To develop internal combustion engines in the near future, designers will have to do the impossible. Even today, a simple atmospheric engine cannot provide the required environmental performance. The German concern VAG provided for the complication of requirements by launching the production of a new generation of turbocharged units more than 10 years ago.
For each brand of the company, these engines have certain differences. Audi cars most often use TFSI engines, which are known to almost every fan of this German brand.
There are many myths built around this type of unit. Many believe that the letter F in the name means absolutely nothing, but was added simply to differentiate the model lines. And TSI engines, according to even some experts, are completely identical to TFSI engines. But this is not true, since they are built on different foundations. Today we will talk both about these engines separately and in terms of comparison with Volkswagen TSI engines.
TSI and TFSI
It's no secret that Skoda, Seat and Audi belong to Volkswagen, which implies joint development of engines. So it turns out that the abbreviation TSI is used on Skoda and Seat Volkswagen models, and TFSI on Audi cars, but the letter designation serves to identify identical engines. The difference between Turbo Fuel Startified Injection and Turbo Startified Injection is only the absence of the word Fuel (from English - fuel) in the designation. Let us immediately note that there is no universal injection internal combustion engine called TFSI or TSI. This is only a general designation for a series of engines with direct injection and additional air charging. We have already looked at the principle of operation of TSI, so we will not dwell on this. In this case, the engine can only have a mechanical supercharger or a supercharger working in tandem with a turbocharger. Depending on the year of production, the abbreviation can be used both by engines with conventional, if this is appropriate, direct injection, and by internal combustion engines using the Miller-Atkinson cycle.
It would be wrong to talk about these engines in the singular, putting them all under the same brush. The same applies to the list of the most common problems and malfunctions that occur when operating TFSI engines. By the way, even now there are enough materials on the Internet written by people incompetent in this matter or compiled before the time when there was a need to separate engine models.
Generation Models
TFSI is a logical development of the direct fuel injection system called Fuel Startified Injection. The main feature of FSI, which allows an atmospheric engine to be both economical and powerful at the same time, is layer-by-layer mixture formation. Thanks to the features of the intake manifold, fuel injection and “tamed” turbulence, the engine can operate both on an ultra-lean and on a homogeneous mixture.
- 2004 - the naturally aspirated 2.0 FSI receives a turbine and some design changes, thereby becoming the first TFSI engine. Initially, the marking could be found not only on Audi, but also on charged versions of the Skoda Octavia (RS), Seat Leon (FR), but later the Octavia RS and Leon FR received only the TSI nameplate. Power – 147 kW. An interesting feature is that the BWA engine has only two operating modes: warm-up (two-stage fuel injection, which allows you to quickly warm up the catalytic converter) and normal (operation on a homogeneous mixture). This means that there is no talk of any layering, which is what the word Startified means. A turbine is used to pump air. 2.0 series EA888, power – 162 kW. The design uses a combined injection system; a mechanical supercharger works in tandem with the turbine. Depending on the car model and year of manufacture, the power of the two-liter “heart” could vary from 170 hp (BPJ, intended for the Audi A6) to 271 hp (Audi TT, Audi S3). Particularly noteworthy are the 2.0 Gen3B units, which use the Miller-Atkinson cycle, and the design involves the installation of the proprietary Valvelift system.
- 2006 – appearance of 1.4 TFSI. A motor that implements the Downsizing idea. The point is that large-volume naturally-aspirated internal combustion engines are being replaced by smaller-volume turbocharged units. The TFSI 1.4 engine is found in the SAHS - 92 kW and CAVG - 136 kW modifications. A feature of the 1.4 engine series EA111 (CAVG) is the use of two-stage turbocharging - a mechanical supercharger and turbine. The main disadvantage of these engines is the stretching of the timing chain, leading to slipping and “meeting” of the valves with the pistons. In the EA211 series, 1.4 motors can produce 90 kW (SMVA) or 103 kW (CPTA).
- 1.2. Depending on the modification, the “heart” can produce from 63 to 73 kW.
- 1.8 series EA113. The BYT motor has a power of 118 kW (equivalent to 160 hp). Turbocharging – gas turbine, timing chain drive. The restyled 1.8 unit of the EA888 series already has 132 kW. The main feature is the combined injection system. This means that fuel is supplied not only to the combustion chamber, but also to the valves. A special nozzle is responsible for injection into the intake manifold. This innovation eliminates the problem of engines with the formation of dirt deposits on the intake valves.
V-shaped internal combustion engines
The TFSI line contains not only in-line models, but also V-shaped “hearts”:
- 3.0 V6 with a power of 213 kW;
- 4.0 V8. TFSI engine with power from 309 to 382 kW. To increase efficiency and reduce emissions of harmful substances, some of the cylinders can be switched off when unnecessary; an energy recovery system is used.
Problems and malfunctions
Among all the malfunctions of TFSI engines, we can highlight:
- stretching of the chain, leading to extraneous knocking during operation and the risk of valves “meeting” the pistons. Troubles can overtake the owner already at 30-40 thousand km. mileage;
- maslozhor. Unfortunately, all petrol engines from the VW-Group suffer from this problem. Constant improvements to the CPG only delay the mileage at which increased oil consumption appears. Often the problem is aggravated by the owners themselves, unknowingly operating the car in conditions that are uncomfortable for the engine. Constant careful operation with only “stroking” the gas pedal and long warm-ups at idle lead to aggravation.
When telling the story of the development of Turbo Fuel Started Injection, we used individual engine letter designations. It is by these numbers and letters that you can accurately identify the model and generation of the engine installed in a particular Audi. When buying a used car with TFSI, you should look for relevant information using these designations. To expand your search for information, match the abbreviations with the designations used for Volkswagen vehicles.
This is interesting: How to disassemble the radiator grille on a Priora
Installation of LPG on TSI, FSI, TFSI engines: features, differences, implementation methods
Audi A3 car: review, news, Audi A3 car - configurations, characteristics, different generations Audi A3 - website Behind the wheel www.zr.ru
Login and registration
Entire site
| News ArticlesTestsBlogsDocumentsMakes and modelsZR ParkPhotos and videosSelectionsTiresSpecial projectsAuthorsZRPD surveys onlineForum | All NewsRoadsTuningInsuranceFuelRetroIncidentsLawCar MarketNew CarsTechnology CuriositiesSports Today, at 15:45, the first Haval H5s arrived at Russian dealers. So far only as show cars, but some dealers are expecting the shipment of test cars literally any day now. Today, at 14:30, AVTOVAZ again raised prices for Lada cars. A little more a little, and the “very best” Lada will cost more than 1,100,000 rubles. Today, at 13:46 Passes via SMS are canceled Issuing digital passes giving the right to travel by car and public transport via SMS will be impossible in Moscow from May 12, 2020 of the year. |
| All ArticlesDetailsRoadsStatisticsConsultantPresentationPerson | Today, at 10:00 Two handles are better than one - a life hack from the reader “Behind the Wheel” Thanks to a small modernization, opening the sliding door of Gas minibuses from the outside will become much more convenient. Today, at 6:0010 500 km with the Haval crossover: engine, assembly and maintenance “ How's the car?" - I heard this question many times over the several months of our life together with Khawale. Usually he laughed it off: this “Chinese” already looks like a car. Yesterday, at 10:00 Test “Behind the Wheel”: do you know the history of our military vehicles? Let's test your knowledge of the history of domestic army vehicles. Mostly from the time of that war, but a few from the post-war period. |
| All TestsTest driveComparative testUsed carsRoad trip | Today, at 8:00 Largus on the secondary market - choosing the right engine and gearbox Oddly enough, the more recent version of the Lada Largus may not be the best choice in terms of reliability. May 8 Skoda Octavia: test of the most desirable version of the fourth generation Octavia is about to hit the market . But the third “Octave” will remain relevant for quite a long time - at least on the secondary market. We tested the optimal version of this machine with low mileage. May 7 Cat 330 tracked excavator: working hard The American company Caterpillar produces special equipment under the Cat brand, which occupies the upper price segment of the market - where the “music is ordered” by buyers for whom it is fundamentally important that their machines can work, as they say, for wear and tear, but at the same time almost not wear out. For crawler excavators, which often work around the clock with two or three shift operators, choosing a brand based on the “expensive and cheerful” principle is completely justified. |
Publications: 143
Ratio: 0
Total: 0
Subscribe to auto
| Acura | Alfa Romeo | Alpina | Aston Martin | Audi | Aurus | BMW |
| BYD | Bajaj | Bentley | Bogdan | Brilliance | Bugatti | Cadillac |
| Changan | Chery | Chevrolet | Chrysler | Citroen | ||
| Daewoo | Datsun | Dodge | DongFeng | FAW | Ferrari | Fiat |
| Ford | Foton | GAC Trumpchi | Geely | Genesis | Great Wall | Haima |
| Haval | Hawtai | Honda | Hyundai | Infiniti | Isuzu | J.A.C. |
| Jaguar | Jeep | Kia | Koenigsegg | LADA | Lamborghini | Land Rover |
| Lexus | Lifan | Lotus | Luxgen | Maserati | Maybach | Mazda |
| McLaren | Mercedes-Benz | Mini | Mitsubishi | Nissan | Opel | Peugeot |
| Porsche | Qoros | Ravon | Renault | Rolls-Royce | SEAT | Saab |
| ShuangHuan | Skoda | Smart | Ssang Yong | Subaru | Suzuki | TATA |
| Tesla | Toyota | Volkswagen | Volvo | Zotye | GAS | ZAZ |
| TagAZ | UAZ |
- Model overview
- News
- Articles
- Tests
- Travel notes
- Reviews
- Modifications
Audi showed the new generation A3 sedan. The company presented official photographs of the sedan, revealed its technical characteristics and indicated the start date of sales.
Compact “lighters” - only four left If you want to drive from traffic light to traffic light, then here is a review of the most interesting models. Oops, all the models that are officially sold in Russia.
The new Audi A3 will appear this year. The car will be produced in three bodies.
Audi A3 Audi A3
Audi > A3
- Model overview
- News
- Articles
- Tests
- Reviews
- Modifications
Audi showed the new generation A3 sedan
The company presented official photographs of the sedan, revealed its technical characteristics and indicated the start date of sales.
Source: https://AutoClub174.ru/rekomendacii/fsi-rasshifrovka.html
Decoding
It’s easy to guess that in this abbreviation “T” stands for turbine. And therefore, one of the main differences from FSI engines is the presence of a turbine. The engine has a turbocharger, which is driven by exhaust gases. The gases are re-burnt. The TFSI engine is even more economical, environmentally friendly and friendly - during operation, a very minimal amount of harmful gases and CO2 will be released into the air.
You will be interested:How dangerous is the new coronavirus?
And now, regarding the abbreviation TFSI. Explanation: turbocharged power unit with stratified injection. This is a system that is now deservedly considered revolutionary for this time. This is an injection system directly into the cylinders with a turbine.
Due to the presence of a turbine, the developers were able to achieve very high performance. Thus, the engine power has increased even more. Now you can get everything that it is capable of and even more from a small-volume engine. Naturally, along with the power, the torque also increased. Fuel consumption remained relatively low, although the engine, equipped with turbochargers, is not particularly economical.
Volkswagen-Audi 2.0 TFSI engine tuning
Chip tuning
Tuning TFSI engines is quite a simple task (if you have money), to increase engine power to 250-260 hp, just go to a tuning office and upgrade to Stage 1. If this power is not enough, then it is worth installing an intercooler, 3″ exhaust pipe, cold intake, more efficient injection pump and flashing, this will increase the output to 280-290 hp. A further increase in power can be continued using the new K04 turbine and injectors from the Audi S3, such configurations give
350 hp Further squeezing the juices out of a 2-liter engine is not so profitable, the price/hp ratio is decreases noticeably.
Source
Characteristics
Often the letters TFSI, which we have already deciphered above, can be seen on Audi cars. On Volkswagen models, the VAG concern installs FSI and TSI, traditional for the brand.
For the first time, a turbocharged engine with stratified direct injection was installed on the Audi A4. The engine had a volume of 2 liters and was able to produce as much as 200 horsepower with this volume. The torque is also quite high - as much as 280 Nm. To get such results on earlier engine models, its volume had to be about 3-3.5 liters, and the engine had to have six cylinders.
But the matter did not end there and in 2011 the TFSI engine was upgraded. The decoding of letters remained the same, but the power increased. With the same volume of two liters, the engineers managed to get 211 horsepower at 6000 rpm. Torque is 350 Nm at 1500-3500 rpm. The engines have excellent traction at low and high speeds.
For comparison, just look at the six-cylinder 3.2-liter FSI with 255 horsepower at 6,500 rpm and 330 Nm of torque at 3,000-5,000 rpm. Let's also look at the technical specifications of the TFSI 1.8 engine for the 2007 model year. It is capable of producing 160 horsepower at 4500 rpm. The maximum torque that can be obtained (250 Nm) is available at 1500 rpm. This engine accelerates the car to a speed of one hundred kilometers per hour in 8.4 seconds. Fuel consumption in the city with a manual transmission is only ten liters.
Even with the naked eye it is clear that FSI engines are losing, and TFSI is a step forward for VAG engineers. Although the company didn’t do anything special - they only installed a turbocharger. But the main nuances of the TFSI engine are there and we will look at them.
Reliability, problems and repair of 2.0 TSI engines (2 gen.)
The second generation 2.0 TSI appeared in 2008 and replaced the 1st generation EA888 (CAW and CCT). It was created on the basis of the second generation 1.8 TSI (CDA and CDH). Approximately the same changes took place here as in the younger brother: a crankshaft with journals of 52 mm instead of 58 mm was used, the hone was made differently to reduce friction, new pistons and rings of a special design were used, an adjustable oil pump was installed, 2 lambda probes, The engine was brought up to the Euro-5 environmental class. But there is also something here that is not present on the 1.8 TSI gen 2. Here they installed an AVS (Audi valvelift system) system on the exhaust camshaft, which can switch the valve lift height between two modes: 6.35 mm or 10 mm. The mode change occurs after 3100 rpm. A variable valve timing system is installed on the intake shaft, as on the 1st generation EA888.
All this provides a power of 211 hp. at 4300-6000 rpm, torque increased to 350 Nm at 1500-4200 rpm. The CDNC and CAEB engines could boast of such indicators. The CDNC engines corresponded to the Euro-5 class, and the CAEB engines were produced under the ULEV 2 standard. They produced software modified CAEA engines for North America and CDNB for Europe, which had 180 hp. at 4000-6000 rpm and torque 320 Nm at 1500-3900 rpm.
In Europe, motors of the CCZ series were sold, which differ from CDN in that they do not have an AVS system. These engines are: CCZA, CCZB, CCZC and CCZD. They all have the same hardware, but different firmware. Their power is 211, 200, 170 and 180 hp. respectively. The torque of all engines is 280 Nm at 1700-5000 rpm.
The production of these engines continued until 2015, when they were completely replaced by the 3rd generation 2.0 TSI.
Disadvantages and problems of 2.0 TSI engines (2nd generation)
Your engine is a complete analogue of the 1.8 TSI CDAB, CDAA and other engines in this series. They all suffer from the same diseases: high oil consumption for various reasons, replacing the timing chain after 100 thousand km, unstable speed, etc. We wrote about all this in this material. Regarding oil consumption, for the 2.0 TSI the pistons are changed to Kolbenschmidt 40247600 with a 21 pin. If there is wear on the cylinders and it is necessary to sharpen them for repair size pistons, then buy Kolbenschmidt 40247610 or 40247620 pistons for the first repair for the second repair.
Improvements
If you look for the difference between TFSI and TSI technologies, the difference lies in the piston crowns. The cylinders in the TFSI are smaller, but the area they occupy is larger. Due to this shape, the engine operates efficiently with low compression.
The engineers also modified the cylinder head - it is equipped with two camshafts made of a more durable alloy. The valves were also made from the same alloy. The intake and exhaust have been significantly modified, and the fuel supply channels have been corrected. The fuel supply itself has also been improved.
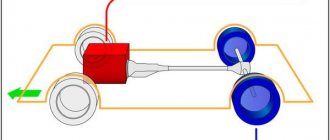
In general, motors with TFSI technology operate on the same principles as other units of the concern. There are two fuel circuits - high and low pressure. The low pressure circuit is a tank, a low pressure pump. There are also filters and sensors. In the high pressure circuit there is an injection system and high pressure fuel pump.
The operating modes of all devices and systems in the circuit are fully controlled by electronics operating according to fairly complex algorithms. During operation, various parameters are analyzed, and then the corresponding commands are sent to the actuators.
This is interesting: What is a steering rack
Specifications
Technical characteristics of the TFSI motor:
| Production | Plant Audi Hungaria Motor Kft. in Gyor |
| Engine make | EA113 |
| Years of manufacture | 2004-2014 |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| Supply system | direct injection |
| Type | in-line |
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Valves per cylinder | 4 |
| Piston stroke, mm | 92.8 |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 82.5 |
| Compression ratio | 10.5 |
| Engine capacity, cc | 1984 |
| Engine power, hp/rpm | 170-271/4300-6000 |
| Fuel | 98 95 (lower power) |
| Environmental standards | Euro 4 Euro 5 |
| Average fuel consumption, l/100 km | 12.6 |
| Engine oil | 5W-30 5W-40 |
| How much oil is in the engine | 4.6 |
| To change the oil you will need liters | 4.0 |
| Oil change interval, km | 15000 (better 7500) |
| Engine life, thousand km | about 300 |
Letters and technology
All the differences lie in the confusion in the lineup. Thus, in 2004, the turbocharged FSI was introduced, now called TFSI. Then a 1.4 engine with two compressors appeared - this is TSI. Around the same time, in 2006, a 1.8-liter turbocharged engine with one FSI compressor was released. It should have also become a TFSI. And so it happened, but only for Audi models. For all other cars of the brand, the engine is called TSI. Knowing this TFSI decoding, you can find out how modern the selected car is.
Pros and cons of using
The positive side of the Fuel Stratified Injection engine is the presence of dual-circuit fuel injection. Fuel is supplied from one circuit at low pressure, and from the second at high pressure. Let's consider the operating principle of each fuel supply circuit.
Unlike conventional gasoline power units, where the fuel enters the intake manifold before entering the combustion chamber, on FSI the fuel enters directly into the cylinders. The injectors themselves have 6 holes, which provides an improved injection system and increased efficiency.
Since air enters the cylinders separately, through the damper, an optimal air-fuel mixture ratio is formed, which allows gasoline to burn evenly without exposing the pistons to unnecessary wear.
TFSI engine for Audi
Another positive quality of using such an aspirated engine is fuel economy and high environmental standards. The Fuel Stratified Injection system will allow the driver to save up to 2.5 liters of fuel per 100 km.
But where there are many positive aspects, there are also a significant number of disadvantages. The first disadvantage can be considered that the aspirated engine is very sensitive to the quality of the fuel. You can’t save money on this engine, because with bad gasoline, it will simply refuse to work normally and will malfunction.
Another big drawback is that in cold weather, the power unit simply won’t start. If we take into account common problems and FSI engines, problems in this line can arise with cold starts. The culprit is considered to be the same layered injection and the desire of engineers to reduce exhaust toxicity during warm-up.
Oil consumption is one of the disadvantages. According to most owners of this power unit, an increase in lubricant consumption is often noticeable. To prevent this from happening, the manufacturer recommends maintaining VW 504 00/507 00 tolerances. In other words, changing the engine oil 2 times a year - during the transition to summer and winter operating modes.
Malfunctions and repairs
As mentioned earlier, TFSI power units are oil guzzlers. Of course, you can change the oil for summer and winter, but for most owners this is not a solution, but only a delay in increasing lubricant consumption. This problem occurs on many power units produced by the VW-Group.
TFSI engine for Skoda
The second significant malfunction, which occurs quite often, is stretching of the timing chain. At the same time, the meeting of pistons and valves begins, which causes a characteristic metallic knock that even auto mechanics have been looking for for a long time.
Description and features of the engine
TFSI engine stands for Turbocharged Fuel Stratified Injection. But there is another abbreviation that is very similar to the one we will talk about now, TFS. For some reason, many drivers mistakenly confuse them and are greatly mistaken. These 2 engines are completely different. They differ in characteristics and design.
There is a motor with which the TFSI actually has common features, this is the FSI, however they also have very strong differences. For comparison, we will take these two engines to talk a little about them. FSI today is a fairly old version of motors, but quite reliable. Over the many years of their existence, such engines have managed to prove themselves in operation and have proven themselves well.
Once again, the German company proved to be at its best in producing high-quality and durable engines. It was the invention and production of FSI that became the impetus for the emergence of injection engines in general.
Over time, the developers were no longer satisfied with the quality of the engines and they set themselves the goal of creating something new, more powerful and efficient. At the same time, they wanted to invent an engine that would emit fewer harmful substances into the atmosphere, that is, it would be more environmentally friendly.
By the way, ecology currently plays a leading role among Europeans in all areas, including mechanical engineering. This area includes the conditions by which the quality of a particular manufactured product is recognized. Therefore, cars are no exception.
That is why, in the production of engines to implement their ideas, they did not touch upon only the one that concerned the injection of the mixture directly into the cylinders themselves. Everything else has changed. Some of the components have been revised and improved. The piston designs have generally been changed so that the engine does not lose its power, but at the same time reduces its compression performance.
2 camshafts were added to the design of the cylinder head, which were made of durable and resistant types of metals. The valves were also made from the same material. The system responsible for fuel intake and exhaust has also been improved. It was improved as follows: the channels that were responsible for the supply of fuel and the removal of waste gases were corrected.
Gasoline supply has also been changed in the TFSI. This system has undergone changes in the form of the installation of a modernized pump, which pumped fuel and gave pressure an order of magnitude higher than in the FSI. As a result, we got more power, but lower consumption. In the previous version of the motors, the pump had only 2 cams, in the modern one another one is added and we now have a three-cam design.
The pump is electric, due to which its firmware was changed. This made it possible for the engine to calculate the amount of fuel supplied, taking into account the needs of the engine. Gradually we came to the main difference between these types of engines: the presence of a turbocharger.
In the abbreviation TFSI, this change occurred in the addition of the letter T. Thus, there was a change in the name from FSI to TFSI. The addition of this letter to the name and the presence of a turbocharger gave this type of engine more power, dynamics and torque.
Now we would like to finally dispel all doubts about the differences between these two engines. After all, both have turbines. And at first glance they are the same and equal to each other. But no, there are still significant differences. Only TSI has two of them.
Firstly, one of them is the fuel supply, which goes into the intake manifold. The second difference is that the design of such a motor provides for the presence of a turbine turbocharger. That is, the design of the engine includes both a mechanical turbine and an electric compressor.
Exhaust gases drive one unit to operate. Another unit increases air pressure. Their work is organized alternately and depends entirely on the operating modes of the motor. TSI are considered more economical and responsive, unlike TFSI.
The Germans most often install TFSI on such car brands as Audi and Skoda. Now it’s worth paying a little attention to problematic issues and the main disadvantages of TFSI engines. Every unit and unit has them, and it wouldn’t be right if we hide them and don’t touch them.
What are FSI engines?
An automobile unit operating using FSI technology was developed in the laboratory of the Mitsubishi automaker. Today, such engines are installed on many brands of cars from various European, Japanese and American manufacturers. The German company Volkswagen is considered the leader in the production of FSI power units. Almost all the cars they produce are now equipped with these units. In addition to them, such engines, but in smaller volumes, are installed by such automakers as: Ford, Mazda, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, General Motors, Hyundai, Infiniti.
The main difference in the design of FSI engines from other internal combustion engines is the supply of fuel under the highest possible pressure directly into the combustion chamber. The use of FSI engines reduces fuel consumption (by approximately 10-15%) and significantly reduces the amount of exhaust gases into the environment.
An important distinguishing feature of the FSI system is the presence of 2 sequential fuel systems that supply gasoline. The first is a low pressure circulating fuel system. It connects the gas tank, strainer, control sensor, circulation pump, as well as the fuel supply pipeline to the second system. The second one supplies fuel to the nozzle, after which it is atomized and supplied to the cylinders for combustion, i.e., ultimately, to perform mechanical work.
First acquaintance with the engine
To begin with, some car enthusiasts do not even understand what kind of TFSI engine this is and how this abbreviation stands for.
This means Turbo fuel stratified injection. In translation here we are talking about a turbo engine with stratified fuel injection. Yes, this is indeed in many ways an analogue of the FSI, only additionally equipped with a turbocharger.
The system was revolutionary for its time, since it was the Germans who were the first to use direct injection into the chamber for each piston separately, managing to connect this with a turbine.
But the decoding of the TFSI marking itself does not yet make it possible to fully recognize this engine. And be sure to compare with TSI.
Many theories, conjectures and myths were built around the motor with the designation TFSI. Some are sure that the letter F has no meaning at all, and this was done solely for the sound of the name, or for the difference in the model range of cars. Allegedly, TSI comes on Volkswagen and Skoda models, and TFSI exclusively on Audi.
You have already become familiar with how the TFSI value is deciphered. But it is equally important to understand what this same TFSI actually means, how it differs from its supposed counterpart, and what the situation looks like in reality.
The technology of the engines in question is based on older internal combustion engines, which have already been discussed here. This is FSI. One of these 2.0-liter engines was actively used in various models under the Seat, Skoda and Volkswagen brands. This is an atmospheric internal combustion engine equipped with a direct injection system. The engine has a reliable base, high-quality design and long service life.
But now cars of more recent generations are equipped with TFSI engines. Their decoding has already made it clear that we are talking about a turbo engine with direct injection. But it has its own important features. In many ways, this will allow us to understand the operating principle of the TFSI series units.
- Other pistons. To improve the performance of the turbocharged engine, the upper part of the pistons has undergone certain changes. New larger recesses are provided here, which allows you to work effectively in conditions of reduced compression.
- Increased efficiency of the internal combustion engine with a parallel reduction in the amount of harmful emissions. This distinguishes the turbocharged version from the naturally aspirated one. This was done in order to comply with new stringent environmental standards.
- Crankshafts and shafts. The principle of operation has changed largely due to the modified form. Additionally, designers use high-strength materials for their manufacture, which allows them to withstand the loads from the turbine.
- Intake and exhaust system. And here changes have occurred. They were aimed at increasing precision and efficiency, since this is one of the main requirements for an internal combustion engine when using a turbocharger.
- Fuel pump. It has become more powerful and reliable. Due to this, it was possible to improve the elasticity of operation at high speeds.
The changes made and the announced features of the engine in question largely make it clear what kind of engine it is, how it works and what its strengths are.
But there is still no escape from comparison with FSI, although most often it is compared with TSI, since both engines are turbocharged.
I would like to remind you that in the middle class of cars, the naturally aspirated FSI is considered one of the best engines in the world. Many such engines can easily cover a range of 400-500 thousand kilometers without requiring expensive repairs or serious intervention. The only condition for long-term operation is high-quality maintenance and the use of suitable motor oils.
Now, having figured out what TFSI means, you should compare TSI and TFSI, look at their capabilities and understand whether the new generation is really noticeably superior to its conventional predecessor.
What is TFSI - decoding and technology features
These motors borrowed their original technology from older FSI engines. The VAG 2.0 FSI engine, which was installed on Skoda, Seat and Volkswagen, was very popular. This is a naturally aspirated engine with direct fuel injection into the cylinders. The unit has a fairly reliable foundation, a well-designed design and a fairly long service life.
We recommend: What is an idle speed sensor used for?
TFSI engine stands for Turbo Fuel Stratified Injection. The name indicates that this is a turbocharged engine with direct fuel injection into the combustion chambers. Here are some features of a turbo engine:
- Changed pistons. Especially for the turbocharged version, the upper part of the pistons was changed; they received large recesses for operation with reduced compression.
- Improved efficiency and reduced emissions compared to the old FSI to accommodate the new engine's challenging environmental regulations.
- The designers changed the shape and operating features of the crankshaft and connecting rods. The changes also affected the quality of the material; the manufacturer increased it for turbo engines.
- The intake and exhaust systems also received changes, they became more precise and efficient, which was vital for the compressor version.
- Of course, the designers had to install a more powerful and reliable fuel pump. This ensured the elasticity of the engine at high speeds.
Basic concepts explain what a TFSI engine is, how it works, and what its main advantages are. If you have ever come across FSI engines from VAG, then you know that they were the most reliable and successful mid-class naturally aspirated engines. Many of them reach 500,000 km without repairs or intervention. It is enough to maintain the unit well and pour expensive oil at the right time.
Comparison of TSI and TFSI
Car enthusiasts are quite naturally interested in what is the difference between TSI and TFSI series engines, since both options are available on the market and you need to choose the best one among them.
Speaking about the difference between them, it’s worth saying right away that TSI and TFSI are built using completely different technologies.
In the case of the TSI, Volkswagen, or rather its engineers, did not use any old naturally aspirated engine as a basis. In this case, the internal combustion engine was developed from scratch. There is an intake manifold and a pair of turbines. Moreover, one turbine is of an electric type and operates, one might say, on a permanent basis. The mechanical turbine is made according to the classical design. Without going into details, the TSI can even be called a biturbo engine.
There is another important difference that allows us to say that TSI is inferior to TFSI. The latter is supported by the borrowing of the basis in the form of an atmospheric internal combustion engine, as well as its modernization. This made it possible to obtain a more reliable cylinder block design. Unfortunately, TSI does not have such an advantage. Because of this, the latter cannot always overcome the mark of 200 thousand kilometers traveled. Plus the turbines themselves are problematic. They fail and begin to create difficulties in the operation of the internal combustion engine. This becomes especially noticeable when TSI service rules are violated.
I would like to add one more point about how the TSI motor differs from the TFSI. Their development and modernization are carried out by different VAG departments. In the case of TSI, all the work is done by specialists from Volkswagen, Skoda, and Seat. It is on their engines that these internal combustion engines are mainly installed. And the TFSI became the property of the Audi brand, just like the FSI.
It is important to understand that all represented brands work together, sharing their technologies and developments. Therefore, seeing TFSI engines somewhere other than Audi models is more than realistic at the moment.
Understanding the differences between the TSI series engines and the newer TFSI engines, it seems obvious which one to choose. After all, the difference between the internal combustion engine under consideration in terms of reliability, structural strength, efficiency and performance leaves no chance for a conditional competitor. But before you decide to buy such a power unit, it’s worth taking an objective look at its strengths and weaknesses.
Problems and weaknesses of TFSI
First of all, it must be said that like any turbocharged engine, the TFSI engine can have problems with the turbine.
Especially if you do not adhere to the rules for handling such motors. But this is a problem common to a whole class of turbocharged engines. Soot on the valves, which was a typical problem for FSI engines, also occurs on the described engines. The symptoms of this problem are:
- drop in traction;
- increased fuel consumption;
- uneven engine operation;
Carbon deposits are removed either with the help of special chemicals or during a major overhaul. The second option, although more expensive, is still preferable, because it is difficult to say where the soot and other solid elements that will be cleaned off by special means will end up.
Another very unpleasant problem, inherent mainly in TFSI engines of the first years of production, is oil consumption, or the so-called “oil guzzler”. And here only major repairs will help you. This problem cannot be resolved by any other means. In addition to oil consumption, which in some cases is quite noticeable, damage or even failure of the catalyst is possible. True, in the latest versions of engines, such troubles arise very rarely.
The TFSI engine also has difficulties with electronic components. In particular, a very common reason for contacting service centers is the failure of the knock sensor. But fixing such breakdowns is much easier than those described above.
Problems with TFSI engines
So, we will take the 2.0 TFSI engine and discuss what owners of cars with these types of engines installed on them most often complain about. The first and quite common problem is oil consumption or, as many car owners put it, “oil guzzling”.
This problem does not exist in new cars, but rather concerns those that have already had more than average mileage. Yes, there is a problem, but it can be solved and there is nothing wrong with it, you just need to contact the service in time and they will help you fix everything. Usually everything is solved by replacing components such as the VKG valve. If this procedure does not solve the problem, then replace the valve stem seals.
The second problem is knocking. It appears when the camshaft chain tensioner has already worn out. This can also be solved and occurs by replacing this unit.
The third problem is loss of power, that is, failures in acceleration occur. The problem is valve #249. Replacing it will solve all the problems.
The fourth problem is that at high speeds the car does not move. Check the injection pump pusher, the problem is there. If this unit is periodically checked (every 15-20 thousand kilometers) and monitored, then replacing it will solve everything.
Fifth problem: we refueled the car, but it won’t start. Check the ventilation valve. This kind of problem concerns American cars more. The most interesting thing is that we named problems that people often encounter.
However, you probably noticed that they are all quickly resolved. We purchased the part, replaced it, and that’s the whole algorithm. Since engines are quite complex, the best option would be to contact specialists in this field if problems arise.
Advantages and disadvantages
The superiority of TFSI over TSI is obvious. These are larger engines, equipped with a turbine, characterized by an impressive service life. If turbines are maintained on time and correctly, they can last about 300 thousand kilometers.
The advantages include adequate fuel consumption, which is pleasantly surprising given such high power parameters.
But for now, this is where the list of advantages ends. Now it’s worth looking at the disadvantages that can characterize a car with a TFSI engine under the hood.
The technology is indeed far from perfect. Work is already underway to eliminate them, and many problems were eliminated literally after the first update. But when buying used cars with TFSI under the hood, remember that these cars with such an engine had the following problems:
- The installation of a turbine on an initially naturally aspirated engine led to the fact that engines became more demanding of fuel quality. You need to choose your gas station carefully, otherwise problems will soon arise.
- Due to the turbine and other innovations, the cost of maintenance has increased significantly.
- Increased maintenance requirements have led to the need for such internal combustion engines to use expensive oil and filters.
- The cost of repair work is extremely impressive for many clients. This is largely due to the fact that only original parts have to be used. And they cost a lot.
- Due to design changes, oil consumption has increased. Therefore, it is important not to forget to top it up periodically. If you forget, the process of oil starvation will begin.
- The timing belt uses a chain that stretches over time. Replacing it is expensive.
In many ways, these problems are typical for engines manufactured before 2014.
Then Audi worked on the errors and eliminated many of them. So the current generation TFSI causes much less criticism.
Main disadvantages and advantages of TFSI technology
As mentioned above, the difference between TSI and TFSI is obvious, and it is not in favor of the first technology. Motors with the letter F in the designation are larger and have a much longer lifespan. The turbines themselves, subject to good maintenance, do not break down up to 300,000 km and 10 years of operation. The list of advantages includes very moderate fuel consumption, given the high power that the company squeezes out of these developments.
Now let's talk a little about the disadvantages of technology:
- engines with turbines have lost their unpretentiousness and omnivorousness, they need good refueling;
- the cost of maintenance has increased significantly, you have to fork out for expensive oils and filters;
- the cost of repairs will be enormously high; all spare parts must be original and expensive;
- high oil consumption is a design feature of engines; you will have to occasionally add lubricant;
- A chain is installed in the timing system, and this causes certain disadvantages in the form of stretching of the chain drive.
All the disadvantages are due to the fact that the engine was produced in great haste in order to install it on cars before the introduction of new environmental standards. Many shortcomings no longer apply to the current generation TFSI engines, but are found only on engines produced in 2012-2014. Otherwise, there are no significant disadvantages with the units; there are no childhood problems or common problems up to mileage limits of 200-250 thousand km.
What's new in TFSI
The letter T in the designation of the TFSI engine tells us about the presence of a turbine in the design of this unit. Accordingly, the power range of the TFSI engine is much wider than that of its predecessor. If FSI engines generally produced one and a half hundred horses, then TFSI engines vary in power range from 172 to 272 horsepower. But the presence of a turbine was not the only innovation in the new engines. The design of the pistons has changed. And thanks to this, the new engine can operate efficiently even at low compression ratios. The valves and both camshafts on TFSI engines are made of high-strength material. The same goes for valves. TFSI engines have a fuel priming pump. It runs on electricity and provides greater pressure when supplying fuel. There are other minor changes.
As a result of all these innovations, TFSI motors significantly outperform their predecessors in the following indicators:
- power;
- efficiency;
- torque;
- level of emissions into the atmosphere;
Sometimes they talk about increased reliability, but this is a controversial point. The presence of a turbine and a fuel pump, as well as the generally higher complexity of these engines, all this does not help to increase the reliability of the unit. Although, in fairness, it should be admitted that the designers strived for this.
As for the successor of the TFSI engine, it was the famous power unit from Volkswagen - TSI. This is also a turbocharged engine, but it is called biturbo or Ywin Turbo. In the design of this engine, in addition to a conventional turbocharger, there is also a mechanical supercharger, which allows you to get rid of such a phenomenon as turbo lag. But we have already talked about this engine, so let’s return to TFSI engines.
What is the difference between TSI and TFSI
In terms of their structure, these are two different engines.
TFSI engine to put it roughly, this is a turbocharged FSI engine, as indicated by the letter “T” in front of the FSI abbreviation. There is one mechanical turbine, which is installed on the exhaust manifold. In such an engine, fuel injection goes directly into the engine cylinders.
TSI engine is also a turbocharged engine. However, this is the so-called “twin turbo” or double turbocharging. The TSI engine is like a mechanical turbine that is powered by exhaust gases, and the higher the pressure, the faster it spins. There is also an electric compressor that forcibly pumps up air pressure almost always. Fuel is supplied not to the engine cylinders, but to a special intake manifold.
Thus, the TSI engine is more modern than the TFSI. The TSI engine's throttle response is higher than that of the TFSI over the entire operating range. And now a short video of the TFSI engine in action.
Predecessor and successor TFSI
The abbreviation TFSI stands for Turbocharged Fuel Stratified Injection and is essentially a development of the famous engine from the German automotive giant, Volkswagen, which was designated FSI or Fuel Stratified Injection. FSI is a gasoline engine with direct fuel injection, which not so long ago was found on various cars from the German manufacturer. This is an economical, fairly powerful engine that has enjoyed the well-deserved love of car enthusiasts.
But progress does not stand still, and therefore VW engineers refined and developed the concept of the FSI engine, the result of this development was the TFSI engine.