Description and meaning of error P0113
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic powertrain code, which means it applies to OBD-II equipped vehicles.
While general, specific repair steps may vary depending on the make/model. The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the temperature of the air entering the engine. The PCM supplies a reference voltage of 5 volts to the Input Air Temperature (IAT) sensor The IAT is a thermistor that changes resistance based on temperature.
As the temperature increases, the resistance decreases. Low temperature resultsin high signal voltage. When the PCM sees a signal voltage higher than 5 volts, it sets this check engine light code P0113.
The function of the intake air temperature sensor is very important when starting the engine, since together with the coolant sensor they provide accurate information for determining the injection time, which avoids problems when starting a hot engine.
An error is generated in the ECU if the actual temperature remains below the minimum temperature for 1.5 minutes. If you reset the p0113 code with a scanner and the cause of the error is not eliminated, the check engine will soon light up again and the car will again operate intermittently.
If you took scanner readings and the display shows error P0113, do not rush to replace the sensor with a new one. First, check the sensor resistance at different air temperatures. This can be done using warm water or a hair dryer, as well as a multimeter. If the resistance changes proportionally with temperature, the sensor is working.
Deciphering error code P0113
Literally, error P0113 (Intake Air Temperature Sensor High) stands for high signal level of the IAT intake air temperature sensor. This sensor (essentially a thermistor) is designed to adjust the engine ignition angle and change the duty cycle (duration) of fuel injection pulses depending on the temperature of the air sucked into the engine.
At high ambient temperatures, warmer air enters the intake manifold. It is known that warmer air has lower density and, accordingly, lower oxygen concentration. To form an accurate fuel mixture ratio (air/fuel), it is necessary to reduce the amount of fuel supplied. This is usually done by the engine control unit by reducing the duration of the fuel injection pulses.
The second function, which is controlled by the DTVV readings, is adjusting the ignition angle. In warm weather, there is no need to set a large ignition timing to simplify the timing of starting the engine in cold weather.
Video - errors P0113, P0112 Volkswagen Golf 6:
The intake air temperature sensor on most cars is combined with a mass air flow sensor (MAF). This has its advantages and disadvantages.
Advantage - the readings of the mass air flow sensor to accurately determine the amount of oxygen are adjusted taking into account data from the intake air temperature sensor.
Disadvantages: if one of the sensors malfunctions, you have to replace the entire assembly, and it has a more complex and unique design, which also leads to an increase in its cost.
DTVV is made on an element called a thermistor or semiconductor thermistor. At negative air temperatures, its resistance is about several kiloohms. As the temperature rises, the sensor resistance decreases and reaches several hundred ohms.
In reference books you can find the exact temperature dependence of resistance for a specific engine model. Based on this, it is easy to check the functionality of the sensor using a multimeter and a container of water. Water is heated to different temperatures and the resistance of the DTVV, the sensitive part of which is immersed in water, is measured.
If the sensor resistance readings, depending on the temperature, differ significantly from the standard values, this indicates that the DTVV is not working correctly. In this case, you can try to clean it. If this does not help, then it must be replaced.
This is interesting: How to reset the service interval of a Renault Megane 2 car yourself
In some cases, error P0113 (high signal level from the intake air temperature sensor) occurs simultaneously with other errors - such as P0111, P0112, P0114. They are also directly related to the operation of the DTVV (thermistor). Error P0111 is associated with malfunctions of the power circuit, P0112 is associated with a low signal level from the intake air temperature sensor, P0114 indicates that information from the DTVV is constantly interrupted (the sensor itself, contacts or wiring is faulty).
IAT sensor
Intake Air Temperature - air temperature sensor in the intake tract. A two-contact sensor for measuring air temperature in the intake tract, thanks to its measurements, the ECU control unit adjusts the idle speed characteristics. It is mounted either in the filter box or directly in the inlet tube.
IAT connection diagram
The electrical circuit for DTVV is shown below:
The sensor is calibrated and produces a voltage proportional to the air temperature. Higher temperatures result in higher voltage being applied to the ECU because the internal resistance of the IAT decreases as it heats up.
Errors associated with high circuit input signal are mainly caused by faulty generators that create excess voltage. Although there may be other reasons, such as short circuits that "leave" current into a particular system from other, unrelated systems operating at higher voltages.
Note that in the case of short circuits, there are likely to be other seemingly unrelated fault codes present.
Diagnosing a "high input" code will always involve thorough testing of the charging system as a first step, followed by isolating the circuit from all other possible voltage sources while checking resistance, continuity, and voltage reference.
How does P0113 occur?
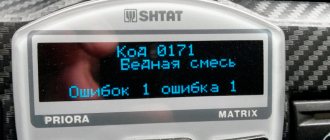
Error P0113 on diagnostic equipment is called "Intake Air Temperature Sensor High". When a problem is detected by the vehicle’s electronic control unit, the “Check Engine” icon lights up on the instrument panel. It indicates to the driver that it is necessary to contact a service center, where specialists using a diagnostic tool will be able to “remove” errors.
In order for the ECU to determine that the engine has a problem with code P0113, the actual temperature must be below the minimum temperature for 1.5 minutes. If this was some kind of temporary failure, the error will disappear only after 4 consecutive ignition cycles in which there were no problems.
Important: Even after 4 problem-free ignition cycles, error P0113 continues to be stored in the control unit’s memory. It will disappear from there only after 40 stable cycles.
It is worth noting that the driver cannot always diagnose a problem with the intake air temperature sensor based on the car’s symptoms. A similar malfunction is indicated by “floating” revolutions and difficulty starting the engine. But such symptoms can also indicate dozens of other errors, so without a diagnostic scanner it is impossible to clearly determine that the car has exactly the error in question.
There are not many methods for eliminating this problem, they all involve the sensor or its circuit: 1) Failure of the intake air temperature sensor.
2) Contamination with oil deposits. 3) Wire break. 4) The contact in the power connector has disappeared.
Symptoms of error P0110
The main symptom of a P0110 code is the Check Engine Light on your dashboard. By checking the engine with diagnostic equipment, a specialist will be able to obtain more accurate information about what is causing the problem.
A number of accompanying symptoms that may indicate P0110 are difficulties when starting the engine in the cold season, as well as “floating” speed. In the warm season, it is almost impossible to determine the presence of an error by the “behavior” of the car.
The fact is that depending on the temperature of the ambient air, respectively, the air that enters the intake manifold, the amount of fuel supplied changes. If error P0110 occurs, which indicates a malfunction of the temperature sensor, the engine goes into emergency mode. In it, for most cars, the computer takes the default intake air temperature at +20 degrees Celsius. Therefore, in winter, if the temperature is lower, problems with starting and operating the engine are noticeable, since in fact colder air enters than the ECU considers, that is, the injected fuel is not enough.
The main causes of DTVV malfunction
In most cases, the P0113 code occurs when the wiring to the intake air temperature sensor is broken. If the sensor output voltage exceeds 4.91 volts for 0.5 seconds or more, the ECU determines that there is an open circuit in the IAT sensor circuit and sets DTC P0113.
The most likely reason for diagnosing error P0113 is a malfunction of the intake air temperature sensor. Theoretically it has a very high service life (more than 10,000 hours). In real conditions, its service life is reduced by:
- dust, dirt, salt coating, oils from the road surface;
- pollution from exhaust gases from ahead and oncoming vehicles;
- condensation settling on the sensor during parking;
- mechanical shaking.
Error P0113 may be the result of a broken contact in the sensor connector. In this case, the control unit diagnoses high resistance in the circuit and acts as if very cool air is being supplied. On the contrary, a short circuit has the same effect as too hot air. The engine control unit may delay ignition, causing a cold start problem. Along with this problem, the following symptoms are possible with error P0113:
- increased fuel consumption;
- change in the nature of exhaust gases;
- problems with starting the engine when cold or hot;
- Unstable engine speed.
This is interesting: Repair of the driver's door lock of Nissan Tiida and Qashqai - restoration of the cable
Wiring break/short to +, ground circuit fault, intake air temperature sensor, ECM
A P0113 code may indicate that one or more of the following has occurred: Faulty inside the IAT sensor Faulty connection when the iat sensor is open in the iat ground circuit or signal circuit short to voltage in the iat signal circuit or reference wiring harness and/or wiring routed too much close to high voltage wiring (eg alternator, spark plug cables, etc.) Faulty PCM (less likely, but not impossible)
On what cars does it appear?
Error P0113 itself is quite universal. It may appear on cars produced by VAZ, companies such as Toyota or Honda.
It is only important to note that an error such as P0113 occurs on a car where there is an electronic control unit and the sensor itself that controls the intake air temperature parameters. This is almost any modern car, starting from the already outdated VAZ 2112 or VAZ 2114, and ending with more recent models such as Ford Focus 2, Ford Transit, Chevrolet Lacetti, Lada Kalina, Priora and Grant. For all of them, seeing code P0113 on the scanner is not a surprise.
Motorists note that error P0113 appeared on various models of Volswagen, Honda, Nissan, BMW and Mercedes.
Regardless of which vehicle the P0113 error occurred on, it should be eliminated. For this, there is a certain algorithm of actions and recommendations from specialists.
How to fix error P0113
Having seen an alarming signal, you should not immediately go to the store to buy it, especially since for some models and brands of foreign-made equipment it is not cheap. There is no guarantee that after replacing the part with a new one, the error code will disappear.
In a dual version with a mass air flow sensor, its cost can be more than 5,000 rubles.
If error P0113 has caused the engine to idle unevenly, you can try disconnecting the mass air flow sensor connector. If at the same time the speed becomes consistently high, it may not be the sensor.
Next, you need to check the resistance of the sensor using a multimeter. In this case, you need to find the pinout of the connector.
At negative ambient temperatures, the resistance should be several kiloohms. When heated, the resistance should drop to hundreds of ohms. A more specific dependence of the DTVV resistance on temperature should be looked for separately for your car brand.
In some cases, cleaning (rinsing) the DTVV with special means helps.
Video - Audi A6 C5 intake air temperature sensor (checking, cleaning DTVV):
One of the simple, inexpensive and reliable methods for checking the operation of sensors is to install a known working one. In this case, you can erase all errors, warm up the engine, make a test drive for at least 10 minutes, then carry out computer diagnostics. If the error disappears, the original sensor should be replaced.
Video - replacing the air temperature sensor on the Opel Astra N:
One of the possible rare causes of error P0113 is a malfunction in the engine control unit. To power this sensor, the control unit has a special voltage stabilizer chip. A stable (reference) voltage of 5 (or 9) Volts is supplied to one of the sensor contacts. Its exact value can be checked using a multimeter. The specific contact number can be determined from the diagram. The sensor should be turned off during the measurement. If the reference voltage does not match (more than the reference voltage or is absent), it is necessary to repair the engine control unit. In this case, the help of a specialist is needed. To check, you can “throw” an unlocked block for testing.
Some engine models, especially V-shaped ones, may have two intake air temperature sensors. In this case, a general error message P0113 is allowed. Each sensor must be monitored individually. In this case, standard techniques are used:
- removing the sensor connectors one by one;
- replacing sensors;
- simultaneous removal of sensor connectors.
During the process of dismantling and installing sensors, extreme care should be taken: the working element of the sensor is small in size and durable, it can be easily damaged.
Sensor check
- With the key in the off position, disconnect the DTVV. With the multimeter set to resistance (ohms) mode, measure the resistance at the sensor terminals. If you get an open circuit or short circuit (∞ Ω or 0.0 Ω), the sensor is faulty. Replace the DTVV.
- If you measured the resistance, compare it to the temperature ⁄ resistance chart. If the engine is cold, then the temperature ⁄ resistance of the IAT should be close enough to the ambient temperature that can be measured with a thermometer. If the resistance matches the ambient temperature, you may still have a problem with the sensor. A sensor that operates correctly at ambient temperatures may be out of range at other temperatures. You can check if the sensor is faulty by measuring the resistance after changing its temperature, for example by placing it in a pan of boiling water or in the freezer.
This is interesting: Checking the strut support bearing at home
Checking the circuit
If the sensor itself seems to be responding correctly to temperature changes, then you can begin testing the circuit.
- With the ignition key turned on (key on, engine off), disconnect the IAT sensor and check the voltage at the connector. There should be 5 volts on one of the wires. If you don't have 5 volts, there may be an open circuit or a faulty ECU.
- The other wire should read 0V. If you can identify the signal wire correctly, check the resistance to ground, which should be 0.0 ohms. An open circuit probably means you have a wiring problem. On the other hand, 0.0 ohms may still indicate a ground fault.
- If there is no reference voltage of 5 V, there may be an open circuit between the ECU and the sensor, a short circuit to ground, or a malfunction of the controller itself. If there is no signal voltage on the other wire, the sensor may be faulty, an open circuit, or a short to ground.
- In the ECU, check the reference and signal voltage. If there is no 5 V, the problem may be in the controller. If the signal voltage is low or absent, check for corrosion or open circuit in the DTVV.
- Turn the key to the off position, disconnect the ECU connector and check the resistance. If the resistance reading matches the sensor, check if the ECU is faulty. If you measure "0.0 Ω" or "∞ Ω", check for an open or short in the wiring to the IAT sensor.
- Unplug the sensor and measure the resistance again, it should now display as an open circuit, "∞ Ω". If you get any resistance, check for a short in the wiring to the IAT sensor.
- Connect a jumper to the sensor connector and check the resistance in the circuit.
- The correct reading should be "0.0 ohms". Any resistance above 1 ohm may indicate corrosion or an open circuit.
- Check resistance to ground. Any resistance below 1000k ohms may indicate a short to ground in one of the IAT sensor wires.
- If you have a diagnostic scan tool, you can perform many of these checks simply by reading the sensor readings from the ECU. Turn the ignition key to read the temperature while the sensor is connected and then disconnected. If there is no change, you have a problem with the circuit. If there are changes, you have a problem with the sensor.
What is an intake air temperature sensor?
The intake air temperature sensor is a very simple device. It can be installed in the car separately on the air filter box, or be part of the mass air flow sensor.
The intake air temperature sensor works as follows. Air passes through it, which goes through the thermistor. Depending on the air temperature, the thermistor changes resistance. When the temperature gets lower, the resistance is higher. When the temperature is higher, the resistance is lower. Accordingly, this data is transmitted to the electronic control module, and based on it, the ECU decides whether to inject more or less fuel, depending on the ambient temperature and the temperature of the incoming air.
Is it possible to continue driving a car?
A failure of the intake air temperature sensor, which stops providing information or detects it incorrectly, simultaneously leads to several unpleasant consequences. First of all, problems begin with the start of the power unit. This is due to the fact that the thermistor works in conjunction with the coolant temperature sensor. The data received from them allows you to accurately “calculate” the injection time, which is especially important when starting the engine “hot”. Along the way, other problems are identified:
- drop in engine power, deterioration in its throttle response;
- Unstable operation of the engine at idle speed.
Depending on the make of the car, there may be other consequences. For example, for cars made in the People's Republic of China Chery, fuel consumption may increase and the rear axle may no longer engage.
Probable Causes
Error P0113 hides certain reasons that led to the recording of the corresponding code in the memory of the control unit.
The main reason lies in a problem with the temperature sensor. But the occurrence of an error may be due to various malfunctions. The main ones are:
- breakdown of the temperature sensor, its complete failure;
- contamination of the controller with oil particles, which reduces sensitivity;
- loss of contact in the connector;
- broken wiring in the electrical circuit.
Statistics show that most often the reason lies in a short circuit in the circuit or in the sensor housing.
Much less often the device becomes contaminated with oil and other deposits, which entails a decrease in the sensitivity of the sensor.
What does code P0110 mean?
Code P0110 is generated when the PCM detects a malfunction in the intake air temperature sensor circuit.
The IAT (Intake Air Temperature) sensor is a thermistor and its resistance changes depending on the intake air temperature. Typically the IAT sensor is located in the intake air duct, but on some vehicles it can be found in the intake manifold.
The IAT sensor transmits important information to the ECU through which it controls parameters such as air/fuel ratio, ignition timing and other similar characteristics.
Typically this is a two-wire sensor with a 5 Volt reference voltage from the controller and a ground wire. The resistance of the sensor changes as air passes through it.
If the air is cold, the resistance increases and a higher voltage signal is generated. If the air is warm, the sensor resistance decreases and a low voltage signal is issued. The control unit monitors this change in resistance and if it detects a deviation outside the normal operating range, a P0110 fault code is generated.
A "circuit fault" indicates a fault in the control circuit, not a faulty sensor or other part. Replacing the sensors will almost never solve the problem of Circuit Failure codes because the code assumes the problem is in the circuitry. This distinction between "circuit" and "sensor/part" is very helpful during diagnosis as it greatly narrows down the list of possible causes.
The causes of "Circuit Failure" codes are essentially the same as those for "Open Circuit", i.e., broken wiring, poor connection between electrical connectors or previously repaired wiring, loss of ground preventing current flow, blown fuses, faulty relays, faulty switches or any of a variety of other problems that prevent current from flowing through the wiring.
How to resolve error P0110?
The intake air temperature sensor circuit is simple - there are only two wires going from the ECU to the IAT sensor.
Connect your car charger
The first step is to connect the car charger. During diagnostics, the vehicle's ignition is usually turned on, and this may drain the battery. Low battery voltage can cause other trouble codes to appear, confusing the situation. So, it is best to connect your car charger.
Connect OBD2 scanner
When diagnosing errors, it is important to have an OBD2 scanner. This device comes in two types - a regular adapter and a scanner for advanced diagnostics. With an OBD2 scanner, you can easily read the error and also use the built-in functions to read and write engine and other system data.
Check for open circuit
Check the wiring and connections around the IAT sensor. Please note that the wiring is close to high voltage circuits, which can be a source of problems. Poor grounding also causes malfunction.
Check sensor input voltage
Using an OBD2 scanner, check the IAT sensor and make sure it has 5 Volts input. If the reading fluctuates or is not close to 5 Volts, then the sensor needs to be replaced.
Check the reference voltage on the ECU
Once you have confirmed that there is a problem with the 5 Volt input voltage, check the reference voltage at the ECU connector. If the voltage on the controller is 5 Volts, but not on the sensor, then there is a break in the wiring from the control unit to the sensor.