The Chevrolet Niva car from the SUV class is a passenger car with off-road capability and satisfactory comfort. One of the main components in the drive of a Chevrolet Niva car is the clutch, designed to periodically connect and disconnect the motor with the drive wheels of the car through the gearbox. Reliable clutch operation has a beneficial effect on the durability of the engine, smooth gear shifting, uniform movement of the vehicle and the driver’s nervous system.
Clutch replacement
The main reasons for replacing the mechanism are loud noise during switching on, jerking during operation, incomplete switching off or switching on. The Sachs clutch is perfect for the Chevy Niva. If, after you disassemble the clutch kit, you cannot identify a fault in specific components, it is better to replace them all.
The Niva is installed on a lift or car pit. The gearbox is removed. If you want to keep the same clutch pressure plate, which is also called the “clutch basket,” then mark its location.
The clutch basket is designed to protect all other parts of the mechanism.
Disconnect the pressure disc and then the driven disc. Check the latter carefully. There should be no cracks in it. Pay attention to the degree of wear of the friction linings and the fixation of the damper springs. Replace the drive if necessary. After this, the clutch basket is put in place and the clutch is adjusted.
To ensure that the clutch on your Chevy Niva lasts a long time, do not constantly keep your foot on the pedal. Many people develop this habit even when they are learning to drive. This only leads to wear on the driven disc and bearing, and your leg gets tired, because in any case you are putting some pressure on the pedal.
Lada 4×4 3D Niva 96 › Logbook › ShNiva clutch, 6 years of operation
After purchasing the previous Niva, some time later the clutch died, the mileage was 70 thousand km, it just skidded like a horse and stank.
In those distant times, it was not possible to replace it myself, and I knew absolutely nothing about this “Subtle Matter” - the Niva Clutch, and therefore I turned to specialists, I don’t know what and how they fixed it for me, but everything that They made it go 60 t.km without any problems. And only the last 10 t.km. The car began to twitch and tremble when the clutch pedal was released. A control test - we stand still, squeeze the clutch, engage 4th gear, release the clutch, it showed that the engine stalls and the clutch does not slip. So, I decided, I’ll drive until... probably the planned replacement of it with a ShNiv clutch, otherwise I didn’t want to push it to the edge and stand there looking rotten like a cardboard fool
in a rut or in the middle of an intersection in the city center.
in 2013, a special occasion came - capital of the jerker! Having removed the engine, I saw that the clutch turned out to be not 2121, but 2106, judging by the reading on the Internet, it is still better than 2121, and as my practice has shown, this seems to be true.
My operating conditions for the clutch weren’t harsh, but they weren’t too hot either. Operating mode: 90% city, 10% off-road, but without fanaticism. The city regime was not so hothouse, the car carried 5 people to the dacha, a trailer with all sorts of rubbish in the summer and a harvest of potatoes, cabbage and God knows what else in the fall,
winter constantly threw frostbitten foreign cars from Toyota Corolla to Hynday Tucson on the tail, so I felt the full load of the clutch.
I rarely drove off-road, usually I just drove through the mud, trying not to burn out the clutch (I really didn’t want to lose it somewhere in the forest). To summarize the old clutch, I’ll say that I’m quite pleased with its performance, but I want more!
In short, I have wanted for a long time, I would even say from the moment I learned about this possibility, to strengthen the critical node of the field - the CLUTCH. I’ve heard too many horror stories about the premature (as always “on time”) failure of the standard VAZ-2121 clutch. How to make this mysterious gain?
In the magazine “Behind the Wheel” about the compatibility of clutches 2121 and 2123. Quote from No. 5 (page 202, answers to questions). 3. Can clutch 21233 be used on a Niva VAZ-21213? A clutch with this index is produced in Turkey by Valeo (can be sold as Turkish). The fundamental difference from others: the diameter has been increased to 215 mm.
Designed for Chevrolet Niva complete with a flywheel, the working surface diameter of which is 215 mm. On Niva and classic cars, only a complete set of such a clutch is used - driven and pressure disks, release bearing (type 2110) with outer diameter 39.5 mm. Another prerequisite is flywheel 2123; it won’t work with anything else.
First, you need to solve the problem with choosing the clutch itself, because the hucksters are not asleep here either and have piled on the shelves all sorts of different colored boxes with super-duper quality kits.
You can argue for as long as you like where they get these kits from and for what money, but here’s a screenshot from the Ketai website for starters
There are a lot of “original” spare parts for Russian-made cars. For reference, this clutch in stores then cost $20.
I didn’t play the lottery with stores and choose beautiful multi-colored boxes, because it’s not like buying 200 grams of expired sweets in Auchan and then riding a white horse once in an unplanned place. That’s why I turned to a dealer who sells Shnivas and services them. Everything is simple there: they bring you the necessary parts from the spare parts warehouse in faceless bags.
Also interesting: Niva 2131: technical characteristics of a 5-door car
Basket, clutch disc and release bearing Valeo, I read a lot that this is crap and should be left to Sachs, but I trusted the choice of the manufacturer Shniv, after all, it’s not profitable for them to then, under warranty, replace this unit ahead of time and waste my money. In general, I bought the basket from them , disc, releaser and flywheel,
Clutch
Design Features
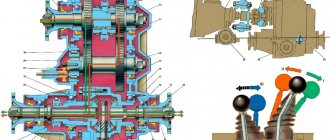
| Rice. 5.1. Clutch assembly: 1 – clutch housing; 2 – flywheel; 3 – bolt securing the clutch housing to the flywheel; 4 – driven disk; 5 – pressure disk; 6 – clutch casing; 7 – clutch release clutch; 8 – gearbox input shaft; 9 – clutch release fork; 10 – central pressure spring |
The vehicle has a single-disc, dry, permanently closed clutch with a central diaphragm spring. The clutch device is shown in.
| Rice. 5.2. Clutch release drive: 1 – tube; 2 – main cylinder; 3 – master cylinder fastening nut; 4 – pedal bracket; 5 – clutch release clutch; 6 – ball joint; 7 – clutch release fork; 8 – clutch release fork cover; 9 – bracket fastening bolt; 10 – bracket; 11 – working cylinder; 12 – valve for removing air; 13 – clutch pedal axis; 14 – clutch pedal; 15 – locking bracket; 16 – master cylinder pusher; 17 – bushing; 18 – locking bracket; 19 – bushing |
The clutch drive is hydraulic, backlash-free, with automatic compensation for wear of the friction linings of the driven disc. The drive consists of a main 2 () and a working 11 cylinder, a clutch pedal, a hydraulic clutch release tube 1 and a hose.
| USEFUL TIPS To ensure a long and trouble-free clutch service, do not constantly keep your foot on the clutch pedal. This bad habit is often acquired while learning to drive in driving schools for fear of not having time to disengage the clutch while stopping the car. In addition to the rapid fatigue of the leg, which is always above the pedal, the clutch is depressed at least a little, and the driven disk slips and wears out. In addition, although the release bearing is designed to operate in constant rotation mode, when the pedal is pressed slightly, it is under increased load, and its service life is reduced. For the same reason, we do not recommend keeping the clutch disengaged for a long time (for example, in traffic jams). If you don’t have to move away right away, it’s better to put the gearbox in neutral and release the pedal. Clutch slipping can be easily determined using a tachometer. If while driving, when you sharply press the accelerator pedal, the speed rises sharply, and then drops a little and the car begins to accelerate, the clutch requires repair. |
Checking the technical condition of the clutch
Check the technical condition of the clutch using the following methods.
| 1. Put the gearbox in neutral, start the car engine and warm it up to operating temperature. When the engine is running at minimum engine speed, disengage the clutch (press the pedal) and engage reverse gear. The transmission should engage without grinding, knocking or other extraneous noise. |
| 2. While the car is moving, change gears. All gears should be engaged without grinding, knocking or other extraneous noise. |
| 3. When accelerating a car, there should be proportionality between the increase in engine speed and the increase in vehicle speed (the clutch should not “slip”). Clutch slipping can be easily determined using a tachometer. If while driving, when you sharply press the accelerator pedal, the speed rises sharply, and then drops slightly and the car begins to accelerate, the clutch requires repair. |
If the indicated signs of normal clutch operation are absent, try removing air from the clutch hydraulic drive. If bleeding the hydraulic drive does not lead to the desired result, remove the clutch for repair.
Bleeding the hydraulic clutch
If, when the pedal is pressed all the way, the clutch does not disengage completely (“drives”), which is accompanied by a characteristic grinding of gears when engaging reverse gear, there may be air in the clutch hydraulic drive. Remove it by bleeding the drive.
In addition, pumping is performed when the hydraulic drive is filled with fluid after its replacement or after repair of system components associated with its depressurization.
You will need: an “8” wrench, a bleeder hose, a container for brake fluid, brake fluid.
| USEFUL ADVICE Carry out the work with an assistant in the inspection ditch. |
| 1. Pour (or add) liquid into the tank to the bottom edge of the filler neck. |
| 2. Place a bleeder hose onto the slave cylinder valve. Place the other end of the hose in a container with a small amount of brake fluid so that it is submerged in the fluid. |
| 3. Press the clutch pedal 4-5 times and keep the clutch pedal depressed. |
| NOTE The assistant must press the pedal sharply, with intervals between presses of 2–3 s. |
| 4. Open the bleeder valve to bleed air from the system. Liquid with air bubbles will come out of the hose into the container. |
| 5. After the flow of fluid from the hose stops, tighten the fitting and release the clutch pedal. |
| 6. Repeat steps 4, 5 and 6 several times until liquid begins to emerge from the hose without air bubbles. |
| WARNING Do not allow the fluid level in the reservoir to drop below the “min” mark. Add fluid in a timely manner, otherwise when the bottom of the tank is drained, air will enter the system and the pumping will have to be repeated again. |
| 7. Remove the hose from the bleeder valve and put on the cap. |
| 8. Add brake fluid to the master cylinder reservoir to the “max” mark. |
Removing and installing the hydraulic clutch reservoir
Remove the reservoir if the brake fluid is excessively contaminated and deposits appear on the walls of the reservoir.
You will need: a 10mm wrench, pliers, a container for brake fluid, brake fluid.
| 1. Unscrew the tank cap. | 2. Unscrew the nut securing the tank bracket. |
| 3. Remove the tank from the bracket. |
| 4. Drain the liquid from the reservoir. |
| 5. Inspect the tank. If deposits are detected... | 6. ...loosen the hose clamp and disconnect it. |
| NOTE The tank can be washed and reused. |
| 7. Install the tank in the reverse order of removal. |
| 8. Fill with fluid and bleed the hydraulic system (see “Bleeding the clutch hydraulic drive”). |
Removing and installing the clutch master cylinder
Remove the master cylinder for replacement or repair if there is a fluid leak, the clutch is not fully disengaged (can be caused by a fluid leak or cuff wear), as well as when the clutch is not fully engaged (as a result of the compensation hole being clogged or blocked by a swollen cuff).
You will need: a 13mm wrench (socket head with extension), pliers, a rubber bulb.
| 1. Use a rubber bulb to pump out the liquid from the tank. |
| 2. Loosen the hose clamp and disconnect it from the master cylinder. |
| 3. Move the hose to the side. |
| 4. Remove the nut securing the pipeline from the master cylinder. Remove the pipeline from the master cylinder hole and move it to the side. | 5. Unscrew the two cylinder mounting nuts and... |
| 6. ...remove it from the car. |
| 7. Install the cylinder in the reverse order of removal. |
| 8. Bleed the clutch hydraulic drive (see “Bleeding the clutch hydraulic drive”). |
Removing and installing the clutch slave cylinder
Remove the slave cylinder for replacement or repair if the clutch does not disengage completely due to a fluid leak.
You will need: keys “13”, “17”.
| 1. Loosen the slave cylinder hose end. | 2. Remove the two bolts of the bracket securing the slave cylinder to the clutch housing. |
| 3. Remove the bracket. |
| 4. Remove the slave cylinder pusher from the clutch release fork and remove the protective cap along with the pusher. | 5. While holding the hose tip from turning and rotating the cylinder, separate them. |
| 6. Drain the fluid from the drive and cylinder into a prepared container. |
| 7. Install the new slave cylinder in the reverse order of removal. |
| 8. Bleed the clutch hydraulic drive (see “Bleeding the clutch hydraulic drive”). |
Replacing the hydraulic clutch hose
You will need: key “14”, “17”, “19”.
| 1. While holding the hose fitting from turning with wrench 1, use wrench 2 to unscrew the pipeline nut and disconnect it. | 2. Remove the bracket securing the fitting to the body bracket. |
| 3. Drain the fluid from the drive into a prepared container. |
| 4. Unscrew the hose end from the working cylinder. |
| WARNING Be careful not to lose the sealing washer. |
| 5. Install the new hose in the reverse order of removal. |
| 6. Bleed the clutch hydraulic drive (see “Bleeding the clutch hydraulic drive”). |
Removing and installing the clutch
The main malfunctions that require removal and disassembly of the clutch to eliminate are:
– increased (compared to usual) noise when the clutch is engaged;
– jerking when the clutch operates;
– incomplete engagement of the clutch (the clutch “slips”);
– incomplete disengagement of the clutch (the clutch “drives”).
| USEFUL TIPS The work of removing and installing the clutch is very labor-intensive, so first make sure that the malfunctions are not caused by defects in the clutch drive. If, after disassembling the clutch, no obvious signs of malfunction of individual components are found, replace all components at the same time. Since the transmission must be removed before removing the clutch, work with an assistant. |
| You will need: an “8” wrench, two screwdrivers, a mandrel for centering the driven disk (can be made from the input shaft of the gearbox by removing the gear). |
| 1. Place the vehicle on a viewing ditch or lift. |
| 2. Remove the gearbox (see “Removing and installing the gearbox”). |
| 3. If you are installing the old pressure plate, mark in any way (for example, punching) the relative positions of the disk housing and the flywheel in order to install the pressure disk in its previous position (to maintain balance). | 4. Remove the six bolts securing the pressure plate to the flywheel, holding the flywheel from turning with a mounting blade. |
| 5. Remove the pressure and driven disks, while holding the driven disk. | 6. Inspect the driven disk. Cracks on the parts of the driven disk are not allowed. Check the wear of the friction linings. If the rivet heads are recessed by less than 0.2 mm, and the surface of the friction linings is oily or the rivet joints are loose, then the driven disk (or friction linings) must be replaced. |
| 7. Check the reliability of the damper springs in the driven disk hub sockets. If the springs are broken, replace the disc. Check the runout of the driven disk if warping is detected during a visual inspection. If the runout value exceeds 0.5 mm, replace the disc. | 8. Using an external inspection, evaluate the condition of the pressure plate diaphragm spring. Cracks on the diaphragm spring are not allowed. The contact points between the spring petals and the clutch release bearing must be in the same plane and have no obvious signs of wear. |
| 9. Install the clutch in the reverse order of removal. |
| NOTE Before tightening the pressure plate mounting bolts, carefully center the drive plate using a mandrel. If this is not done, installation of the gearbox will be difficult. |
Replacing the clutch release bearing
A sign that the clutch release bearing needs to be replaced is increased noise when the clutch pedal is pressed.
| 1. Remove the gearbox (see “Removing and installing the gearbox”), if it was not removed to repair the clutch. |
| 2. Disengage the bearing from the fork. | 3. Pull back the fork and... |
| 4. ...remove the bearing. |
| 5. Install the new bearing in the reverse order of removal. |
| 6. Lubricate the splines of the input shaft with a thin layer of lubricant LSC-15 or Litol-24. |
| 7. Install the gearbox and removed components in the reverse order of removal. |
How to remove the gearbox on a VAZ 2121 Niva
The basket looks like a steel circle with a bulge. The design of the device contains release elements, which, when the clutch is engaged, act on the driven disk. These elements are driven by a release bearing, which operates through human mechanical action.
The driven disk has the shape of a round base, consisting of friction linings. This disc is a torque transmitter. It connects directly to the flywheel of the Chevy Niva engine.
Clutch replacement Niva 21214 repair
In normal mode, while the car is moving, the disc is engaged with the flywheel, and they rotate together. When you press the clutch pedal, the disc is acted upon by the release elements of the basket (petals), which move it away from the flywheel. At this time, the torque on the gearbox shaft disappears and the transition to the next gear can be made.