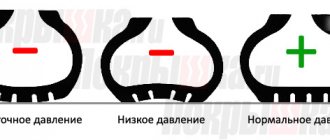
Atmosphere pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the air pressure at a given location. It usually refers to the pressure of a column of air per unit surface area. Changes in atmospheric pressure affect weather and air temperature. People and animals suffer from severe pressure changes. Low blood pressure causes problems of varying severity in humans and animals, from mental and physical discomfort to fatal diseases. For this reason, aircraft cabins are maintained above atmospheric pressure at a given altitude because the atmospheric pressure at cruising altitude is too low.
The aneroid contains a sensor - a cylindrical corrugated box (bellows) connected to an arrow, which rotates when the pressure increases or decreases and, accordingly, the bellows compresses or expands
Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude. People and animals living high in the mountains, such as the Himalayas, adapt to such conditions
Travelers, on the other hand, should take the necessary precautions to avoid getting sick due to the fact that the body is not used to such low pressure. Climbers, for example, can suffer from altitude sickness, which is associated with a lack of oxygen in the blood and oxygen starvation of the body
This disease is especially dangerous if you stay in the mountains for a long time. Exacerbation of altitude sickness leads to serious complications such as acute mountain sickness, high altitude pulmonary edema, high altitude cerebral edema and extreme mountain sickness. The danger of altitude and mountain sickness begins at an altitude of 2400 meters above sea level. To avoid altitude sickness, doctors advise not to use depressants such as alcohol and sleeping pills, drink plenty of fluids, and rise to altitude gradually, for example, on foot rather than by transport. It's also good to eat plenty of carbohydrates and get plenty of rest, especially if you're going uphill quickly. These measures will allow the body to get used to the oxygen deficiency caused by low atmospheric pressure. If you follow these recommendations, your body will be able to produce more red blood cells to transport oxygen to the brain and internal organs. To do this, the body will increase the pulse and breathing rate.
First aid in such cases is provided immediately
It is important to move the patient to a lower altitude where the atmospheric pressure is higher, preferably to an altitude lower than 2400 meters above sea level. Medicines and portable hyperbaric chambers are also used
These are lightweight, portable chambers that can be pressurized using a foot pump. A patient with altitude sickness is placed in a chamber in which the pressure corresponding to a lower altitude is maintained. Such a chamber is used only for providing first aid, after which the patient must be lowered below.
Some athletes use low pressure to improve circulation. Typically, this requires training to take place under normal conditions, and these athletes sleep in a low-pressure environment. Thus, their body gets used to high altitude conditions and begins to produce more red blood cells, which, in turn, increases the amount of oxygen in the blood, and allows them to achieve better results in sports. For this purpose, special tents are produced, the pressure in which is regulated. Some athletes even change the pressure in the entire bedroom, but sealing the bedroom is an expensive process.
PSI to atmosphere: translation instructions
Bar (metric) to pound per square inch (psi, British and American)
Hello everyone! We have already encountered such a phenomenon as various measurement measures that are adopted by automakers from different parts of the planet. Today I propose to familiarize yourself with how to convert psi to atmospheres, as this information can be of real practical value. So, let's go...
Why do we need pressure measurement units?
In the process of servicing vehicles, especially foreign-made ones, one has to deal with how many atmospheres (BAR) is the pressure in the wheel tires. Many drivers always have a pneumatic compressor at hand, often made in China. You can see the psi designation on it, for example, 200 or 300 psi. This is the maximum value for which the equipment is designed - this is what is used in most European countries.
Domestic car enthusiasts are more familiar with the traditional “atmospheres” in which it was customary to indicate tire pressure. Today, there are tables available on the Internet that accurately make it possible to convert from one unit of measurement to another. The abbreviation PSI has a very specific meaning - it means how many pounds are in 1 square inch. It is this indicator that most imported car manufacturers have adopted.
Nuances of translation in different units
On the body of many “pure Europeans” the value in psi is already indicated, which the manufacturer targets. For cars of foreign brands that are assembled on our territory, the technical atmosphere indicator applies. So, the approximate ratio will be as follows:
1 Atmosphere contains 14 PSI.
Confusion may arise if the tire or compressor (by the way, which one is better to choose, read here) shows the acceptable values in the BAR. In fact, 1 Bar is approximately equal to 1 atmosphere, so you can use this ratio. For those. For those who are interested in how this all turned out mathematically, here is a simple proof:
- 1 pound contains approximately 0.453 kilograms;
- at the same time, there are 6.4516 cubic centimeters in every square inch.
We find that one PSI will contain 0.07 kg/cm3, or in each atmosphere, on the contrary, there will be approximately 14 PSI. Despite the fact that such designations may not be entirely familiar to a Russian driver, translation is usually not difficult. The need may arise when purchasing car tires or devices for inflating air. At the same time, Chinese manufacturers often indicate several designations in their products for convenience.
How to count as quickly as possible
Despite some errors in calculations during translation, they are so insignificant that they do not cause any inconvenience in practice. To measure pressure, it is quite enough to use whole numbers and decimal parts. Most household pressure gauges are limited to a maximum of 60 PSI. Now you have enough knowledge and understanding. How do the various units of measurement that may be associated with tire pressure relate to each other?
As we said above, if your car tire or pump has the designation described above, then you can use a regular calculator for the translation, using the above mathematical calculations as a basis. Or you can resort to using special online calculators or ready-made tables with the values given in them. In these ways, you can make transfers from one unit of measurement to another, or vice versa. The ratios will be fair in any case and are suitable for cars and trucks, buses, and motorcycles. With this, we’ll say goodbye, dear car enthusiasts, and subscribe to Andrey Kulpanov’s blog to keep abreast of the most interesting news. Bye!
Place for contest advertising
avto-kul.ru
What is PSI
Most often, in Russia, motorists measure tire pressure in atmospheres. But it’s good to know that this is not the only option for measuring pressure that is used in the world. Depending on the country, tire pressure can be measured in bars, Pascals or PSI, in addition to atmospheres.
It is important to understand the definitions of common units of measurement:
- Atmospheres. This is a pressure of 1 kilogram of mass per 1 square centimeter of area. A distinction is made between technical and physical atmosphere. The first is equal to 735.5 mmHg, the second is 760 mmHg. Most often, when it comes to car tires, the technical and physical atmosphere are considered identical.
- Bars. They are usually equated to atmospheres in a ratio of 1 to 1. Despite the fact that the bars are equal to 750.06 mm Hg.
- Pascals. Rarely does anyone use the Pascal unit for tire pressure. But, for general development, it will be useful to know that 1 atmosphere is 101325 Pascal.
- PSI. A unit that is common in America, so information about tire pressure in PSI can often be found in the instructions for an American car. PSI refers to pounds of pressure per square inch. 1 PSI unit is 51.715 mmHg.
As you can see, the atmospheres and bars are close to each other, while the PSI is significantly different from them
Therefore, it is important, if the pressure in the technical documentation is specified in PSI, to be able to convert it to atmospheres
Converting from PSI to atmospheres or bar
There is a simple rule that will help you convert pressure from psi to atmospheres or bar with acceptable accuracy. To do this, the pressure in psi must be divided by 14. The resulting result will be the pressure in bars or technical (physical) atmospheres. For many cars, the normal pressure is 26 psi, that is, 1.8 atmospheres. In summer, you can increase the pressure to 28–29 psi, which will be 1.9–2.0 atm. In winter, if there is snow or ice on the roads, it is advisable to reduce the tire pressure to 23–25 psi, which corresponds to 1.6–1.7 atm.
Correct tire pressure is one of the keys to safe and economical driving, but it is not always possible to use a compressor that displays the pressure in usual values. After reading this article, you learned how to convert pressure from psi to atm, so you can always maintain optimal tire pressure.
In my article today, I would like to look at the problem that some car owners face. Here's what it's all about.
Some of the pneumatic pumps are measured in technical atmospheres (this is the unit of measurement that is most understandable and familiar to the average car enthusiast), while another part of them, foreign-made, often Chinese, does this in the PSI indicator, which is obscure to the average Russian. So, for example, on inexpensive Chinese compressors there is often a mark of 300 PSI, which is not at all the name of the sediment brand. It is just an indicator of tire pressure.
And since this type of pressure indicator is little known in some countries, many simply do not know how to interpret this measurement and how to convert this figure into more understandable units.
Therefore, now we will understand what the PSI indicator is, and whether it is possible to convert PSI into atmospheres and, if so, how this can be done.
Relationship between different units of measurement
What pressure should be in the tires of a passenger car? tire pressure in MPa
Using the table, you can compare different values and find out how 1 bar will be measured in atmospheres, or find out how much kPa 1 kgf/cm2 is.
Pressure units correspondence table:
Instantly convert pressure units and express atmospheres in mm Hg. Art. can be sent.
The list shows the most frequently encountered transitions:
- bar = 100 kPa
- bar = 1 tech. atm (at)
- bar = 750 mmHg pillar
- bar = 0.1 MPa
- bar = 1.0197 kgf/cm2
A bar is one of the quantities that can be used to measure pressure. It has nothing in common with a barrel, that is, a unit of volume of oil. Is it only the first three sonorous letters that unite them?
Let's compare the values:
- 1 pa = 0.00001 bar
- kilopascal = 0.01 bar
- pascal = 9.869210-6 atm
- kpa = 9.869210-3 atm
- megapascal = 9.8692 atm
- kilogram force/cm2 = 0.98 bar
- atm = 101325 Pa
If you need to convert bars into atmospheres, feel free to click here - without any hassles, everything is very clear.
General information
In physics, pressure is defined as the force acting on a unit surface area. If two equal forces act on one larger and one smaller surface, then the pressure on the smaller surface will be greater. Agree, it is much worse if someone who wears stilettos steps on your foot than someone who wears sneakers. For example, if you press the blade of a sharp knife onto a tomato or carrot, the vegetable will be cut in half. The surface area of the blade in contact with the vegetable is small, so the pressure is high enough to cut that vegetable. If you press with the same force on a tomato or carrot with a dull knife, then most likely the vegetable will not cut, since the surface area of the knife is now larger, which means the pressure is less.
In the SI system, pressure is measured in pascals, or newtons per square meter.
Let's summarize
We need to say a few words about the “foreigners” in our table - the “psi” and “psf” measurements.
Pounds scuare feet (psf) are pounds per square foot; they, like “psi” (pounds scuare inches) - pounds per square inch, can measure pressure when described in English-language sources. So, for example, one kgf/cm2 is approximately equal to 14 psi.
And this video clearly illustrates with a concrete example how to convert one unit to another within the SI system:
Having delved into the topic, you will soon learn how to convert not only MPa to kilogram s/cm2, but also make the reverse conversion, i.e. Convert kilogram s/cm2 to MPa.
Unit conversion
In fact, the translation between atm and PSI does not cause any great difficulties. In this case, there is no need to be a mathematical genius and carry out complex calculations.
If you want to ensure the correct pressure in your tires, but you are not sure how many atmospheres correspond to PSI, there is one simple rule you can use.
Suppose your technical documentation indicates PSI units, but the tire pressure can be created by relying on a pressure gauge with a bar measurement unit. Everything is elementary. You take the PSI that the car manufacturer specified in the regulations and divide it by 14.
Let's assume you know exactly how much PSI, according to technical regulations, should be in properly inflated tires of your car. The documentation states that the tires should be inflated to 26 PSI. Just divide 26 by 14 and you get the required value. As a result, we have an output of 1.8 atmospheres or bar. There is no fundamental difference between the last two units.
As you know, for many cars, a pressure of 1.8 atm is quite normal and quite common.
Using this principle, you can easily quickly determine what PSI system should be in your car tires to ensure the correct and optimal performance of the car.
If a more accurate measurement is required, which is hardly necessary for motorists, then the corresponding pressure table will come to your aid. It clearly shows to what number of atmospheres or bar PSI corresponds, and vice versa. But to maintain tire pressure, it is usually enough to simply divide the pressure according to the inch system by 14. And everything will immediately become clear and obvious.
There is no urgent need to constantly sit with a calculator, multiplying or dividing something. If you own one car and use it constantly, but the recommendations specify PSI values, then it will be enough to do the calculation once, convert the values to bars or atmospheres and continue quiet operation.
There is no need to buy a new pressure gauge or throw away your old measuring device, where atm or bar is indicated. For convenience, after calculating, you can check the table, and then write on the inner surface of the gas tank flap with a permanent marker what pressure you should have in your tires. Only in already familiar units of measurement.
This will be a kind of reminder for the rest of the time that you drive this car, unless you switch to new tires that differ from the regulated ones, and they may require slightly different pressure.
Just remember that the automaker may recommend using different tire pressures depending on the season the vehicle is used. In the warm season, the values are usually higher, but in winter it is necessary to make the tires softer, provide a larger contact patch on the surface and achieve better grip.
In practice, pressure units in the form of PSI should not cause any problems or panic. You take this figure, divide it by 14, and that’s it, now you see what the pressure should be in bars or atmospheres.
Pneumatic and electric tools for cars
There are various tools that are designed to handle pressures greater than 60 lbf/in², for example let's take a 300 PSI car compressor. The electric pump operates from the vehicle's on-board 12-volt network, with its help you can quickly and easily inflate a tire on the road, check the tire pressure, the power cord is connected to the cigarette lighter socket. This device is equipped with a convenient carrying handle, it also has a flashlight, and the compressor is convenient to use at any time of the day. The maximum value on the pressure gauge scale is 300 lbf/in², which, translated into our usual system of readings, turns out to be almost 20.5 Atmospheres. The power cord of the device is so long that it is enough to place the compressor next to any wheel of the car. It's likely impossible to get an impressive 20 Bar from the device, but the numbers on the scale are impressive.
The Tornado AC-580 compressor is declared by the manufacturer more modestly, its scale is designed for pressure up to 150 PSI, but with the help of this device you can inflate the tire not only on a passenger car, but also on a light-duty truck with a load capacity of up to one and a half tons (for example, on a Gazelle "). The tire compressor is capable of producing up to 30 liters of compressed air per minute, operating continuously for up to 20 minutes, the cable length is 1.9 m. Tornado is also powered from the cigarette lighter socket, the device has very compact dimensions and low weight (1.5 kg).
Various air impact wrenches operate on compressed air, for example, model JTC-3921. The tool is designed for operating pressure from 90 to 120 PSI, most often used in car repair shops for quick and convenient disassembly and assembly of components and assemblies.
The impact wrench produces a maximum torque of 624 Nm and weighs only 2.65 kg. The powerful metal body ensures a long service life of the tool; the maximum rotation speed reaches 8000 rpm.
The trunk of a car is a mini auto repair shop. Drivers often carry with them everything they need for urgent repairs: a set of wrenches, a jack, a tire pump, a pressure gauge to measure tire pressure. These devices are used especially often. If you notice low pressure in the tires, pump them up; large - slightly lowered.
On the contrary, when overinflated, the car goes easier and faster, detects the slightest movement of the steering wheel, but slips on snow and mud, and may not fit into a sharp turn.
In both cases, you get a set of wrenches, a pump and a pressure gauge, and this is where the problems begin. How to correctly measure the pressure in the wheels, if some manufacturers show it in atmospheres (domestic transport), others in Bars (you can figure it out somehow), and others in incomprehensible “PSI”? PSI - what is it and how many atmospheres is it? The analysis of the issue begins with a clear concept of “atmosphere”.
How to use an online calculator?
Description of the calculator functionality
- Left column of the calculator. Contains a selection of initial values. A precise technical description of the quantity is displayed below each column.
- Right column of the calculator. Contains the final translation value. Under each column there is a detailed description of the final transfer amount.
- Getting results. To convert MPa to pascals, enter the values of the original value. The online calculator will quickly translate the original data.
To convert extremely large and small numbers, a separate concept is used: computer exponential notation. Using this method, it is possible to write numbers with high concomitant abbreviations.
Who is the online calculator designed for?
- For specialists who conduct scientific research. You can easily convert, for example, a bar to a torr.
- For vehicle owners. Very often it is necessary, for example, to convert MPa to bars. This data is used to analyze the condition of the fuel line, as well as to check the nominal tire pressure of the vehicle.
- Car owners use a calculator when converting a single value into MPa in the process of filling car parts with freon.
Pressure in geology
Quartz crystal illuminated by laser pointer
Pressure is an important concept in geology. Without pressure, the formation of gemstones, both natural and artificial, is impossible
High pressure and high temperature are also necessary for the formation of oil from the remains of plants and animals. Unlike gems, which primarily form in rocks, oil forms at the bottom of rivers, lakes, or seas. Over time, more and more sand accumulates over these remains. The weight of water and sand presses on the remains of animal and plant organisms. Over time, this organic material sinks deeper and deeper into the earth, reaching several kilometers below the earth's surface. The temperature increases by 25 °C for every kilometer below the earth's surface, so at a depth of several kilometers the temperature reaches 50–80 °C. Depending on the temperature and temperature difference in the formation environment, natural gas may form instead of oil.
Diamond tools
Natural gemstones
The formation of gemstones is not always the same, but pressure is one of the main components of the process. For example, diamonds are formed in the Earth's mantle, under conditions of high pressure and high temperature. During volcanic eruptions, diamonds move to the upper layers of the Earth's surface thanks to magma. Some diamonds fall to Earth from meteorites, and scientists believe they formed on planets similar to Earth.
Synthetic gemstones
The production of synthetic gemstones began in the 1950s and has been gaining popularity recently. Some buyers prefer natural gemstones, but artificial stones are becoming more and more popular due to their low price and lack of hassles associated with mining natural gemstones. Thus, many buyers choose synthetic gemstones because their extraction and sale is not associated with human rights violations, child labor and the financing of wars and armed conflicts.
One of the technologies for growing diamonds in laboratory conditions is the method of growing crystals at high pressure and high temperature. In special devices, carbon is heated to 1000 °C and subjected to pressure of about 5 gigapascals. Typically, a small diamond is used as the seed crystal, and graphite is used for the carbon base. From it a new diamond grows. This is the most common method of growing diamonds, especially as gemstones, due to its low cost. The properties of diamonds grown in this way are the same or better than those of natural stones. The quality of synthetic diamonds depends on the method used to grow them. Compared to natural diamonds, which are often clear, most man-made diamonds are colored.
Due to their hardness, diamonds are widely used in manufacturing. In addition, their high thermal conductivity, optical properties and resistance to alkalis and acids are valued. Cutting tools are often coated with diamond dust, which is also used in abrasives and materials. Most of the diamonds in production are of artificial origin due to the low price and because the demand for such diamonds exceeds the ability to mine them in nature.
Some companies offer services for creating memorial diamonds from the ashes of the deceased. To do this, after cremation, the ashes are refined until carbon is obtained, and then a diamond is grown from it. Manufacturers advertise these diamonds as mementos of the departed, and their services are popular, especially in countries with large percentages of wealthy citizens, such as the United States and Japan.
Method of growing crystals at high pressure and high temperature
The method of growing crystals under high pressure and high temperature is mainly used to synthesize diamonds, but recently this method has been used to improve natural diamonds or change their color. Various presses are used to artificially grow diamonds. The most expensive to maintain and the most complex of them is the cubic press. It is used primarily to enhance or change the color of natural diamonds. Diamonds grow in the press at a rate of approximately 0.5 carats per day.
Author of the article: Kateryna Yuri
Unit Converter articles were edited and illustrated by Anatoly Zolotkov
Converting pressure values from PSI to Atmospheres
Units of measurement that are incomprehensible to Russian people are used not only in America, but also in many European countries; if you convert 1 PSI to Bars, you get the number 0.068046. To make it clearer, it is easier to determine the ratio of one number to another - it turns out that one kilogram per square centimeter is 14.504 times greater than lbf/in². For simplicity of calculations, the ratio 1/14 is most often taken, in which case it is easier to calculate the resulting result. For example, the pressure gauge showed 50 PSI, we get by dividing approximately 3.57 kg/cm² in our usual standard, respectively, 100 PSI will be twice as much, equal to approximately seven Atmospheres.
You have to use a measurement system with pounds per square inch involuntarily, because even the recommended tire pressure on many foreign cars is indicated in these units. Also, the letters PSI are often indicated on imported tire compressors, and they are mainly found on Chinese-made products, although pressure gauges often have several scales at once.
Getting to know PSI
Now we should talk about what kind of unit of measurement PSI is.
In relation to tires, PSI can also often mean pressure. This unit of measurement is widely used in the USA and other countries where the inch system of measurements is used.
If you ask a person who lives according to the inch (English) system what the atmosphere in tires means, he will answer approximately the same as our person about PSI. Surely nothing at all, since such units, which are familiar to us, are not used there. This means there is no need to worry about this. We'll fix everything.
When dealing with the issue of PSI, it is important to note the following. And it is quite natural to ask how much PSI should be to create the correct pressure in the tires of any car where other units of measurement are used
And it is quite natural to ask how much PSI should be to create the correct pressure in the tires of any car where other units of measurement are used.
In the case of domestic motorists, there is a need to convert one unit to another. This will go a long way toward understanding how much PSI your car's tires should actually have.
Atmosphere pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the air pressure at a given location. It usually refers to the pressure of a column of air per unit surface area. Changes in atmospheric pressure affect weather and air temperature. People and animals suffer from severe pressure changes. Low blood pressure causes problems of varying severity in humans and animals, from mental and physical discomfort to fatal diseases. For this reason, aircraft cabins are maintained above atmospheric pressure at a given altitude because the atmospheric pressure at cruising altitude is too low.
The aneroid contains a sensor - a cylindrical corrugated box (bellows) connected to an arrow, which rotates when the pressure increases or decreases and, accordingly, the bellows compresses or expands
Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude. People and animals living high in the mountains, such as the Himalayas, adapt to such conditions
Travelers, on the other hand, should take the necessary precautions to avoid getting sick due to the fact that the body is not used to such low pressure. Climbers, for example, can suffer from altitude sickness, which is associated with a lack of oxygen in the blood and oxygen starvation of the body
This disease is especially dangerous if you stay in the mountains for a long time. Exacerbation of altitude sickness leads to serious complications such as acute mountain sickness, high altitude pulmonary edema, high altitude cerebral edema and extreme mountain sickness. The danger of altitude and mountain sickness begins at an altitude of 2400 meters above sea level. To avoid altitude sickness, doctors advise not to use depressants such as alcohol and sleeping pills, drink plenty of fluids, and rise to altitude gradually, for example, on foot rather than by transport. It's also good to eat plenty of carbohydrates and get plenty of rest, especially if you're going uphill quickly. These measures will allow the body to get used to the oxygen deficiency caused by low atmospheric pressure. If you follow these recommendations, your body will be able to produce more red blood cells to transport oxygen to the brain and internal organs. To do this, the body will increase the pulse and breathing rate.
First aid in such cases is provided immediately
It is important to move the patient to a lower altitude where the atmospheric pressure is higher, preferably to an altitude lower than 2400 meters above sea level. Medicines and portable hyperbaric chambers are also used
These are lightweight, portable chambers that can be pressurized using a foot pump. A patient with altitude sickness is placed in a chamber in which the pressure corresponding to a lower altitude is maintained. Such a chamber is used only for providing first aid, after which the patient must be lowered below.
Some athletes use low pressure to improve circulation. Typically, this requires training to take place under normal conditions, and these athletes sleep in a low-pressure environment. Thus, their body gets used to high altitude conditions and begins to produce more red blood cells, which, in turn, increases the amount of oxygen in the blood, and allows them to achieve better results in sports. For this purpose, special tents are produced, the pressure in which is regulated. Some athletes even change the pressure in the entire bedroom, but sealing the bedroom is an expensive process.
Hydrostatic pressure
Hydrostatic pressure is the pressure of a fluid caused by gravity. This phenomenon plays a huge role not only in technology and physics, but also in medicine. For example, blood pressure is the hydrostatic pressure of blood on the walls of blood vessels. Blood pressure is the pressure in the arteries. It is represented by two values: systolic, or the highest pressure, and diastolic, or the lowest pressure during a heartbeat. Devices for measuring blood pressure are called sphygmomanometers or tonometers. The unit of blood pressure is millimeters of mercury.
Digital blood pressure machine, also called a sphygmomanometer
The Pythagorean mug is an interesting vessel that uses hydrostatic pressure, specifically the siphon principle. According to legend, Pythagoras invented this cup to control the amount of wine he drank. According to other sources, this cup was supposed to control the amount of water drunk during a drought. Inside the mug there is a curved U-shaped tube hidden under the dome. One end of the tube is longer and ends in a hole in the stem of the mug. The other, shorter end is connected by a hole to the inside bottom of the mug so that the water in the cup fills the tube. The principle of operation of the mug is similar to the operation of a modern toilet cistern. If the liquid level rises above the level of the tube, the liquid flows into the second half of the tube and flows out due to hydrostatic pressure. If the level, on the contrary, is lower, then you can safely use the mug.
FAQ
1 bar how many atmospheres?
To get an approximate result of how many atmospheres are in one bar, you need to divide the pressure value by a factor of 1.013. That is, 1 bar is 0.98 atmospheres
. Therefore, when converting one unit of measurement of small pressure (up to 10 bar) to another, it is generally accepted that 1 bar ≈ 1 atm. This ratio in calculations will give an error not exceeding 2%.
1 MPa is how much bar?
To find out how much bar is in one megapascal, it is enough to multiply the pressure value expressed in MPa by 10. That is, 1 MPa = 10 bar
.
1 MPa is how many KGS cm2?
To convert one MegaPascal to a pressure value expressed in kilogram-force per square centimeter, it is enough to multiply the MPa value by 10.197. Thus 1 MPa = 10.197 kgf/m²
.
KGS how many atmospheres?
When converting kgf/cm2 to atm, it is necessary to divide the pressure value expressed in KGS cm2 by 1.033. Using this ratio, you can convert any pressure value expressed in kilograms of force per atmosphere.
Source
A little about atmospheres
Largus how much pressure should be in tires
As already mentioned, in most cases the pressure unit is the atmosphere. But not everyone understands what it even means.
The atmosphere is called pressure, which is equal to 1 kilogram per cm2. This is about 0.1 MPa (megaPascal).
In relation to the atmosphere, there are 2 standards:
- Technical. Denoted as at or at. In the technical case, 1 atm corresponds to 735.56 mmHg.
- Physical. This is already atm or atm. The difference is small since it is 760 mmHg.
Do not forget that the difference between 1 atm and 1 bar is also insignificant. The latter corresponds to 750.06 mm. mercury column. Because of this, 1 atm = 1 bar. For motorists, the slight error between two units of pressure measurement is not taken into account. This will not affect the condition of the tire in any way.
Russian and European pressure designation
Atmospheric pressure (Atm) shows the force of an air column per unit surface area. The symbol of this physical quantity is 1 Atm, or 1 kgf/m2. For chambers of different diameters, the recommended pressure will vary significantly.
We are used to measuring this value in atmospheres (Atm), however, in European countries the symbol “PSI” is used to indicate pressure. Thus, Psi is an alternative to familiar atmospheres. If you see “300 PSI” on the compressor, we are not talking about the brand of the product, but about the pressure. Now we have to convert PSI into atmospheres.
Understanding the symbols
In European countries this value is calculated in pounds per inch squared. Russians don’t know either inches or pounds. To make this task easier, let’s use the usual Bars. The unit of pressure and gravity The bar corresponds to a unit of technical atmosphere, or 14 Psi. That is, 14 Psi will be equal to 1 Bar
or one atmosphere.
If the instructions for the machine indicate a recommended pressure of 30 Psi, then it is necessary to divide the number 30 by 14. As a result, we get approximately 2 Atm. Using this calculation formula for converting PSI to atmospheres, you can always find out the exact value in familiar units.
How to convert bars to other units
To convert bars to other pressure units, you need to remember that
1 bar = 10 5 Pa = 0.98692 atm = 750.06 mm Hg. Art.
Accordingly, let's say 1.7 bar = 1,275.1 mm Hg. Art.
And in order not to make calculations manually, you can use special online converters for converting pressure units, for example, such as
Length and distance Mass Measures of volume of bulk solids and foodstuffs Area Volume and units of measurement in culinary recipes Temperature Pressure, mechanical stress, Young's modulus Energy and work Power Force Time Linear velocity Plane angle Thermal efficiency and fuel efficiency Numbers Units for measuring the amount of information Exchange rates Dimensions women's clothing and footwear Sizes of men's clothing and footwear Angular velocity and rotation frequency Acceleration Angular acceleration Density Specific volume Moment of inertia Moment of force Torque Specific heat of combustion (by mass) Energy density and specific heat of combustion of fuel (by volume) Temperature difference Coefficient of thermal expansion Thermal resistance Specific thermal conductivity Specific heat capacity Energy exposure, thermal radiation power Heat flux density Heat transfer coefficient Volume flow Mass flow Molar flow Mass flow density Molar concentration Mass concentration in solution Dynamic (absolute) viscosity Kinematic viscosity Surface tension Vapor permeability Vapor permeability, vapor transfer rate Sound level Microphone sensitivity Sound Pressure Level (SPL) Brightness Luminous Intensity Illumination Computer Graphics Resolution Frequency and Wavelength Diopter Power and Focal Length Diopter Power and Lens Magnification (×) Electrical Charge Linear Charge Density Surface Charge Density Volume Charge Density Electric Current Linear Density current Surface current density Electric field strength Electrostatic potential and voltage Electrical resistance Electrical resistivity Electrical conductivity Electrical conductivity Electrical capacitance Inductance American wire gauge Levels in dBm (dBm or dBmW), dBV (dBV), watts and other units Magnetomotive force Magnetic strength fields Magnetic flux Magnetic induction Absorbed dose rate of ionizing radiation Radioactivity. Radioactive decay Radiation. Exposure dose Radiation. Absorbed dose Decimal prefixes Data transmission Typography and image processing Units of timber volume Calculation of molar mass Periodic table of chemical elements D. I. Mendeleev
1 megapascal = 10 bar
Initial value
Converted value
pascal exapascal petapascal terapascal gigapascal megapascal kilopascal hectopascal decapascal decipascal centipascal millipascal micropascal nanopascal picopascal femtopascal attopascal newton per square meter meter newton per square meter centimeter newton per square meter millimeter kilonewton per square meter meter bar millibar microbar dyne per sq. centimeter kilogram-force per square meter. meter kilogram-force per square meter centimeter kilogram-force per square meter. millimeter gram-force per square meter centimeter ton-force (kor.) per sq. ft ton-force (kor.) per sq. inch ton-force (long) per sq. ft ton-force (long) per sq. inch kilopound-force per sq. inch kilopound-force per sq. inch lbf per sq. ft lbf per sq. inch psi poundal per sq. foot torr centimeter of mercury (0°C) millimeter of mercury (0°C) inch of mercury (32°F) inch of mercury (60°F) centimeter of water. column (4°C) mm water. column (4°C) inch water. column (4°C) foot of water (4°C) inch of water (60°F) foot of water (60°F) technical atmosphere physical atmosphere decibar walls per square meter barium pieze (barium) Planck pressure seawater meter foot sea water (at 15°C) meter of water. column (4°C)