Published:
21.03.2016
The crankshaft or, more simply, the crankshaft is the part inside the car engine that is responsible for transmitting the rotation of the pistons to the transmission system. Bearings are located at both ends of the shaft and serve to reduce friction when the shaft rotates inside the block.
The crankshaft bearing reduces friction when the pistons rotate
The crankshaft bearing is a consumable item because it is subject to strong mechanical stress during operation. Yes, and sudden temperature changes play a role. Therefore, it has to be replaced from time to time. Failure to promptly eliminate this seemingly insignificant detail can cause serious damage to the car's engine.
How to determine a breakdown
Visually, it is very difficult to understand that a malfunction in the crankshaft has occurred due to bearing failure. To do this you will have to completely disassemble the engine. But there are several signs that reliably indicate a breakdown:
- Severe crankshaft vibration or uneven operation due to imbalance. The reason for this is precisely a faulty bearing.
- Oil getting into the transmission system. This occurs due to damage to the seal by a faulty bearing. The oil seal cracks and some of the oil leaks out into the transmission.
Damage to this part affects not only the crankshaft, but also the input shaft located in the gearbox. As a result, problems with the transmission may occur.
Purpose
The axle bearing is located on the rear side of the crankshaft and serves to align and support the transmission input shaft. The main load when the crankshaft rotates goes to the main and connecting rod bearings. Since various axial forces act on the element in question rather weakly, it fails due to a design defect or over long runs due to natural wear. The crankshaft axial bearing is a conventional rolling or sliding bearing. It is worth pointing out that on many cars the structural unit in question is not provided as such, and the task of centering and ensuring uniform rotation of the gearbox input shaft is assigned to the bearings located in the gearbox.
Symptoms of a problem
Replacing the support bearing of the gearbox input shaft is a rather complex technological process. The point is not so much in removing the old part and installing a new product, but in the need to dismantle many units to gain access to the repair area. That is why it is important to correctly diagnose the malfunction so as not to carry out repairs in vain. The main signs indicating a breakdown include:
- rustling or rustling sound when the engine is running. The symptom can easily be confused with wear on the release lever. The difference is that the extraneous noise from a worn release lever immediately fades out when you press the clutch pedal and touch the petals of the diaphragm spring, while the support bearing of the gearbox input shaft will still rotate for some time by inertia, emitting characteristic sounds;
- Difficulty moving the gearshift lever. Since a broken crankshaft bearing does not perform its functions, a slight runout appears when the gearbox input shaft rotates. The effect of difficult shifting can also occur due to wedging, as a result of which when you press the clutch pedal, the driven disk does not fully open from the flywheel. At the same time, when parked with the internal combustion engine switched off, the gears may be difficult to engage, since the crankshaft bearing will “brake” the input shaft, preventing the helical gears from turning a little and engaging.
Is it possible to drive like this?
Often, replacing the crankshaft axial bearing is combined, for example, with replacing the clutch release or kit. It is quite unpleasant to have to undertake time-consuming and complex repairs just because of such a detail. If the rustling has just begun, then another few thousand kilometers can often be overcome without problems. But you shouldn’t delay replacement either, since jamming will damage the seat on the gearbox input shaft. Subsequently, the new spare part will no longer be able to perform its direct function. Therefore, it is not worth leading to complete destruction. In addition, some pressing methods using improvised means assume the integrity of the races and rolling elements.
Preparatory work
Since the crankshaft support bearing is located inside the engine, the engine itself must be removed to remove it. You don’t have to do this, but then the replacement procedure will become much more complicated and will require more effort. In addition, one bearing is most often not replaced. This is usually part of a car engine overhaul or gearbox and clutch removal for repair or replacement.
What to do before replacing a damaged part:
- Drive the car onto a viewing hole or overpass. For work safety, install special wheel chocks.
- Open the hood and disconnect the battery terminal with the minus sign.
- Inside the car, disconnect the gearshift lever by pressing on it and inserting a screwdriver into the bushing. While moving the screwdriver down, you need to simultaneously pull out the handle. After this, you need to remove the bushing rod - this can be done by unclamping it with two screwdrivers.
- Remove the cover that is located around the gear shift lever. It is screwed on with self-tapping screws, so this will not be difficult to do.
- On the gearbox itself, disconnect the terminals of the reversing lights and the speedometer drive cable.
- After this, disconnect the starter and move it forward a little. Then remove the clutch drive.
- To disengage the cardan, you need to unscrew the coupling from it, which is located on the gearbox side.
- Next, you need to unscrew the bolts securing the gearbox to the engine, holding the gearbox itself. Only two people can handle this.
- Pull the box back and pull out the input shaft. Remove the box, disconnect the clutch basket fastening and pull it out along with the disc.
- Lastly, the engine flywheel is removed, after which the desired assembly will become visible.
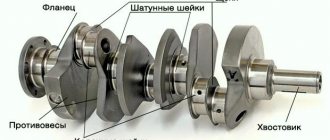
How to remove a bearing from a crankshaft with your own hands?
Car owners with vehicles of the classic VAZ series, during the entire life of using the car, may not even ask themselves the question of how to remove the bearing from the crankshaft. The axial or support roller bearing serves to ensure that the crankshaft is on the same axis with the gearbox input shaft. It is located at the rear of the crankshaft and hidden behind the clutch.
The crankshaft bearing has small dimensions:
- width – 14 mm;
- inner diameter of the holder – 15 mm;
- outer diameter – 35 mm.
Removing the crankshaft bearing
Now let's look at how to remove the crankshaft bearing. There are two options:
- To remove the part, you can make a hook with your own hands. To do this, you will need a piece of rod about 400 mm long and with a diameter of 6 to 8 mm, as well as a metal cylinder with a through hole, the diameter of which is larger than the rod.
The hook is made like this:
- step back 10 mm from the edge of the rod and bend this small edge at an angle of 90 degrees;
- put the cylinder on the rod;
- At the other end of the rod, fasten the segment so that you get a T-shaped end.
To remove the bearing, you need to insert a metal rod into its cage and hook the part with a manufactured bend. By knocking on the T-shaped end and turning the rod with each blow, you can pull out the desired part.
- If you don't want to make a jig or don't have the right materials, you can remove the bearing from the crankshaft using a bolt or a 14.5mm diameter metal cylinder. You need to select the bolt and cylinder so that they fit into the hole with a small margin in diameter - not too loose and not too tight.
The dismantling procedure in this case is as follows:
- first you need to pour grease or other lubricating fluid into the space behind the bearing through the corresponding hole;
- the cylinder or bolt is first inserted into the inner race and then hammered until it stops;
- as soon as the rod is completely inserted into the hole, add more lubricant;
- Due to the large amount of lubricant and rod pressure, the bearing will come out of the crankshaft seat.
Types and structure of crankshaft bearings
The following types of crankshaft bearings can be distinguished: support and thrust. According to the type of execution, they can be rolling or sliding.
- Rolling bearings. In such bearings, balls (or rollers) enclosed in a cage move along a closed path between the outer and inner rings of rotating bodies. The bearing is placed on the shaft and tightly inserted into the engine block. Such bearings are used as support on crankshafts of small-volume engines (for example, mopeds, walk-behind tractors). A rolling bearing is also used to support and rotate the gearbox input shaft and is installed in the crankshaft flange.
- Sliding bearings are installed in the assemblies of the main (support) and connecting rod journals of the crankshaft. Such bearings are made from steel tape in the shape of two “crescents” or cylindrical bushings connected to each other and to the engine block with a special lock. On top, the bearings with journals are secured with caps and bolts. A special “anti-friction” coating is applied to the friction surface of the crankshaft bearings, which prevents wear. Grooves and holes in the bearing body allow it to be forcibly lubricated. On older engines, there are crankshafts in which the front and rear main journal bearings (the outer ones at opposite ends) are made in the form of uncut bushings.
Moped crankshaft with support roller bearings
Rolling bearing in the crankshaft flange
The size of the bearings, or rather their thickness, is selected depending on the condition of the crankshaft journals. Over time, the journals wear down to compensate for wear, and manufacturers produce repair bearings. As a rule, there are 4-5 repair sizes. To fit the crankshaft journals to the new bearings, the crankshaft is ground to the next repair size.
In the operation of the crankshaft, it is necessary to prevent longitudinal axial displacements. A sliding bearing is also used for this, but it is installed in a vertical plane. This type of bearing is a thrust bearing. It has the shape of “half rings” and is installed between the planes of the shaft bed and the end of its cheek. The half rings prevent the shaft from moving forward or backward during loads. In modern engines, crankshaft main bearings are often combined with thrust bearings.
Half ring shaped crankshaft thrust bearing in engine blockCrankshaft main bearing kit with aligned thrust bearings
Installing a new part
Replacing the crankshaft bearing is completed by installing a new part. Unlike removing the old crankshaft bearing, installing a new one does not require much time or effort.
Before installation, you need to clean the crankshaft seat, from where you recently removed the old part, and simply insert a new one in its place. No additional cleaning or lubrication is required because the new part is already lubricated and protected from dirt.
To change a bearing to a new one, you do not need detailed knowledge of the car's structure, but it will require enough time and effort. But such a procedure is necessary. This allows you to maintain the performance of the engine and gearbox and save yourself from more serious repair costs in the future.
If you know other, easier ways to replace a crankshaft bearing, please share them in the comments to this article. Or tell us about your own experience of carrying out such an operation.
The task of the crankshaft in a car
The main task of the crankshaft is to convert the reciprocating movements of the pistons into a certain torque. During cranking, it takes on variable loads from gas pressure, as well as from the total rotating mass. The entire device is one of the parts of the crank mechanism. This is the most expensive part in the entire engine design.
In the automotive version, the crankshaft has the appearance of a solid, single structure and is non-separable. It is for this reason that this is one of the most expensive parts in the engine, because if any element becomes unusable, you have to change the entire structure. For example, for the most ordinary foreign car, a used part costs about 2,000 rubles, but a new one costs from 15,000 rubles.
Of course, the crankshaft can be repaired by balancing or straightening, but if the damage is serious, then replacing the crankshaft is inevitable.
DIY crankshaft bearing replacement for VAZ 2105-2107
The crankshaft of an internal combustion engine operates under extreme conditions. The crankshaft spins at high speeds, experiences dynamic loads, and therefore requires bearings and forced lubrication of friction pairs. In addition, such a part must be fixed with minimal backlash. For example, the permissible gap in the mating surfaces of the connecting rod journal, connecting rod bearing and the VAZ 2106 crankshaft connecting rod itself should be no more than 0.1 mm. For durable and stable operation, the crankshaft needs bearings.