Malfunctions of the contactless ignition system of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
Sometimes when diagnosing a carburetor gasoline engine of a passenger car, difficulties arise in determining the cause of a particular malfunction.
This happens because the symptoms of their manifestation are very similar. For example, carburetor malfunctions and ignition system malfunctions will have almost the same effect on engine performance. In this article we will try to understand what problems in the operation of a car engine arise due to a malfunction of the ignition system. Car engine does not start
— Battery is faulty
— The switch is faulty
— Hall sensor is faulty
— The insulation of high-voltage wires is “broken”
— The distributor cover is “broken” or is heavily oxidized, its contacts are destroyed
— Ignition distributor rotor (slider) burnt out
— The ignition coil is faulty or its cover is “broken”
— High-voltage wires are connected in the wrong order
— Defective spark plugs, their insulation is “broken,” the gap between their electrodes does not correspond to the norm
— Incorrect ignition timing
Ignition is either too early or too late. How to correctly set the ignition timing on VAZ 2108, 21081, 21083 engines is described in detail on the page “Setting the ignition timing of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars.”
— The low voltage circuit of the ignition system is faulty (contacts have oxidized, wires are broken, connectors have come off...)
Read more about the inability to start the carburetor engine of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars in the article “The carburetor engine does not start (reasons related to the ignition system).”
For comparison, you can see what reasons exist that the engine cannot be started due to a carburetor malfunction.
The car engine runs erratically (troits) or stalls at idle
— The gap between the electrodes of the spark plugs does not correspond to the norm
— Heavy carbon deposits on the spark plug electrodes
— Defective spark plugs (“insulator broken”)
— Incorrect ignition timing
— The switch is faulty
— The centrifugal ignition timing regulator in the distributor is faulty (weights stick, their springs are weakened or broken, damper rings are lost)
Causes of rough idle related to the carburetor are outlined on the “Rough Idling” page.
Dips and jerks in engine operation
— Incorrect ignition timing
— The gaps between the electrodes of the spark plugs do not correspond to the norm
— Defective spark plugs
— The noise suppression resistor in the rotor (runner) of the distributor burned out
— Wear or damage to the contact carbon in the distributor cover
— Current leakage through “broken” insulation of high-voltage wires, spark plug insulator, ignition coil cover
For the causes of malfunction related to the carburetor, see the page “Failure when pressing the gas pedal.”
The engine does not develop full power, its throttle response is reduced
All of the above causes of malfunctions lead to loss of power, throttle response of the car engine, and increased fuel appetite. You can only add
— Malfunction of the vacuum ignition timing regulator in the distributor due to jamming of its plate
Notes and additions
Five more articles on the site on the ignition system of VAZ cars
HOW TO CHECK THE SWITCH ON THE STAND?
I bought my Corish switch from 08, I also bought a coil from OKI, I bought new spark plugs and armor wires. He and I put together a piece of equipment called “INVERTER” - as the article here says. They gathered everything into a ball - you’re not working and that’s all, tell me what to do, biker people. Is it possible to somehow start it without an inverter so that the spark kicks out, of course without Hall!? Also: Is it necessary to use the power that is supplied to Hall or is it possible without it? Yes, and how to check the COMMUDATOR?
Serenkiy_Kozlick
The switch is checked using an oscilloscope and a square wave generator
Serenkiy_Kozlick
If necessary, I can write up an article somehow
Without the hall it would be shit.
Installed in 2 hours.
for Programmer
: I myself know that it can be installed quickly, but there’s just nowhere to put it yet.
for Serenkiy_Kozlick
:
More details please. As I understand it, rectangular pulses are not at all necessary; sinusoidal ones will also work. Current amplitude? Where to submit? What frequency? And what amplitude at the output should be. Of course, I can guess how it all works, but I would like to be on the safe side!
for Aric
: buy a hall sensor and check it.
on the same miniature machine on which the inverter was assembled, assemble a pulse generator Hz at 50-100
I have a low frequency generator, what is the amplitude at the input? And what should be the output?
for Aric
:tl level. amplitude of 4 volts
By the way, such a contraption (made on the “remaining”, those on free generator inverters) will help you get home with faulty cams or without them at all.
for manowar
:
And this is really a thought! I'll have to try it. You can display a trimmer so that you can quickly adjust the frequency.
and connect it with the throttle
Yeah, only linearity will have to be built.
Collected. Sparkle. at least light a cigarette. Highly recommend! Even without a Hall sensor it produces good performance (so far, only on a stand, but I think there will be no miracle, and it will work on a chapere too!) RESPECT to everyone and HAPPY NEW YEAR.
Symptoms and causes of malfunction
Switch malfunction is one of the most common causes of engine interruptions. Often the cause of switch failure is a “bad ground”. This especially often occurs after long-term car repairs or due to oxidation of contacts. As a result, the switch does not send impulses to the ignition coil and the engine simply does not start. In this case, either repair or replacement of the switch is carried out.
The main symptoms of a switch malfunction are:
- Drop in acceleration dynamics
- Engine fails under hard acceleration
- Engine "troits"
What kind of switch can there be in a car?
Modern switches are efficient and reliable thanks to microprocessors. Now stores sell different models. All switches can be divided into:
- Transistor. They have contacts that can burn or simply wear out. This means that they have a short service life.
- Thyristor. They are similar to transistor ones, but have one difference - high voltage occurs in the capacitor. When the system is activated, the capacitor is connected to the coil winding. The next discharge produces a spark.
- Hybrid. There is a cam distributor here. The electronic part includes a commutator and a coil. It is a hybrid of electronics and mechanics. Due to electronic elements, this unit is more reliable and economical. The sensors here are replaced with cams, they are simply connected. The design is convenient - after all, when the switch fails, you can switch to the old coil. Then the cam ignition starts.
- Contactless are the most effective devices. Their parameters are much higher than those of other types of switches. With the beginning of the use of electronics, manufacturers began to abandon contacts - signals began to be transmitted from the Hall sensor.
Switch replacement
The functionality of the switch is checked using a test lamp. If the lamp does not blink when the crankshaft rotates, this means that the switch does not send impulses to the ignition coil and needs to be replaced.
In some cases, the problem lies not in the switch itself, but in the wiring. The system may malfunction if the wires that connect the switch to the coil or ignition switch are broken. In this case, a specialist checks the condition and reliability of the wire connection. Detected problem areas can be replaced with new ones, and loose connections can simply be fixed.
The practice of operating switches shows that the cause of problems may be a break in the wires between the ignition distributor sensor and the switch itself. In this case, damaged wires are also replaced.
If the switch cannot be restored, it is replaced. As a rule, this procedure takes no more than 15-20 minutes. At the same time as this service, we recommend that you carry out a full diagnostic of the car's electrical wiring, since engine problems are often associated not only with faulty devices, but also with the condition of the wiring.
How to choose, replace and repair a VAZ switch correctly
During the operation of the vehicle, the switch may fail, partially or completely disrupting the operation of the engine. The main sign of a broken switch is a weak/unstable spark or its complete absence. If other reasons for the appearance of such a symptom are excluded, then you should check the switch, and if it is faulty, replace it. The simplest test is to connect the open wire going from the commutator to the primary winding of the coil (terminal “K” on the coil and terminal “1” on the commutator), a test lamp or a tester (this must be done with the ignition off). If the switch is working, then when you turn on the ignition the lamp will blink; if this does not happen, then it is better to install a new switch.
As a replacement, you should take a switch of the same type that was previously installed on the car, or analogues compatible with other elements of the ignition system. For example, distributors of the 3706 model series and ignition coils 3705 are compatible with switches 036.3734, 76.3734 (and other 3734), but other options are also possible.
Replacing the switch on all VAZ models is simple:
- Turn off the ignition, remove the terminal from the battery;
- Disconnect the electrical connector with the wiring harness from the switch;
- Unscrew the two mounting screws/bolts and dismantle the device;
- Install a new switch, having first cleaned its installation site from dirt and traces of corrosion;
- Make all electrical connections.
After replacing the electronic switch, it is necessary to adjust the ignition timing, and sometimes make other adjustments. No additional operations with the switch itself are required. If the part is selected and installed correctly, the ignition system of a VAZ car will function normally in any conditions.
Purpose, principle of operation of the ignition coil
The device is the most conservative part in a gasoline internal combustion engine. Its prototype was invented in Germany by the engineer Ruhmkorff in the mid-nineteenth century. It replaced magnetos in automobile engines in the early 20th century.
The main purpose of the device is to convert low-voltage electrical pulses with an amplitude of about 12 Volts (vehicle on-board voltage) into high-voltage pulses with an amplitude of more than 15,000 Volts. High voltage is necessary to break down the working area of the spark plug.
According to the type of design and ignition circuit, the coils are classified:
- single;
- double (triple, four-block);
- individual.
Ignition coil design
Single devices are used in systems with an ignition distributor. Twins are used in four-cylinder internal combustion engines without a distributor. One part forms a high-voltage pulse to the 1st and 4th cylinders, the second serves the 2nd and 3rd. Triple and quad coils are sometimes used in six-cylinder and eight-cylinder engines, respectively. Individual coils are widely used in modern cars. They are installed on each spark plug individually. A custom spark plug coil has a number of advantages over conventional ones:
- failure of one of the devices does not lead to a complete stop of the engine;
- it is easier to organize an electronic control scheme;
- the absence of a mechanical ignition distributor makes the system more reliable;
- distribution of pulse load reduces currents and increases service life;
- it is easier to identify a faulty device, which is easily done by computer diagnostics;
- Most individual coils have a pulse amplifier installed; it is controlled by low signal currents, which reduces electrical interference and increases the reliability of electrical equipment.
By type of control they are divided into:
- contact;
- electronic;
- with built-in switch (pulse amplifier).
In the ignition contact bobbins, a low-voltage pulse is generated by a chopper. When the primary circuit is switched by a breaker, an electromotive force pulse is induced in the primary circuit. The device is an autotransformer that increases the pulse amplitude N times, where N is the transformation coefficient equal to the ratio of the number of turns in the secondary to the primary winding. The transformation ratio of contact devices exceeds 1000.
Contactless systems use electronic coils. Their transformation ratio is higher and they form a stable spark. During repairs, contact and non-contact devices cannot be interchanged.
A built-in switch is installed on most individual coils, often installed on dual coils. Their disadvantage is a higher probability of failure due to the presence of electronic components.
Options
So, we have these simple boxes with network ports. As I already said, ports can be of different types. That is, work with both twisted pair and coaxial and fiber optic cables. There are combined switches.
For example, there are two offices: central (where the server is located) and secondary. The secondary one can be connected using fiber optics. That is, the communication port will be optical. But then all other local ports will be of the Ethernet type. As you can see, switches can have a different number of ports - it all depends on the user’s needs. Small ones are usually used at home or small offices. Large ones are often used in large organizations.
Also, ports can have different speeds. More often they use input ports of 1000 Mbit/s per second, and local ones of 100 Mbit/s. If the organization uses busier traffic, then local ports can be 1-2 Gbps or even use fiber at a higher speed.
PoE
In addition, some models have support for PoE ports. A PoE port is a special input that allows you to power the device via a network cable. For example, you have a camera that needs to be installed in a hard-to-reach place where there are no separate outlets. Then power can be supplied via the PoE output. That is, the device will be connected to the network and to power at the same time.
SFP
SFP ports allow you to use “optics” to connect remote devices. Typically, twisted pair cables have a short range of 50-100 meters. Fiber optics can go much further. Also, the optical cable is more reliably protected from electromagnetic influence and has a smaller diameter.
Mpps
Another very important characteristic is the packet service speed. From the name it is clear that this parameter should be quite high in large local networks. Measured in Mpps (million packets per second). In small networks, weak devices from 2.0 to 10.0 Mpps are used. In large companies working with traffic, up to 71.4 Mpps. It’s clear that the higher this indicator, the more expensive the switch.
Table size
We use a table of MAC addresses. If the local network is too complex and there are not enough tables, the network may slow down, since the switch will need to rewrite new addresses with old ones. One address takes up 48 bits. In some cases, the engineer needs to initially calculate how big the table will be.
Mounting method
Can be divided into two types: tabletop and wall-mounted. The first option is usually installed in server cabinets. The second option can be mounted anywhere and screwed onto either the ceiling or the wall. Such types are used precisely away from the server when connecting a large number of machines.
Symptoms of malfunction
More often than not, the bobbin does not suddenly fail. This is usually preceded by a number of warning symptoms.
The main symptoms of a faulty ignition coil:
- misfires in one or more cylinders, they can be determined using a scanner by the presence of the “triple” effect of the engine;
- the appearance of “breakdown tracks” on the housing can be determined visually when starting the engine in the dark;
- the occurrence of cracks and chips in the dielectric zone;
- overheating of the structure;
- burning of rubber tips of high-voltage wires;
- oiling, contamination.
If the above symptoms appear, you should consider purchasing a replacement device. You can't stand by and watch an ignition coil die. In the event of a sudden coil failure, further independent movement will be impossible (unless you have individual coils installed).
Ignition coils
What is a switch in a car?
This term refers to the device responsible for the appearance of a spark. The spark occurs in the ignition unit, and the switch in the car is the unit that coordinates this process. The ignition system is divided into two components - a control unit and a unit where the spark discharge occurs. The control system controls the moment the spark appears, and the execution unit is engaged in its formation.
Previously, cars had a fuel ignition system with battery ignition. It was based on the principle of self-induction. Such a system worked for a long time - until the advent of a fundamentally different element base. It has a simple transistor circuit. Regulation is carried out using current passing through the bobbin. The basic principle remains unchanged - the switches still operate on electromagnetic induction.
Causes of ignition coil failure
Let's look at the reasons why the ignition coil fails.
Natural wear and tear
Like all electrical and electronic units, the reel has a certain trouble-free operation life. The average service life of ignition coils is approximately seven to ten years of operation or 150,000 - 200,000 thousand mileage. The device is operated in extreme conditions with large differences in temperature, humidity, and the possibility of ingress of moisture, dirt, and foreign liquids. In this case, large currents flow through the primary winding, and a high-voltage pulse is formed in the secondary winding.
Electrical breakdown
Let's figure out why the ignition coil breaks. Firstly, over time, as a result of high temperature changes, the dielectric insulation cracks, and salty moisture, which is a conductor, can enter microcracks. For voltages of more than 15,000 volts generated in the secondary winding, even pure undistilled water acts as a conductor. Secondly, during operation, the physical properties of the dielectric and rubber insulation of the tips of high-voltage wires, especially those of dubious production, change. High-voltage breakdown can be caused by the installation of non-standard high-voltage wires in which there is no distributed current-limiting resistance. A breakdown can occur as a result of severe contamination or waterlogging. Even in the event of a single breakdown, irreversible changes occur in the structure; further operation is not recommended.
Overheat
Some vehicles have ignition coils installed directly at or near the top of the engine. If there is no air access to their structure for natural ventilation (this is possible when installing additional equipment), the device may overheat and fail.
Mechanical load.
The coil mount must be standard. Some car enthusiasts neglect these requirements by “hanging” it on homemade structures.
Wear of spark plugs, high-voltage conductors
Despite the fact that the circuit has a limiting resistance, wear of spark plugs and high-voltage conductors can cause electrical breakdown in them. Then the load current increases and the bobbin may overheat.
Generator voltage regulator relay malfunction
Sometimes it leads to an increase in the voltage of the vehicle’s on-board network and failure of the electronic amplifier (switch).
Malfunction of the contact group of the lock, electronic switch
If, during parking, +12 Volts are constantly supplied to the coil in the event of an abnormal closure of the lock contact group, the device may overheat and fail. The same situation is possible if the switch is faulty.
To prevent premature failure, all possible causes of malfunction of the ignition coil in the car should be eliminated as much as possible.
Checking the voltage on the coil windings
Features and functions
If you need a network switch, then I advise you to look at the important functions that a particular device should support. Depending on the support, the price will rise or fall. In some cases, certain features are not needed, and therefore it is not worth paying extra for them. It all depends on the network load.
- Flow Control or flow control is available in all switches. Proper flow control reduces the risk of network hang-ups;
- Storm Control – or protection against broadcast storm. A storm is a situation when a switch receives too many packets on the network, as a result they begin to be lost, some information does not reach or stops being transmitted altogether. Very often occurs as a result of loops. An important feature for large networks.
- Jumbo Frame or increased packets - used only in large networks. Then there is a real opportunity to increase the packet size to speed up data transfer. To do this, the receiving device must also support this function, and the channel must be of a certain size.
- IGMP Snooping is often used in IP television. When traffic is distributed point-by-point to a specific user. On the one hand, the network is unloaded. On the other hand, the switch must have considerable power in order to constantly calculate paths and respond to requests from new users.
- Mode support : Half-duplex – support for sending packets in both directions, but simultaneous transmission is prohibited. That is, it is transmitted in turn
- Duplex – simultaneous transmission.
- Stacking or expansion - used if a standard switch does not have enough ports. Then one or more switches are connected. The technologies of each company are different, and you need to take into account the speed of the stacking bus for a particular model.
- QoS support – traffic prioritization according to the IEEE 802.1p standard. When higher priority traffic is allowed through, while the rest sits in queue. Also, due to this technology, the data transfer speed in the network is equalized. As a result, the chance of congestion on the line is reduced.
- Link aggregation according to the IEEE3ad standard. Only expensive devices are supported. Ability to send data packets over multiple cables and ports to increase speed;
- VLAN – dividing a network into subnets. For example, the accounting department does not see the HR department and does not have access to their network, and vice versa.
- Loopback Detection - helps protect the network from loops - when packets start endlessly walking around the network. The problem is that the sender can also endlessly send packets to the network and clog it;
- Traffic segmentation – dividing ports into separate segments. The separation occurs at the physical level for greater reliability;
- Traffic mirroring is a simple check of all traffic to ensure network security.
- Support for Internet protocols - everything is clear here; in addition to the usual functions, the device must be able to distribute traffic from the global network.
- Wi- Fi support – for connecting to a local network using radio waves according to the IEEE 802.11 standard.
You can read more about Wi-Fi here.
Symptoms of a problem
The main signs of ignition coil failure are lack of ignition. If it is a single device with a distributor, then in all cylinders; if it is a double or single device, then in those served by it. The absence of a spark is not necessarily a 100% sign of a faulty coil. Perhaps the limiting resistor has burned out, the spark plug is faulty, the high-voltage wire has broken, or there is a malfunction in the ignition system. A comprehensive fault diagnosis is required.
Visual signs that the ignition coil is not working:
- the presence of “breakdown tracks”, oxides on the coil;
- change in dielectric color;
- burning of contacts and connectors;
- traces of overheating on the body;
- increased pollution.
Diagnostics of device health
It is recommended to carry out in-depth diagnostics of the device at a specialized service. A professional stand will allow you to evaluate the condition of the unit in various engine operating modes in the range from 0 to 8000 rpm. The manufacturer categorically does not recommend diagnosing using artisanal methods. This is dangerous not only for the car’s electrical system, but also for the person trying to carry out such diagnostics.
If the car’s dashboard is equipped with a voltmeter, and the car owner knows how to check the VAZ switch, then a simple way is available to him to preliminary assess the performance of the device. One of the functions of the switch is to turn off the power to the ignition coil when the engine is not running but the ignition is on. With such a shutdown, the voltage in the on-board network increases noticeably. This means that to check the functionality of the device, you should insert the key into the lock, turn it to the ignition position, but do not turn the starter. At this time, you must carefully monitor the readings on the voltmeter.
In the first seconds, the arrow will freeze approximately in the middle of the scale, and after 8-10 seconds it will noticeably move to the right. Since the device worked, the coil turned off, the voltage increased, and the voltmeter responded, then everything is in order. If a switch fails, it usually happens entirely. It is unlikely that the secondary function remained operational, but the basic one failed. So, with a high probability, the device can be considered working.
How to identify a faulty ignition coil
The procedure for checking the serviceability of the coil depends on how many ignition coils are in the car. If your car has individual ignition coils, in order to identify the faulty one with a high degree of probability, you can swap the supposedly faulty and known-good coils. If, as a result of this replacement, a spark appears in the cylinder in which there was no spark, and disappears in the other, therefore, the bobbin is truly faulty. In the same way, you can check dual and block coils, but you will have to modify the circuit, which is not always convenient.
How to determine which ignition coil is not working without making changes to the electrical circuit
To do this, you need to stock up on thick dielectric gloves and a dry rubber mat. The use of only ordinary dielectric gloves is unacceptable: they can withstand a breakdown voltage of 6300 Volts; the voltage applied to the candle is approximately three times higher.
If your car has two or more ignition coils, if one of them malfunctions, the car should start, but struggle a lot. By removing the tips of the high-voltage wires of the spark plugs or connectors from individual coils one by one, the stability of the engine is assessed. If the internal combustion engine has not changed its operation as a result of removing the connector, then there is no spark in this cylinder. If the engine starts to shake even more, or stalls altogether, there is a spark, the bobbin is faulty, or it is not receiving impulses or power.
High voltage arrester
Multimeter
If the car engine does not start at all and does not catch, you can evaluate the serviceability of the coil using the parametric method. For this you will need a multimeter. An ordinary coil like the Zhiguli one can be ringed without difficulty. To do this, first set the multimeter’s measurement limit to the resistance measurement mode of 200 Ohms or “diode, continuity” and measure the resistance between the coil terminals + and K. The resistance should be in the range from 0.2 to 1.0 Ohms. Please note that during measurement at this limit a small error may appear, which will slightly increase the multimeter readings. Then switch the multimeter mode to the limit of 20 kOhm and measure the resistance value of the second winding (between terminal K and the copper tip into which the high-voltage wire is inserted). The resistance should be in the range of 1 kilo ohm to 3 kilo ohms (2000 - 3000 ohms).
It is impossible to check a coil with a built-in pulse amplifier using this method, since the lead of the primary winding is not connected to its terminals. A common malfunction of individual devices is breakdown of the limiting resistor. It is located under the rubber extension of the reel structure, which is easily removed. The resistor should be removed and its resistance measured with a multimeter at a limit of 20 kilo-ohms. It should be between 1 and 3 kilo-ohms.
Megaohmmeter
You can also evaluate the insulation resistance if you have a megohmmeter at your disposal. The insulation resistance (between the copper contact into which the high-voltage spark plug wire is inserted and the housing) must be more than 300 megaohms. This measurement is of an evaluative nature. If the resistance is less, the coil is probably faulty, if the resistance is more, it is probably working, it is impossible to judge more precisely.
A simple three-terminal coil can be checked “by weight”, that is, by assembling a simple circuit. The +12V voltage from the battery is connected to the + terminal, a high-voltage wire is inserted into the connector, and a spark plug is connected to the second terminal. The spark plug body is connected to the metal part of the engine. Next, connect a stranded insulated conductor with a cross-section of 2 sq. mm to contact K. Holding the insulation, briefly touch the metal part of the engine with the other stripped end of the wire. A spark should jump where the engine touches and through the spark plug. In electronic coils, the spark from the spark plug is less intense. You cannot experiment with this method for a long time.
Some specialized service stations have self-made inspection stands. Their use requires special methods.
What switches and where to buy
Naturally, if you have a foreign car, then it is better to purchase the spare parts you need at the appropriate dealership centers or stores that officially represent the manufacturer of your car. Well, if you are the happy owner of the wonderful heritage of the Soviet automobile industry, you can safely start searching for the parts you need in the auto and radio markets. True, you need to be careful.
Based on many years of experience, and on practical tests that were personally carried out on many brands of proximity switches, there are two ignition system switches that have proven themselves to be excellent.
- Emergency switch K562.3734 (or K563.3734 TU11 KZhShchG 023-94).
- “Kalashnikov and Co. Plasma ignition” TU 4573-001045363119-97.
Why them? Firstly, both switches are produced in domestic factories. They are designed to work specifically in our conditions; all other analogs, be they Chinese or Korean, cannot withstand the loads that Soviet-made cars are accustomed to. Secondly, as mentioned above, it was experimentally established that only these switches quite consistently produce acceptable current interruption results.
The first, due to its original circuit by which it was assembled, generates pulse discharges that make it possible to achieve a current amplitude of up to 12-13A, while the consumed current charge is only 2A, and depends on the shaft rotation speed. Another significant advantage of this switching device is the moderate temperature range in which it operates. While there are some obvious drawbacks, the size of the switch itself could be somewhat smaller.
The second is, in general, innovative know-how. The switch “Kalashnikov and Co. Plasma Ignition” connects two devices: the main working unit, and a spare one. Like the previous switch, this one showed fairly high performance in both the duration of the spark torque and the strength of the breaking current pulse.
But its main advantage lies not in the main unit, but in the backup unit, which is designed to operate in conditions where not only the main switch unit fails, but also the Hall sensor. I had to verify the latter circumstance for myself.
“Kalashnikov and Co. Plasma Ignition” was set to nine as standard for operation, and when the main switch unit of the ignition system failed, it was necessary to switch to the backup one. The only downside is that you have to do it manually. When turned on, the unit immediately responded with a welcoming squeak from under the hood. Of course, you won’t be able to give it gas, the design principle of the switch system does not allow it, but by maintaining minimum speed, you can get to the garage or service station.
One of these solutions is the car switch, which at one time turned the automotive world upside down. This is what a switch in a car is and why we need it, and we’ll look at it in our article.
Spark plug
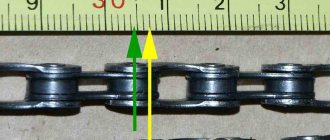
Typical spark plug faults:
- electrical erosion and chemical wear of electrodes
- carbon deposits
- damage to the central electrode insulator
Carbon deposits are cleaned with scrapers or sandblasting using an E-203-0 device. The gap between the electrodes is adjusted by bending the side electrode. For spark plugs of various engines it should be in the range of 0.4-0.8 mm. Cleaned spark plugs are tested for uninterrupted spark formation at a pressure of 0.8 MPa and tightness at a pressure of 1.0 MPa using an E-203P or M514-2 device. If the pressure drop exceeds 0.05 MPa in 1 minute for spark plugs with glass sealant and in 10 s with thermocement sealant, then the spark plugs are considered faulty. For serviceable spark plugs, sparking should be uninterrupted. The performance of the test spark plug can be checked by comparison with the reference one.