to disassemble it;
- During repairs, parts are reassembled, if necessary, the shaft is welded and ground, then we select the oil to fill, and after assembly we tighten the adjusting screw.
Using the Grand Cherokee as an example, replacing the steering gear consists of the following sequence of actions:
- jacking up the front axle and installing it on temporary supports;
- by removing the front left wheel and the fender liner inside the arch, we gain access from below;
- remove the washer tank;
- unscrewing the bolt that secures the steering cardan to the gearbox;
- dismantling the power steering tubes going to the gearbox;
- The bipod of the steering gear and 4 crankcase mounting bolts are removed.
Removing the steering gearbox
Thus, regardless of the design of the gearbox of the steering system of the machine, most often the gap between the transmission parts is adjusted or the entire unit is replaced. For repairs, sets of gaskets and shaft seals, transmission oil and gear packing are produced. The shafts are restored by folk craftsmen; the manuals do not contain information on the dimensions of the seating surfaces, since the unit is considered non-repairable.
Repair related work
The steering gear, just like any other unit, is prone to failure. Repairing a steering gearbox is much easier if you understand the cause-and-effect series of problems. Having familiarized yourself with the main problems, their high-quality elimination in the shortest possible time is quite possible.
- The steering gearbox is leaking. This problem occurs frequently and is detected visually by traces of oil under the vehicle. The reasons are varied: from oil seal leakage to corrosion of the input shaft. The first option requires the installation of new oil seals, seals, and gaskets. The second case involves grinding the shaft with subsequent standardization of gas thermal spraying.
- A feeling of “tight” steering, which is observed due to increased effort to turn the steering wheel. To check whether the steering gear needs repair, you should check the steering wheel steering gain with a specially designed torque wrench. After this, the results obtained are compared with factory data. If the indicators do not meet the established standards, they proceed to diagnostics on a specialized stand. This operation is intended to obtain data on the pressure, flow rate of the working fluid, and the presence of its leakage onto the steering gear. Such a development of events requires the help of an experienced craftsman and in no case independent work. The last resort is to repair the steering gear by completely replacing it.
- Play in the steering wheel. The first reason is a breakdown of the steering column crosspiece element, the second is specifically the gearbox play. This will require complete disassembly of the unit, further study of the condition of the parts and replacement of outdated components. The work performed on the device involves bench adjustment.
- Knock in the steering gearbox. A problem of this kind is detected when a certain kickback is felt in the steering wheel. The reason for this is wear of the thrust bearings. This requires replacement of damaged parts with further bench adjustment.
To repair the unit, park the car on a level, horizontal area with the front wheels straight. Models with an air bag for the driver require removal of the ignition key with the steering column locking.
The following manipulations are:
- Disconnecting the negative cable from the battery.
- Set the handbrake and engage first gear. For automatic models, this means moving the selector to the Park position.
- Marking the position of the steering lever in relation to its mechanism. Unscrewing the fastening nut. Using a puller, remove the lever from the axle.
- Removing the trim panel under the instrument panel.
- Unscrewing the bolt connecting the lower column mount. Disconnecting the steering column shaft from the gearbox.
- Place a container to collect fluid under the steering gear.
- Unscrewing the connecting nut and removing the hydraulic tubes from the steering mechanism with their preliminary mark. Here it is recommended to seal the ends of the tubes and all openings so that fluid loss is minimal.
- Unscrewing the fastening bolts and removing the metal thermal insulation shield.
- Unscrewing the mounting bolts and nuts and then removing the steering mechanism. After removing all the gaskets, you should remember their location to make installation easier.
Knock in the gearbox
Knocking in a car is an unpleasant and annoying thing, and there can be several reasons for the source of the noise, so it is sometimes difficult to determine the original source of the problem. If you hear a clear knocking or clicking sound in the gearbox when turning the steering wheel, then try adding transmission oil; perhaps its level has completely dropped. It would be good to completely change the oil. This operation should be performed once every 2 years or every 30-40 thousand km. The level is checked using any clean rod inserted all the way. The gearbox must first be wiped to prevent dirt from entering. Next, unscrew the oil channel cap and pump out the old oil with a syringe. Any transmission oil is suitable for replacement. Pump it up to a mark of 15-20 mm from the neck. The knocking should now go away. If the knocking noise remains, this is due to wear on the steering gear worm or bearing, which will have to be replaced.
Pros and cons of steering gear
The advantages include the self-braking effect, large gear ratios due to the use of only two parts, low noise levels and smooth running.
The disadvantages of a worm-type steering gear are increased wear, excessive heat generation due to friction forces, jamming and relatively low efficiency. To prevent jamming and rapid wear, it is necessary to adjust the mechanisms and comply with assembly accuracy requirements.
The main advantage of a worm gearbox over a gearbox is that the initial contact of the links occurs along a line, rather than at a point. The input and output shafts in a worm-type steering gearbox can be crossed at different angles (most often at 90°). Another significant advantage is that with the same gear ratio, the worm gear takes up much less space.
Repair and assembly
Correct and timely maintenance of the steering gear is the key to long-lasting and reliable operation, but there are times when breakdowns do occur. In this case, repairs with complete or partial disassembly simply cannot be avoided.
When repairing, it is necessary to pay attention to some features and important points, the use of which will increase the reliability of the mechanism and improve its characteristics
Steering gear repair
To remove and disassemble the gearbox, it is necessary to hang the front of the car and remove the steering rods. From inside, unscrew the bolt securing the supply shaft from the gearbox shaft. Adjusting the steering gearbox of the VAZ 2107. Next, disconnect the gearbox
from the spar, by unscrewing three bolts with spanners. In the engine compartment, remove the hoses and parts that are located in the line of the steering rods.
When the gearbox is unscrewed and removed from the shaft in the cabin, we pull it out of the engine compartment by turning the bipod to the left
Particular attention should be paid to the condition of the gaskets, their location and degree of wear. An unreliable seal can lead to loss of lubrication or contamination of internal cavities
The next step is to unscrew the plug and remove the oil from the steering gear housing, after which you need to unscrew the bipod.
Gearbox
We put it on a stand made of two boards so as not to damage the shaft splines and unscrew the nut, then remove the bipod. Additionally, you can screw the nut onto the shaft until the ends are mutually aligned. Next, disconnect the steering gear cover by gradually unscrewing the locknut of the adjusting bolt and remove the cover, gradually moving it towards the worm.
In this case, you need to be especially careful with the gaskets if they are in good condition; at the slightest jam or pressing out, the gasket must be replaced. The next step is to remove the bipod shaft, press in the worm shaft and remove the seals. All cavities must be washed and wiped with a rag, checking for dents, chips and any other damage. It is also necessary to check the crankcase for the presence of metal shavings, which indicates wear of certain parts. It is imperative to check the gaps and play in the mating parts and check the wear of the working surfaces. After carrying out a defective inspection of the steering gear, we replace damaged parts if necessary.
We carry out assembly in the reverse order, making sure to lubricate the parts with oil, and all oil seals with grease (lithol). Install a new cover gasket with an adjusting screw. Replacing the steering gearbox on a VAZ 2104, VAZ 2105, VAZ 2107. We mount the bipod, tightening the nut as much as possible
Then we install the steering gearbox in its normal place, special attention must be paid to the connection of the worm with the intermediate shaft, distortions and misalignments are not allowed here
It is also necessary to align the direction of the bipod and the steering wheel. The average position of the bipod can be determined by counting the number of shaft revolutions and dividing by two. Next, tighten the gearbox mounting nuts (it is advisable to install new ones), attach the steering rods to the bipod. Fill the gear housing with oil and use the adjusting bolt to select the play in the steering gear. To avoid damage to wheel tires and loss of controllability of the VAZ vehicle 2121
, it is necessary to diagnose the camber (toe) on a stand.
By adhering to these simple recommendations, you can improve the handling of the VAZ, increase driving safety, and the durability of the steering gearbox and the mechanism as a whole. Application of steering gear
the worm type on the VAZ
2121
has been paying off for many years, not to mention decades.
Having the need for periodic adjustment and maintenance, the gearbox ensures trouble-free operation throughout its entire service life. The simplicity of the design makes it possible to confidently operate the car in any road conditions, without fear that the steering wheel will fail. The gearbox
has high maintainability and is easy to maintain.