Today we will talk about the causes of knocking in a car engine, how dangerous this phenomenon is, what to do in a given situation depending on its complexity, and how to diagnose a malfunction.
Quiet, measured noise of operation without extraneous sounds of the car’s power plant pleases every car owner, because this indicates the complete serviceability of the engine.
But the appearance of extraneous sounds during operation, in particular knocking, makes the driver worry.
There are more than enough reasons for knocking in engines, some of them only indicate the need for maintenance, but there are knocks that are a signal of major problems with the engine.
Causes of engine knocking
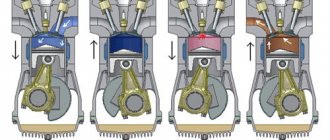
The knock itself is formed when one element of the power plant hits another.
At the same time, the noise in the engine varies, it occurs under certain conditions and disappears when they change.
In most cases, knocking is a signal of problems with certain mechanisms - the timing belt, crank mechanism, cylinder-piston group, but they also appear in other components of the unit.
Criteria for the nature of the knock.
Extraneous noise generated in the power plant can be divided into several criteria:
- The power of sound;
- Cause-and-effect relationships;
- Sound (metallic knocking, etc.);
- Cyclicality.
Let's look at each of the criteria.
The knocking sound in the engine may be weak and barely audible - in this case, the car can continue to be used, but it will not hurt to carry out diagnostic work.
There is an average knock that can be heard clearly, but it is not difficult to drown it out, for example, with loud music.
A car with such knocking noises can be used for a short period of time, enough to be able to get to a garage or service center.
Distinct loud sounds coming from inside the power unit indicate significant problems in its operation.
With such sounds, the engine is turned off and the car is delivered to the garage or service only by a tow truck or in tow, since serious problems may arise with the engine.
Cause-and-effect relationships in the occurrence of knocking occur after non-professionals intervene in the power unit.
That is, whether, on the contrary, failure to perform technical work or repairs will lead to engine malfunctions.
Sources of knocking (metallic) in the engine:
- Oil that is not recommended for use on this engine or counterfeit products;
- Poor quality or defective parts that were installed during repairs can also cause knocking in the engine.
- Severe wear of the components will naturally lead to the appearance of extraneous noise.
Types of sound and how they differ
Based on the sound, engine knocking is divided into loud and dull.
A loud knock, also called metallic, occurs when parts made of hard metals collide with each other, and there is no oil layer between the parts.
A dull knock in the engine occurs when parts strike, one of which is made of soft metal, and there is an oil layer between the parts.
Cyclicality
By the cyclical nature of the knocks, you can roughly determine which mechanism requires intervention.
Thus, a knock in the engine occurs in proportion to the rotation of the crankshaft, indicating possible problems with the cylinder-piston group, gas distribution or crank mechanisms.
The source of spontaneous knocking that occurs haphazardly may be located in the engine attachment.
For example, a knocking sound can be made by a loose generator, and the noise will arise due to the vibration of the power unit.
Why does the engine knock when hot?
In our article we will tell you why the engine knocks when hot and strange noises appear.
Often, the engine begins to knock when the gaps between parts increase to a critical value. With normal lubrication and provided that the parts are well cooled, increased noise appears between parts that have a gap between them that is twice as large as the maximum permissible nominal gap. Note that the larger the gap, the stronger the motor knocks.
So, we figured out that the engine knocks due to the impact of one metal part against another. This suggests that very high loads occur in these places. Impact loads quickly destroy mating surfaces, and the rate of destruction directly depends on the force of the impacts. And the force itself already depends on the size of the gap, that is, the larger the gap, the faster the mating parts are destroyed. In other words, we can say that the knocking in the engine will constantly progress (become stronger).
The rate of destruction depends on many factors:
— engine design;
— applied loads to the parts of the unit;
— engine cooling conditions;
— presence of complete lubrication.
However, it is worth saying that some engine parts can operate in this state (with a knock) for many thousands of kilometers and, on the contrary, when shock loads occur, certain engine parts fail after tens of kilometers.
The engine may “knock” even if there is a permissible gap between the mating parts. The reasons for such knocking are high loads on the unit or jamming and misalignment of the mating part. After eliminating such a problem, the knocking usually disappears (if the parts did not develop defects during faulty operation).
Knock of parts in a “hot” engine
The problem of a knocking engine “when hot” is very serious, since it is almost impossible to eliminate it on the road. The maximum that can be done is to check the engine oil level with a dipstick. Lack of lubrication causes damage to the mating parts, which leads to an unpleasant knocking noise. If you are lucky, after adding oil to the required level, the engine will stop knocking.
The next step is to determine which engine parts are causing the knocking noise. First, we advise you to find out what happens to the engine under load:
— does this knock appear with greater force;
— whether it progresses over time.
If the answers to these questions are positive, then most likely the problem lies in the crankshaft bearings. It is dangerous to move with such a malfunction - the unit will soon fail.
In addition, knocking in the engine “when hot” can appear in the valves when the number of crankshaft revolutions increases and the pressure in the lubrication system decreases at the same time.
How to correctly identify the malfunction and eliminate it - we will consider further.
In cases where the engine knocks, you need to check not only the intake valve, but also the exhaust valve. It is necessary to ensure the pressure in the system required for the normal functioning of the entire unit. Note that to satisfy this condition, you need to use oil that will match its viscosity to the specific climatic conditions of your region and seasonality.
The knocking of valves “when cold” is most likely caused by wear on the pusher. Leaking tappets do not allow oil to pass well into the valve mechanism, which is what causes an unpleasant knocking sound. This problem is eliminated by adjusting the valves.
If the engine oil pressure is normal, then you need to remove the valve cover and check the size of the gaps. As a rule, it is the increased gap that causes knocking, leading to wear of the mating parts. The clearances are adjusted using special feeler gauges inserted into the gap between the top of the rod and the rocker arm.
In conclusion, I would like to note that a knocking sound in the engine, especially if it happened “hot”, is a reason for immediate diagnostic and repair work. It is possible that to find out the reasons you will have to disassemble the entire engine, or maybe you will get by with only partial disassembly. Be that as it may, this problem cannot be left unresolved.
Remember that the correct diagnosis and quick solution to the problem determines whether your car’s engine will serve you or not.
Trick knockers
In addition, there is such a thing as “deceiver” knocks.
The essence of this concept is that a knock that seems to accurately indicate a certain malfunction has a completely different nature.
For example, when a diesel engine creates a load, a loud knocking sound appears, signaling problems with the crank mechanism. But the same knocking noise occurs with this engine when there is a malfunction in the power system.
Or, over time, a loose crankshaft pulley will begin to make sounds very similar to the knocking of the crankshaft itself, so it is important to first determine what exactly was the source of the extraneous sounds.
In any case, the occurrence of extraneous noise should not be ignored and professional diagnostics cannot be avoided.
Extraneous knocking noises when the engine is idling
Let's look at the causes of knocking in the engine under different operating modes.
First, let's look at the reasons for its occurrence at idle.
Here you first need to determine the behavior of the knock in the future.
Thus, a slight knocking sound in the engine at idle, emanating from the middle part of the engine, having a uniform intensity, while the sound intensity decreases somewhat with increasing speed, presumably indicates that small third-party parts or debris from parts have entered the cylinder.
This problem is eliminated by removing the block head and removing foreign objects.
The same knock, but increasing with increasing speed, signals wear of the cylinder-piston group, damage to the piston skirts due to overheating.
This malfunction can only be eliminated by replacing the cylinder-piston group.
The appearance of a similar noise, but with half the intensity, and heard in the upper part of the unit indicates a violation in the operation of the timing belt.
If a knock is present not only in idle, but also in other modes, this indicates wear on the camshaft and a violation of valve adjustment.
If the thermal gap is adjusted using hydraulic compensators, then the knocking noise as the speed increases, as a rule, decreases. This indicates a malfunction of the latter.
Problems with the cylinder head are solved by removing the valve covers, determining the source of the sound, replacing worn elements or adjusting the clearance.
A uniform knocking sound, significantly increasing with increasing speed, if it comes from below, this indicates the destruction of the balancer shaft bearings, the beginning of the destruction of the connecting rod liner, and deformation of the connecting rod itself.
These are some of the most dangerous causes of noise.
If at idle you hear an uneven sound that completely disappears as the speed increases, this is a signal of problems with the bearings of the engine attachments, for example, a malfunction of the pump bearing.
A muffled, uneven knock that appears at idle and disappears as the speed increases indicates that the permissible oil level has been exceeded due to working fluids or fuel getting into it. In this case, an internal breakdown of the cylinder head gasket occurred and antifreeze began to flow into the oil.
All of the above malfunctions, except for destruction of the connecting rod bearings and balance shafts, are generally not very dangerous; the driver has the opportunity to deliver the car under its own power to a service center or garage.
Read more: Why is the hydraulic compensator knocking?
Diesel engine noise in cold and hot weather
As a rule, on a diesel power plant, sounds and noises are associated with plunger pairs (not critical), faulty injection pump (high pressure fuel pump), crankshaft, etc. Let's consider all the main reasons below.
If the crankshaft knocks on a diesel engine
Knocks in a diesel engine appear no less frequently than in a gasoline engine.
Most often the crankshaft knocks on such internal combustion engines. This is called connecting rod knocking and is a very serious sign of internal combustion engine failure, including turbodiesel engines. If on a gasoline unit the same knock is of a different nature, then on a diesel unit it indicates extended play in the connecting rod journal. As a result, the piston hits the cylinder head and noise appears.
Another reason, no less problematic. It may indicate a loose connecting rod nut. This sound, compared to the first one, is duller and more reminiscent of a quiet clanging of metal (a similar sound is produced by an incorrectly aligned timing belt).
When diagnosing crankshaft sounds of a diesel engine, it is not customary to do so, as in similar cases with a gasoline engine. In other words, turning off the power to each cylinder will not work here, since the crankshaft will continue to work, and the piston will hit the cylinder head (cylinder head).
Attention. It is strictly forbidden to drive a car with a diesel engine if the connecting rod is knocking. The car must be urgently delivered to the service station by tow truck (or, in extreme cases, towed). Here they will bore the crankshaft, replace the bearings, make the necessary adjustments, grinding, etc.
It is interesting that crankshaft knocks are heard most clearly when the lubricant has not yet had time to fully reach the bearing group. After thorough heating, the problem is signaled less intensely and the previous noise disappears. But on an unheated internal combustion engine, the sound is measured, reminiscent of a clang and alternating dull noise. The rhythm of sounds will increase with increasing speed.
As mentioned above, the shaft can also rattle due to the appearance of excessively increased play that has arisen in the connecting rod-main bearings.
It is better to entrust the work of eliminating backlash to a professional. It takes a lot of time and effort
Operating a car engine with dirty lubricant or low-quality oil, as well as untimely replacement of it in a diesel engine, can also lead to increased clearances and wear. And the crankshaft can also knock due to fuel getting into the lubricant when the cylinder head is damaged.
An equally well-known cause of diesel noise is the clogging of the oil strainer. Because of this, small pieces of debris and shavings then penetrate into the crankshaft bearings.
Also, knocking in a diesel engine occurs as a result of a drop in oil pressure or lack of lubricant - an essential component of bearings. The problem is often caused by unstable functioning of the oil pump.
We recommend: The engine does not develop power: what to do?
If the camshaft is noisy
The noise from the camshaft is quieter than the crankshaft
The camshaft of a diesel power plant is distinguished by a less sonorous hum, more noticeable in the first stage at the time of starting the unit from cold. In terms of rhythm, the camshaft sound is almost half as loud in frequency when compared with the same crankshaft frequency. As soon as the lubricant reaches the camshaft bearings, the noise disappears (usually this takes no more than 3 seconds after starting).
A factor causing such knocking of the unit is faulty bearings. Over time, they wear out, which leads to knocking. The rest of the noise factors are similar to the crankshaft ones, with only one difference - the noise of the unit increases as it wears out and on a hot engine.
It is allowed to use a car with such a problem under the hood, but only for a short time and under one condition - if there are no hydraulic compensators in the timing belt. Otherwise, their presence will lead to more serious consequences, further defects that are much more difficult to repair.
Detonation sounds: causes and consequences
On diesel engines, early injection of fuel can cause detonation combustion of the combustible mixture. This leads to rough and incorrect operation of the power plant.
You can understand the essence of detonation in more detail like this. During detonation, the fuel does not burn as it should, but explodes. The entire portion of fuel burns instantly, and the pressure on the piston increases sharply. As a result of all this, a shock wave is formed, destroying not only the piston itself, but also the entire group: liners, rings.
Engine detonation is considered a rather dangerous sign.
The main distinguishing feature of detonation in a diesel installation is the characteristic iron clang. By the way, detonation in this internal combustion engine can easily occur due to faulty injectors.
Other reasons that can become a source of noise in a diesel engine:
- If the installation is noisy after a service station where the cylinder head gasket was changed, the sound will resemble the knocking of valves. This is not the case for everything to go away by itself. You will have to go to the service center again and order a repeat replacement procedure (the knocking sound is due to the fact that the piston hits the protruding part of the gasket).
- Knocks that often occur at idle. This is most likely knocking in the fuel injection pump area. By the way, the same sounds characterize the noise of plunger pairs. Note. The fuel injection pump is checked at a special type of stand.
- Knocks may appear due to incorrect operation of the hydraulic compensators. When the latter fail, a characteristic knocking sound is observed. In case of strong noise when cold, with a gradual decrease in knocking as the engine warms up, the expansion joints are replaced, and the engine is cleaned using a special technology.
- Insufficient chain or timing belt tension. The knocking noise increases as soon as the engine speed increases. The noise is created due to the fact that the belt drive hits the protective casing.
- As a result of a violation of the gas distribution phases. This often happens after installing a gasket that is not the original size.
Engine knocking when cold
An uneven sharp metallic knocking sound when cold, intensifying as it warms up, indicates:
- Turning of the connecting rod bearing around the axis or its destruction;
- Significant wear of the main liners, deformation of the crankshaft journals. In this case, the sound comes from the bottom of the motor;
- It is possible that sound may occur in the middle part of the engine due to significant wear of the mounting holes of the piston pins; it usually appears with a sharp increase in engine speed.
Many of the noise sources described are also typical for the engine operating conditions described below.
Knock at low speeds
A knocking sound in the engine at low speeds when the engine is not warmed up, if it comes from the top, indicates problems with the hydraulic compensators.
A uniform knocking sound in the upper part, which intensifies significantly when warming up, signals the beginning of destruction of the valve seat.
It is worth considering the possibility of damage to the bearings of attachments.
It is also possible that the valve timing is disrupted due to the timing belt slipping, as a result of which the piston bottoms come into contact with the valves, hence the knocking sound in the engine.
Filling with low octane gasoline can lead to detonation in the engine, which is why knocking occurs.
If you detect extraneous noise while the engine is running cold at low speeds, it is better to immediately try to determine where exactly the noise is coming from.
If the knocking sound in the engine comes from the top, the car can still be driven for a short time.
If sharp noises appear from the lower part of the engine, it is better to immediately stop the power plant and deliver the car to the repair site by tow truck or in tow.
Motor diagnostics by ear: cutting off extraneous sounds
Engine noise can say a lot
It is important to remember that in order to correctly diagnose knocks and noises, the car’s power plant must warm up to 80–85 degrees after starting, otherwise the readings can be considered erroneous. It is best to take measurements not by ear, but with the help of a stethoscope, and preferably modern electronic equipment
Based on the nature and originality of extraneous knocks, it will be easy to determine a specific malfunction
It is best to take measurements not by ear, but with the help of a stethoscope, and preferably modern electronic equipment. Based on the nature and originality of extraneous knocks, it will be easy to determine a specific malfunction.
The sounds due to the weakened fixation of the engine to the body resemble the noise of a motor
Initially, the entire diagnostic process associated with the motor can be divided into several stages. The first of them, wiretapping, is what experienced car enthusiasts do, this is how experts begin their work, this is how beginners try to show what they know about cars.
And in general, the proverb incorrectly advises, at least in this case, “it’s better to see once”... In our case, it would be more accurate to hear once than to see a hundred times, i.e. face the problem head on.
The first thing to do when listening to sounds is to determine, or rather, prove that they are produced by the engine, and not by other components or elements of the car. For example, suspension components, hanging elements that have lost their former fixation, etc. often knock.
In the same logical way, you can remove from the list of causes some other sounds not produced by the internal combustion engine. For example, if you shake the power plant from below, you will be able to identify sounds that are associated with mounting the engine to the body or frame.
Sometimes the problem with fastenings is solved by welding metal corners
More interesting points:
- If there is a whistling or buzzing sound, doubts should fall primarily on the alternator or timing belt, camshaft drive or components in the pump area.
- The squealing most likely indicates problems with the belts (jumping), freezing of the pump, lack of lubrication in the generator, etc.
It is clear that by dismantling belts or other elements and filling in the amount of lubricating fluids, you can exclude them from the diagnostic analysis.
Thus, the first and most important thing that is done in the process of diagnosing an automotive power plant is to check its “environment”. The purpose is clear - this proves that sounds and knocks belong to the engine
To better understand the nature of problematic car engine sounds, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with them in more detail.
- The sound comes from the top of the engine, reminiscent of the ringing of metal. Typically, this metallic noise indicates problems with the valves. Most likely, this symptom indicates improper valve adjustment or excessive wear. If the noise increases as the speed increases, and even suddenly, the nature of the malfunctions indicates a much broader nature of the sounds - for example, it may be a matter of gaps.
Worn valves indicate an approaching overhaul.
- The noise is similar to the quiet friction of iron bars against each other. The sound changes as engine speed increases or decreases. The knocking comes mainly from the front end of the internal combustion engine. Most likely this is a symptom of a weakened timing chain. If the car is equipped with a chain and not a belt, an experienced car owner should be familiar with this sound.
- The noises are low-medium tonality, practically unchanged as the engine speed increases. As a rule, the sounds come from the bottom of the motor. This kind of knocking is more dangerous than others, as it indicates increased wear of the “internals” of the engine.
- Clanking, very loud. Appears more often when accelerating or maneuvering a car. In most cases, it indicates detonation knocks. The sounds are made by the pistons, which absorb the shock wave from the explosion of the combustible mixture. Among experienced car enthusiasts, this noise is usually called “finger tapping.”
Third-party sounds on startup
Engine knocking during startup most often occurs due to malfunctions in the lubrication system.
Poor performance of the oil pump, insufficient amount of oil and clogging of the channels with pollutants leads to the fact that the oil does not have time to reach all the rubbing surfaces in time, which is why grinding and knocking noises are heard.
Due to problems with the lubrication system, oil does not flow into the hydraulic compensators, without which they begin to knock.
If noises appear during startup, it is advisable to stop the engine and check the oil level. If necessary, bring the level to the desired value.
If this does not help, you can change the oil and pre-flush the system.
Next, if the knocking noise persists during startup, you need to check the condition of the oil pump.
Determining engine defects
If serious knocking noises appear in the engine (in the piston group, CV joint), the engine must be removed and troubleshooting carried out. To determine the cause of the malfunction, the entire internal combustion engine is disassembled and the following is removed:
- cylinder head with camshafts;
- sump (oil sump);
- crankshaft pulley;
- flywheel clutch;
- pistons with connecting rods;
- crankshaft.
During troubleshooting, the cylinder liners are inspected - there should be no scoring, wear, or ovality. The gap between the piston and the liner is considered acceptable to be no more than 0.15 mm; the measurement is made with a feeler gauge for adjusting the valves, while the piston rings are removed from the piston.
Measuring the camshaft supports and crankshaft journals must be done using a micrometer, and if someone tries to check the condition of the shafts using a caliper, then this is a fool’s errand. The crankshaft should have wear on all supports of no more than 0.03-0.04 mm, and if the c/v journals have a smaller diameter, then the shaft must be ground. Usually the crankshaft is ground in a “circle”, that is, all supports - main and connecting rod - are adjusted to the repair dimensions. In some cases, grinding only the main journals is allowed if the connecting rod bearings are in perfect condition.
The camshaft must have wear on the bearings from the nominal size of no more than 0.05 mm; if the wear is greater, then the shaft must be changed - due to wear on the bearing journals, the pressure in the lubrication system will be lower, and knocking in the engine may also occur due to the slack. You should also carefully inspect the r/shaft cams - they should be smooth, without scoring.
During a major overhaul, the following parts must be replaced:
- oil seals and gaskets;
- valve stem seals;
- tension rollers, timing belt (chain) along with shoes and dampers;
- liners in a circle;
- piston rings/pins and pistons.
If the internal combustion engine has a significant mileage, the oil pump must also be replaced - it is unknown how long the used part will last, and the life of the power unit directly depends on the pressure in the oil system.
If the water pump has a high mileage, it should also be replaced during overhaul; it is especially important to replace it on engines with a timing belt drive. The thing is that on many internal combustion engines, the timing belt drives not only the r/shafts, but also the water pump, and when the pump jams, the belt breaks with all the very unpleasant ensuing consequences. And the repair of complex motors should always be trusted to specialists; you should not rely on your own strength if you have insufficient qualifications.
Causes of sounds when hot
Knocking in the engine when “hot” can occur for all of the above reasons.
In any case, it is important to determine the nature of the extraneous noise, the approximate place where it is coming from, and then take action.
Almost always, in road conditions, it will not be possible to eliminate the malfunction; the car will need to be delivered to the repair site to accurately determine the cause.
But preliminary diagnostics will tell you which way the car will have to be delivered.
If there is a knocking sound at the top, you can drive the car under your own power, but check the oil level before doing so.
A sharp sound from the bottom of the engine will indicate a problem with the crank mechanism, which is why the car must be delivered by a tow truck.
Where does knocking come from when the engine is hot?
The reasons can be very different, and the first priority when detecting knocking noises is to understand what parts are causing it. The service life of the engine as a whole depends on finding the cause in a timely manner and quickly solving problems.
- The most harmless reason lies not in the mechanism, but in a decrease in the engine oil level. When the engine knocks when hot, in road conditions the most that can be done is to use a dipstick to find out the current engine oil level. Lack of lubrication provokes friction of adjacent parts against each other, they can be damaged, which causes the appearance of characteristic knocking sounds.
When adding oil to the required level, the knocking should stop.
- It is necessary to listen to the intensity of the knocking noises; if there is a clear increase in them, then it is better to contact a car service center and conduct engine diagnostics. If the knocking in the engine when hot is uniform and is characterized by subsidence with increasing temperature, and no visible malfunctions or problems are detected, the car can be operated for tens of thousands of kilometers before it needs to be repaired.
- The knocking noise may come from the crankshaft. If the engine is under load, and the knocking occurs with increasing force, progressing over time, then the search for the problem is narrowed to the crankshaft bearings. It is dangerous to continue driving with such a malfunction, otherwise the situation will worsen and the engine will need to be overhauled.
- A knock in a hot engine can be produced by the valves when the crankshaft speed increases and the pressure in the lubrication level system decreases at the same time. In order to get rid of the knocking, you first need to normalize the pressure in the system so that the engine functions normally. It is important to select only a motor oil whose viscosity and properties satisfy the climatic conditions of a particular region, taking into account the season.
If the oil pressure is normal and the knocking does not stop, then you will have to remove the valve covers and check the clearances. Increasing clearances is the main reason for knocking and subsequent wear of parts.
This phenomenon is typical for cars with significant mileage, where gaps appear due to long use and natural wear of parts. The gaps must be set correctly; they are adjusted using a special set of feeler gauges that are placed in the spaces between the rocker arm and the top of the valve.
- As engine temperature changes, knocking noises can either increase or decrease. The first case is due to the fact that worn parts may expand slightly when warmed up, thereby reducing the gap, and this in turn leads to the natural disappearance of the knock. This situation is often observed in the cylinder-piston group of the engine. The second case is related to the heating of the engine oil. As you know, when the engine is hot, it liquefies, which can increase knocking in the bearings of the crank mechanism. Continuing to drive a car while the engine is knocking is very dangerous. To avoid serious damage to the engine unit, it is better to call a tow truck and take the car to a service station, where specialists will identify the exact cause and immediately eliminate it.
- Sometimes knocking occurs due to the human factor. A simple example: forcing a puddle at high speed leads to water hammer, which can lead to bending of the connecting rod. It happens that the part replaced during repair had a broken geometry, was of poor quality, or was installed incorrectly. The load on such parts increases significantly, which inevitably leads to deterioration of lubrication and an increase in temperature in the area of their operation. The result is rapid wear, increased gaps, and subsequently knocking.
It is important to understand that if a car owner saves on spare parts when overhauling an engine, this will not lead to anything good. If you don’t trust the car service center, you should try to purchase spare parts yourself, choosing the original manufacturer or an analogue with a good reputation.
If, after checking the gaps of the connected parts, it turns out that they correspond to the standard, it can be assumed that the engine is knocking when hot due to intense loads, or due to long-term operation in an overheated state. As a result, strong friction of parts quickly destroys the lubricant.
When the gaps are set less than normal, when the parts are deliberately ground together very tightly, knocking also occurs due to increased load, temperature increases, and lubrication conditions worsen.
It also happens that the parts do not touch, but there is a knock. This is possible due to severe deformation of one of the parts. For example, a hydraulic shock that occurs in the cylinder of the block head leads to “shortening” of the connecting rod.
In this case, the piston, when moving, begins to touch the crankshaft at bottom dead center. Or the pistons, during their stroke, may touch the edge of the exposed cylinder head gasket. On diesel engines, knocking is often caused by incorrect timing, in which the valves do not reach the pistons a little.
It is important to observe the knocking noise as the engine load increases.
There are two options here:
- The knocking changes in character as the load increases.
With increased engine load, the knocking will increase in those parts where the work increases, i.e. in the crank mechanism. The temperature factor in conjunction with the load also works here. As the temperature rises, the oil dilutes, which increases the knocking noise of, for example, a damaged bearing in a crankshaft.
However, if the defect is in the piston body, an increase in the engine temperature, on the contrary, will reduce the gap due to the expansion of the part, and therefore the knocking will probably subside.
- The knocking has nothing to do with the load and depends only on the rotation speed.
Knocks can increase significantly with increasing engine speed. This could be a valve hitting the piston, a defect in the balance shaft bearing, or a foreign object getting between the piston body and the cylinder head.
The more rotation, the greater the load on weak points, and the more the parts are deformed. High temperatures in the above situations will only worsen the situation - the viscosity of the oil will decrease and the parts will heat up even more.
When the knocking frequency is less than that of the crankshaft, problems with the gas distribution mechanism are suspected. The knocking noise increases with increasing temperature due to increasing clearances in the valve drive mechanism. Under load, the knocking does not change in character, however, as the speed increases, the hydraulic compensators can begin to knock, which can mask the true problem.
Knocks with an uneven frequency that do not change in character as the load increases can indicate wear on the thrust shaft bearings, a loose fit, or defects in the pulleys and flywheels.
There are knocks that, when diagnosed, can lead to an incorrect diagnosis; at service stations they are called “deceptive knocks.” They can only be recognized by experienced specialists, and unscrupulous car repair shops, taking advantage of the illiteracy of car owners, can overhaul the engine and make good money.
Among the deceiving knocks there are:
- the knock of hydraulic pushers often resembles the knock of connecting rod bearings;
- a sharp knock of a diesel engine indicates that the fuel equipment is in a faulty condition, although it is similar to the knock of connecting rods;
- a loose camshaft pulley bolt may produce a noise similar to a crankshaft knock;
- a knocking sound, along with a characteristic buzzing and whistling sound, can be produced by a generator, as well as a water pump;
- a squeal with an intermittent whistle is characteristic of a slipping alternator belt or a jammed water pump;
- sounds resembling rustling can indicate problems with the timing chain or belt;
- A clear metallic knock can only indicate engine detonation.
When trying to diagnose the cause of the knocking yourself, the first thing you should do to eliminate extraneous sounds, squeals and rustles is to check the timing belt tension, then temporarily dismantle the generator, camshaft and water pump. This will significantly speed up the identification of the real cause of the knocking.
Features of knocking in the engines of VAZ cars
The described causes of third-party noise are typical for all engines, including VAZ models.
In addition to the above sources of the problem in classic models, knocking in VAZ engines can be caused by a strong stretch of the timing chain or a weakening of the chain tensioner.
And for models starting from the VAZ 2108, additional increased noise may occur due to wear of the belt tensioner bearing.
Diesel engines, additional possible sources of knocking.
If a diesel engine knocks, in addition to problems with the crank mechanism, cylinder-piston group and timing, the knock can be caused by problems with the power system, in particular, malfunctions with the injection pump, turbine or injectors.
Or a violation of the timing of fuel injection.
Read on the topic: Do-it-yourself turbine repair.
Renault diesel engine problems
Four-cylinder DCi diesel engines with a volume of 1.5/1.9/2.2 liters, produced from 2001 to 2009, are not very reliable. The main problem with these power units is the knocking noise that occurs in the crank mechanism. These motors must not be overheated or overloaded; the engine oil must be changed promptly. The K9K 1.5 liter internal combustion engine is considered the weakest; it can turn the connecting rod bearings already at a mileage of 130-150 thousand km.
We recommend: I washed the engine, but the car won’t start - what’s the reason?
It should be noted that gasoline engines are much more reliable - the crank mechanism is problem-free, and the crankshaft fails on them only when starved of oil or when using low-quality engine oil.
Sound diagnostics
If a problem arises that the engine is knocking, as already said, it is first of all important to determine the nature of the knock, as well as the location of its occurrence.
Some of the reasons can be diagnosed without disassembling the power plant.
Thus, a special device - a technical phonendoscope - will allow you to more accurately determine the location of the noise.
Using it, the engine is listened to and it is determined in which mechanism or system malfunctions have occurred.
You can also use more advanced equipment, for example, a motor tester.
Read more: Car diagnostic devices.
A simple procedure will allow you to determine the destruction of the connecting rod liner.
It is done like this: with the engine running, when a loud knocking noise appears, the high voltage wire is removed from the spark plug one by one on each cylinder.
If the fault lies in the connecting rod bearing, then disconnecting the wire on the cylinder that has the problem will significantly reduce the knocking noise.
If noise occurs, when there is a suspicion of destruction of the bearing of any attachment, you can determine which equipment has problems by disconnecting their drive from the on-board network.
If after this the extraneous noise disappears, the faulty equipment is replaced or sent for repair.
Knocks at the top of the engine.
They are diagnosed sequentially. First, the condition of the cylinder head elements and their fastening is checked.
Then the valves are adjusted or the hydraulic compensators are washed. At the same time, the level and condition of the oil are checked.
Then the head is removed from the engine and a full range of restoration work is carried out.
Middle and lower part of the engine.
An accurate determination of the sources of knocking in the lower part of the engine is possible only after disassembling the engine.
Since severe wear of the cylinder-piston group also causes unwanted sound, therefore, if a knock occurs in the middle part, the condition of this group can be assessed by measuring compression.
Knock or detonation?
Most even experienced motorists mistakenly mistake detonation for knocking, which has received the common name - knocking fingers.
It is worth noting that the phenomenon of detonation has nothing to do with knocking occurring in the engine.
Detonation is a consequence of:
- use of low-quality fuel;
- engine overheating;
- constant formation of carbon deposits on valve heads, inside combustion chambers or bottom parts of pistons;
- early ignition.
The danger of this phenomenon is that it destroys parts of the power unit.
Note that the described sounds (with the exception of detonation and valve knocking) are permanent companions of old cars with high mileage.
Their appearance is a signal to immediately contact a car service for engine repair.
In addition to these knocks, you can also hear sounds that occur when the bearings of the generator or water pump fail.
You can check this by removing the belt from the generator or pump drive and starting the engine. A breakdown in one of these units is indicated by the absence of knocking noises.
If the knock is caused by detonation, its presence can be determined by the behavior of the power plant. If it continues to work for some time after a forced stop, there is detonation in the cylinders.
Diesel power plants.
Diagnostics in these engines is carried out identically to those described, but their fuel system can be diagnosed only after removing its elements and only on special stands.
Also read how to diagnose a car using a laptop.