How to profitably exchange a used car
To guarantee the legality of the used car exchange service and its objective cost, the purchase and sale process should be carried out at a trusted auto center. Here the client will be offered:
- Diagnostics of the old model, on the basis of which its cost will be determined;
- Selection of cars for exchange, completely new or with a clean mileage history: all cars undergo forensic examination, therefore the car dealership will never sell a car with a “dark past”;
- Legal support of the transaction: the client enters into a notarized agreement and, if necessary, can use the credit services of the car dealership’s partner bank;
- Efficiency of the service: the client does not need to look for buyers for his vehicle; he does not need to settle issues with the traffic police or the bank. The listed functions are the task of the auto center.
Read here! Engine sump
Thus, with minimal documents, it is possible to buy an improved car within one to three days. The used car exchange service makes it possible to regularly change the owner’s vehicle fleet by purchasing its best models.
Tact
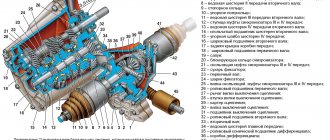
The movement of the piston inside the engine cylinders is called the duty cycle. The cycle consists of valve timing phases, which can be used to determine the moment of opening and closing of the valves. In a four-stroke vehicle, the full cycle occurs after turning the crankshaft by 720 degrees, in a two-stroke vehicle - by 360.
To provide the shaft with constant force during the power stroke in the engine cylinders, the knees of the unit are located at a certain angle relative to each other. The angle is affected by the number of cylinders, the type of installation and the location of the cylinders.
How to determine the operating order of internal combustion engine cylinders depending on the strokes.
| Half-turns of the crankshaft in the cylinders of a diesel and carburetor unit | Angle of rotation | Engine cylinder numbering | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| First | 0-180 | Exhaust gas release | Power stroke | Fuel and air intake | Compression of the air-fuel mixture |
| Second | 180-360 | Fuel and air intake | Exhaust gas release | Compression of the air-fuel mixture | Working stroke |
| Third | 360-540 | Compression of the air-fuel mixture | Fuel and air intake | Working stroke | Exhaust gas release |
| Fourth | 540-720 | Working stroke | Compression of the air-fuel mixture | Exhaust gas release | Fuel and air intake |
Engine Tactics
The operation of engine cylinders consists of the following stages:
- Intake - the piston moves to bottom dead center, and the combustion chamber is filled with the air-fuel mixture through the intake valve. The exhaust valve is closed.
- Compression - both valves are closed, the piston moves to top dead center, compressing the fuel composition. Due to compression, the temperature in the chamber increases significantly, and the pressure in the engine cylinder also increases. An important parameter that affects the efficiency of a car is the compression ratio. The indicator means the ratio of the complete filling of the cartridges and the volume of the combustion chamber. For cars with a high octane number, high-octane fuel is required.
- The working stroke is when the valve is in the closed position, the mixture is ignited by the spark plug. Under the influence of pressure in the cylinder of the car engine during fuel combustion, the piston goes down, rotating the crankshaft. For efficient performance, it is necessary that the fuel burns completely before the piston reaches BDC. This is ensured by setting the ignition timing. In modern cars, adjustment is carried out by a built-in electronic unit. Older models are equipped with a mechanical regulator.
- Exhaust - the power stroke ends with the exhaust of exhaust gases from the engine cylinders. At this stage, an important process occurs - purging the engine cylinders. Purging of the engine cylinders is ensured by the simultaneous opening of the intake and exhaust valves. After the piston reaches TDC, the intake stroke begins.
Volkswagen 1.2 TDI PD and 1.4 TDI PD
Both small diesel units with pump injectors appeared in 1999. The youngest disappeared from the list of proposals after a few years, while 1.4 was produced until 2010. The 1.4-liter unit can be found in VW Group models: Audi A2, VW Lupo, Polo, Seat Ibiza/Cordoba and Skoda Fabia.
Durability is also questionable. Problems appear after 150-180 thousand km. Most often, the turbocharger and high-pressure fuel pump fail, and sometimes the electronics fail. But the most serious drawback is the critical increase in the axial clearance of the crankshaft. Dismantling and grinding are not justified due to imbalance.
Repair of car components
The cylinder block structure consists of parts that operate in aggressive conditions, and therefore are often subject to breakage and wear.
Restoring an engine cylinder block consists of the following operations:
| No. of works | Operations Performed | Technical equipment. |
| 1 | Grinding the surface of the crankshaft bearing stop | Vertical milling machine |
| 2 | Replacing worn camshaft bushings | Press-fitting device |
| 3 | Repairing threaded holes | Drilled equipment, set of drills, lantern, die |
| 4 | Pressing out the fastening pins | Special press |
| 5 | Boring, repair of engine CPG cover. Adjustment by plane, installation by holes | Vertical milling machine |
| 6 | Processing the body for sleeves and boring for thrust edges | Vertical boring machine |
| 7 | Boring of main bearing seats | Horizontal boring machine |
| 8 | Gas-thermal spraying on treated bearing seats | Special technological equipment |
| 9 | Double-circuit boring of the body | Honing machine |
| 10 | Washing the engine and cleaning the oil channels | Equipment for jet washing of parts. |
| 11 | Painting the block | Spray gun. Compressor. |
Repair of the engine cylinder block ends with a control inspection on the test plate. Using a feeler gauge and indicator devices, the installation rigidity and alignment of the mounting components in the engine cylinder block are checked. After the engine cylinder body has been restored, a leak test is carried out.
Cylinder head assembly
Repair of the engine cylinder head is performed for the following reasons:
- broken drive shaft belt;
- cylinder head deformation due to overheating;
- duration of service lines;
- incorrect assembly after repair of the unit cylinder block.
Defects of engine cylinder head parts
You can restore defects using the following steps:
- grinding valves;
- the cylinder head is polished;
- gaskets and belts are being replaced;
- Bushings and valve seats are bored.
Post-repair control
After troubleshooting, the cylinder head is painted and the pressure in the cylinder is checked.
An indicator that indicates the effective performance of engine cylinder block parts is compression.
What is the pressure in the cylinders of different brands of engines?
| Vehicle make | Cylinder pressure kg/cm² |
| Chevrolet Cruze 1.6-1.9 | 14-13 |
| Chevrolet Lacetti 1.5-1.8 | 12-12,5 |
| Kia Rio (2011-2016) | 12,5-13 |
| Mazda 6 2.0-2.5 | 16-15 |
| Daewoo 1.5-1.8 | 10,5-11 |
| For diesel engine | |
| YaMZ 236 | 33-38 |
| Kamaz | 29-35 |
| YaMZ 238 turbocharged | 33-38 |
| MAN F90/2000 | 3038 |
| D 240-245 | 24-32 |
The final stage, painting
Before painting the engine cylinder block, it is necessary to carry out preparatory operations, which consist of the following points:
- cleaning parts from adhering dirt, oil, carbon deposits;
- removing traces of corrosion (if any);
- grinding contaminated threaded channels.
The cylinder head is painted separately so that the air and oil passages do not become clogged.
The operation of the cylinders is not dependent on painting, but it is important to protect the block from contamination.
How to paint the engine depends on financial capabilities. Online stores offer a wide variety of products that can be used to treat the surface of parts after repairing the engine block and cylinders.
Greetings, Friends. Due to the fact that I consider it necessary to pass on the accumulated knowledge to the younger generation, and mechanics now do not want to study, but only earn money by doing stupid maintenance and changing filters, I will leave some things here. So. Today we’ll talk about the operating order of the cylinders of internal combustion engines. One of my favorite topics. Otherwise it’s all women, humor, psychology, aphorisms... It’s time to know the honor))
We start, of course, with the simplest thing, that is, with an inline four. Everything is simple here. The order is 1-3-4-2, or 1-2-4-3, as on ZMZ-402 (Volga Gas)
But there are also V-shaped and opposed quads, however, this does not change the essence of the operating procedure.
Next up is the straight six. The order is as follows: 1-5-3-6-2-4, or as experienced drivers used to say, 15 bottles at 3.62 for four))) This is hard to forget)))
Next comes the V-shaped six with the operating order: 1-4-2-5-3-6. One of the most unbalanced engines, if you do not take into account 5, 3 and 2 cylinder four-stroke engines.
Well, now my favorite, namely the good old and inimitable V-8!
At first glance, it has two operating orders: 1-5-4-2-6-3-7-8 or 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2. You might ask why? But because America and Europe count cylinders differently. For Americans, the first cylinder (in the direction of travel of the A/M) is on the front left. Next, the cylinders are counted from left to right, front to back, in a checkerboard order: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 For Europeans, the first cylinder is on the front right in the direction of travel of the vehicle, then in order, also from front to back: 5 1 6 2 7 3 8 4 Thus, if you draw two diagrams and superimpose one on top of the other, you get the same thing.
And finally the V-12 engine. Order: 1-12-5-8-3-10-6-7-2-11-4-9
That's all for now. If anyone wants to add or correct, you are welcome. I hope it will be useful to someone))) All the best.
First of all, we draw your close attention to the fact that the concepts of “cylinder numbering” and “cylinder operating order” (there are also options for “engine operating order” and “ignition operating order”) are not the same thing. These concepts are related, but not equivalent. The ignition sequence in the cylinders of automobile engines, as a rule, does not coincide with the numbering of the cylinders. A firm rule that can be remembered is that the first cylinder (No. 1) is always considered the main one, and the No. 1 spark plug is always installed on it.
How cylinders are numbered, types of their location in the engine
Since the invention of the first internal combustion engine, engineers have had a very important goal - to extract maximum power from a specific volume of the power unit. Trying to solve this problem, designers conducted experiments with the number and layout of combustion chambers.
At various times, production car models used both small single-cylinder internal combustion engines and huge units with 16 cylinders. On different models, the combustion chambers are located and numbered differently, and this information will be very useful for a novice car enthusiast.
Cylinder liner defects
Cylinder liners wear out due to friction between the piston and the mirror (the inner wall of the cylinder). As a rule, increased wear can occur due to the following reasons:
— not enough oil on the cylinder walls
-the engine did not work for a long time, and all the oil flowed into the crankcase
-use of oil of inappropriate viscosity
— corrosion occurs due to the use of water as a coolant
-chips and scratches occur due to incorrect installation or dismantling (all actions for removing cylinder liners must be carried out according to the rules with a special puller)
- if the engine is not used correctly