Types of galvanizing
Today, car manufacturing companies use three main types of body galvanizing:
- galvanic;
- thermal;
- cold.
The second can be done on one or both sides of the body, which, when finished, is immersed in molten zinc. There is also a technology according to which molten zinc is applied to a sheet of metal during rolling. Cars from Volvo, GM, Porsche and Ford brands undergo thermal galvanization. It is very effective and protects the car from corrosion even after further processing.
Galvanic galvanizing involves soaking the finished part in a bath containing zinc electrolyte. The current affects the zinc, which, in turn, sticks to the metal surface of the body. This technology is very common among Japanese and European car manufacturers.
Cold galvanizing is less reliable than previous types, but it is also much cheaper, which is why it is used for galvanizing the bodies of economy variants. It is the application of finely dispersed zinc in the form of paint to the surface of a car body.
Auto body galvanizing kit
Overview of lubricants for calipers and guides
An experienced car enthusiast can already figure out how to lubricate the caliper guides while driving. For a novice car enthusiast, this question is open. Characteristics of lubricant brands will help in solving this problem.
Molykote Cu-7439 Plus
This mass is produced in the USA, it consists of fine chemical powder and oil. This brand is very popular today. The demand is explained by such qualities as:
- Wide temperature range.
- Resistant to pressure.
- Not subject to evaporation.
- Does not react to the action of solvents and cannot be washed off with water.
The product is supplemented with elements that prevent the destruction of solid parts, souring and the connection of parts with scale. Vehicle manufacturers Land Rover, Nissan, Honda, Subaru recommend this lubricant to their customers.
Grease MS-1600
This product is produced in Russia. This is a high temperature paste. It can exhibit positive qualities when exposed to temperatures from -50 to +1000 degrees. Chemical compounds, acids, alkalis, and water do not have a significant effect on the product. The lubricant does not damage equipment made of plastic and rubber, has properties that protect solid parts from destruction, and has flammable characteristics.
The paste is white in color and is used for moving pad ends and for caliper piston processing. MS-1600 paste does not react with brake solutions: DOT 3, DOT 4, DOT 5.0, DOT 5.1. The cost of the mass, packaged in 100-gram tubes, is about 350-400 rubles. You can purchase a five-gram sticker; it will be enough to replace a set of pads and cost less than a hundred rubles.
XADO VeryLube
The said mass is very accessible to the average car owner. It is used to process brake caliper guide equipment, which will protect the pads from jamming and seizing. The mass is sold in the form of a green liquid, packaged in containers holding 320 ml. Temperature range: from -35 to +400 degrees.
It is applied by applying 5 parts of lubricant, and the layer is applied after the previous one has dried. For those who are not inclined to pay extra and want to purchase a product of high quality, this lubricant will be a good purchase. The only thing you need to consider is that the lubricant consumption is a little more than usual. The cost of the goods is no more than 300-400 rubles.
SLIPKOTE 220-R DBC
This type of lubricant is considered excellent for all calipers. It has another area of use - water supply systems. Experienced motorists recommend using SLIPKOTE 220-R DBC, considering it indispensable for guides. Most car enthusiasts choose this brand when the question arises of how to lubricate the brake caliper guides. But difficulty arises when lubricant must be purchased. It is practically impossible to find it on the territory of Russia; all that remains is to order it from abroad.
The temperature range is from -46 to +299 degrees. It is made from pure unnatural oil, thickener and additives that give the lubricant anti-corrosion, anti-oxidation and anti-wear qualities.
Lubricants are supplied by the manufacturer directly to factories that produce cars under the SLIPKOTE brand. Products can be purchased through major automobile companies. However, lubricant is not cheap. One small 85 gram tube sells for approximately 1200-1300 rubles.
It is strictly forbidden to use mass in drum brakes.
LIQUI MOLY Bremsen-Anti-Quietsch-Paste
This type of lubricant is not recommended, despite the manufacturer’s assurance that it is effective at temperatures from -40 to +1200 degrees. Disadvantages of lubricant include:
- Not intended for lubricating caliper guides.
- Sold on sites of irresponsible sellers who hide its shortcomings.
How to detect chronic heart failure
A complication of most heart diseases if left untreated is chronic heart failure. It is characterized by the inability of the heart to pump blood throughout the body in the required volume. As a result, tissues and organs lack nutrients and oxygen.
What types of lubricants are there?
If you meticulously find out who produces these lubricants, you will find out that for the famous brands indicated on the packaging, these lubricants are produced by specialized companies. But the conversation is not about them, but about how these substances are divided, and which one is better suited for lubricating the guides and other elements of the caliper.
In this case, they can be divided into several different types, each of which contains several lubricants that correspond in their characteristics to the operating conditions of various elements of the disc brake caliper.
Synthetic or mineral pastes with added metals
In the first group, it is worth considering high-temperature lubricating pastes with Anti-Seize properties. These lubricating substances contain entirely or partly a synthetic as well as a mineral base. With the addition of synthetic thickeners, submicron particles of metals such as molybdenum or copper. Also, instead of metals, solid substances of lubricants can be used, which work successfully at super-temperature values. This group includes:
- Complex lubricating paste products.
- Metal-free pastes.
- Lubricants containing copper or molybdenum disulfide.
They can be used to cover anti-squeak plates, pressure springs, and the back side of the pads.
Here you can highlight pastes from the following major brands: Huskey, Loctite, Wurth, LIQUI MOLY, Textar, Mannol Kupfer, Valvoline Cooper, Motip Koperspray, Bosch SUPERFIT.
Mineral oil based pastes
The second group includes synthetic lubricating pastes, which are based on mineral oil with the addition of a bentonite thickener, containing fatty acids and metal particles. Their distinctive feature is the absence of a dropping point with a working range from –45°C to +180°C. Excellent for lubricating brake caliper guides (fingers). Here are several such pastes from different manufacturers: ATE Plastilube, Loctite Plastilube, Molykote.
Synthetic oil based pastes
Well, the third group includes lubricating pastes intended for all moving elements of the disc brake caliper: piston in the cylinder, guides (pins), etc. They are compatible with most rubber-based materials, elastomers and plastics. They are based on highly purified synthetic oils with the addition of a stable thickener and additives with anti-wear, antioxidant and anti-corrosion properties.
Such lubricants are insoluble in water, brake fluid, acids and alkalis. They also have low volatility and high dielectric strength. These lubricating pastes are produced by the following brands: Molykote, Permatex, SLIPKOTE.
Domestic manufacturers in this segment have distinguished themselves with MS-1600 paste.
From the description it is clear that the optimal choice is lubricating pastes of the third group, because it is not for nothing that many machine manufacturers recommend them.
Requirements for brake caliper lubricants
Standard lubricants like Litol-24, graphite grease, and any general purpose grease are not suitable for use in brake calipers. The reason is simple. The droplet formation temperature of standard lubricants does not exceed 60-70 °C.
From time to time, the calipers heat up to 500-600 ° C; accordingly, ordinary lubricant will leak out of the unit without a trace at the first heating.
To be fair, it must be said that such a high temperature occurs only in the friction zone of the brake pad friction lining on the brake disc. Thanks to the massive design of the caliper, heat is evenly distributed throughout the mechanism, and at the points farthest from the pads the temperature reaches a maximum of 200-250 degrees.
If we don’t want the brakes to fail at the most critical moment, caliper lubricants must meet certain requirements:
- The melting point of the lubricant must be above 500 °C.
- The lubricant should not be aggressive towards rubber parts (guide boots, brake cylinder piston boot and cuffs).
- The lubricant should not be dissolved by brake fluid and water, as well as road reagents.
- The composition must be compatible with all types of elastomers used in brake mechanisms (rubbers based on propylene, ethylene, ethylene-propylene copolymers).
Who produces lubricants for calipers, groups of lubricants
In most cases, the brands that make classic lubricants do not make caliper lubricants. To do this, you need to work with other materials, as well as have the appropriate equipment.
Interesting on the topic: Running in winter studded tires. Is it necessary?
In order to sell their products, companies producing special lubricants for calipers sign contracts either with well-known brands of lubricants or with brands that produce spare parts for brake systems. Sometimes they are taken under the wing of car manufacturers.
Here are a few of the main brands that produce lubricants that interest us:
- HUSKEY Specialty Lubricants . Known under the HUSK-ITT Corp brand, they produce a full range of caliper lubricants. May be marketed under the Huskey and Slipkote .
- Kluber Lubricarion Munchen KG also sells all groups of lubricants for brake calipers.
- Molykote brand produces caliper lubricants under the Dow Corning Corp. .
Of course, there are many more of them on sale. However, brakes are too important a mechanism to lubricate them with just anything.
All caliper lubricants are divided into three categories depending on the purpose of their use:
- Lubricants that can withstand high temperatures , their main property is anti-seize. They are used to lubricate the mating parts of brake pads and anti-squeak plates. Most often they are labeled as Anti-Seize. This is the most broadly targeted group of lubricants. This includes lubricants containing copper, graphite, aluminum inclusions, molybdenum disulfide, ceramics, magnesium silicate and other non-metallic additives.
- The edges of the pistons of the working brake cylinders, plastic bushings, and parts in contact with elastomers (oil seals, seals) belong to the second group of lubricants. They are labeled as Rubber Grease . The use of any silicone lubricants in this case is unacceptable.
- The third group of lubricants is the most common. It includes universal lubricants for all moving elements of the caliper. Suitable for parts that come into contact with plastic and elastomers.
Why lubricate brakes?
Under normal driving conditions, the outer casing of the caliper heats up to +150-200°C, and if the driver likes to brake sharply and is a supporter of an aggressive driving style, then up to +300°C. Rubbing parts are heated to higher temperatures: pads - up to +600°C. The caliper is constantly in contact with dirt, water, and powders used to treat roads against ice. Wear of the piston rings leads to leakage of brake fluid, which is also not harmless to the components of the unit. Lubrication performs a protective function. It protects parts from harmful effects and extends their service life.
The design provides that the caliper must move along guides that resemble long bolts with a short thread section. Over time, under the influence of external factors, the lubricant on the fingers thickens and dries, significantly complicating the braking process and contributing to wear of parts. You need to know how often the caliper guides should be lubricated. A high-quality composition must be replaced along with caliper parts that have expired, for example brake pads. If the lubricant cokes earlier, then change it in a timely manner. The old composition is cleaned off and a new one is applied. The fact that the paste has become unusable is indicated by uneven and rapid wear of the pads, creaking, and knocking of the brakes. In the future, the situation worsens, up to the jamming of parts. It is necessary to lubricate not only the guides (fingers), but also other parts:
- cylinder walls;
- the inside of the boot;
- outer sides of the pads;
- clamping brackets.
And each element requires a composition with special properties. Not all guides need to be treated with lubricant. Manufacturers such as TEVES, LUCAS, ATE install a plastic bushing. By definition, it does not need to be lubricated. If it doesn't work properly, it is simply replaced. You can also polish the guides to improve their sliding properties if they become coked or corroded. However, it is useless to polish “fingers” that show signs of serious wear. Lubrication won't help either. Therefore, if they are knocking, they need to be replaced.
What can't you lubricate?
Is it possible to lubricate caliper guides with substances that have proven themselves to be effective for other parts? For example, copper grease or lithol? If you act on the principle “everything is better than nothing at all,” such lubricants may be suitable. However, it will not be possible to truly protect the surfaces of the guides in this way. The fact is that the calipers of modern disc brakes are designed for extra-heavy, extremely intense work.
The temperature during friction between the disc and the pad reaches 500-600 degrees Celsius. When removing and dissipating thermal energy, other parts of the calipers heat up to 150 degrees or more. We are talking not only about aggressive driving on sports tracks, but also about driving on fairly rough terrain. Also, in any environment, the caliper is affected by water and salts that cover the road surface. Not to mention the impact that far from neutral brake fluid has.
Obviously, such loads require special lubricants designed to operate brake caliper guides under extreme conditions. The properties of all other lubricants are contraindicated here: coking, being washed out by water and dissolving in the brake fluid. With prolonged use, conventional lubricants are deposited on the plastic and elastomer parts of the calipers. This has a detrimental effect on them and causes brake failure when driving, which jeopardizes the safety of the driver and those around him.
List of lubricants for calipers and guides
Caliper lubricant MS 1600 made in Russia. Our lubricant is very popular and highly effective, the temperature range is -40 C ... +1000 C. The color is white. Does not corrode rubber and plastic parts. It is used to lubricate the guides and caliper piston, as well as the non-working and end surfaces of brake pads.
The cost of MS-1600 is approximately up to 500 rubles for 2021. The weight of the tube is 100 grams. To replace one set of pads, about 5 grams of this lubricant is enough, which is why it is sold in such small quantities, the cost of which is about 80 rubles.
We recommend: G Energy Expert G 10w 40: oil for high mileage engines
IMPORTANT! MC 1600 cannot be used with brake fluid marked DOT 5.0!
Dot 3, Dot 4, Dot 5.1 can be used with other brands of brake fluids.
Slipkote 220-R DBC / Slipkote (Silicone Disc Brake Caliper Grease and Noise Suppressor). This lubricant has proven itself to be an excellent element for lubricating caliper guides, which can even be used in a water supply system.
The temperature range of such a lubricant is from -50 to +300 C. It consists of pure synthetics, a thickener and an additive that provides protection against corrosion. The downside of this brand is that it is more expensive than others, costing approximately 1,200 rubles per 85 gram tube.
IMPORTANT! For vehicles with a drum brake system, Slipcoat 220-R DBC cannot be used. Alternatively, you can use Husky 2000
The next brand of lubricant for calipers and guides is Xado Verylube. It is cheaper than its competitors. Its use prevents the brake pads from jamming on the caliper guides.
Sold in the form of a spray, color green, can volume 320 ml. Operating temperature range -45 ... +400 C. Does not corrode rubber parts. Apply in layers, apply, wait until it dries, apply again, and so on 5 layers. The price is about 250 rubles.
American brand of lubricant Molykote Cu 7439 is made from finely ground copper powder and semi-synthetic oil. One of the most common brands for calipers. Retains its properties at temperatures from -30 to +600 C.
It is not washed off or dissolved by water or brake fluid. Evaporation is close to zero. Withstands high pressure. Thanks to its composition, Molikot Ku 7439 lubricant protects against corrosion and sticking of parts.
And the next brand of lubricant, LIQUI MOLY Bremsen-Anti-Quietsch-Paste, was originally for calipers, but those who used it on their cars complained about problems arising in the operation of the caliper and guides.
After this, the manufacturer changed the purpose of the Likui Moli Bremsen Anti-Squeak Paste lubricant to anti-squeak use. Therefore, it is better not to use it on the guide pins of calipers; this is also stated by the manufacturer himself on the official website.
We recommend: Liqui Moly 10w-40 Teilsynthetisch Optimal engine oil
When lubrication is not effective and replacement is required
Sometimes owners try to “cure” the knocking noise of worn guides with lubricant, but if the wear on them is high and the caliper is literally hanging on its fingers, the paste will not help - only repairs. By the way, on some cars, parts of the brake system begin to make themselves known by knocking during the warranty period. For example, a similar thing was noted in the case of Chevrolet models, in which the problem manifested itself at runs of up to 30 thousand kilometers and was associated with a “disease” of the guides.
If the “fingers” are worn out, it is recommended to purchase a repair kit that includes guides, boots and fasteners. The main thing is not to get into parts that are defective or made from low quality material. Unfortunately, this happens. Caliper rattling is also possible when the guide seats are worn out. This can be treated by installing special rubber bands on the pins.
What to lubricate when replacing brake pads
When replacing the front or rear brake pads, you need to apply lubricant to the caliper guides. This will protect them from souring, deformation, corrosion, and also reduce mechanical wear. If the vehicle has an ATE brake system with open guides, the use of special agents is strictly prohibited.
To reduce high-frequency sound, you need to apply a thin layer of paste between the plate and the non-working side of the pad. It is recommended to coat the ends of the consumables with a special agent. This prevents the pad from rubbing against the caliper. It is prohibited to use block lubricant for the guides - the rubber boots will swell. The tightness will be lost, moisture will get inside, and the corrosion process will begin.
When replacing brake pads, lubricant is also applied to the plates holding them. It reduces the volume of extraneous sounds and protects against rust. It is worth applying the paste not only to the staples, but also to the seats.
For reliable operation of disc brakes, it is recommended to lubricate the piston. This will allow it to move freely inside the cylinder.
It is important that the composition does not react with the brake fluid. The effect of thermal fluid on lubrication is discussed in more detail in the video:
It is not necessary to remove the piston to apply the product.
There is a high risk of cuff rupture, so when servicing the unit, it is important to balance the risk of damage to the boot and the need to change the lubricant on the piston. If you do not have the necessary skills, it is better to contact a car service center.
Treat fastening joints with special means. Then it will be easier to disassemble the mechanism. To prevent spontaneous unscrewing or damage to the thread, it is necessary to control the tightening torque using a torque wrench.
If replacing the pads involves installing a new disc, the surface underneath should be coated with an anti-stick agent. Copper grease in aerosol cans is suitable. The spray torch must be directed carefully so that the liquid does not fall on rubber or plastic surfaces.
What and where to lubricate
Things to consider when using a lubricant:
- If there is creaking and other extraneous sounds when braking, the anti-creaking plates must be treated with the product. Please note that parts must be lubricated on both sides. The part that is installed to the working cylinder piston does not need to be processed.
- To simplify the procedure for moving the piston, its surface is treated with lubricant. At the same time, it is important not to overdo it, since the excess part of the substance will begin to be squeezed out of the anthers over time.
- When operating a car, it is necessary to regularly treat the springs that are used to press the pads. It would be useful to lubricate the surfaces of the latter. Lubrication of the friction layer, which is considered working, is not allowed.
- Using a lubricant for brake guides, it is necessary to treat the so-called fingers, that is, the calipers themselves. The amount of substance must be sufficient. But if there is a lot of lubricant, it can get on the working surface of the pads, which should not be allowed.
Installation of trailer hitch
If you decide to tackle the installation yourself, prepare for it mentally and physically. Plus, don’t forget about vehicle registration. I already talked about this HERE.
When everything is ready for installation work, we begin to create miracles in our garage.
- Remove anything unnecessary from the trunk of your Renault that might be in the way. You will also need to remove the spare tire and muffler. Place the car over a hole or lift the rear end with jacks. Prepare a set of tools, drawings with dimensions included with the trailer hitch, and remove the negative from the battery;
- Now remove the factory plugs. You will find them on the right and left under the trim inside the trunk. They are simply pryed off with a screwdriver and removed;
- Fastening bolts are inserted into the freed hole. Look underneath the crossover and make sure they protrude from there. Inside the spar, do not forget to install bushings that will protect the bolts;
- Install side lugs (brackets, if anyone has forgotten) on the ends of the bolts, secure with washers and nuts, but just push them on without tightening. Then you can adjust it as needed;
- Now it’s the turn of the cross beam. It's quite easy to install;
- Align the holes on one side and on the side, attach it to the nut. The same thing is done on the other side;
- Adjust the position of your beam. Now you can tighten the bolts properly;
- The installation of the mechanical part is completed with a tow hook.
If you watch a visual video, it will be easier for you to carry out all these manipulations. Don't forget, this is still half the job. The main goal is to make the connection not only mechanical, but also electrical.
Electrical component
Before installing the towbar electrics, read the instruction manual for your Renault Duster. Here you will need to deal with the matching block. What it is and why it is needed, I already wrote HERE.
We proceed something like this:
- First, the negative terminal from the battery is disconnected;
- now we find the terminals in the rear lamp shades, which are responsible for their operation;
- we lay a cable with wiring from the outlet to our trunk;
- we separate the wires by color so that the trailer hitch wiring matches the color of the wiring on the car (this is where the operating manual and the factory instructions for the towbar come in handy);
- wires must be copper and stranded with a minimum cross-section of 1.5 mm2;
- the ends are clamped and insulated;
- the trailer hitch socket is mounted on the cross beam of the towbar using several screws;
- the wiring goes into the trunk and is neatly hidden there;
- the ends of the wiring are fixed in the terminal harnesses and connected in a standard hole.
As you can see for yourself, there is nothing particularly difficult with installing towbars on the Renault Duster crossover. And there shouldn’t be any problems with the choice. So go for it!
What not to use when lubricating guides
There are a few rules regarding what is prohibited, advised and not recommended for lubricating a moving part:
- It is prohibited to coat the surface with copper and ceramic pastes. These compounds are only suitable for lubricating the pad insert into the caliper. Trade name: anti-squeak compounds.
- You cannot lubricate with graphite and copper compounds that are not included in the model repair kit with the boot - the lubricant dries out quickly and the finger will jam.
- Litol is not used for optimal finger movement. Litol becomes fluid from high temperature, flows out and corrodes the anther.
- Service compounds intended only for the braking system.
Which caliper lubricant is better?
The answer to this question is both simple and complex: of course, it is best to use high-quality materials, but chosen correctly. Remember that low-temperature materials dry out or wash out quite quickly, leading to completely disappointing results such as soured and jammed guides and pistons, as well as squeaking pads.
The main thing is to know what you are choosing. For example, for fingers you should use a grease based on a thickener and synthetic oils that can withstand high temperatures - it will not “leak” or coke. At the same time, anti-squeak compounds for the back of brake pads are harmful in the case of fingers.
How to lubricate brake caliper guides
How to lubricate the caliper guides to completely protect them from any destructive influences? The rules here are simple, and for all types of lubricants and car brands they are approximately the same. By following simple step-by-step instructions, you can quickly learn how to lubricate brake caliper parts yourself, without wondering how to do it correctly.
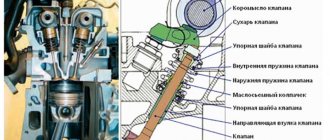
Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove the caliper body.
- We remove the guides along with the anthers.
- We clean the bushings from old grease.
- Lubricate the guides and insert them into place.
- Reassemble in reverse order.
In order for the caliper to close back, it is necessary to retract the cylinder using special pliers. If they are not available, improvised objects will do: a wooden block, the shaft of an ax or hammer, etc.
Recommended Lubricants
What is the best way to lubricate the caliper guides? If we talk about professional lubricants produced by automobile concerns, they are quite expensive - usually about $20. On the other hand, they are always enough for a long time. If, for example, you are the owner of a Toyota, then it is recommended to choose Toyota White Grease, etc. Based on the names of the concerns, the easiest way is to choose the most suitable lubricant specifically for your car. By doing this, you probably won't go wrong.
Multi-purpose lubricants are often used by owners of sports cars and other machines intended for use in extreme conditions. They will not harm any other car that undergoes regular strength tests on Russian roads. We are talking primarily about Slipkote® 220-R DBC.
Types of lubricants
It’s worth pointing out right away that manufacturers divide lubricants into two types - paste and spray. Before we move on to listing their types and brands, it is necessary to decide what characteristics the caliper lubricant should have. With an aggressive driving style or driving along mountain serpentines, the caliper temperature can reach +300°C, and in urban conditions it can heat up to +150°C...200°C. In addition, the caliper is affected by moisture, dirt, and reagents that are sprinkled on the roads. Therefore, the lubricant for calipers and its guides should be:
- non-aggressive towards rubber and plastic parts of the machine;
- do not lose their properties when exposed to water, brake fluid or other substances that can wash or dissolve it;
- high-temperature lubricant, that is, not to lose its temperature properties at +180°C or more;
- should not lose its physical properties in severe frosts (from -35°C and below).
Commonly used cheap lubricants do not provide the described conditions. We are talking about graphite paste, lithol, nigrol and their other analogues. That is, for the normal operation of the brake system, and in particular the caliper, it is necessary to use modern developments.
Currently, manufacturers produce the following groups of lubricants for calipers:
First group
— mineral or synthetic pastes using metals. They are of the high temperature extreme pressure type. Their operating range is very wide, and is approximately -185°C...+1100°C (each lubricant has its own operating range).
The substance is based on synthetic or mineral oil, to which thickeners have been added, as well as metal particles (copper or molybdenum). These include the following subtypes:
- complex pastes, which include copper, aluminum and graphite powder;
- copper, containing copper and graphite powder;
- pastes without metal particles, instead of which magnesium silicate and ceramics are used;
- lubricants based on copper or molybdenum disulfide.
Examples of specific brands of lubricants of this type:
- complex pastes - HUSKEY 2000 Lubricating Paste and Anti-Seize Compound for High Temperature, Loctite No. 8060/8150/8151, Wurth AL 1100;
- copper pastes - HUSKEY 341 Copper Anti-Seize, LIQUI MOLY Kupfer-Paste, Mannol Kupfer-Paste Super-Hafteffekt, Marly Cooper Compound, Molykote Cu-7439 Plus Paste, Motip Koperspray, Permatex Copper Anti-Seize Lubricant, Pingo Kupfer-Paste, Valvoline Cooper Spray, Wurth SU 800;
- metal-free pastes - HUSKEY 400 Anti-Seize, TEXTAR Cera Tec, LIQUI MOLY Bremsen-Anti-Quietsch-Paste;
- pastes with molybdenum disulfide - HUSKEY Moly Paste, Assembly Lubricant & Anti-Seize Compound, Loctite No. 8012/8154/8155.
Pastes belonging to this group can be applied to GUIDE PINS of brake calipers and any highly loaded friction surfaces, except for the working surfaces of brake pads!
Second group
— Pastes based on mineral oil. They contain bentonite, which acts as a thickener. In addition, metal particles and fatty acids are added here. The main advantage of mineral-based lubricants is stable operation in the temperature range from -45°C...+180°C. That is, the paste does not flow out and does not lose its properties. Thus, it is excellent for lubricating the guide calipers of vehicles operated under gentle conditions. An example of this type of lubricant is Teroson VR500.
Third group
- lubricants based on synthetic oil. These are the most universal compositions, since they are suitable not only for lubricating calipers, but also other elements of the car’s braking system. Lubricants are made from purified synthetic oil, as well as additives that have anti-corrosion, anti-oxidation, and anti-wear qualities. The composition also includes a thickener. Lubricants based on synthetic oil have excellent characteristics. They do not dissolve in water, brake fluid, alkalis and acids, do not evaporate, and also have dielectric properties. The operating temperature range is approximately -40° to +300°C.
Examples of lubricants are Molykote AS-880N Grease, Permatex Ultra Disk Brake Caliper Lube, SLIPKOTE 220-R Silicone Disc Brake Caliper Grease and Noise Suppressor, SLIPKOTE 927 Disc Brake Caliper Grease.
The scope of their use is wide. They are used to lubricate sliding and rolling bearings, as well as other parts operating under conditions of high temperature and significant pressure.
One of the most popular types of pastes and sprays for calipers and guides are copper greases, which are a type of lubricant that uses metal. Let's look at it briefly.
Operating conditions for calipers
Disc brake calipers function in difficult conditions of use. They are exposed to critically high temperatures, reaching 600 degrees. Especially in situations of sudden braking or when moving along mountain serpentines.
As a result of further heat removal and cooling of the elements, the temperature can be reduced to 180 degrees. Brake calipers (CT) operate under conditions of exposure to water, pollution, as well as reagents that road services sprinkle on roads during the cold season. If the piston sealing rings wear out during vehicle operation, brake fluid may also leak into the caliper lubrication system. To prevent malfunction of the unit, it is necessary to use special lubricants.
Treating guide supports with lubricant
Sweaty palms - prevention
If sweaty hands only bother you occasionally, preventative measures will help you avoid more significant problems in the future. By following simple tips, you can significantly reduce the frequency of unpleasant processes and their intensity. When your palms sweat, prevention in the form of losing excess weight, normalizing your menu, or avoiding stress is quite effective. Additionally, try:
- regularly visit the sauna or bathhouse to remove toxins;
- do not eat too hot food;
- fall in love with daily contrast showers;
- use special cosmetics;
- Use antibacterial soap to wash your hands.
And in conclusion, I want to reassure you that science does not stand still; in recent years, active work has been carried out to find the latest methods of getting rid of the problem of hyperhidrosis. If your palms sweat, prevention will help you wait until the time when a reliable, optimal way to cure excessive sweating is successfully found.
Useful links:
Requirements
To choose the right lubricant for pins (guides), pistons in caliper cylinders and other elements, you need to focus on the requirements described below:
- The lubricant must be non-aggressive to rubber, elastomeric and plastic parts.
- It must remain resistant to brake fluid, water and other aggressive substances that can dissolve and wash it away.
- It is necessary that this lubricant can be high-temperature and withstand heat of 180°C or more. That is, so that it does not melt under increased thermal loads and does not leak.
- It also needs to not lose its properties at sub-zero temperatures, which can reach –35°C and below.
Therefore, you should not listen to “figures” who broadcast that you can use lithol and other similar lubricating substances for these purposes. After all, this is fraught not only with breakdowns of this unit, but also with the possibility of significant financial losses in the event of an accident.
How to lubricate calipers: guides and cylinders
When you service or change brake calipers, you need to lubricate their contacting and rubbing surfaces: guides (pins), working cylinder piston, clamping brackets.
You can read about this in the manual of any car. And purely logically, this is understandable to any car enthusiast. But if you do this incorrectly or use lubricants that are unsuitable for these purposes, then you can only cause harm by rendering the components of the caliper unusable. In order to understand how to properly lubricate all elements of the caliper, as well as how to do this, you need to understand the following questions:
- Under what conditions does the caliper operate?
- What requirements must the lubricant chosen for it meet?
Types of lubricants
Classifying lubricants by type, they are divided into paste and spray. The car caliper can heat up to almost +300 C when driving outside the city in mountainous areas with heavy use of the brakes. In urban conditions, the caliper heats up to approximately +200 C. The calipers are not protected from external abrasive substances and moisture. In this connection, the lubricant for them must have good characteristics that ensure reliable operation of the devices.
Properties and characteristics of the lubricant:
- do not have acidity, that is, do not corrode metal and rubber;
- if water or brake fluid gets on it, it should not spread;
- withstand high temperatures, approximately +200 C;
- withstand severe frosts, up to approximately -35 C
- should not lose its properties.
Many people use cheap lubricants that do not have such effective physical and chemical characteristics.
Cheap lubricants include: litol (litol 24, litol 24RK, cyatim 201), graphite lubricant, nigrol, grease. Hence, smart drivers conclude that for reliable operation of the braking system it is better to use special lubricants for calipers and guides.
Classification by brand, that is, by manufacturers of fuels and lubricants:
- the first group of SMEs (mineral or synthetic pastes);
- the second group of PMM (mineral oil-based pastes);
- the third group is SSM (lubricant based on synthetic oil).
A feature of the first group, mineral and synthetic pastes using metals, is that they can withstand very high temperature conditions, about +180 ... +1000 C. Each type of lubricant has its own temperature range.
To make lubricants of the first group, mineral oil or synthetics are used, as well as thickeners, and also particles of the metal molybdenum or copper.
The first group of lubricants is divided into subgroups:
- Complex paste. The composition of the complex includes copper, aluminum and graphite powder.
- Copper. Copper paste contains copper and graphite powder.
- Paste without metal particles. Metal-free paste includes magnesium silicate and ceramic.
- Grease with copper or molybdenum disulfide.
As an example, I will give some brands of lubricants in this group:
Brands of the first subgroup (complex paste): Huskey 2000 Lubricating Paste and Anti-Seize Compound for High Temperature, Loctite No. 8060/8150/8151, Wurth AL 1100.
Brands of the second subgroup: HUSKEY (Husky) 341 Copper Anti-Seize, LIQUI MOLY Kupfer-Paste, Mannol Kupfer-Paste Super-Hafteffekt, Marly Cooper Compound, Molykote Cu-7439 Plus Paste, Motip Koperspray, Permatex Copper Anti-Seize Lubricant, Pingo Kupfer-Paste, Valvoline Cooper Spray, Wurth SU 800.
Brands of metal-free pastes: Husky number 400 Anti-Seize, TEXTAR Cera Tec, LIQUI MOLY Bremsen-Anti-Quietsch-Paste.
Brands of the fourth subgroup with molybdenum disulfide: HUSKEY Moly Paste, Assembly Lubricant & Anti-Seize Compound, Loctite No. 8012/8154/8155.
All pastes of the first group are applied to brake caliper pin guides and all surfaces with high friction friction. Who doesn't know, the surfaces of the brake pads are not lubricated.
The second group includes pastes based on mineral oil. This paste contains the thickener bentonite, metal particles and fatty acids. The operating temperature range of such a lubricant is -45 C ... +180 C. It follows from this that if you use this type of lubricant, then the car must be operated so as not to drive on steep slopes and frequent braking. This is, for example, the Teroson VR500/Teroson VR500 brand.
The third group of synthetic oil lubricants. It has excellent physical and chemical characteristics. Due to the fact that such a paste contains purified synthetics, a thickener and additives that protect against corrosion, oxidation and wear, this lubricant does not spread or evaporate, it is also not soluble in water and brake fluid, it is a dielectric, that is, it almost does not conduct electricity. Operating temperature -40 C… +300 C.
This group includes the following brands of manufacturers: Molykote AS-880N Grease, Permatex Ultra Disk Brake Caliper Lube, SLIPKOTE 220-R Silicone Disc Brake Caliper Grease and Noise Suppressor, SLIPKOTE 927 Disc Brake Caliper Grease.
What types of silicone lubricants are there?
Based on their state of aggregation, the following types of silicone lubricants are distinguished.
Aerosols
Solvents are sometimes added to aerosol materials to reduce viscosity. In this case, at the time of application the material has good penetrating ability, and after the solvent evaporates it becomes thicker.
Aerosol lubricants are the most popular form of silicone lubricants. They are easy and convenient to apply. They do not require additional tools for application. Aerosol cans are constant attributes that about half of all car owners constantly carry with them.
However, this type of material also has disadvantages. When applied, they form a conical “torch”. As a result, the lubricant gets not only into the treated areas, but also into the adjacent areas. In addition, aerosol cans have a rather fragile design, so they must be protected from thermal and mechanical influences.
Liquids
Such materials are essentially pure silicone oil. Depending on the purpose of the product, they are manufactured with different viscosities.
They are produced in vials, vials, bottles, cans, canisters and larger containers. Sometimes bottles are equipped with special applicators, which, when used, are automatically saturated with the lubricant contained in the package. The lubricant is applied to the surface and rubbed with an applicator.
Another method of application is through an oil can. Many bottles have elastic packaging and are equipped with a thin, elongated spout that allows you to accurately dose the lubricant and apply it to hard-to-reach places.
Lubricants can also be applied in the standard way - using a brush or sponge.
How to clean the caliper
As you know, in order to lubricate a mechanism well, it is necessary to first clean it of dirt and old grease.
Brake cleaner is very suitable for these purposes. Not because it is a brake cleaner, but because it cleans everything well and at the same time has a low price for a fairly decent volume of 500 ml. And this is also TRW
Article number PFC105
This cylinder cost me 50 UAH. and I use it wherever I need to clean something
But in such a seemingly simple matter, not everything is so simple either. YouTube is literally filled with videos on cleaning brakes. Everyone is literally obsessed with this. Everything would be fine if not for one thing...
The whole point of instructive articles and videos comes down to the fact that it is necessary to spray the contents of the can at any angle onto the brake disc and brake caliper. And after evaporation, the brakes of your car will shine and will brake better, since you have washed off all the dirt and dust from them from abrasion of the pads.
At these moments I have a picture before my eyes of how this cleaner washes out all the lubricant from the guide pads and other places, and given the fact that most of these cleaners are made of oil, the swelling rubber bands of the anthers actively complement this sad picture.
Therefore, my opinion is that it is necessary to use such cleaners after disassembling the caliper and removing all the anthers. Only after this clean everything and wait for the cleaner to evaporate. Then you can apply new lubricant and install rubber seals and boots.
All of the above, although this is my personal opinion, I sincerely advise you to listen to it. It seems to me that this will help you avoid many problems and disappointments when servicing the caliper.
And, of course, the first thing you need to do is take care of the anthers, since none of these lubricants can fully perform their function if the anthers are torn or stretched.
And what happens if you don’t notice a worn boot in time, look here