Why does this happen
There are a lot of reasons for this, but they are all connected with one timing system (gas distribution mechanism). A little history for understanding.
Manufacturers around the world, including domestic ones, have always struggled with the quietness of car operation. Remember the first rear-wheel drive VAZs (01, 02, 03 - 07). They all had similar engines, they worked relatively quietly when they were new, but then they began to make a lot of noise, this happened already at 10 - 15,000 kilometers (I myself had many such cars, so I know first-hand) to get rid of this sound, it was necessary to adjust the valves (by the way, such “noisy” operation also affected the consumption and stability of the engine).
This was a fairly common procedure on a classic drive. The reason for this was the development, as well as the expansion of the metals that the valve wore (or rather its upper part), onto a special cam. In general, the design was not so perfect; it had to be adjusted periodically. The noise disappeared, and the engine thrust became better. But soon another timing mechanism was invented, which included “hydraulic compensators” in its design. They already made adjustments automatically, and the noise did not appear for many thousands of kilometers, it was really a “leap” forward, the only thing needed was good oil (this is where synthetics and semi-synthetics begin to appear). However, after a lot of wear and tear, the rumble and “dieseling” still appeared. Now I will try to tell you point by point:
1) Oil.
It’s corny – but it’s true! If you fill in the wrong oil that your car is supposed to, and God forbid you run into a fake, then your unit will let you know with “diesel” sounds - it will make noise. This also manifests itself with high mileage on one oil (20 - 30 thousand), this should not be done under any circumstances! You will kill the engine. Change the oil only to normal oil, buy from trusted stores.
2) Hydraulic compensators.
These devices may fail, the engine will make noise and operate unstably. We just change it, this was especially common on our VAZs.
3) Production of camshafts and valves.
Despite today's almost perfect technologies, wear is also present in these parts, mainly in the places of contact - the shaft and the valve “mechanism” (there can be all sorts of cams, nickels, etc.). True, this happens at very long distances, I think closer to 200 - 250,000 kilometers.
4) "Pastel" camshaft.
For some car models, the pastel (shaft mount), even when new, may be slightly wider than necessary. Therefore, when you start the engine, you may hear a strange rumble (similar to the operation of a diesel engine), but after the engine warms up, the metal expands and the gap decreases, so the rumble goes away. By the way, this can occur on almost all car models due to the high wear of this fastener - the pastel.
5) Timing chain and its tensioners . ON many cars, the timing chain can stretch, for example on powerful versions of the TSI engine; of course, it has “tensioners” that keep it in place (tensioned). However, the stretching is often very high, this will cause an incomprehensible rumble in the motors, which indicates one thing - you need to change the chain and the mechanisms that tension it. This is a very popular fault on many cars, both well-known brands and our classic VAZs.
6) Timing belt and its tensioning system . Almost identical to the chain, however, the belt itself does not make noise, and it breaks more often than it stretches. But its tensioning system can make noise; as a rule, there are rollers that fail over time, so they will also need to be changed.
7) The valves themselves . This often manifests itself during a major overhaul; perhaps the technician did not “lap” (fill the mirror) the valve correctly. Thus, it does not close correctly, it encounters an obstacle - such sounds are possible. True, it’s quite easy to check in which cylinder there is such a sound, you need to look at the compression in it, if it is at a low value, then it’s definitely the valve.
These are probably all the reasons why the engine is “diesel”! I tried to reveal the problem as much as possible.
Now a short video version of the article
What to do if the diesel engine is filled with gasoline
Let's start with the fact that among experienced domestic diesel drivers there is a method when truck drivers deliberately add gasoline to diesel fuel in winter. This is done so that the fuel does not lose its fluidity. Fill in gasoline so that its amount does not exceed 8-10% of the total amount of fuel in the tank.
For this reason, there is a misconception that a small amount of gasoline will not harm a diesel engine. Let us immediately note that for a Soviet tractor or KamAZ this is real. As for the diesel engine of a modern truck or car, then such methods cannot be resorted to.
Foreign manufacturers even indicate that if the diesel engine was filled with gasoline, the engine then started and the car moved, then the following actions are necessary:
The presence of chips, which is detected by a magnet, will require replacement of the entire diesel engine power system: injection pump, injectors, fuel filters, fuel tank, etc.
Now let's get back to the practical situation. If you fill up with gasoline and the diesel car does not start, then it is quite possible to get rid of it by flushing the fuel system and replacing the filters. Don't try to start the engine again! Immediately call a tow truck to quickly transport the car to a service station.
It will be necessary to dismantle and drain the fuel tank, replace filters, and flush the fuel system. As practice shows, these actions are sufficient and costly repairs can be avoided. If you have driven a certain distance after refueling and stalled, after which the engine will no longer start again, then two scenarios are likely:
Everything will directly depend on how much damage gasoline has caused to fuel equipment. If after refueling there is a sharp drop in engine power, rough operation of the diesel engine and other symptoms noted above, then there is a high probability of driving on a mixture of gasoline and diesel fuel. In this case, it is necessary to immediately stop driving the vehicle, turn off the engine and take appropriate measures to properly diagnose, flush and/or repair the power system.
What does “diesel gasoline engine” mean?
A special feature of diesel engine is the increase in engine operating noise. It is better to leave a car with such a breakdown in the garage; it is unsafe to drive it. Typically, diesel combustion indicates damage to the power unit, which is best eliminated at the time of its early manifestation. Otherwise, you will soon have to carry out major repairs.
Diesel engines make more noise than gasoline engines because their ignition system is designed in a special way. Dieselization of a gasoline engine is the appearance of noise characteristic of diesel engines. Noise usually appears when the engine is running cold or idling. There can be many reasons for this unpleasant phenomenon, but they are all related to the timing belt assembly.
CPG - problems with it
Now let's talk about the CPG (cylinder-piston group). If you hear distinct knocks, crunches, impacts, etc. from the engine, then further movement of the car is undesirable. You need to understand that the longer the engine runs, the situation will only get worse and the more expensive the repairs will be. The reason for what is happening must be found out as quickly as possible. In order to get to the service, it is better to call a tow truck and refuse to drive yourself.
In the case of low knocks in the lower part of the crankcase of the power unit, there is a high probability that the main bearings are knocking, and the knocking intensifies with increasing load on the engine or with increasing crankshaft speed. If this sound occurs, the engine should be turned off immediately. Knocking of the main bearings is possible as a result of low pressure in the lubrication system. In this case, the warning lamp on the dashboard may light up. In this situation, you should not move. If you hear a ringing metallic sound from the middle part of the engine, it also does not bode well. Apparently, this knocking noise is coming from the connecting rod bearings. The sound is quite clearly audible under load. The malfunction can be identified by sequentially disconnecting the spark plugs. If you turn off the spark plug in a faulty cylinder, the sound will disappear. Driving with such damage should also not be continued.
Why else can a gasoline engine perform like a diesel engine? The reason may lie in the piston pins. Despite the similarity with detonation, this knock is present in all engine operating modes and intensifies with increasing load. It can be determined in a similar way by turning off the spark plugs. With this type of knocking, you can get to the service station yourself, but you should first check the oil level. There is no need to load the engine while driving, i.e. avoid increased speed. With high mileage in the engine, the pistons themselves in the cylinders may knock directly, usually when the engine is cold. Gradually, as the engine warms up, the intensity of the sounds will decrease. The sound produced is somewhat similar to a diesel engine. When the engine warms up to operating temperature, the knocking noise disappears. Despite the fact that the engine can be operated with such a problem, it is still not worth loading it, and it is advisable not to delay repairs.
Malfunctions in the timing system
The diesel effect is also possible due to timing problems. Let's look at the most common reasons:
- valve knocking;
- knocking of hydraulic compensators
As for the knocking of valves, it can be distinguished by its characteristic metallic tint. It is most clearly heard in the cylinder head in the area where the valves are located. The sound is clearly audible when the engine is running at low and medium speeds. It is undesirable to drive for a long time with knocking valves. You can get to the service yourself.
Regarding hydraulic compensators, we can say that when they knock, the sound is very reminiscent of the operation of a diesel engine. It is worth noting that even on a serviceable engine, meaning a gasoline engine, hydraulic compensators can knock when cold, literally for several minutes. As it warms up, the sound should become less noticeable and disappear completely when the engine reaches operating temperature. If the knocking does not disappear, then the cause may be motor oil that is not suitable for a particular engine. In addition, there may be problems with oil pressure in the engine lubrication system. If any of the hydraulic compensators fails, this will be clearly noticeable by a metallic knock in the area of the valve covers when the engine is warm. In this case, the sound can be present either constantly or occur periodically. The intensity of the knocking of the hydraulic compensators will change as the crankshaft rotation speed changes.
What conclusion can be drawn from all of the above? If any kind of extraneous noise, knocking, etc. appears that is not characteristic of normal engine operation, further operation of the vehicle should be stopped. If you do not stop the engine in time, then there is a possibility of not only serious damage, but also complete damage to the engine without a chance of recovery. I hope that from this article you will not only learn why a gasoline engine works like a diesel engine, but also gain a lot of useful information that will be useful in the future.
Source
Refueling with low-quality fuel
Many systems and devices of the power unit can contribute to the fact that a gasoline engine operates like a diesel engine. However, there is one external reason that contributes to the appearance of unusual sounds. This is low-quality fuel.
The main property of gasoline, which characterizes its resistance to detonation (explosive pre-ignition), is the octane number. If the engine is designed for AI-95 gasoline, and at the gas station you were filled with low-octane fuel, troubles are inevitable.
- Under certain loads, fuel detonation occurs, accompanied by detonation knocks reminiscent of the ringing of piston pins and, remotely, the sound of a running diesel engine.
- To increase the octane number, octane-increasing additives are added to low-grade gasoline, which are deposited in the nozzles of the working injectors on an injection engine. The supply of fuel to different cylinders becomes uneven, which leads to harsh engine operation. In advanced cases, the injectors become completely clogged, as a result of which the engine begins to “trouble.”
- The additives contained in “bodied” gasoline cover the electrodes of the spark plugs with a layer of red soot, and due to misfires, the engine again “troubles.”
Tip: try to refuel at chain gas stations located in large populated areas or along busy highways. If you run out of fuel, fill up the minimum amount of gasoline at the first gas station you come across in order to get to the nearest verified gas station.
Extraneous sounds due to timing belt faults
Timing problems can also cause a gasoline engine to operate like a diesel engine. Most often, the gas distribution mechanism begins to make obvious noise for two reasons:
As for the hydraulic compensators, their knocking is clearly distinguishable “when cold” and the sound resembles the operation of a well-warmed-up diesel engine. Hydraulic compensators may knock a little on a fully functional gasoline engine in the first minutes after starting, thus layering on the characteristic “clicking” sound of the operating injectors of an injection engine. With the onset of even slight warming up, the sound similar to the operation of a diesel engine should become less intense, and completely disappear at operating temperatures.
If this does not happen, then the reason may be unsuitable engine oil, problems with oil pressure in the lubrication system of a gasoline engine, etc. The failure of only one hydraulic compensator will be manifested by a distinct metallic knock “when hot” in the area of the valve cover. The sound can be either constant or occurring periodically. Most often, the hydraulic compensator knocks at the same level in terms of sound intensity; the rhythm will change in the same way as the crankshaft rotation speed changes.
Ignition system malfunctions
As mentioned above, low-quality gasoline has a detrimental effect on the operation of spark plugs. However, even when using good fuel, do not forget about replacing them regularly. Previously, spark plugs were most often changed when the engine began to clearly lose its dynamic qualities or have difficulty starting.
Today, most manufacturers recommend in service books to replace spark plugs annually or after 15 - 20 thousand kilometers. In this case, they are not the cause of deterioration in engine performance. However, you can buy defective products, and then signs of their poor performance will appear, including misfires.
Therefore, you should not buy cheap candles from an unknown manufacturer - the savings may backfire. Missing sparks can also be caused by the ignition distributor and the high-voltage part of this system: wires and coils.
How can these problems be solved?
Having determined what problems may result in the engine running loudly, we will try to consider their solution:
Solving problems with the thermostat or gas distribution system will require turning off the engine completely and cooling it. This situation can occur when a very small gap is installed in the valves. In this case, the engine operates jerkily. To eliminate the problem, you need to use a feeler gauge to set the required gap size. After which it is recommended to check the tension of the belt drive. The thermostat can cause problems by leaking excess fluid. This leads to insufficient cooling of the engine, and as a result, its loud operation. To get it to work properly, you need to thoroughly clean the thermostat or replace the old one with a new one.
Thermostat
- Now let's look at the next problem - late ignition. Upon release of the incoming mixture, combustion continues. In this case, it is recommended to set the octane corrector to the zero position. If the engine begins to operate intermittently, it is best to loosen the distributor housing and adjust the ignition using the control lamp. In this case, it is necessary to eliminate the play of the slider - to do this, holding it with your hand already during the ignition process, re-fasten the housing.
- Unstable engine operation may indicate a problem with the carburetor. This problem can be detected if there is a smell of gasoline, which is especially noticeable when the hood is opened. This may also be accompanied by the accumulation of fuel liquid - this indicates that the seal is broken. To get rid of these problems, remove excess fluid and clean the intake tract. For this purpose, it is enough to idle for a few minutes. A violation of the tightness indicates wear of the valve, which is best replaced with a new one or restored the old one.
- During operation, loosening or oxidation of clamps and wiring terminals may occur. To solve this problem, it is enough to carry out the usual cleaning of contacts and connection points.
- The use of fuel that has a low octane number may cause the propulsion system to operate excessively loudly. To fix this problem, you need to switch to gasoline of the brand recommended by the car manufacturer. This will solve many problems that may arise on our roads and, as always, at the most inopportune moment.
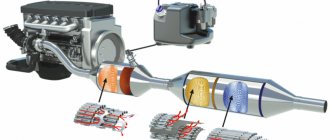
Exhaust system leaking
The exhaust system can reproduce the richest sound gamut. Thanks to constructive measures, developers achieve a noble exhaust sound character.
However, the consequences of winter operation lead to the fact that one day you will hear a rattling sound from the muffler of your car, reminiscent of the exhaust of a direct-flow muffler. From now on, all street racing fans will perceive this sound as an invitation to compete at the traffic lights.
The reason that the engine rumbles like a diesel engine is a leak in one or another element of the exhaust system. All of its components can burn out: the main and additional mufflers, the resonator, the catalytic converter of the exhaust gases, the corrugation, the exhaust pipe (pants) and the exhaust manifold gasket.
Before reaching this state, a small fistula appears through which gases escape (the leaky part “cuts,” as drivers say). Finding the location of the damage is often difficult, so the hole gradually increases until listening to the lion's roar of the exhaust becomes unbearable.
Sometimes there is no external damage, but the tractor sound is present. This happens when you knock out burnt ceramic honeycombs from the catalyst and drive with such an “improvement”.
Early or late fuel injection
For proper operation of a diesel engine, it is necessary to set the fuel injection mode at which it will be optimal (fuel supply will be timely).
If a diesel engine operates in an early fuel injection mode, that is, ahead of the cycle, then the power of the internal combustion engine increases, but accelerated wear of engine parts occurs. Therefore, the advance angle and the desired engine output must be balanced.
High-pressure fuel pumps themselves are able to regulate the supply time, namely, the injection pump is able to raise the diesel speed when it is cold, that is, it creates an early fuel injection mode. Then, when the diesel engine warms up, the idle speed is reduced to optimal. The fuel supply advance also becomes normal, average for power and wear of internal combustion engine parts.
During engine load, there must be late injection so that the supplied fuel is completely burned. The design also provides for automatic advance adjustment by changing the pressure of the supplied fuel by a high-pressure pump. The regulator, which changes the injection timing independently, is mounted in the fuel pump.
A worn injection pump results in the injection advance angle not matching the crankshaft speed. Because of this, the motor triples.
If the engine rumbles like a diesel engine, it is necessary to urgently eliminate the cause
Why can’t you operate a gasoline engine with such malfunctions? With the so-called “dieseling”, the internal combustion engine is subjected to strong mechanical stress. Any malfunction under this operating mode only progresses. In addition, the chain of breakdowns grows like a snowball.
The most minor problems are: loss of power, increased fuel consumption, discomfort when driving the car. Even if symptoms appear when warming up (or disappear after the engine warms up), urgent diagnosis is necessary.
Why dieselize a gasoline engine?
The fact is that a diesel engine always operates rougher than a gasoline internal combustion engine, creating unique and clearly distinguishable knocking noises. This is explained by a different principle of ignition of the mixture in the cylinders, which occurs from compression, and not from the spark plug.
We also recommend reading the article about why a diesel engine can stall during a cold start and after reaching operating temperature. From this article you will learn about the main malfunctions that cause noisy and unstable operation of the power unit.
Malfunctions of a particular engine system can, with a high degree of probability, be localized by the behavior of the motor in different operating modes, determined by ear, etc. You can also visually assess the color of the exhaust gases, which will indirectly indicate the problem. If a gasoline engine “knocks” like a diesel engine, runs unevenly or troits, then the reasons may be as follows:
Wear of ShPG parts
The connecting rod and piston group is subject to significant loads during engine operation. As long as the gaps between the rubbing surfaces do not exceed the permissible limits, a gasoline engine is much quieter than its diesel counterpart.
However, as the gaps increase as a result of natural wear and tear, metallic knocks of various types begin to superimpose on the pleasant rustling background. The gasoline engine operates almost like a diesel engine. Sources of knocking in the connecting rod and piston group:
- Main bearings, wear of which is accompanied by low-frequency knocks emanating from the crankshaft beds. The sound changes according to load and crankshaft speed. A possible cause of wear is engine oil starvation. The appearance of such sounds requires urgent contact with a car service in order to minimize possible consequences.
- Connecting rod plain bearings. These parts produce distinct, loud metallic knocks, the source of which is the middle of the cylinder block. Knocks are heard especially clearly when the load increases. To determine their source, the spark plugs are turned off one by one. Driving with such symptoms is fraught with engine destruction.
- The piston pins produce high-pitched ringing sounds, somewhat reminiscent of detonation knocks. This sound is less dangerous than knocking of crankshaft bearings, although in any case it must be eliminated. Before visiting a repair service, you can drive for a while, avoiding increased load and high engine speeds. You should also monitor the operation of the lubrication system, and most importantly, monitor the oil level.
- Worn pistons. They make dull knocks, somewhat reminiscent of the rumble of a diesel engine, which can be heard after a cold start. As the engine heats up, their audibility decreases. You can drive in quiet mode, but you shouldn’t put off major engine repairs too much.
Attention: when a knocking noise in the engine appears suddenly, you must stop driving and call a tow truck to get to the nearest auto repair service.
A little history of the diesel engine
In 1890, Rudolf Diesel developed the theory of the “economical thermal engine,” which, due to strong compression in the cylinder, improves efficiency. Diesel became the first person who managed to patent his theory, although similar ideas had been expressed somewhat earlier by Ackroyd Stewart. His idea was to draw air into the cylinder and, after compression, it was pumped into a container into which fuel was also injected. Reklama: INTELLECTUS anglų kalbos kursai suaugusiems ir įmonėms bei vasaros dienos stovyklos Kaune, Vilniuje ir Klaipėdoje https://intellectus.lt/dienos-stovykla-vilniuje/ To start the engine, it was necessary to heat it with a lamp from outside, and after starting, it worked without required heat outside.
Rudolf Diesel
E
Stewart did not consider the benefits of high compression, he simply experimented with the possible exclusion of spark plugs from the engine, that is, he failed to pay attention to the only important and large advantage - fuel efficiency. Therefore, the theory of R. Diesel formed the basis for the creation of modern engines with compression ignition
Most likely, this was the reason for the name “Diesel engine”, “diesel engine” and so on.
Diesel formed the basis for the creation of modern compression ignition engines. Most likely, this was the reason for the name “Diesel engine”, “diesel engine” and so on.
For what reasons do injectors start knocking?
The injector begins to make unnecessary sounds due to an excessive dose of fuel that is supplied to the cylinder. This happens due to unregulated fuel equipment.
Attention! To understand in which of the cylinders hard combustion occurs, you need to gradually loosen or unscrew the fittings from the injectors one by one. If the sound weakens, it means there really is a lot of fuel. This method is relevant for older models of units.
Excessive noise may occur due to wear of the nozzles. Such damage can be eliminated by replacing the nozzle. In some cases, adjusting the injection pressure helps. However, the effect of this will not last long. Flushing the needle and nozzle cavity to remove deposits may help. But this won't last long.
The injector nozzles have the fifth production accuracy group. Manufactured according to standards, the part does not allow the penetration of water and dirt. The sprayer is lubricated with fuel. When the edge of this mechanical device is damaged, injection occurs poorly.
Noise on a gasoline unit before starting and when warm
The noise on a gasoline internal combustion engine is much more extensive. There are many parameters taken into account here that make it easier to identify a single cause. For example, the nature of the noise and its nature on a gasoline engine can indicate a specific cause much more accurately.
- Knocking when cold after the engine is started.
- Engine knocking when hot after warming up.
- Knocking when cold.
- Knocking sound at idle.
- Engine knocking only occurs at high speeds under load.
Some important points to note are given below
- Detonation on a gasoline internal combustion engine causes a strong knocking sound. As you know, the engine operates in four combustion cycles. Ignition must take place strictly at a specific moment in the cycle-cycle mode. But one difficulty can arise with gasoline - in some cases, this fuel can ignite before the spark plug gives a spark.
This situation is called detonation. The knocking is frequent and loud, in some cases synchronized with the engine speed, and more often appears under excessive loads. For example, if a motorist is loaded to the limit and is driving uphill, when the car skids for a long time, etc.
The characteristics of knocks in a gasoline power plant are also determined by the sound tone of the knocks. For example, if the sound is dull, then this often indicates the appearance of a gap in the crankshaft. In addition, crankshaft knock on a gasoline unit can be detected precisely at the time of planting. A clunking sound will indicate excessive crankshaft clearance. A clunking sound may indicate camshaft problems. As with a diesel internal combustion engine, the knock frequency of the camshaft is several times lower than that of the crankshaft. The valves on a gasoline unit knock twice as often as the crankshaft. But you can also recognize this sound by its localization, mainly in the upper part of the internal combustion engine. In addition, experienced craftsmen are able to determine the knocking of valves by a loud knocking sound in different operating modes of the unit. Valve knocking in internal combustion engines occurs due to increased or natural wear. Sometimes it is enough to adjust the valves, and the knocking stops instantly. In difficult cases, they need to be replaced.
Video review about the causes of engine knocking
In a word, everything in the engine can knock, starting with the gap and ending with any element with broken geometry. Determining on your own the most likely source of knocking noises is not so easy. You need experience, specific knowledge, etc. Of course, additional information will help: how it knocks, what force, in what mode of operation, frequency of impacts, etc.
Source