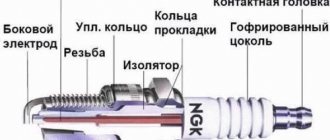
If any component in your car breaks down, you can buy a new one, repair the old one, or replace it with a used one. At the same time, used parts are often called “contract”. Is this definition correct? Let's try to understand this issue.
Parts dealers obtain used parts from vehicle dismantling, from a remanufacturing shop, or from inventory where parts end up after an erroneous replacement or after being replaced with a better-performing part.
Cargo carrier companies
Delivery of auto parts is carried out by freight forwarding companies
- Business Line
- SDEK
- PEC
- KIT or GTD
- DPD
- Pony Express
- ZhelDorExpedition
- Energy
Delivery time for spare parts:
- if parts are in stock - immediately after payment;
- to order - within 5 days.
What data is needed from the buyer
- Full name
- Series and Passport Number
- City (town) where to send
Responsibility to the buyer ends at the moment of transfer of the goods to a third party - a transport company or a person who receives the goods on behalf of the client.
Upon full payment of the goods
We ship with any transport company, but for Russian Post you still need to immediately pay the delivery cost in addition to the cost of the goods. Because they require payment for delivery before delivery.
With partial payment (Prepayment)
The purchase amount must exceed 3,000 rubles. We send only by “Business Lines” and “PEC” - with the procedure for changing the recipient.
How the process works:
- approved with the manager where to send;
- made a partial payment for the auto part;
- received a TRACK number to track the cargo on the website;
- when the cargo arrives in your city, the remaining amount is paid;
- We start the procedure for changing the recipient. It lasts from 1 hour to 2 hours. (the goods arrive to our logistician. When you pay the remaining amount, the recipient changes to you);
- You pick up the goods and the warranty time starts counting from the next day (14-30 days).
【Additional payment for goods must be made before receipt】
What are contract spare parts and where do they come from?
These are used parts and components removed from old, scrapped and unclaimed new cars. There are strict rules for operating a car abroad. This is due to strict technical regulations and concern for the environment.
In Europe and Japan, technical standards and rules for car repair are strictly observed. The older the car, the more parts in it need to be replaced according to the rules. Even serviceable spare parts must be replaced: without this, the owner simply will not receive a registration certificate.
It costs more than buying a new car. Therefore, car owners often prefer to dispose of a car in good condition in exchange for purchasing a new one. And the “old” car is disassembled for spare parts and exported to other countries.
Unclaimed cars are also scrapped if they are obsolete and do not comply with new technical regulations. After a car has been declared unfit or unprofitable for further use, it goes to auction or a recycling plant. Here contract spare parts are purchased individually or the entire machine.
Regular bus
We recommend receiving large and heavy goods and components (axle, engine, gearbox) using a regular passenger bus.
Advantages:
- Cheapest delivery method
- One of the fastest ways
- Sometimes the only way
- your locality may be the end point of the route and the bus will be at the bus station all day.
These points cover all other shortcomings. Because, for example, the cost of delivering an engine to Crimea is 2 times cheaper (approximately 2000-2500 rubles) than any of the transport companies. And when it comes to delivery, sometimes transport companies deliver the goods in 2 weeks, and by bus in 2-3 days.
Flaws
- the bus may not pass through your city;
- can follow the route only on certain days of the week;
- it may pass through your locality at night or at other times of the day;
- You may have to receive the goods on the highway along the route.
Why choose contract spare parts?
Probably, the answer to this question is already in the article. All that remains is to summarize.
- The seller of contract spare parts, as a rule, still provides a guarantee.
- Spare parts with a contract, imported from abroad, are less worn out than those that were removed in Russia (even with the same mileage, if we compare the operation of the car in Russia and abroad).
True, they are cheaper than new parts, but somewhat more expensive than second-hand ones, that is, those that were filmed in Russia. The increased price is justified; the reasons for this are indicated in the subparagraphs.
Delivery regions:
- Russia:
Far Eastern Federal District:Amur region
- Jewish Autonomous Region
- Transbaikal region:
Chita
- Arsenyev
- Ulan-Ude
- Komsomolsk-on-Amur
- Yakutsk
- Kirov region:
Kirov
- Arzamas
- Novotroitsk
- Kuznetsk
- Berezniki
- Belebey
- Saransk
- Almetyevsk
- Zhigulevsk
- Balakovo
- Votkinsk
- Dimitrovgrad
- Novocheboksarsk
- Arhangelsk region:
Arkhangelsk
- Babaevo
- Kaliningrad
- Volkhov
- Apatity
- Velikiy Novgorod
- Pskov
- Petrozavodsk
- Vorkuta
- Kabardino-Balkaria:
Nalchik
- Makhachkala
- Vladikavkaz
- Essentuki
- Grozny
- Altai region
Angarsk
- Kemerovo
- Achinsk
- Barabinsk
- Omsk
- Abakan
- Seversk
- Kurgan region:
Mound
- Ekaterinburg
- Ishim
- Langepas
- Zlatoust
- New Urengoy
- Belgorod region:
Alekseevka
- Alexandrov
- Bobrov
- Ivanovo
- Kaluga
- Kostroma
- Dace
- Balashikha
- Eagle
- Ryazan
- Vyazma
- Michurinsk
- Rzhev
- Novomoskovsk
- Rybinsk
- Astrakhan region
Volgograd
- Anapa
- Bataysk
You can pay for your order in one of the following ways:
Cash payment at the point of issue.
In Belgorod, it is possible to pay for goods in cash at the warehouse without prepayment. When ordering in other regions of the Russian Federation - after making a partial prepayment.
Online payment by payment card
When choosing this payment system, you can pay for your order with a Visa, Mastercard or MIR payment card in Buscenter. All your confidential data (card number, registration data) is fully protected in accordance with PCI DSS security standards. Information is transmitted via the secure Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol and closed banking networks with the highest degree of protection. For additional authentication of the Cardholder, the 3D-Secure protocol is used. If the Issuer supports this technology, you will be redirected to its server to enter additional payment details."
What are contract body parts?
Contract parts are parts of used cars that have been dismantled. Sometimes any spare parts presented on the secondary market are called contract, regardless of origin. These contract spare parts must meet the following requirements:
- the car from which they were removed was operated within the country where disassembly was carried out (Japan, USA, a number of European countries);
- disassembly is legal, spare parts were imported to Russia with accompanying documents and went through the customs clearance process;
- after disassembly, testing was carried out, and the seller guarantees that the parts will last a certain period of time;
- the parts are “native”, original, and not analogues installed during repairs.
In Japan, cars can be dismantled after an accident, but more often owners get rid of cars with low mileage and in excellent condition due to the peculiarities of the legislation. To successfully pass a scheduled technical inspection, it is necessary to replace a number of parts, even if their actual service life has not yet been exhausted, so the technical inspection is expensive. And the older the car, the more often it should be carried out:
- for the first time – 3 years after purchase;
- for cars that have been in use for 3-10 years - every 2 years;
- for cars over 10 years old - annually.
Therefore, the cost of buying a new car is not much higher than the cost of maintaining the old one. A lot of cars in excellent condition end up on the secondary automobile market in Japan, but it is not profitable for the Japanese themselves to buy them, and it is not profitable for Russians to pay high duties for importing used cars into the country. But used parts are subject to a small duty, so used or salvage cars are sent to dismantling yards, where they are dismantled, the removed parts are sorted, they are tested and sold to companies specializing in the supply of contract spare parts to Russia.
After disassembly, all contract spare parts are sorted
The condition of different parts removed from the same car varies. For example, in damaged cars the body can be hopelessly damaged, but some internal components avoid damage and have a solid working life. If a car is sold in order not to pay for technical inspection, parts of the internal systems that were subjected to the greatest load may be worn out, but the body is impeccable.
Cat in a poke
The main problem with buying a contract motor is that its real condition is not always known even to the seller. Nobody disassembles the engine, how the previous owner of the unit drove and the service history is a mystery shrouded in darkness. At best, the technicians will measure the compression and see if the ECU is complaining about something critical. Unfortunately, there is nothing much you can do here. If you decide to buy a used one, you need to be prepared for the risks associated with it.
What is the difference between contract and used spare parts from a car disassembly?
Contract parts are imported from abroad. They are operated there and are strictly tested for safety and quality before sale. The auction organizer or recycling plant provides a complete set of documents for all spare parts.
Regular used parts from disassembly are removed from damaged, problematic or old cars that were operated and serviced in Russia. The quality of used parts from disassembly may be poor, or it may be excellent, therefore, when choosing spare parts from disassembly, always inspect them carefully.
Not always car dismantling shops can provide a complete set of documents and confirm the purity of the transaction (for example, if spare parts were removed from a stolen car). This may complicate further paperwork with the traffic police (for example, registering an engine replacement).
There are still advantages to such a purchase: used spare parts are much cheaper than new ones, often cheaper than contract spare parts. In addition, purchasing from disassembly significantly saves time if the part is needed in a short time. When choosing used parts from disassembly, evaluate all the pros and cons - then the purchase will not be an unpleasant surprise.
Useful tips
As you can see, only a competent approach to the issue of selecting a contract motor or gearbox allows you to get the maximum benefit from the use of such units. In this case, the most important aspect is to obtain a written guarantee from the seller of a particular contract unit.
Before purchasing, you must separately check the number of the contract engine with the number reflected in the documents, and the readability of the engine number on the cylinder block. You should also obtain from the seller the full accompanying documents for the internal combustion engine (a numbered unit card, which is issued during customs clearance, etc.). It is optimal to first make copies of all documents, and then contact the traffic police to verify in advance the possibility and legality of replacing the engine.
Also, we should not forget that after replacing the engine, it is necessary to register it with the traffic police, since the engine number is not indicated in the registration document, but it is recorded in the registration documents and must match. The main thing is that when replacing, you need to install an internal combustion engine of the same type,
power and volume
. Otherwise, the registration procedure may be greatly complicated.
Finally, we note that engine replacement should also be trusted only to experienced and qualified specialists, and the final decision on installing contract components should be made only after preliminary troubleshooting of existing units.
Is it possible to buy contract spare parts?
If these are truly contract spare parts with all the expertise and characteristics, then why not? As user reviews and forum posts show, contract parts are durable. And foreigners, as a rule, care about their business reputation, which cannot be said about Russian entrepreneurs.
When purchasing spare parts with a contract, require that the owner also provide documents. Otherwise, it will be an ordinary used part, and its price will be much lower. And when buying used, bargain. Don't be fooled.