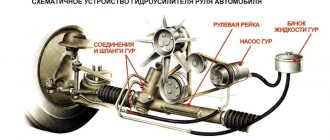
Even if the car driver has great physical strength, turning a tight steering wheel is unlikely to give him pleasure. Therefore, power steering appeared a long time ago, and the hydraulic principle became the classic way to reduce drive resistance.
Then designers began to widely use electric amplifiers, but hydraulics are still used because they have their advantages.
Functions and purpose of power steering
As the name suggests, power steering is used in the steering mechanism of a car. Power steering enhances the driver's actions while the vehicle is maneuvering. Such a system is installed in trucks so that the driver can turn the steering wheel at all, and passenger cars are equipped with this mechanism to increase comfort.
In addition to facilitating effort when driving, the hydraulic booster allows you to reduce the number of full turns of the steering wheel to achieve the required position of the front wheels. Cars that do not have such a system are equipped with a steering rack with a large number of teeth. This makes the task easier for the driver, but at the same time increases the number of complete turns of the steering wheel.
Another purpose of power steering is to eliminate or soften shocks coming to the steering wheel from the drive wheels when the car drives on a road with poor surface or runs into an obstacle. It often happens that in a car without this auxiliary system, when driving, the steering wheel is simply torn out of the driver’s hands when the wheels hit a large uneven surface. This happens, for example, in winter when driving on deep ruts.
Components of the amplifier. Types of power steering
In general, the main task of an amplifier in a passenger car is to increase safety, and only then to ensure comfort.
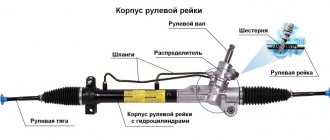
The power steering device includes several main components:
- pump;
- distributor;
- power cylinder;
- connecting pipelines.
Elements of hydraulic booster
Two types of hydraulic boosters were used on the equipment:
- Combined (integrated).
- Separated.
The combined type is distinguished by the fact that the distributor and cylinder are integrated into the steering mechanism, which makes it possible to significantly reduce the metal consumption of the structure and make it more compact. Thanks to this, it has become widespread, including on passenger cars.
The split type was used on a number of trucks. Its peculiarity lies in the fact that the power cylinder is a separate element that interacts with the steering drive. But because of this decision, the power steering design turned out to be more cumbersome, so it is not used on passenger cars.
Pump
From the name of the amplifier it is clear that the main working element in this mechanism is liquid. Since it is incompressible, when pressure is created, a force can be obtained that will perform the required function.
And this pressure is created by the pump. In a simpler mechanism, the pump is belt driven from the crankshaft. This design element can be gear (less common type) or rotary (also called blade). Most often, the second option is used on cars.
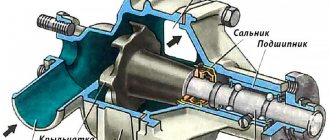
The design of a rotary-type power steering pump is very simple. Its main elements are a housing with supply and outlet fittings and a shaft, at one end of which a drive pulley is installed, and at the other - a rotor with blades. This rotor is located in a specially shaped chamber - the stator (its role is played by the housing). Due to this shape of the stator, liquid is pumped, which is then supplied to the outlet fitting leading to the distributor.
Power steering vane pump
The disadvantage of a pump driven from the crankshaft is that the pressure generated varies depending on engine speed. Because of this, the force created by the power steering at low speeds is insufficient, and at high speeds it is excessive, which leads to the appearance of an effect such as an “empty steering wheel” (“feedback” of the steering control is absent, so the information content of the steering control is very small).
Operating principle of gear and rotary pumps
To eliminate this drawback, the power steering pump device includes a pressure regulator that maintains it at a given value. It functions very simply - when the pressure is exceeded, the regulator, moving, opens a bypass channel between the supply and outlet channels and part of the pressure is released.
Distributor
Liquid under pressure created by the pump is supplied to the distributor. The task of this component is to distribute fluid flow depending on the steering position. The most widely used valve in passenger cars is the rotary type spool valve. This unit is an intermediate link between the column shaft and the steering gear.
Rail distributor device
The distributor consists of two elements - a shaft and a rotary spool. These elements are mounted on a torsion bar, which connects the column shaft and gear.
The distributor is approached by a supply fitting from the pump, a return line (through which the liquid returns to the pump) and two terminals leading to the power cylinder.
Distributor operating diagram
The essence of the distributor's operation is this: when the steering wheel rotates, the resistance coming from the wheels leads to twisting of the torsion bar, which in turn ensures the rotation of the spool relative to the distributor shaft. Because of this, some channels open and others close, that is, a redistribution of the fluid flow occurs.
Cylinder
The power cylinder acts as an actuator. In the combined type of power steering, it is completely integrated into the steering mechanism. The piston is the steering rack, which additionally has a washer with seals, and the cylinder is the housing. The piston divides the cylinder into two chambers connected by pipelines to the distributor.
Operating principle of power steering
So, the hydraulic booster is needed to make it easier for the driver to maneuver the car. This is the principle on which the mechanism works.
When the car’s engine is running but not going anywhere, the pump pumps fluid from the reservoir to the distribution mechanism and back in a vicious circle. As soon as the driver begins to turn the steering wheel, a channel corresponding to the direction the steering wheel is turning opens in the distributor.
Liquid begins to flow into the cavity of the hydraulic cylinder. On the reverse side of this container, power steering fluid moves into the reservoir. The movement of the steering rack is facilitated by the movement of the rod attached to the piston.
The main requirement for steering a vehicle is to ensure that the rotary wheels return to their original position after a maneuver when the driver releases the steering wheel. If you keep the steering wheel turned, the steering rack turns the spool. It is aligned with the timing gear drive shaft.
Since no more force is applied, the distributor aligns and no longer exerts any force on the piston. The mechanism stabilizes and begins to idle, as if the wheels were standing straight. The power steering oil again circulates freely along the line.
When the steering wheel is positioned to the extreme left or right (all the way), the maximum load is placed on the pump, because the distributor is no longer in the optimal position. In this situation, the liquid begins to circulate in the pump cavity. The driver can hear that the pump is working in increased mode by a characteristic squeak. To facilitate the operation of the system, just release the steering wheel a little. This ensures free movement of fluid through the hoses.
The following video explains how power steering works:
Power steering - the design and principle of operation of power steering on a Lego model!
Design of a power steering vane pump
Design of a vane pump
Structurally, the pump consists of the following elements:
- frame;
- rotor;
- lid;
- stator;
- needle bearing;
- pulley;
- stuffing box;
- engine speed increase sensor;
- flow control valve.
In addition to these elements, the design of the device contains many other small parts.
Power steering device
The power steering system is designed in such a way that even if it fails completely, the car can still be safely driven. This mechanism is used on almost any type of steering. The most common application is rack and pinion systems.
In this case, the gur consists of the following elements:
- Reservoir (similar to an expansion tank for the cooling system or brakes);
- Power steering pump;
- Power steering distributor;
- Hydraulic cylinder;
- High and low pressure connecting hoses.
Power steering reservoir
The tank is a reservoir from which oil is sucked by the pump for the operation of the mechanism. The container has a filter. It is needed to remove chips and other solid particles from the working fluid that may interfere with the operation of some elements of the mechanism.
To prevent the oil level from dropping to a critical value (or even lower), the tank design has a hole for the dipstick. The power steering fluid is oil-based. Thanks to this, in addition to the required pressure in the line, all elements of the mechanism are lubricated.
Sometimes the tank is made of transparent, durable plastic. In this case, a dipstick is not needed, and a scale with the maximum and minimum oil levels will be marked on the wall of the tank. Some mechanisms require short operation of the system (or several turns of the steering wheel left/right) to determine the exact level.
The dipstick, or in the absence of one, the tank itself, often has a double scale. On one part the indicators are indicated for a cold engine, and on the second - for a warm one.
Power steering pump
The function of the pump is to ensure constant circulation of oil in the line and create pressure to move the piston in the mechanism. In most cases, manufacturers equip cars with a vane modification of pumps. They are mounted on the cylinder block. A timing belt or a separate pump drive belt is put on the device pulley. As soon as the motor starts running, the pump impeller also begins to rotate.
The pressure in the system is created due to engine speed. The greater their number, the greater the pressure created in the hydraulic booster. To prevent excessive pressure from being created in the system, the pump is equipped with a relief valve.
There are two modifications of power steering pumps:
- Adjustable. This modification maintains stable pressure in the line due to a change in the working volume of the device;
- Unregulated. Such modifications are equipped with a pressure reducing valve, which maintains stable pressure in the line.
More modern pumps are equipped with an electronic pressure sensor, which sends a signal to the computer to open the valve at increased pressure.
Power steering distributor
The distributor can be installed either on the steering shaft or on the steering gear drive. It directs the working fluid into the desired cavity of the hydraulic cylinder.
The distributor consists of:
- Torsion bar - a rod that works to twist. One of its edges is inserted into the cavity of the distributor shaft, and the other is fixed inside the spool.
- Shaft – a hollow cylindrical element. It has channels for oil movement. It connects to the driveshaft of the steering mechanism;
- A spool connected to the power steering shaft. At the other end it is connected by a gear to the steering mechanism.
There are axial and rotary modifications of distributors. In the second case, the spool engages the teeth of the steering rack due to rotation around the shaft axis.
Hydraulic cylinder and connecting hoses
The hydraulic cylinder itself is a mechanism that experiences pressure from the working fluid. It moves the steering rack in the appropriate direction, which makes the driver’s work easier when performing maneuvers.
Inside the hydraulic cylinder there is a piston with a rod attached to it. When the driver begins to turn the steering wheel, excess pressure is created in the cavity of the hydraulic cylinder (about 100-150 bar), due to which the piston begins to move, pushing the rod in the appropriate direction.
From the pump to the distributor and hydraulic cylinder, the fluid flows through a high-pressure hose. Often, a metal tube is used instead for greater reliability. During idle circulation (reservoir-distributor-reservoir), oil moves through the low pressure hose.
Advantages and disadvantages of power steering
It is difficult to talk about the disadvantages of power steering, since this system has proven itself to be reliable and quite simple. Can be compared with other power steering: ESD and EGUR, which are installed on new cars with modern electronics. Compared to them, the classic power steering looks a little cumbersome, but it does not require precise and coordinated operation of sensors, the ECU and the electric drive itself.
The power steering system has few disadvantages:
- A certain loss of engine power, which is spent on driving the hydraulic pump;
- The need for maintenance every 2-3 years, since wear products and solid particles damage the amplifier mechanism.
The advantages are ease of control, maneuverability, comfort and safety. Well, reliability, since power steering failures happen quite rarely.
Types of power steering
Modification of power steering depends on the performance of the mechanism and its technical and dynamic characteristics. There are these types of power steering:
- Spool version - has high efficiency, used in budget cars and middle-class models;
- Nozzle/flap option - disadvantages include low efficiency and requires more energy when the load increases. Due to such indicators, the use of this power steering modification increases the load on the power unit. They have high sensitivity, therefore they are most often used in bridge-type hydraulic boosters;
- Jet version - has no friction force in the distributor cavity, and is also easy to operate and durable. Such hydraulic boosters are not picky about oil quality;
- The electric option is a modern technology that functions even when the engine is turned off. Mainly installed on sports cars and premium cars.
Some modern power steering systems use a hydraulic radiator to cool the hydraulic fluid.
Power steering device diagram
There are two types of power steering: standard and electric power steering, which is equipped with a special electronic control unit and solenoid valve. In general, their design is similar and will fit perfectly into any steering mechanism. Nowadays, most cars are equipped with a steering rack, so let’s look at the power steering and power steering devices using its example.
The main parts of the hydraulic booster include:
- Spool type distributor
- Special pump
- Tank in which the working fluid is stored
- Working cylinder
- Fluid transfer hose system
The power steering unit can be additionally equipped with a speed sensor, solenoid valve and a special control unit.
The working cylinder and distributor are installed on the steering rack and form a single unit with it. The purpose of the pump is to create the necessary fluid pressure and is driven by a belt drive from the engine crankshaft.
Maintenance
The steering mechanism and hydraulic booster are reliable mechanisms in a car. For this reason, they do not require frequent and expensive maintenance. The most important thing is to follow the regulations for changing the oil in the system, which are determined by the manufacturer.
As part of power steering maintenance, it is necessary to periodically check the fluid level in the reservoir. If the level drops noticeably after adding the next portion of liquid, you should check whether oil is leaking at the hose connections or at the pump seal.
How it works
See also
What is athermal glazing in a car: how it works
In order to correctly understand not only the device, but also the operating principle on which the power steering is based, we should consider several illustrative situations. Plus, the video will help you visualize many moments.
Having presented several situations, in each of them we will briefly explain what happens to the amplifier.
see also
Passenger semi-trailer: design description, buy or make it yourself
- The car is stationary, the wheels are straight
. Now the power steering is not working and the special fluid is simply gradually pumped throughout the entire system, from the reservoir to the distributor, and back; - The steering wheel begins to rotate
. The torque from the steering wheel goes to the distributor shaft, and then to the torsion bar, which begins to twist. In this case, the spool does not rotate, which is due to the force of friction. When moving relative to the presented spool, the shaft in question opens a special channel. This allows fluid to begin flowing into a specific cavity in the cylinder. The cavity directly depends on which direction the rotation occurs. The liquid begins to put pressure on the piston with the rod, which allows you to move the steering rack and quite easily turn the wheels to the left or right; - The rotation has ended, but the steering wheel remains in the turned position
. As the rack moves, it rotates the spool and aligns it with the shaft. Namely the shaft of the considered distributor. Now the distributor is in neutral, and the liquid begins to simply continue to circulate through the system. No serious work is done at this moment; - The steering wheel is in its extreme position and held
. This is the heaviest load on the power steering. This is due to the fact that the distributor is not able to return to neutral, and the liquid actively circulates in the pump itself. This makes noise. As soon as the steering wheel is released, everything returns to normal.
An important advantage of the unit in question is that the steering mechanism will still remain operational, even if the power steering itself fails.
Frequency of power steering fluid replacement
In theory, the power steering fluid is not under the aggressive influence of high temperatures, as in an engine or gearbox. Some drivers do not even think about periodically changing the oil in this system, except in cases where the mechanism is being repaired.
Despite this, manufacturers recommend periodically changing power steering oil. Of course, there are no strict limits, as is the case with motor oil, but this regulation depends on the intensity of the mechanism.
If a car travels about twenty thousand kilometers a year, then the fluid can be changed no more than once every three years. The reasons for periodic fluid changes are:
- Insignificant, but still heating of the oil during circulation through the main line;
- Natural aging of the product;
- The appearance of foreign particles due to wear caused by friction of metal parts (the problem arises if the mechanism is made of low-quality materials).
If, when checking the oil level in the tank, the car owner smells burnt oil, it means it is already old and needs to be replaced.
Here is a short video about how this work is done correctly:
How to change power steering fluid
Power steering pump design.
Now let's go through the components of the power steering system separately. Probably the most frequently failing part of this system is the pump, since it works the hardest, constantly creating excess pressure in the system. There are two main types of pumps:
- lamellar
- gear
In the first case, pressure is created due to the rotation of a rotor with movable blade plates (see video)
Scheme of operation of a vane pump
The essence of the work is to change the volume between the rotor, stator, plates and end disks, which is achieved by positioning the axis of rotation of the rotor with eccentricity relative to the center of the stator (i.e., the axis is shifted to the side). Accordingly, on one side the gap between the rotor and stator is larger than on the other. When moving in a larger part of the gap, the plates move out under the influence of centrifugal force, and when moving towards a smaller gap, they move back. As the space expands, a certain vacuum (low pressure) is formed, which sucks the hydraulic fluid into the chamber. Then, narrowing, the chamber approaches the hole in the direction of discharge and the liquid is thrown out there with force, forming increased pressure in the system.
This type is the most common in the automotive industry because it has the best efficiency, and can also be dual-circuit (the second circuit can supply pressure to the hydraulic suspension), as well as adjustable.
In the second case, the rotation of two gears inside the pump housing is used to pump fluid into the system.
Diagram of operation of the power steering gear pump
One of the gears is driving, the second is driven. When the teeth separate, a vacuum is created, which sucks liquid into the pump. Next, the fluid moves along the outer radius of rotation of the gears in the spaces between the teeth and is forcefully thrown into the discharge line before the teeth engage. This type is simpler and, as a result, more reliable in operation.
Basic faults and troubleshooting methods
Repairing power steering often comes down to replacing seals. The work can be done by purchasing a power steering repair kit. Power steering failure occurs extremely rarely and is mainly due to fluid leakage. This manifests itself in the fact that the steering wheel turns tightly. But even if the amplifier itself fails, the steering continues to function.
Here is a table of main faults and solutions:
| Malfunction | Why does it occur | Solution option |
| While driving, shocks from uneven surfaces are sent to the steering wheel. | Poor tension or wear on the pump drive belt | Replace or tighten the belt |
| The steering wheel turns hard | The same problem with the belt; The level of the working fluid is below the minimum value or close to it; A small number of crankshaft revolutions during idle operation; The filter in the tank is clogged; The pump creates weak pressure; The amplifier system is aired. | Change or tighten the belt; Replenish the fluid volume; Increase engine speed (adjust); Change the filter; Restore the pump or replace it; Clamp the hose connections. |
| It takes effort to turn the steering wheel to the middle position | Mechanical pump failure | Replace the oil seal, pump repair or replacement |
| Turning the steering wheel to one side requires a lot of effort | Pump faulty | Repair the pump or replace the seal |
| It takes more effort to turn the steering wheel quickly | Poor drive belt tension; Low engine speed; System too airy; Pump broken. | Adjust the drive belt; Adjust the engine speed; Eliminate air leaks and remove the air plug from the line; Repair the pump; Diagnostics of the steering mechanism elements. |
| Decreased steering feedback | The fluid level has dropped; Air-conditioning of the power steering system; Mechanical malfunction of the steering rack, tire or other parts; Parts of the steering mechanism have worn out (not a problem with the power steering). | Eliminate leaks, replenish the lack of oil; Remove the air lock and tighten the connections so that air does not leak; Diagnostics and repair of the steering mechanism. |
| Power steering hums during operation | The oil level in the tank has dropped; The pressure relief valve is activated (the steering wheel is turned all the way). | Check for a leak, eliminate it and replenish the volume; Eliminate airing; Check the serviceability of the pump; Check whether sufficient pressure is generated by the pump; Do not turn the steering wheel all the way. |
If the car is equipped with an electric booster, then if any alarm signals appear, you should immediately contact a specialist. Electronics are tested using appropriate equipment, so without the necessary skills it is better not to try to repair anything in the electrical system yourself.
What is power steering and why is it needed?
Anyone who has ever driven a car that is not equipped with power steering (or electric power steering) has probably noticed that at low speeds it takes a lot of effort to turn the steering wheel. At the same time, if the car is moving at a fairly significant speed, then the opposite effect is observed: the steering wheel turns too easily, almost without any effort. This creates considerable inconvenience when driving a car (especially for inexperienced drivers) and, as experience and statistics show, often causes emergency situations.
That is why, even at the dawn of motorization, designers began to think about how this drawback could be mitigated. As a result, in 1925, American Francis Davis decided to install power steering on his personal car Pierce-Arrow Roadster. It should be noted that the design of this device was by no means an innovation even then: the fact is that long before the mid-twenties of the last century, hydraulic amplifiers were already actively used on sea vessels.
Power steering operating principle
If the car is stationary, moving straight, the pump pumps idle hydraulic oil inside the system. When the steering wheel begins to move, the torsion bar begins to twist, and the spool rotates relative to the distribution sleeve. At the same time, connecting hoses open, through which oil from the tank enters a certain chamber in the power cylinder (this depends on which direction the car maneuvers under the influence of turning the steering wheel). And from another chamber, hydraulic oil simultaneously enters the tank through open ducts. The cylinder piston moves the steering rack, while simultaneously transmitting force to the steering rods that turn the wheels.
If the car maneuvers at low speed, then the efficiency of the power steering is maximum. This is achieved by increasing the number of revolutions of the pump motor. An increase in its performance contributes to an intensive flow of hydraulic fluid into the cylinder and the force applied to turning the steering wheel decreases significantly. Increasing the speed of the machine reduces the rotation speed of the electric motor, and the solenoid valve comes into action, which reduces the flow of the hydraulic system channels, and more effort has to be applied to turn the steering wheel.
Pros and cons of power steering
The indisputable advantage of power steering and its main property is to make the work of your hands easier when maneuvering during parking. But the amplifier has another useful property - it softens the force on the steering wheel from impacts on uneven roads.
The disadvantage of power steering is the absence or low reaction force on the steering wheel. The hydraulic booster assists the driver too much, eliminating the return force that provides the “feeling of the car.” And when developing and adjusting the chassis, designers need to achieve excellent information content of the steering drive and at the same time not make the steering wheel too tight. There are many factors to consider: pump efficiency, rear and front suspension geometry, wheel mounting angles, overall tire characteristics, and even body torsional rigidity!
Therefore, good cars in this regard are extremely rare. Still, many companies deliberately abandon information content in favor of comfort, knowing the sympathy of their clientele. A striking example of this is Toyota cars. Although in Europe the opposite is true.
The fruits of the designers' labor are delightful. Another task for them is to make sure that at low speeds the steering wheel remains light, and at high speeds it becomes elastic and informative. There are different ways out of the situation. An electrohydraulic pressure modulator has been added to the circuits of German hydraulic boosters from the well-known company ZF (all models of Jaguar, Audi A6 & A8, BMW 5 and 7 series). As the speed increases, it holds back the pressure in the working circuit, which is why the assistance of the hydraulic booster is equal to zero.
We recommend: Design and principle of operation of automatic transmission solenoids
There is another way to solve the problem - to drive the power steering pump from an electric motor instead of the crankshaft. By changing the rotation speed of the electric drive using electronics, it is possible to vary the efficiency of the pump as desired.
Power steering service
The owner of a car equipped with power steering can independently perform the following operations:
- monitor the level and condition of the liquid in the expansion tank;
- periodically inspect the pipes and fittings for cracking and oil leaks;
- change the hydraulic fluid at the intervals specified in the operating instructions;
- monitor the appearance of extraneous noise that occurs when the pump bearings are critically worn;
- Change the drive belt in a timely manner so that it does not break somewhere along the way.
The fluid poured into the power steering system serves not only as a working fluid, but also as a lubricant for the pump. Therefore, when adding or replacing, it is important to use oils recommended by the manufacturer, otherwise the unit may fail prematurely.
Power steering: main characteristics, advantages and disadvantages
Power steering is designed to make it easier for the driver to control the car. This “device” significantly reduces the effort required when turning the steering wheel. When did the first hydraulic boosters appear, and how do they work? About this in our article.
The history of the appearance of the hydraulic booster
During the first decades of its existence, no power steering existed at all. It must be said that some modern simple commercial vehicles, such as ZAZ Chance or Reault Kangoo in their factory configuration, are produced without an amplifier to this day.
On the first models there was no need for power steering: since the speeds were low, the requirements for handling were quite modest. Manufacturers also did not immediately become interested in comfort, and the tires were very narrow, with a small contact patch with the road. And the only way to make working with the steering wheel easier was to increase the diameter of the steering wheel and the drive gear ratio.
The first amplifiers appeared in the late 30s, and their owners were mining dump trucks.
What were the first power steering systems? At first these were simple pneumatic boosters, powered by air brake compressors. However, hydraulics turned out to be not only more expensive and more complex than pneumatics, but also more accurate and quieter. The first power steering (hereinafter referred to as power steering) appeared in 1951. Its owner was the Chrysler Crown Imperial. Three years later, power steering appeared in Europe on the Citroen DS 19.
What is power steering?
In short, power steering is a mechanism based on a pump. It is driven by the crankshaft belt. As a result, oil is sucked from the tank and pumped under high pressure into the distributor. The latter monitors the amount of force on the steering wheel and helps turn the wheels, doing this in a strictly dosed manner. For this purpose, a tracking device is used, built into the section of the steering shaft. As a rule, this is a torsion bar.
When the car is stationary or driving in a straight line, there is no load on the steering shaft, the torsion bar is not twisted, the metering channels of the distributor are blocked, and the oil drains back into the reservoir.
When the steering wheel turns and the wheels begin to exert resistance, the torsion bar begins to twist with a force proportional to the force on the steering wheel. The dosing channels open and the oil enters the actuator. Foreign cars, as a rule, use ATF oil (the same as for automatic transmissions).
Main advantages of power steering
- Power steering greatly facilitates the work of your hands when performing various maneuvers, especially parking ones.
- The transmission of shocks caused by road unevenness to the steering wheel is significantly weakened.
Disadvantages of power steering
Lack or absence of reactive force on the steering wheel. Since the power steering helps the driver too actively, the latter often loses the “feeling of the car.” Therefore, designers put a lot of effort into finding a compromise between the aforementioned “feel” and driver assistance.
Since the manufacturer has to take into account many factors such as pump performance, front suspension geometry, rear suspension parameters, wheel alignment, tire characteristics and much more, it becomes clear that finding a car with perfect power steering is extremely difficult.
Power steering properties largely depend on the manufacturer. For example, Toyota relies on comfort, sacrificing information content, and European manufacturers do exactly the opposite. Therefore, in order to have an idea of the power steering located in the car, you must first study the manufacturer’s traditions in this area.
Power steering care
As a rule, the failure of any component of the power steering is associated not with “congenital” defects, but with a violation of operation. Therefore, the motorist should regularly do the following:
- Monitor the oil level in the tank;
- Monitor the tension of the drive belt and, if necessary, adjust it;
- Ensure careful monitoring of the tightness of the system;
- Replace the oil and filter element every year or two. They also need to be changed if the color of the oil has changed. By removing old fluid, the motorist carries out a comprehensive cleaning of the entire power steering system;
- It is necessary to regularly look at the power steering fluid reservoir, monitoring its level. The color of the liquid can be seen on the dipstick by unscrewing the cap. On more advanced cars, you can find a low power steering fluid level indicator on the dashboard.
If any extraneous sounds occur, leaks are detected, or if the machine begins to behave inappropriately, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics at a service station as soon as possible.
You should avoid holding the steering wheel in the extreme position for a long time (more than 5 seconds). This may cause the oil to overheat. In addition, prolonged operation of the machine with a non-working pump results in accelerated wear of the distributor and steering mechanism parts, since they are not designed for this operating mode.
Avoid running into obstacles. When the car “jumps” onto the curb, the driver only feels a slight push on the steering wheel. Although, without power steering, the steering wheel would respond with a strong jerk, which could even cause injury.
It should be remembered that if the load is not felt on the steering wheel, this does not indicate that the car can easily overcome any obstacles.
The power steering pump can develop high pressures, maintaining the desired position of the steering rack shaft. If you drive recklessly onto the curb in this position, the system will try to maintain the wheel position set by the steering wheel, which, in fact, will provoke a strong impact on the curb. As a result, the likelihood of damage to the steering rack and tie rods increases. Rotating the steering wheel when the wheels are pressed tightly against the curb can lead to approximately the same consequences (as an option, actively working the steering wheel when driving on a rut).
Under no circumstances should you accelerate with your wheels turned too far while standing on a secondary road waiting for clearance. This significantly increases the pressure on the power steering, which can damage the pump and sealing elements. If low temperature is added to this, the viscosity of the working fluid will increase and its flow through calibrated holes and valves will be significantly more difficult, and the load on the system will noticeably increase. Therefore, do not start driving in cold weather without first warming up the car. Also try to avoid heavy steering when leaving a parking lot.
Electric power steering
This type of amplifier is completely devoid of hydraulics. Unlike power steering, in which the working fluid constantly moves through the pipes, consuming additional fuel, the electric power steering consumes energy only while the steering wheel is rotating. In addition, it does not depend on temperature changes and engine speed.
In addition, the efficiency of the electric steering motor significantly exceeds that of the hydraulic pump. It is more reliable:
- Does not have hose belts, seals, gaskets;
- Has no liquids;
- Does not require maintenance (topping up and replacing working fluid).
This is exactly what most car enthusiasts would like. True, professionals, despite all these advantages, complain about the artificiality of sensations while driving.
Source: https://nivus.ru/info/articles/gidrousilitel-rulya-osnovnye-kharakteristiki/