Motorists who prefer to independently maintain and repair their vehicle are probably very familiar with such an element as the camshaft, or simply the camshaft. If someone is not so familiar with the structure of the car, then it is worth saying that the camshaft is located directly in the power plant. Moreover, this element plays a vital role in the operation of the engine. When describing the characteristics of a car, they talk about fuel consumption, power, horsepower and speed. But all these parameters very much depend on the performance of the camshaft. Therefore, it is extremely important to know what kind of unit it is, how it functions, and what malfunctions may occur.
Operating principle and purpose of the camshaft.
What is a camshaft
What does the camshaft look like?
The camshaft is a rod on which several so-called cams are located. These are irregularly shaped parts that rotate on a shaft axis. They correspond to the number of inlet valves of the cylinders and are located exactly opposite them. The set of cams is selected so that rotation guarantees stable and uniform combustion of fuel in the cylinders. And the operation of the entire camshaft is clearly synchronized with other engine mechanisms.
On both sides of the cams, support journals are placed on the shaft, holding it in bearings. One of the most important shaft components is the oil channels. The physical wear of parts, the power characteristics of the motor and the stability of its operation depend on their condition. To supply oil, a through hole is made in the camshaft axis with leads to the support bearings and cams.
Camshaft functions
In an internal combustion engine, the camshaft is responsible for opening and closing the intake and exhaust valves, that is, for gas distribution directly in the combustion chamber of the engine. The efficiency of the engine depends on the design features of the engine and the camshaft itself, as well as the correct timing adjustment: power, dynamics, efficiency. The evolution of engines also entails some changes in the shape and functions of the camshaft: systems are created that adjust the gas distribution to the speed of rotation, shafts for intake and exhaust are installed separately, and, of course, materials and methods of processing metals change.
How the camshaft works
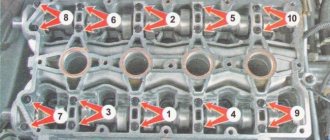
Camshafts in the cylinder head.
The camshaft is a key functional component of the gas distribution mechanism, which determines the order in which the valves open to launch the air-fuel mixture into the cylinders. The synchronous operation of this mechanism ensures continuous alternate combustion of fuel portions in the engine chambers. In some car models, the gas distribution mechanism has several camshafts.
The design, location, composition and characteristics of the camshaft cams are entirely dependent on the engine model. In some cars, the camshaft is located in the cylinder head, while in others it is located in the base. The top location is currently considered optimal, as it facilitates repair and maintenance. The camshaft is connected to the engine crankshaft by a belt or chain drive, because it is what drives it.
Operation and repair of camshafts
The camshaft is a fairly reliable part that will last at least until the first major engine repair. If you have a classic engine model without hydraulic compensators, every 10-15 thousand kilometers you need to monitor the camshaft clearances with rockers and adjust them. In all types of engines, the tension of the timing belt or chain should be monitored. Such nodes have a limited service life. Over time, chains can stretch and interfere with the engine block during operation.
Camshaft faults
Camshafts, like all “rubbing” parts, are subject to mechanical wear. The bearings also become unusable, and the camshaft oil seal may collapse and lose its shape. A broken camshaft can subsequently damage other engine mechanisms.
The causes of such problems may be:
- natural wear of the camshaft;
- low quality oil;
- insufficient oil pressure;
- insufficient oil level;
- violations of engine temperature conditions (outside the operating temperature range, the oil becomes liquid and partially loses its properties);
- mechanical damage, for example, the tension roller and camshaft belt have a limited service life; if the timing belt breaks, the engine and camshafts can suffer significant damage.
Camshaft diagnostics and repair
Possible problems with the camshaft are indicated by noise during its operation. The cause of the noise may be the camshaft bearing, which requires replacement.
If the camshaft is knocking, most likely the wear of the working surfaces has led to critical play. Typically, shafts have tolerances for the size of the groove and curvature. If noise occurs, it is necessary to measure the camshaft surfaces. A camshaft knock is a reason to urgently contact a service center.
A drop in engine oil pressure can also indicate camshaft wear.
Measuring the diameter of the camshaft journals with a micrometer
If an ECU error appears about a violation of the camshaft position sensor (camshaft position sensor), then you need to check the sensor itself. Over time, the sensors may fail, or the problem is only in the contacts, the “check” lights up. Replacing the camshaft sensor will definitely solve the problem, the error should go away.
How to check the camshaft? The most reliable way is to remove the camshafts. If they have obvious, noticeable burrs and streaks, restoration or replacement is necessary. To determine the exact output values, micrometers of various modifications will be required. If repairs are unavoidable, it is necessary to perform a full diagnostic of the cylinder head and all timing components.
This is interesting: Technical characteristics of 2ZZ GE 1.8 l/190 l. With.
Development on the camshaft journal
How to restore camshafts? Camshafts that have acceptable dimensions of wear and curvature are subject to restoration. In case of relatively minor wear, the shaft is only slightly corrected by grinding. For more significant wear, the surface is electroplated with chromium or iron. When significant restoration is required, metal surfacing is performed using gas or electric arc welding. Then the contact surfaces are precisely adjusted. The camshaft bed (the place where the camshaft is installed) is machined on a special machine or manually using “reamers”. All elements are carefully polished and brought to nominal sizes. Such procedures require serious knowledge of process technology and the availability of special equipment.
Various reamers for camshaft journals and bearings
Welded camshaft lobes before grinding
Camshaft replacement
How to install a new camshaft yourself? Replacing a camshaft is a complex procedure, but if you have the necessary knowledge and skills, this operation can be performed in a home workshop. Before starting work, carefully study the components and mechanisms of the engine, and find out how to remove its elements.
There are two ways to replace the camshaft: by removing or without removing the cylinder head. If you decide to “remove the head”, consider the need to buy a new gasket.
Cylinder head VAZ 2106 1 - cylinder head; 2 - camshaft; 3 - rear camshaft bearing housing; 4 - gasket; 5 — cylinder head cover; 6 — front camshaft bearing housing; 7 — camshaft oil seal
How does a camshaft work?
How does a camshaft work?
When viewed transversely, the cam has the shape of a drop. When rotated, the extended part of the cam pushes against the valve pusher and causes the valve to open. This provokes the supply of an air-fuel mixture for combustion. With further rotation, the cam “releases” the pusher, and it, under the action of a spring mechanism, returns the valve to the closed position.
The camshaft gear has twice as many teeth as the crankshaft. This is due to the fact that during one engine operating cycle the crankshaft makes 2 revolutions, and the camshaft makes 1.
The engine configuration may include two camshafts. The layout of the gas distribution mechanism with a single shaft is used in budget cars, where the cylinders have 1 pair of valves. Two camshafts are needed in models with two pairs of valves on the cylinders.
How to choose a camshaft
A new camshaft must be selected based on the reason for the replacement:
- Replacing the damaged part with a new one. In this case, a similar one is selected to replace the failed model.
- Engine modernization. For sports cars, special camshafts are used in conjunction with a variable valve timing system. Engines for everyday driving are also being modernized, for example, increasing power by adjusting the phases by installing non-standard camshafts. If you have no experience in performing such work, then it is better to entrust it to professionals.
What should you look for when choosing a non-standard camshaft for a particular engine? The main parameter is cam camber, maximum valve lift and overlap angle.
To see how these indicators affect engine performance, see the following video:
How to choose a camshaft (part 1)
Cost of a new camshaft
Compared to overhauling the entire engine, the cost of replacing a camshaft is negligible. For example, a new shaft for a domestic car costs around $25. Some workshops will charge $70 for adjusting the valve timing. For a major overhaul of the engine, along with spare parts, you will have to pay about $250 (and this is at garage service stations).
As you can see, it is better to carry out maintenance on time and not subject the motor to excessive loads. Then it will serve its owner for many years.
What does the camshaft sensor do?
The camshaft position sensor determines the angular positions of the timing belt relative to the crankshaft and generates corresponding signals in the electronic engine control system. As a result, ignition and fuel injection are adjusted. On gasoline cars, a malfunction of this device blocks the operation of the ECU and prevents the engine from starting. In diesel models, starting is possible, but still difficult.
Like the crankshaft sensor, the camshaft sensor operates based on the Hall principle - the magnetic field in the device changes when the magnetic gap is closed by a special tooth located on the shaft or drive disk. When a tooth passes near the sensor, a signal is generated and sent to the electronic control unit. The frequency of the pulses is directly related to the rate of rotation of the camshaft, based on which the ECU makes adjustments to the operation of the engine. By constantly obtaining data on the position of the piston of the first cylinder, consistent and timely injection is ensured.
2015-10-11 Camshaft (camshaft)
Four-stroke piston internal combustion engines are now in the majority of cases equipped with a gas distribution valve mechanism (hereinafter referred to as timing). Other schemes, for example, with a spool or piston (Knight system) timing system, are currently practically not used. One of the main components of the timing valve is the camshaft (the term camshaft , sometimes cam shaft). There are engines with electromagnetic valve drives. In this scheme there is no camshaft. Currently, such engines are not installed on production passenger cars, but, for example, BMW has them.
During operation, the camshaft (there are several of them, more on this below) is subject to significant loads, wear, and sometimes mechanical deformation for a variety of reasons. For example, cracks appear, cam shaft deflections, scuffs, scratches on the bearing journals and cams, and metal fatigue accumulates. There is a need to perform such type of work as replacing the camshaft. The part (sometimes the unit) is not repairable, although sometimes some types of repair work can be performed. It all depends on the nature and extent of the damage. Therefore, in most cases it is necessary to buy a camshaft.
In addition to the camshaft, other timing elements often require repair and replacement, such as:
- camshaft oil seal, sometimes rear, sometimes front, take this into account when replacing the camshaft oil seal;
- camshaft position sensor or simply camshaft sensor;
- plain bearings;
- camshaft valve and other parts of the valve group (oil seals, drive elements, guide bushings);
- timing drive components (pulley (nowadays this solution is practically not used), gears, drive sprockets, chain or belt).
These, of course, are not all the parts that require maintenance, replacement (and sometimes repair) in the timing valve. But one thing remains the same - if you do not maintain the gas distribution mechanism in good condition, and do not carry out the work specified by the regulations on time, then engine repair is guaranteed. Without a working timing belt, the engine will not work. And even if it does work, then a violation of the valve timing is an extremely unpleasant thing in terms of the fact that fuel consumption increases and engine performance decreases, especially with regard to power. And components of interconnected systems, ignition, power supply (fuel injection), and exhaust gas removal (exhaust) also fail. And the power unit itself suffers no less from this.
Therefore, keep an eye on the timing belt. Carry out the work prescribed in the maintenance regulations for your car in a timely manner. The Avto.Tatar car portal will help with this. We provide information about car services in Kazan that service the timing belt, as well as restore its functionality, perform such types of work as replacing the camshaft, as well as replacing the camshaft oil seal, major or routine repairs of the engine, its timing belt.
We also provide information about sellers who in the capital of Tatarstan have the opportunity to buy a camshaft and other timing elements that are in demand during maintenance and restoration of engine performance. Moreover, for all parts of the power unit, including the camshaft, the price in our catalog is one of the most affordable.
Main purpose and functions of the camshaft
Camshaft
– a basic component, a timing valve part of a four-stroke piston power unit. Its main, one might say primary, task is to open and close the exhaust as well as the intake valve of the camshaft at a strictly specified moment. There are more than two valves in a cylinder. Accordingly, there are several camshafts, some are responsible for the exhaust valves, others for the intake valves.
A number of engines use systems that change valve timing, which allows you to change the opening and closing phases of the intake valves, and sometimes simultaneously the exhaust valves, the opening period and lift parameters, which optimizes the operation of the engine and interconnected systems in general.
Modern power units use an electronic control system. Put d
Camshaft position sensor. Hence the auxiliary task - to optimize the functioning of the ignition and injection systems.
Everything else directly depends on the design features of the individual power unit. Let's outline just a few possible options.
So, in some cases, the camshaft is responsible for the operation of the oil pump in the lubrication system. As a rule, torque is transmitted via an intermediate shaft; there are other solutions.
The second point, however, is more typical for carburetor engines rather than injection engines, but still. Sometimes the camshaft is also responsible for the operation of the fuel pump, which supplies fuel to the injection system, and other equipment, for example, the ignition distributor. These are just the most common solutions; there are many others.
Schemes, layout, terms
Let's start with the basics. The most important parameter is the location of the camshaft. When engine repairs, camshaft replacement, and timing service are performed, you should take into account where the camshaft is located. Both the engine design and the type of timing drive directly depend on this.
In general, two schemes are most widespread. The first is when the camshaft is located in the cylinder block, lower location, lower arrangement. Now it occurs, but rarely.
The second is when the camshaft is located in the cylinder head (hereinafter we will use the term cylinder head), the so-called overhead arrangement, which is now most common. Therefore, we focus special attention on it.
There are other schemes, for example, the lateral arrangement of camshafts in the cylinder head of boxer engines.
And that is not all. It is important to understand where and how the camshaft valve works. There are again several options, two main ones.
Nowadays, the majority of engines use an overhead valve arrangement (it differs in angle of inclination, strictly vertically at an angle of 90° or other options; R-, VR-, V-, W-shaped depends on the layout of the engine cylinders). That is, two main schemes are used. The most common is OHC. Both the camshaft valve and the camshaft itself are located at the top of the engine. The second is a less common OHV scheme. This is when the camshaft valve is at the top and the camshaft itself is at the bottom. The third scheme is when the valves are not located vertically, but horizontally at an angle. Boxer engines, in which the cylinders are at an angle of 180° to each other, are a special case.
Now about the second scheme. Bottom placement of valves is practically never found, the camshaft is also at the bottom, SV diagram. Previously used quite often.
And one last important point. The OHC scheme is quite variable. Depending on the engine layout and the number of camshaft valves, there is more than one. To indicate their number, a certain letter is added to the OHC. For example:
- S + OHC, it turns out SOHC (one camshaft), as a rule, there are two valves per cylinder, sometimes, extremely rarely, four;
- D + OHC, it turns out DOHC (two camshafts), there are three, often four, valves per cylinder, sometimes more;
- Q + OHC, it turns out QOHC (four camshafts), a very rare scheme on engines with a V-, W-shaped layout, with three or more valves per cylinder.
Using this information, you can now easily understand in terms how many camshafts are in the engine, how they are located and where to look for the camshaft valves. If we take modern power units, the most commonly used are DOHC and SOHC schemes.
Design features
Now about the design. The camshaft consists of two main elements, the first is the cams (they are also called eccentrics), the second is the support journals, as the name implies, they serve to support the camshaft in the seat. As a rule, one of the bearing journals is equipped with a locking device that prevents axial displacement of the camshaft. There are several ways to fix the camshaft. Sometimes yokes are used, sometimes journal bearings (bushings, liners).
The number of cams is not less than the number of valves. In the majority of cases, their number is equal to one cam per valve. But there are options when several cams work on one valve, thus changing the valve timing, for example, Honda has an i-VTEC system. Keep in mind that the cam profile is different; as a rule, it is teardrop-shaped, but it can be round, “square” and more exotic shapes.
The number of camshaft journals is usually equal to the number of crankshaft journals, although this is not an axiom; there are other options.
The camshaft has its own friction pairs, parts that interact with each other, these are the camshaft bed (or liners) and the support journal (shaft), as well as the camshaft cams and valve drive elements or the valves themselves (more on this below). Therefore, there is a need to lubricate the cams and bearing journals. If the shaft is located in the cylinder block, then there are no special problems with this. When the camshaft is at the top, lubrication is carried out under pressure and oil channels are provided in the design. And the camshaft oil seal is responsible for the tightness of the lubrication circuit in such a situation. Depending on the engine design, a front camshaft oil seal and a rear camshaft oil seal are installed. This is a consumable item and the camshaft oil seal needs to be replaced periodically. Camshaft covers and a number of other parts are also used, depending on the design.
Modern engines are distinguished by the presence of a control system. Therefore, it is also mandatory to install a camshaft position sensor (also known as CMP in English, phase sensor, in Russian DPRV or simply camshaft sensor). It determines the angular position of the camshaft at a certain point in time. This information is required for optimal operation of the ignition systems, as well as fuel injection.
According to the principle of operation, the camshaft sensor is:
- inductive;
- magnetoelectric, operating on the principle of the Hall effect;
- optical
Keep in mind that there is not one camshaft position sensor, but several, and on the same engine of different types. The first two types are the most common; an optical camshaft sensor is very rare, for example, used by Japanese Mazda.
The price of a camshaft depends not only on its design, but also on the material of manufacture. In most cases, this is either cast iron or certain grades of steel. According to production technology, the predominant number of shafts are forged; there are also cast hollow ones (with an oil channel) and prefabricated ones (cams and bearing journals are connected to each other in a certain way). Separately, we also note tubular camshafts, but they are still rare.
The design of the camshaft is largely determined by the type of timing drive; there are several options:
- belt, a timing belt is installed connecting the pulleys or gears (adjustable, split or non-adjustable, continuous) of the upper camshaft and crankshaft; in addition, sometimes there is a tensioner, support and tension rollers;
- chain, a timing chain (single-, double-row, gear or roller) is used, connecting the drive sprockets of the upper camshaft and the crankshaft; a tensioner, damper and other components are additionally installed;
- gear, in this scheme the camshaft and crankshaft gears are used, if the camshaft is at the bottom, then direct gear transmission of torque from the crankshaft is used, they are located nearby, if the camshaft is at the top, then additional intermediate gears are installed;
- combined.
If we talk about a combined drive, then there are a lot of options. For example, a belt and chain, crankshaft and camshaft are connected by a belt, and the chain is used to transmit torque from one camshaft to the other. Or gear-chain. There is a gear on the crankshaft, it is connected to an intermediate gear, which has a toothed sprocket, on which a chain is put, which provides connection with the toothed sprocket on the camshaft. There are many other schemes. But basically the timing drive is either chain or belt. The rest is exotic.
And the last point is the location of the camshaft, which is especially important when the engine and its timing belt are being repaired. Let us note two features. In a bottom-up arrangement with overhead valves, the camshaft and the valve drive do not have a direct connection; the intermediate element is called a rod. In the lower-valve scheme with lower valve placement, as well as the most common upper-valve, overhead-valve scheme, the connection between the cams and the valve drive is direct.
Principle of operation
Based on the design features, the operating principle of the camshaft is as follows. The crankshaft rotates and engages the timing drive, transmitting torque to the camshaft. It also begins to rotate, the cams engage either the pushers, then the rods and the valve drive, or the valve drive itself, or the valves themselves and their rods.
We use the term “valve drive” and have not explained what it is. The thing is that in most cases (there are exceptions) the camshaft cams interact with the valve stems not directly, but through a certain device.
Modern engines use either cup tappets or rocker arms. One important point. In order to automatically adjust the existing thermal valve clearances, that is, the distance between the cams and the valve drive components, hydraulic compensators are used on a number of engines. Sometimes, very rarely, other solutions are used. In the lower-valve overhead valve design, the cams act on the pushers, which act on the rod, which acts on the rocker arms or rockers.
If the drive is direct, without a rod, then we note that sometimes rocker arms with an adjusting eccentric or four supporting surfaces, special levers are used, in some cases two rocker arms are responsible for one cam.
We got a little distracted. The force from the cams is transmitted to the valve drive (pushers or rocker arms). They act on the rods and force the intake or exhaust camshaft valve to move in the cylinder depending on the stroke. This ensures that the fuel-air mixture enters the cylinders (camshaft inlet valve) and exhaust gases are removed (camshaft exhaust valve). It has already been said that the number of valves is different. The simplest scheme is one inlet and one outlet valve each. There are two inlet, one outlet, a pair of inlet and outlet, sometimes there are three inlet and two outlet. Engineering ideas do not stand still; they can come up with other schemes. And all this affects the number of installed camshafts, their design and placement.
The operating characteristics of the camshaft depend on the profile of the cams. Thus, cams with a wide and smooth profile are used on lower camshafts, and with a narrow and pointed profile - on overhead camshafts. This is typical for sports car engines and is an element of their tuning. Production models are equipped with camshafts with cams with a standard profile.
The most important characteristics of the camshaft:
- valve lift parameters (measured in millimeters);
- phases of closing and opening of valves;
- valve opening time, measured in degrees of crankshaft rotation.
This concerns the principle of operation and the main operating parameters of the camshaft.
Maintenance, tuning, breakdowns and repairs
The camshaft may fail. Very often the cause of a breakdown is the timing drive, especially if it is a belt drive and the belt breaks. The pistons meet the valves, which can go to the cylinders, camshaft and crankshaft. The engine will need to be overhauled and sometimes replaced. Therefore, the timing drive must be monitored and the timing belt must be replaced according to regulations.
Maintenance, in addition to replacing the belt, sometimes the timing chain, involves adjusting the thermal clearance of the valves (if there are no hydraulic compensators), in some situations, washing and cleaning from dirt (in the overhead configuration it is enough to remove the valve cover), and other work.
The main causes of camshaft failure:
- wear, both cams and journals wear out, supporting components, as well as interconnected components, the same camshaft oil seal, as a result, replacement of the camshaft oil seal is in demand, as well as liners (bearings, if any), yokes (if used);
- mechanical deformation, timing belt breakage were noted, sometimes the chain jumps, stretches, the camshaft bed is damaged due to various objects, camshaft play (“axial runout”), there are many other reasons;
- current conditions of use of the vehicle, especially if they are difficult;
- driving style, if it is sporty, aggressive, with sharp accelerations and braking, then this reduces the service life of the engine as a whole;
- design features of the engine, timing belt and camshaft;
- low quality engine oil, lack of lubrication of friction pairs, incorrectly selected oil, malfunction of the lubrication system as a whole, the oil filter and pump may be faulty, the tightness of the lubrication circuit is compromised;
- use of low-quality counterfeit parts;
- lack of or unprofessional maintenance, timing belt does not forgive errors and requires maintenance;
- careless, poorly thought out tuning, in a word, unqualified intervention and change in the design scheme.
There are many reasons indicating that the camshaft or related components, the same camshaft sensor, camshaft oil seal, yokes or plain bearings, elements of the variable valve timing system, valve drive, among them:
- reduction in engine operating parameters (fuel consumption increases, power decreases, dynamic characteristics decrease);
- the appearance of extraneous knocks and noises;
- inability to start the engine, it simply won’t start, these are already critical breakdowns, including destruction of the crankshaft, bent valves, broken cylinders and pistons, this means either a major overhaul of the engine or its replacement;
- a number of others.
As for the camshaft itself, there are several breakdowns characteristic of this timing part (assembly), among them:
- deformation of the working surface of the cams and bearing journals (cracks, chips, scuffs, scratches);
- violation of the tightness of the connections (pay attention to the camshaft oil seal, it is better to change it, although it is expensive, despite the fact that the part is cheap, replacing the camshaft oil seal is very important, otherwise problems with the camshaft and drive are guaranteed, and you never know where else the oil will end up in the engine compartment , there is a big disaster);
- camshaft deflection;
- critical wear of threaded connections, seats, keyways;
- other breakdowns.
To determine faults, complex diagnostics is required, including through troubleshooting and subsequent instrumental and visual diagnostics. The camshaft position sensor and other electronics are checked using computer diagnostics. Other diagnostic methods are also used.
Camshaft repair is more exotic. It all depends on the nature and complexity of the damage. Sometimes done:
- leveling the existing deflection using straightening or using a press;
- restoration of the working surface of the cams and bearing journals (grinding to the next repair size);
- replacing yokes or support bearings, sometimes restoring the bed;
- other work (grooving, spraying, surfacing).
But in most situations, the camshaft is replaced. Consumable spare parts are also replaced in case of breakdowns. For example, the camshaft oil seal is replaced, damaged bearings (if any), and a faulty camshaft sensor must be replaced.
On our auto portal you can choose an auto store in Kazan where the price for a camshaft is within reasonable limits. After repairs are completed:
- checking the geometric parameters of the camshaft installation;
- setting up the timing, setting the valve timing, checking the thermal clearances of the valves;
- other works.
Also, in addition to maintenance and repair, sometimes, at the request of the car owner, tuning is carried out, replacing the serial camshaft with a tuned one (low-level, universal (low-middle), high-speed) or sports. But you need to do this thoughtfully.
Do you need service, repair, or camshaft tuning in Kazan? Contact our car portal Avto.Tatar ! We will help you choose a car service center that will provide all the necessary services, and sellers who offer all the spare parts required for this type of work, including buying a camshaft and other parts.
Breakdowns and their causes
A faulty camshaft most often reveals its condition with a characteristic knocking sound, which occurs due to wear of bearings or cams, shaft deformation, or mechanical failure of one of the elements. Such breakdowns occur both due to manufacturing defects and as a result of natural wear and tear.
Camshaft knocking also occurs when poor engine oil is used or due to unregulated fuel supply. Because of this, the cylinder valves and cams work out of sync - the engine loses power, consumes too much fuel and runs unstably.
Other causes of camshaft failure
In addition to oil starvation, the causes of breakdowns can be overheating, from which the metal “leads”, natural wear (sooner or later everything wears out, no matter how hard you try), breakdowns of adjacent parts (pulley, chain or timing belt), as well as the initially low quality of the camshaft ( bad metal, imprecise manufacturing). The signs can be identified visually or even by ear: a characteristic symptom of a camshaft malfunction will be a knocking sound when starting a cold engine (at the beginning of the problem, the knocking noise disappears when the engine warms up, and as the situation worsens, the engine will knock constantly).
Wear and scoring on journals, bearings, oil seals or cams is a clear signal to replace the part.
A low-quality camshaft may bend (deformation, as a rule, is not determined visually, but only with special equipment) due to deflection of the bearing journals. For passenger cars, the permissible degree of camshaft curvature is 0.05 mm; if more, vibration increases and adjacent engine components fail.
If the shaft is installed incorrectly, as well as the engine is not assembled correctly (the mounting bolts of the cylinder head, camshaft, pulleys and gears are not tightened), vibration occurs during operation. The shaft breaks off the fasteners, after which the engine in most cases is sent for overhaul. Cracks may appear on the camshaft itself, and the grooves for the pins break under load.
It is not advisable to repair the camshaft: no amount of grinding or spraying will restore its original properties. In case of failure, the part is simply replaced with a new one, simultaneously installing new mounting bolts and checking the chain or timing belt.