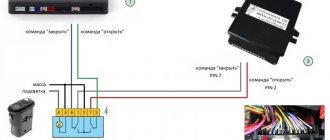
Although Toyota cars are very reliable and durable, even Toyotas can suffer from breakdowns and experience engine problems.
If there is an engine or emissions problem, your Toyota will turn on the Check Engine on your dashboard. You may also receive other alerts such as VSC and Trac Off.
In this guide, you will learn about common problems that cause your Toyota warning light to turn on. Additionally, you will find step-by-step instructions on how to read and clear your Toyota check engine light using an OBD2 scanner.
Symptoms
The first thing that happens is that your Toyota check engine light is constantly on . Other common symptoms you may notice include:
The engine is running poorly
Traction light or VSC Light turns on
Check if engine light flashes when accelerating
The engine misfires or shakes
Poor gas reaction
If you experience any of the symptoms described, this is an indication that your engine is not working properly. To avoid any further damage, start looking for a suitable place to safely stop and shut down the engine, and check a few basic items as shown below.
In some cases, your Toyota check engine light may come on without other symptoms. Most likely the problem is related to emissions. Please be aware that the vehicle may have increased emissions and fuel consumption. Don't ignore your Toyota check engine light, even if there are no obvious performance problems.
“TRC OFF” light on Toyota: How to solve the problem with traction control
Car owners often notice that the “TRC On” light is on.
This is traction control. What this feature protects against and controls on modern cars, as well as what to do if “TRC Off” lights up, the reader will find in this article. The traction control system first appeared in 1971 in America on such famous cars as Cadillac and Buick. It began to be used on luxury cars of the German brand Mercedes since 1987. After the 2000s, manufacturers began to include TRC in every car.
Common problems
A Toyota check engine light can come on for many reasons, ranging from a loose gas cap, a faulty ignition coil or spark plug, and even a blown head gasket. Let's take a look at the common problems that cause the check engine light on Toyota.
Fuel cap
Check engine light on Toyota Camry, Corolla, Sienna, 4Runner, Highlander, Matrix, Avalon, Rav4, etc. may come on if you do not tighten the gas cap . Find a safe place to stop. Make sure you install the gas cap.
If the gas cap is installed, tighten it.
Spark plug
Many Toyota owners don't realize that spark plugs are maintenance items.
Most Toyota vehicles require spark plug replacement between 90,000 and 120,000 miles.
If you don't replace your Toyota spark plugs within this time frame, they will eventually fail to cause the check engine light to come on. Additionally, you are more likely to get a misfire at the point where the engine starts to shake.
Idle control system
If you have an older Toyota with a cable drive, you may have problems with the idle air control system. In most cases , the idle air control valve becomes dirty or blocked by carbon buildup. This problem can be solved by cleaning the parts with carburetor cleaner. The throttle position sensor may also be faulty. Symptoms include a rough idle and hesitation when accelerating from idle. Code P0505
Vehicle speed sensor malfunction
Although Toyota is generally very reliable, it is well known for vehicle speed sensor failure.
This will trigger the check engine light in combination with the ABS/TC/Cruise lights. But a speedometer that doesn't work is a clear sign of a problem with the car's speed sensor.
The sensor is located on the output side of the transmission. Be sure to check the wiring and connector for damage. Typically you will receive a code P0500.
Crankshaft position sensor
If you are experiencing sporadic "won't start" situations, or your Toyota is shutting down for no apparent reason, you may have a bad crankshaft position sensor.
Before replacing the sensor itself, carefully inspect the wiring as it may suffer from heat damage. Code P0335.
Timing circuit
Check engine light on Toyota Camry, 4Runer, Highlander with V6 engines may be due to a stretched timing chain .
Although they are designed to last a lifetime, they may experience circuit overstress or tensioner failures. This can cause timing problems and associated engine error codes. Usually not a problem unless your Toyota has reached 200,000 miles and the timing chain has not been replaced.
Mass air flow sensor
If you experience a rough idle, lack of power, or hesitancy when accelerating, it's likely that your engine is running lean. Most Toyota engines have mass air flow sensors. This adds some complexity, and a possible vacuum leak causes the MAF to reset. Another common problem is an incorrect reading from a dirty MAF sensor. Do not use anything other than MAF cleaning fluid for cleaning. Code: P0171.
Oxygen sensor/catalytic converter
A check engine light caused by emissions control issues is something you're likely to encounter if you drive a high-mileage Toyota.
Although this will be signaled as low catalytic converter efficiency, it is possible that you have a faulty downstream oxygen sensor. Be sure to rule this out before replacing the much more expensive catalytic converter. Codes: P0420 to P0431.
Engine sucks
Many Toyotas made in the 2000s are susceptible to oil sludge caused by a blocked PCV valve.
This can cause a variety of problems ranging from high oil consumption, rough idling or check engine light, and even complete engine failure at highway speeds.
The telltale sign is a cloud of blue smoke during startup or acceleration. You may also receive emissions control related codes such as P0420.
Variable valve timing
Most Toyota engines have variable valve timing (VVT). The above oil sludges, as well as poor maintenance in general, tend to have a negative impact on it. In most cases it is a VVT filter that becomes clogged with lubricated oil.
What to do when your Toyota check engine light comes on?
Check the gas cap
Make sure the gas cap is on and securely sealed. Find a safe parking spot. Stop the engine and set the parking brakes. Open the fuel tank cap and make sure the fuel tank cap is tightly closed. Turn the gas cap clockwise until you hear a click sound several times. The check engine light will reset on its own within two to three days. An OBD2 scanner can be used to reset the Toyota warning light if there are no other problems.
Control the car
Allow the engine to cool. Then check the engine oil level and the coolant level in the overflow tank. You can continue your journey if you do not notice any performance issues and the check engine light is not flashing .
Reading Trouble Codes (DTC)
Read codes using an OBD2 scanner through the diagnostic port under the dashboard. See instructions in the next section.
How to diagnose Toyota check engine light
- Locate the OBD2 port under the dashboard.
Connect your OBD2 scanner. Turn on the ignition, but do not start the engine.
Turn on the scanner and let it communicate with the car. Select Read Codes from the main menu.
- Press enter and the fault codes will be displayed on the screen. Scroll to see all codes. the Current, Pending and Persistent codes .
- Write down all the codes and research all the codes online.
Don't start replacing parts on your Toyota based solely on the fault code. Contact a mechanic for advice if necessary.
Check engine flashing
Image
Your Toyota check engine light may flash when accelerating or idling. In addition to the blinking check engine light, the engine will also shake.
These symptoms indicate a misfire in one or more engine cylinders.
When driving a Toyota, check that a flashing check engine light can damage the catalytic converter and cause the engine to overheat. Restarting the engine or easing off the throttle may help your engine return to normal operation.
We do not recommend that you drive your Toyota if your check engine light is flashing.
FAQ
Toyota VSC and Check Engine Lights On
Disable Trac and Check Engine Light on Toyota
- Typically, the traction control light will come on when the check engine light turns on on your Toyota. Traction control turns off, but this does not mean there is a problem with the Trac system. Simply fix the check engine light problem and the Trac Off light will also be reset.
Is it normal for a Toyota check engine light to come on after an oil change?
The only reason Toyota checks the check engine light after an oil change is if the sensor accidentally trips. Otherwise, there's no reason to get an oil change on the route to get your Toyota CEL running.
Can I reset my Toyota check engine light by disconnecting the battery?
Yes, you will reset the check engine light, but that will not solve the problem. If you think the problem has been fixed, drive for a couple of days and the light will go off on its own. Another disadvantage of disconnecting the battery to reset the Toyota check engine light is that any trouble codes that may help you diagnose the problem will be cleared from memory.
Show similar tags
toyota check engine light codes flashing toyota check engine light toyota check engine light vsc reset engine light check toyota check engine light toyota awd toyota check engine gas tank light toyota engine light diagnostics. Toyota check engine light is not on Toyota Toyota Check Light oil change Turn off the Toyota check engine light. Toyota check engine light C1201 Toyota check engine light VSC Trac off Toyota check engine gas tank reset Toyota check engine light cold weather Toyota check engine light VSC 4WD Toyota check engine light on but no codes Toyota check engine light and turn off light on Toyota check engine light engine and VSC Toyota check engine light after oil change Toyota check engine light and gas cap Toyota Venza check engine light awd toyota rav4 check engine light awd Toyota Tacoma check engine light and track Toyota Highlander check engine light and go out Toyota 4runner check engine light and go out Toyota 4runner check engine light and VSC Toyota Highlander Check Light engine management systems toyota sienna check engine light and VSC Toyota Sienna check engine light and track Toyota Rav4 Check engine light VSC and 4WD on Toyota Avalon check engine light VSC Trac off Toyota Avalon Check engine light toyota auris check engine light toyota avanza check engine light reset toyota avanza check engine light toyota check engine light flashing toyota camry check engine light flashing toyota highlander check engine light flashing toyota sequoia check engine light flashing toyota corolla check engine light flashing toyota avalon check engine light flashing on Toyota 4Runner check engine light is flashing Toyota rav4 check engine light is flashing Toyota Sienna check engine light is flashing Toyota T100 check engine light is flashing Toyota Prius Check engine is flashing Toyota Yaris check engine light is flashing Toyota Camry 2007 check engine light is flashing Toyota engine light is flashing and battery light is on 2000 Toyota Avalon Check Engine Light Blinking 2002 Toyota Camry Check Engine Light Blinking 2004 Toyota Toyota Sienna Check Engine Light Blinking 2006 Toyota Toyota Avalon Check Engine Light Blinking 2001 Toyota Telica Check Engine Light Blinking 1999 Toyota 4runner Check Engine Light Blinking
VSC and TRC off errors
What is tpms in a car and how does the tire pressure monitoring system work?
If TRC Off and VSC light up together on a Toyota Avensis, this means that there is a problem with either the wheels or the engine or the wiring has broken.
It is necessary to diagnose the sensor information through computer software. If the car owner is an experienced mechanic, then he can do this at home. If the driver does not have experience working with diagnostic equipment or a scanner, then it is recommended to go to a service station.
Attention! Experts and experienced car owners do not recommend clearing VSC and TRC OFF errors on Toyota Avensis or Auris by removing the terminal from the battery pack. If the problem was not a computer firmware glitch, it will happen again
and a minor malfunction will turn into a major overhaul of the entire machine.
On Toyota Avensis, the TRC Off and VSC lights usually light up as garlands. A third Check Engine light is added to these. These are common mistakes that are discussed by owners of Prado cars, Toyota Progress NC 300, on specialized forums.
The problem appears at different times of the year. The intensive occurrence of the error is due to the cold weather during the winter season, to which cars are not accustomed and the computer may malfunction. But often Toyota's TRC Off lights up when the fault is in the car itself.
When VSC lights up together with TRC in a Toyota Avensis, problems can be:
- with the engine, if the “Check Engine” light also comes on. Failure of the engine results in the following types of malfunctions that a driver without a scanner will notice: increased fuel consumption, decreased power when driving on flat terrain, difficulty shifting gears, sudden stops or jerking of the car;
- damage to the wires going to the ABS sensors;
- low tire pressure;
- poor contact on the stops;
- if the steering wheel has recently been replaced and calibration has not been performed.
Attention! Experts confirm that on Toyota Avenis and Auris, the lighting of the VSC and traction control lamps is a common glitch. It is recommended to check the connectors, move them, disconnect them and insert them back
All-wheel drive Rav 4 1st generation
The Rav 4 10 uses permanent all-wheel drive STD I , which is a follower of the traditional Toyota FullTime 4WD . The distribution of moments is made in equal proportions between the two rows of wheels. This is achieved through a symmetrical, tapered center differential. The locking design is a multi-disc hydromechanical clutch.
At the same time, RAV4 10 was equipped with two types of gearboxes:
- A241H – with hydraulic control system;
- A540H - with full electronic control, while on models released after 1994 there is no control button.
To adjust the load distribution between the axles, there is a button C.DIFF AUTO , which is located on the center console. It is only missing on Toyota RAV4 equipped with A540H type gearboxes manufactured after 1994.
When the button is disabled, 4WD works with a free center differential. By turning on the button, the distribution between the drive wheels can be adjusted automatically. In this case, the range of changes in the maximum blocking coefficient is limited by two selector positions - L and R.
For normal 4WD operation, it is recommended to constantly use the automated load distribution between the axles. It is displayed only when the vehicle is towed or when driving with a spare tire.
The Toyota RAV4 4WD STD I operating principle provides the best reliability and efficiency.
Second generation 4WD Rav 4 design
For the second generation Toyota Rav 4, a new type of 4WD was used. The all-wheel drive design is made according to the STD II . It involves blocking the center differential using a viscous coupling.
This design was previously used on Toyota cars, where mechanics were installed as a transmission. Despite the significant simplification of the design compared to the first generation models, reliability remained at the same level. At the same time, there is a significant decrease in characteristics.
The design provides for the combination of the center and front differential between the wheels. At the same time, five satellites are mounted in the latter. In normal operation, the Torsen rear limited-slip differential is not loaded, but can be forced into gear.
How to use traction control correctly?
The traction control system is an independent active safety system on Toyota cars. However, on some brand models, this module is also necessary to implement directional stability control (VSC) - when stabilization works, traction control sensors and anti-lock brake systems are used. On SUVs or crossovers, a locking differential is also used when the module operates.
Traction control is activated by default when the ignition is turned on, and the exchange rate stabilization module starts working at speeds of 15 km/h or higher. Both devices allow you to increase the vehicle's controllability on the highway, but can cause a decrease in off-road performance.
It is recommended to forcibly disable the anti-skid when driving onto unpaved or slippery surfaces, so that the electronics do not choke the engine's traction. In this case, after some time the module will automatically switch to the active state. It is not advisable to disable the anti-skid system in the city or on the highway.
All-wheel drive Rav 4 3rd, 4th and 5th generations
Toyota RAV4 3rd, 4th and 5th generations use an automatic all-wheel drive system. It consists of a multi-plate clutch that is controlled electronically. The electronics signal transmits torque to the rear wheels. Clutch blocking is affected by front wheel slip and the stabilization system. This improves vehicle control on slippery surfaces.
The Rav 4 3 has a function for forced locking of the clutch when driving in off-road conditions at a speed of no more than forty kilometers per hour. For this purpose, there is a Lock button located on the center console.
To coordinate the operation of 4WD, electric power steering and stabilization system on the Toyota RAV4, the Integrated Active Drive . If you get into a skid, the system adjusts the fuel supply, brakes the wheels individually and distributes torque to the front axle in the range from 55 to 100%. The force on the steering wheel is also reduced for the direction in which you need to turn to get out of a skid. Especially for Integrated Active Drive, Japanese designers installed a plug-in electromagnetic rear axle clutch on the Rav 4.
The Toyota RAV4 all-wheel drive transmission has the following operating principle. The cardan shaft is connected via a coupling to the input shaft of the rear axle gearbox. In normal mode, only the front axle is engaged, but if necessary, torque is redistributed to the second axle.
Depending on the specific configuration of the Toyota RAV4, the following all-wheel drive control options can be used:
Using the AUTO button, which allows you to use two modes - 2WD and AWD. In the first, only the front axle will work, with the button disabled. And when it is turned on, 4WD goes into automatic mode, accordingly, the additional axle will be put into operation as needed.
By means of the LOCK button, which ensures operation in automated mode or with the maximum degree of clutch blocking. The second mode is activated after pressing.
Some models are equipped exclusively with an AWD complex, which functions constantly.
4WD hybrid Toyota Rav 4
Japanese developers also use hybrid all-wheel drive for the Toyota Rav 4. Its operation is ensured by a gearbox and an electric motor. The following variations are used:
- classic three-shaft;
- compact two-shaft with a low-power electric motor.
Their operating principle is identical. The front axle operates in constant mode. In this case, there is no direct mechanical connection between the axes. Connection to the rear operation is carried out through a separate electric motor -generator and a two-stage gearbox.
One of the types of all-wheel drive transmission Rav 4 5th generation
The new generation Toyota Rav 4 all-wheel drive is called Dynamic Torque Vectoring AWD . The work is based on torque vectoring, which allows you separately distribute the load on the rear wheels depending on road conditions. Also, the 4WD design allows the wheels to be completely disconnected from the incoming torque. This is possible thanks to the ratchet type coupling.
The features of the fifth-generation Toyota RAV4 all-wheel drive can theoretically improve cross-country ability and increase vehicle stabilization. Fuel consumption is also reduced due to the even distribution of torque across the wheels. When there is no load, the rear axle is automatically disabled.
What is ASR / TRC (Traction Control System) in a car
Traction control - what is it? Not every experienced motorist can answer this question easily and quickly. Nevertheless, this system, firmly established under different names in cars of various brands, is considered one of the most effective means of active safety, with which manufacturers pin a number of hopes in the field of reducing accidents on the roads.
p, blockquote 1,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 2,0,0,0,0 —>
We will try to understand what modern traction control is and understand how effective it really is.
p, blockquote 3,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 4,0,0,0,0 —>
TRC (Traction Control) system
This security system is used mainly on expensive models of Honda and Toyota cars.
The operation of this system complements the others by preventing the car from skidding. The operating principle of this system involves reducing traction and torque to prevent dangerous situations. The operation of this system is noticeable when passing dangerous turns with slippery surfaces. Thanks to this system, a car with a driven front axle will not go off course even with a sharp release of gas in a turn. The TRC system is even installed on all-wheel drive vehicles, such as the Toyota RAV 4.
So, modern cars are stuffed with various electronic assistants and this, of course, has a positive effect on road situations, because thanks to such systems there are fewer accidents due to poor road grip, and drivers without experience driving in winter are not afraid of icy roads.
ASR / Traction Control - what is it?
p, blockquote 5,0,0,0,0 —>
So, let's figure out what traction control is? In simple terms, this is a system that includes a clutch that redistributes torque between the driving wheels of the car, an anti-lock braking system that selectively brakes the wheels, as well as a set of sensors with a control unit that coordinates the actions of these devices to dampen car skidding and wheel slip.
p, blockquote 6,0,0,0,0 —>
In fact, today traction control combines the capabilities of anti-skid and anti-slip systems, although it was originally created as an effective tool to combat slippage.
How the Traction Control system works.
So we’ve sorted out the general concepts, and now let’s talk about everything in more detail. How does the system understand that a wheel or several wheels have begun to slip? In fact, everything is very simple. If the sensor begins to transmit data to the electronic unit that the speed of one of the drive wheels has begun to increase sharply, then this means that it has lost traction with the road surface and something needs to be done about it. Here the electronic unit either reduces traction or brakes the wheel. In order to reduce cravings, the following methods are used:
Of course, as already mentioned, the system can not only electronically influence the situation, but also mechanically; special electro-hydraulic actuators are installed on the wheels, with the help of which the system can briefly slow down the slipping wheel, thereby also increasing the torque on the opposite wheel. end of the axle, wheel. On modern cars, the DTC system is a component of the DSC system - a dynamic stability control system. The Traction Control system can be disabled, but it is usually not disabled separately, but disabled together with the DSC system. The traction control system itself uses the same sensors as the anti-lock braking system (ABS) and the emergency braking assistance system (Brake Assist), which means that cars with the DTC system installed also have these 2 auxiliary systems.
Advantages and disadvantages of modern Traction Control Systems
p, blockquote 17,0,0,0,0 —>
Modern traction control systems have a number of advantages and disadvantages. The first, of course, includes greater driving safety, because the system itself is capable of “recognizing” the risk of skidding and extinguishing its development.
p, blockquote 18,0,0,0,0 —>
On the other hand, such “assistance” relaxes the driver, which can lead to less caution when driving on slippery surfaces. In addition, do not forget about situations where wheel slip is not evil, but, on the contrary, can be a driver’s assistant.
p, blockquote 19,1,0,0,0 —>
By the way, this statement does not apply to fans of drifting and high-speed driving on race tracks, but to those drivers who often drive off-road or in deep snow. For example, traction control and anti-skid systems can play a cruel joke if you decide to overcome the “pull” of virgin snow.
p, blockquote 20,0,0,0,0 —>
By artificially limiting the speed, the system is able to turn off the car’s engine at the most crucial moment, and such a “gift” will end in the search for a tractor. To avoid such unpleasant situations, almost all automakers provide the ability to disable traction control, for which a separate button is used on the car’s center console.
p, blockquote 21,0,0,0,0 —>
As a rule, it is marked with a corresponding designation (on the same Toyota crossovers it is “TRC off”). Using the key, you can deactivate the system in order to successfully overcome a difficult area.
p, blockquote 22,0,0,0,0 —>
TRC - what is it and how does it work using the example of Toyota Avensis?
The module prevents wheel slipping when driving on slippery surfaces or during lateral acceleration - when there is a lack of traction between the tire and the road surface.
When TRC is disabled
The operating principle of the device is based on analyzing the rotation speed of each wheel of the vehicle's drive axle with data transmission to the electronic control unit. When the rotation speed of one wheel increases relative to the other, the ECU equalizes the difference by applying the brakes or programmatically limiting engine power. This helps prevent wheel slipping and maintain a high coefficient of adhesion to the road surface.
Using traction control in real operation
p, blockquote 23,0,0,0,0 —>
Despite the fact that many modern cars have a traction control option, not all drivers know how to use this system. Let's try to figure out how to use the traction control system using the example of a Toyota RAV-4.
p, blockquote 24,0,0,0,0 —>
In normal driving mode, the “default” so to speak, the TRC system on Toyota is constantly activated. Its intervention in control is completely invisible at first glance, but when one or more wheels of the car hit a slippery section of the road, the system comes into action, “directing” the car in the desired direction and preventing the development of a skid.
p, blockquote 25,0,0,0,0 —>
In practice, this can be noticed by the selective activation of the anti-lock brake system, which is accompanied by a characteristic crunch, as well as a decreasing response to the gas pedal. In addition, a corresponding indicator flashes on the dashboard, indicating that the system is activated.
p, blockquote 26,0,0,0,0 —>
Is it possible to turn it off?
Some old believers, and those who like to “go sideways” and start, often turn off these systems (again, don’t forget about the first releases of X-RAY, where turning off was simply necessary).
Is it possible to disable the traction control system there or not? And how to do this?
In modern foreign cars this is as easy as shelling pears. There is a special button, press it, the “OFF” icon lights up on the dashboard (next to the car that is slipping). You can go without it.
ON some foreign cars, such as Volkswagen or AUDI, pressing once completely does not turn off the system, you need to press and hold for about 8 - 10 seconds
BUT there are cars that don’t have any buttons, but you need to turn them off (again, X-RAY). Then you can use the collective farm method (which, by the way, does not always work, and sometimes you can get CHECK ENGINE ). Usually they look for the fuse and simply pull it out of the circuit. BUT I DO NOT RECOMMEND YOU TO DO THIS! Often with ANTIBOX, ESP is also cut off, sometimes ABS can be too. So the car becomes completely analog, so to speak.
Now we are watching a useful video.
This is where I end my material, I think it was useful to you. Sincerely yours, AUTOBLOGGER.
Similar news
- How often (when) should you change the brake fluid? Is it necessary at all...
- Drum or disc brakes. What's better? Main differences
- Anti-squeak plates for brake pads. Why are we needed and...
In Toyota cars TRC OFF - what is this button and how to use it
p, blockquote 27,0,0,0,0 —>
In order to disable the stabilization system, as already mentioned, the driver will need to press the button labeled “TRC off” on the center console of your Toyota. This should be done as consciously as possible - only if wheel slip is really a necessary condition.
p, blockquote 28,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 29,0,0,1,0 —>
In addition to the above-mentioned off-road driving, it also makes sense to disable the traction control in cases where intensive acceleration of the car is necessary (for example, to overcome difficult sections on the road by “moving”).
p, blockquote 30,0,0,0,0 —>
It is worth mentioning separately the fact that in the Toyota crossover TRC is not completely disabled, that is, pressing the “TRC off” key only briefly deactivates the system. In addition, the system automatically turns on when the speed reaches 40 kilometers per hour, as indicated by the inscription “TRC on” on the dashboard.
p, blockquote 31,0,0,0,0 —> adsp-pro-2 —>
Accordingly, if you need to turn it off again, the button will have to be pressed again. This precaution by the manufacturer is justified by safety standards, since today traction control is considered one of the most effective safety systems.
p, blockquote 32,0,0,0,0 —>
In fact, this statement is supported by statistics on road accidents in different countries, and many independent organizations are lobbying for the introduction of legislation requiring the use of TRC systems on all cars sold on the market, regardless of configuration.
p, blockquote 33,0,0,0,0 —>
What is TRC in a Toyota car?
The traction control system is a set of mechanisms and electronic components of a car that are designed to prevent slipping of the drive wheels. The TCS system (Traction Control System) is the trade name for a traction control system that is installed on Honda vehicles. Similar systems are installed on cars of other brands, but they have different trade names: TRC traction control system (Toyota), ASR traction control system (Audi, Mercedes, Volkswagen), ETC system (Range Rover) and others.
Activated TCS prevents the vehicle's drive wheels from slipping when starting out, sharp acceleration, cornering, poor road conditions and rapid lane changes. Let's consider the principle of operation of TCS, its components and general structure, as well as the pros and cons of its operation.
Working principle of TCS
The general principle of operation of the Traction Control System is quite simple: the sensors included in the system record the position of the wheels, their angular speed and the degree of slippage. As soon as one of the wheels begins to slip, TCS instantly eliminates the loss of traction.
The traction control system copes with slippage in the following ways:
- Braking of slipping wheels. The braking system is activated at low speeds – up to 80 km/h.
- Reducing car engine torque. At speeds above 80 km/h, the engine management system is activated, which changes the amount of torque.
- A combination of the first two methods.
Note that the Traction Control System is installed on cars with an anti-lock braking system (ABS - Antilock Brake System). Both systems use the readings of the same sensors in their work; both systems have the goal of providing the wheels with maximum grip on the supporting surface. The main difference is that ABS limits wheel braking, while TCS, on the contrary, slows down a rapidly rotating wheel.
Device and main components
Traction Control System is based on elements of the anti-lock braking system. The wheel spin control system uses an electronic differential lock as well as an engine torque management system. The main components required to implement the functions of the TCS traction control system:
- Brake fluid pump. This component creates pressure in the vehicle's brake system.
- Switching solenoid valve and high pressure solenoid valve. Each drive wheel is equipped with such valves. These components control braking within a specified loop. Both valves are part of the ABS hydraulic unit.
- ABS/TCS control unit. Controls the traction control system using built-in software.
- The engine control unit. Interacts with the ABS/TCS control unit. The traction control system puts it into operation if the vehicle speed is more than 80 km/h. The engine control system receives data from sensors and sends control signals to actuators.
- Wheel speed sensors. Each wheel of the car is equipped with this sensor. The sensors record the rotation speed and then transmit signals to the ABS/TCS control unit.
TCS enable/disable button
Note that the driver can disable the traction control system. Usually there is a “TCS” button on the dashboard that turns the system on/off. Disabling TCS is accompanied by the illumination of the “TCS Off” indicator on the instrument panel. If such a button is missing, the traction control system can be turned off by removing the corresponding fuse. However, this is not recommended.
Advantages and disadvantages
Main advantages of Traction Control System:
- confident car start from a standstill on any road surface;
- vehicle stability when cornering;
- traffic safety in various weather conditions (ice, wet surfaces, snow);
- reduced tire wear.
Note that in some driving modes, the traction control system reduces engine performance and also does not allow full control of the vehicle’s behavior on the road.
Application
The TCS traction control system is installed on cars of the Japanese brand “Honda”. Similar systems are installed on cars of other automakers, and the difference in trade names is explained by the fact that each automaker, independently of the others, developed a traction control system for its own needs.
The widespread use of this system has significantly increased the level of vehicle safety when driving due to continuous control of adhesion to the road surface and improved controllability when accelerating.
Traction control system
Find out how a car's traction control system works and what types there are. Diagrams and videos about the principle of operation of the system.
articles:
- What is traction control
- Description of the ASR system
- PBS functions
- How does antibux work?
- A type of antibux
- Pros of traction control
For about 20 years now, various security systems have been installed on cars, monitoring the safety of car braking and acceleration. Today, any modern car has such technologies.
Having gone through a long period of time and a difficult path, from simple systems up to entire complex systems that are combined into several traction control systems.
What is traction control system?
The traction control system, or APS for short, is also called “traction control (PBS)”; in English you can also see two names for this technology - Dynamic Traction Control (DTC) and Traction control system (TCS), in German it is called Antriebsschlupfregelung (ASR) .