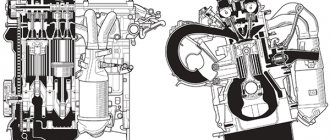
Engine history
In Russia and around the world, Japanese cars from the Toyota concern enjoy deserved popularity due to their reliability, excellent technical characteristics and relative affordability. Japanese engines, the heart of the concern's cars, played a significant role in this recognition. For several years, a number of products from the Japanese automaker were equipped with the 4A FE engine, the technical characteristics of which still look good to this day.
Appearance:
Its production began in 1987 and continued for more than 10 years - until 1998. The number 4 in the name indicates the serial number of the engine in the “A” series of Toyota power units. The series itself appeared even earlier, in 1977, when the company's engineers faced the task of creating an economical engine with acceptable technical performance. The development was intended for the B-class car (subcompact according to the American classification) Toyota Tercel.
The result of engineering research was four-cylinder engines with power from 85 to 165 horsepower and volume from 1.4 to 1.8 liters. The units were equipped with a DOHC gas distribution mechanism, a cast iron body and aluminum heads. Their heir was the 4th generation, discussed in this article.
Interesting: The A-series is still produced at the joint venture Tianjin FAW Xiali and Toyota: 8A-FE and 5A-FE engines are produced there.
History of generations:
- 1A – years of production 1978-80;
- 2A - from 1979 to 1989;
- 3A – from 1979 to 1989;
- 4A - from 1980 to 1998.
Maintenance schedule 4A FE 1.6 l/110 l. With.
The 4A FE inline petrol engine must be serviced within the following periods:
- The engine oil life is 10,000 km, then the lubricant and filter need to be replaced;
- the fuel filter must be replaced after 40,000 miles, the air filter twice as often;
- The service life of the battery is set by the manufacturer, on average 50 - 70 thousand km;
- spark plugs should be changed every 30,000 km and checked annually;
- crankcase ventilation and adjustment of thermal clearances of valves are carried out at the turn of 30,000 vehicle mileage;
- Antifreeze is replaced after 50,000 km; hoses and radiator must be inspected constantly;
- the exhaust manifold can burn out after 100,000 km.
Replacing the timing belt
The initially simple design of the internal combustion engine allows you to carry out maintenance and repairs on your own in the garage.
Specifications 4A-FE
Let's take a closer look at the engine markings:
- number 4 - indicates the number in the series, as mentioned above;
- A – engine series index, indicating that it was developed and began production before 1990;
- F – talks about technical details: four-cylinder, 16-valve unboosted engine driven by a single camshaft;
- E – indicates the presence of a multi-point fuel injection system.
In 1990, the power units in the series were modernized to enable operation on low-octane gasoline. For this purpose, a special power system for leaning the mixture, LeadBurn, was introduced into the design.
System illustration:
Let us now consider what characteristics the 4A FE engine has. Basic engine data:
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Volume | 1.6 l. |
| Developed power | 110 hp |
| Engine weight | 154 kg. |
| Engine compression ratio | 9.5-10 |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Location | Row |
| Fuel supply | Injector |
| Ignition | Distributor |
| Valves per cylinder | 4 |
| BC building | Cast iron |
| Cylinder head material | Aluminium alloy |
| Fuel | Unleaded gasoline 92, 95 |
| Environmental Compliance | Euro 4 |
| Consumption | 7.9 l. – on the highway, 10.5 – in city mode. |
More about the engine
4a-fe - the most common A-series engine, has been produced without significant upgrades since 1988. Such a long life in production without modifications was possible due to the complete absence of serious design flaws.
In mass production, 4a-fe and 7a-fe engines were installed on cars of the Corolla family, without any changes. For installation on Corona, Carina and Caldina, they began to be equipped with a lean-burn system, or in English Lean Burn. This improvement, as the name suggests, is designed to reduce exhaust emissions and specific fuel consumption. The modernization consists of changing the shape of the cavities of the intake manifold and moving the fuel injectors to the head of the block as close as possible to the intake valves.
Due to this, the uniformity of mixing of the air-fuel mixture is improved; gasoline does not settle on the walls of the manifold and does not enter the cylinder in large drops. This leads to a reduction in fuel losses and, as a result, it becomes possible to operate the engine on a lean mixture. With a normally operating Lean Burn system, gasoline consumption can drop almost below 6 l/100 km, and the loss of power will be no more than 6 l. With.
But engines running on a lean mixture are sensitive to the condition of spark plugs, high voltage wires and the quality of the fuel. Therefore, there are frequent complaints from our owners of Japanese cars with Lean Burn about instability of idle speed and “failures” in transient conditions.
Device Features
Design features of 4A FE:
- in-line cylinders, bored directly into the cylinder block itself without the use of liners;
- gas distribution - DOHC, with two overhead camshafts, controlled by 16 valves;
- one camshaft is driven by a belt, the second camshaft receives torque from the first through a gear;
- the injection phases of the air-fuel mixture are regulated by the VVTi clutch; the valve control uses a design without hydraulic compensators;
- the ignition is distributed from one coil by a distributor (but there is a later modification of the LB, where there were two coils - one for each pair of cylinders);
- the model with the LB index, designed to work with low-octane fuel, has reduced power and reduced torque to 105 horsepower.
Interesting: if the timing belt breaks, the engine does not bend the valves, which adds to its reliability and attractiveness from the consumer.
Models of cars in which the Toyota 4Y engine was installed
The 4Y engine was installed on cars produced by the engine developer himself:
The subsidiary also found room for 4Y:
The attractiveness of the technical parameters was the reason for the installation of 4Y in the brainchild of other automakers:
To this day, the engine is successfully installed on loaders. This includes both Toyota’s personal special equipment, for example, Toyota 6FG10, and vehicles from other manufacturers. For example, Geneo 8FG is produced primarily only with a 4Y motor.
Toyota 4Y engine installed on a Daihatsu Rocky car
Version history 4A-FE
During its life cycle, the motor went through several stages of development:
Gen 1 (first generation) - from 1987 to 1993.
- Engine with electronic injection, power from 100 to 102 horsepower.
Gen 2 – rolled off production lines from 1993 to 1998.
- The power varied from 100 to 110 horsepower, the connecting rod and piston group and injection were changed, and the configuration of the intake manifold was changed. The cylinder head was also modified to work with new camshafts, and the valve cover received fins.
Gen 3 – produced in limited quantities from 1997 to 2001, exclusively for the Japanese market.
- This engine had increased power to 115 “horses”, achieved by changing the geometry of the intake and exhaust manifolds.
Third generation
Production lasted three years from 1989 to 1991. Changes are observed on the surface of the valve cover, the color of which has changed to silver. The letter designation of the motor was painted in red. This engine received the nickname “Red Top”, which translated into Russian means Red Top. The compression ratio increased to 10.3:1. Thanks to the experience gained from designing previous engines, Toyota designers decided to reduce the geometry of the intake duct. This led to the engine receiving a new nickname "smallport", which means "Little Channel" in Russian. The T-VIS system was not used in this generation.
To increase the service life of the motor, the following modifications were made:
- Installation of additional oil sprayers located under the lower surface of the pistons.
- The thickness of the connecting rods has been increased.
- The production of fingers was carried out according to the thickness of the fingers, which was 20 mm.
- The installation of a sensor that controls air flow was carried out in two types MAF and MAP, which depended on the market for which the engine was produced.
In the power plant supplied to the Japanese market, the power parameter was 125 hp. and the torque is 149 Nm, and in American market engines these figures were 128 hp. and 105 Nm respectively.
The 4A-GE engine was first introduced in 1983. The Toyota Sprinter Trueno AE86 and Toyota Corolla Levin AE86 were the first cars to install this power plant. 4A-GE was installed on the AE86 body according to the scheme of a rear-wheel drive car. Its transverse installation began with the Toyota MR2. 1991 was the last year in America that the 4A-GE engine was installed in the Toyota Carolla. The Geo Prizm GSi car was equipped with this power unit from 1990 to 1992. All, without exception, modifications of the 4A-GE were equipped with forged pistons, unlike Toyota units, in which they were cheaper, cast.
From 1990 to 2005, Toyota was a sponsor of the Atlantic Championship. At this time, the completed modification 4A-GE from Toyota Racing was installed on Formula Atlantic cars. The cylinder head of this “charged” engine has been modified. Thanks to this change, the power parameter was 240 hp. at a rotation speed of 8400 rpm. The maximum rotation speed was 12 thousand rpm, but this contributed to a reduction in engine life.
Pros and cons of the 4A-FE engine
The main advantage of the 4A-FE is its successful design, in which, in the event of a timing belt break, the piston does not bend the valve, avoiding expensive overhauls. Other benefits include:
- availability of spare parts and their availability;
- relatively low operating costs;
- good resource;
- the engine can be repaired and serviced independently, since the design is quite simple, and attachments do not interfere with access to various elements;
- The VVTi clutch and crankshaft are very reliable.
Interesting: when production of the Toyota Carina E began in the UK in 1994, the first 4A FE internal combustion engines were equipped with a control unit from Bosh, which had flexible settings. This became a lure for tuners because the engine could be re-tuned to extract more power while reducing emissions.
The main disadvantage is considered to be the above-mentioned LeadBurn system. Despite the obvious efficiency (which led to the widespread use of LB in the Japanese car market), it is extremely sensitive to the quality of gasoline and in Russian conditions demonstrates a serious drawdown in power at medium speeds. The condition of other components is also important - armored wires, spark plugs, and the quality of the engine oil is critical.
Weaknesses of the 4A engine
- Lambda probe;
- Absolute pressure sensor;
- Engine temperature sensor;
- Crankshaft seals.
Weaknesses of the engine in more detail...
Lambda probe
Failure of a lambda probe or, in other words, an oxygen sensor does not happen often, but in practice it does occur. Ideally, for a new engine, the service life of the oxygen sensor is small, 40 - 80 thousand km; if the engine has a problem with the piston and with fuel and oil consumption, then the service life is significantly reduced.
Absolute pressure sensor
As a rule, the sensor fails due to a poor connection between the inlet fitting and the intake manifold.
Engine temperature sensor
It does not refuse often, as they say rarely but aptly.
Crankshaft oil seals
The problem with crankshaft seals is related to the elapsed life of the engine and the elapsed time from the moment of manufacture. It manifests itself simply as a leak or squeezing out of oil. Even if the car has low mileage, the rubber from which the seals are made loses its physical properties after 10 years.
Where was the 4A FE placed?
The engine was equipped exclusively with Toyota cars:
- Carina – modifications of the 5th generation 1988-1992 (sedan in the T170 body, before and after restyling), 6th generation 1992-1996 in the T190 body;
- Celica – 5th generation coupe in 1989-1993 (T180 body);
- Corolla for the European and US markets in various trim levels from 1987 to 1997, for Japan - from 1989 to 2001;
- Corolla Ceres generation 1 – from 1992 to 1999;
- Corolla FX – generation 3 hatchback;
- Corolla Spacio – 1st generation minivan in the 110th body from 1997 to 2001;
- Corolla Levin - from 1991 to 2000, in E100 bodies;
- Corona – generations 9, 10 from 1987 to 1996, T190 and T170 bodies;
- Sprinter Trueno - from 1991 to 2000;
- Sprinter Marino - from 1992 to 1997;
- Sprinter – from 1989 to 2000, in different bodies;
- Premio sedan – from 1996 to 2001, T210 body;
- Caldina;
- Avensis;
- MR2.
Characteristics
Toyota 4A 1.6 power units (exact volume 1587 cc) were produced from 1982 to 2002. They used a cast iron cylinder block. Power indicators for different modifications of 4A series engines vary from 78 to 170 horsepower, with a torque value from 117 to 206 N*m. The compression ratio, depending on the modification of the power unit, ranges from 8 to 11. The injection system also depends on the engine version, whether a carburetor or an injector is used.
For 4A-FE engines it was allowed to use the following brands of gasoline: AI 92 and AI 95. The volume of oil poured into the engine is from 3 to 3.7 liters. What kind of oil to pour into the engine is decided depending on climatic conditions. The following brands can be used: 5W-30, 10W-30, 15W-40, 20W-50. The characteristics of the 4A-FE engine allow a maximum oil consumption of up to one liter per thousand kilometers.
4A-FE motors with the specified factory technical characteristics have a service life of 300,000 km.
Consumption
The fuel consumption rate depends on the vehicle on which the 4A-FE engine was installed. Below are gas mileage data for specific car models:
- Toyota Avensis in the T220 body with a five-speed manual transmission: in urban mode 10.6 l/100 km, in country mode – 6.1 l/100 km;
- Toyota Corolla with a four-speed automatic transmission: when driving in populated areas 10.3 l/100 km, on the highway – 6.4 l/100 km.
Modifications
The choice of 4A series engine versions is quite wide. The first to be developed in 1983 was a 4A-C carburetor power unit with eight valves and a capacity of ninety horsepower. Analogue versions were also developed for the European and Australian markets. They were marked: 4A-L, -LC, -E, -ELU, -F. Their power ranged from 78 to 100 horsepower. Over time, the engine has undergone quite serious changes. The following variations of the 4A series engines were developed:
- Injection version 4A-FE, which had several generations. Among them:
Block 4A-FE
- The 4A-FE Gen 1 was first equipped with fuel injection in 1987. Model of the power unit with a capacity of 100-102 hp. produced until 1993;
- the modernized 4A-FE Gen 2 used a new connecting rod and piston group, changed the design of the camshaft and fuel supply system, and also increased the maximum power to 110 hp;
- The latest version of the engine was 4A-FE Gen 3. It differed slightly from the second generation engine. Power increased to 115 horsepower.
- Subsequently, the 4A-FHE (110 hp) internal combustion engine model was produced. It involved improving the design of the 4A-FE engine;
- After this, Toyota and Yamaha jointly developed a version of the 4A-GE engine. During its existence, it has undergone five generations. Engine brands were distinguished by increased power, which amounted to:
- 124 hp – 4A-GE Gen 1;
- 125 hp – 4A-GE Gen 2;
- 128 hp – 4A-GE Gen 3;
- 160 hp – 4A-GE Gen 4;
- 165 hp – 4A-GE Gen 5.
Karina E
What models was it installed on?
The 4A-FE modification engine was used for the following car models:
- Avensis T220 from 1997 to 2000;
- Carina AT171/175 from 1988 to 1992 and AT190 from 1984 to 1996;
- Carina II AT171 from 1987 to 1992;
- Carina E AT190 from 1992 to 1997;
- Geo Prizm based on Toyota AE92 from 1989 to 1997;
- Corolla/Conquest AE92/AE111 from 1993 to 2002;
- Celica AT180 from 1989 to 1993;
Toyota Celica T200
- Corolla AE92/95 from 1988 to 1997, AE101/104/109 from 1991 to 2002, AE111/114 from 1995 to 2002;
- Corolla Ceres AE101 from 1992 to 1998;
- Corolla Spacio AE111 from 1997 to 2001;
- Sprinter AE95 from 1989 to 1991, AE101/104/109 from 1992 to 2002, AE111/114 from 1995 to 1998;
- Corona AT175 from 1988 to 1992, AT190 from 1992 to 1996, AT210 from 1996 to 2001;
- Sprinter Carib AE95 from 1988 to 1990, AE111/114 from 1996 to 2001
Other engines in the series
4A
The basic model that replaced the 3A series. The engines created on its basis were equipped with SOHC and DOHC mechanisms, up to 20 valves, and the “fork” of output power ranged from 70 to 168 forces on the “charged” turbocharged GZE.
4A-GE
This is a 1.6-liter engine, structurally similar to the FE. The characteristics of the 4A GE engine are also largely identical. But there are also differences:
- GE has a larger angle between the intake and exhaust valves - 50 degrees, in contrast to 22.3 for FE;
- The camshafts of the 4A GE engine are rotated by a single timing belt.
Speaking about the technical characteristics of the 4A GE engine, we cannot mention the power: it is slightly more powerful than the FE and develops up to 128 hp with equal volumes.
Interesting: a 20-valve 4A-GE was also produced, with an updated cylinder head and 5 valves per cylinder. It developed power up to 160 forces.
4A-FHE
This is an analogue of the FE with a modified intake, camshafts and a number of additional settings. They gave the engine greater performance.
4A-GZE
This unit is a modification of the sixteen-valve GE, equipped with a mechanical air pressurization system. 4A-GZE was produced in 1986-1995. The cylinder block and cylinder head have not undergone any changes; an air supercharger driven by the crankshaft has been added to the design. The first samples produced a pressure of 0.6 bar, and the engine developed power up to 145 horsepower.
In addition to supercharging, engineers reduced the compression ratio and introduced forged, convex pistons into the design.
In 1990, the 4A GZE engine was updated and began to develop power up to 168-170 horsepower. The compression ratio has increased, and the geometry of the intake manifold has changed. The supercharger produced a pressure of 0.7 bar, and the MAP D-Jetronic mass air flow sensor was included in the engine design.
The GZE is popular with tuners because it allows the installation of a compressor and other modifications without major engine conversions.
4A-F
It was the carburetor predecessor of the FE and developed up to 95 horsepower.
4A GEU
The 4A-GEU engine, a subtype of GE, developed power up to 130 horsepower. Motors with this marking were developed before 1988.
Engine tuning Toyota 4A-GE (4A-FE, 4A-GZE)
Chip tuning. Atmo
Engines of the 4A series were born for tuning; it was on the basis of the 4A-GE that the well-known 4A-GE TRD was created, which in its naturally aspirated version produces 240 hp. and spinning up to 12,000 rpm! But for successful tuning you need to take the 4A-GE as a basis, and not the FE version. Tuning 4A-FE is a dead idea from the start and replacing the cylinder head with a 4A-GE will not help here. If your hands are itching to modify the 4A-FE, then your choice is supercharging, buy a turbo kit, install it on a standard piston, blow to 0.5 bar, get your ~140 hp. and drive until it falls apart. In order to drive happily ever after, you need to change the crankshaft, the entire CNG to a low level, bring the cylinder head to a low level, install larger valves, injectors, a pump, in other words, only the cylinder block will remain original. And only then is it rational to install the turbine and everything accompanying it? That is why a good 4AGE is always taken as a basis, everything is simpler here: for GE of the first generations, good shafts with a phase of 264 are taken, pushers are standard, a direct-flow exhaust is installed and we get around 150 hp. Few? We remove the T-VIS intake manifold, take shafts with a phase of 280+, with tuning springs and pushers, give the cylinder head for modification, for Big Port the modification includes grinding of the channels, fine-tuning of the combustion chambers, for Small Port also preliminary boring of the intake and exhaust channels with the installation of enlarged valves, spider 4-2-1, set to Abit or January 7.2, this will give up to 170 hp. Further, a forged piston with a compression ratio of 11, phase 304 shafts, a 4-throttle intake, a 4-2-1 equal-length spider and a direct-flow exhaust on a 63mm pipe, the power will rise to 210 hp. We install a dry sump, change the oil pump to another one from 1G, maximum shafts - phase 320, power will reach 240 hp. and will spin at 10,000 rpm. How we will modify the 4A-GZE compressor... We will carry out work on the cylinder head (grinding the channels and combustion chambers), 264 phase shafts, 63mm exhaust, tuning, and we will count about 20 horses as a plus. The SC14 compressor or a more efficient one will allow you to increase the power to 200 forces.
Turbine on 4A-GE/GZE
When turbocharging 4AGE, you immediately need to lower the compression ratio by installing pistons from 4AGZE, take camshafts with phase 264, a turbo kit of your choice and at 1 bar the pressure will reach 300 hp. To get even higher power, as in an evil atmosphere, you need to tune the cylinder head, put the forged crankshaft and piston at ~7.5, a more efficient kit and blow 1.5+ bar, getting your 400+ hp.
ENGINE RATING: 4