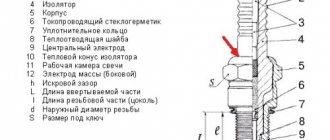
Video tutorials on car design
It's hard to imagine life without a car.
Even those who have never been and will not be closely associated with road transport in their lives will, no, no, and will intersect with a car directly or indirectly. Therefore, it is imperative to know the structure of the car, at least in general terms. In the end, time requires deeper knowledge, and there is more and more technology around, and in order to be with any technology, if not on friendly terms, then at least on a friendly footing, you need to know the basic principles of its operation. Content:
Car installation and repair
THE CAR CONSISTS OF:
3) Vehicle transmission - is responsible for transmitting torque from the engine to the drive wheels, and also changes the magnitude and direction of this torque. The design of the transmission fundamentally depends on the number of drive axles. A car in which all axles are driven is called all-wheel drive.
The vehicle's transmission consists of
TEXT BOOK CAR STRUCTURE
In order to study the structure of a truck and a passenger car, you need to consistently study the textbook materials. For effective learning, we recommend studying the material schematically, in the following sequence:
1) Purpose of the car (before studying the structure and operation of the car, you need to know its purpose) ;
2) The structure of the car (the first step is to study the general structure of the car, then you can begin to study the structure of the units and systems of the car);
3) The principle of operation of a car (if you have studied the purpose and structure of a car, it will be easier for you to understand the principle of operation of a car).
This scheme for teaching the structure of a car will help you study the textbook “Design of a Car” in the shortest possible time. It is necessary to adhere to the schematic nature of training when considering the structure of all units and systems of the car.
Not every experienced motorist knows how a modern car works , and if you are a beginner, you will definitely have to deal with issues of vehicle maintenance, repair and diagnostics . And situations may arise in which you will have to repair the car yourself . In order to understand how to repair a car yourself , you need to study books on car repairs.
How a car works: key concepts and terms
We do not set ourselves the goal of giving in a few words a detailed picture of such a complex and knowledge-intensive invention as a car. Not at all. It is enough to master the terms and understand the principle of operation of the main components of the car, and then intuition will do its job, but the terms are very important. This is the basis of technical culture, so let’s make a reservation right away - there have never been, no, and cannot be any gizmos, squiggles, pimples, twists, twitches and other rubbish in the car. Each detail has its own name, so we will treat the technology with respect. Then the car won’t play tricks.
And also - abbreviations. They are only good when the entire engineering staff of a large automobile plant gathers for an evening meeting. Only there, among engineers, is it natural to hear GKL, DMRV, GKTRO, KVVUSH and other abbreviations that no one understands. The correct naming of components and assemblies also expresses a certain respect for both the technology and the interlocutor. The device of the car for beginners, the video of which we offer, is presented from one angle, and we will try to complement it as much as possible.
Knots, assemblies, nuts and bolts
Now let’s start from the beginning and before considering specific issues regarding the design of the car, it is worth defining a number of terms. It is very important:
- a part is an integral part of a structure, which is made either from one workpiece, or is an integrally interlocked two or more small parts (piston, bushing, shaft);
- unit - a set of parts that are interconnected with each other in one way or another and require the performance of one or several mechanical operations (steering linkage, clutch);
- unit - a set of parts and assemblies designed to function fully and autonomously and perform mechanical work (engine, gearbox, gearbox).
Now that we almost know all the basic, fundamental concepts, we can begin to consider the structure of the car and the principle of operation of its components and assemblies.
How the motor works
A car is a complex complex of interconnected systems in which nothing happens without mutual influence. Every change in the state of the car as a whole and individual components are interdependent, so look at the car from a global point of view, as a self-sufficient autonomous closed system. We need a car for transportation, so the presence of such a unit as an engine in it will not be a surprise.
As a rule, a modern car, or not so modern one, moves with the help of an internal combustion engine. The principle of its operation is that fuel entering its systems certainly burns, and the chemical-physical energy of fuel combustion is converted into mechanical, rotational energy.
The structure of an internal combustion engine completely replicates the structure of a heat engine - it is a pair: a cylinder and a piston, a system of intake and exhaust valves. The mixture of fuel and air enters the space above the piston, is compressed and explodes from the spark generated by the spark plug.
General structure of the car
The main components in the design of a car, as we wrote above, are:
All of them consist of many individual elements, parts, assemblies and assemblies.
The engine is the heart of the car. It is a source of mechanical energy and sets our car in motion. The most widespread in the automotive industry are internal combustion engines and diesel engines. However, in recent years, cars equipped with electric and hybrid engines have become increasingly popular.
The car body can have a frame or frameless design. As a rule, in modern passenger cars there is no frame, and all components and assemblies are attached directly to the body. That is why such a body is called a load-bearing body - this design solution for the vehicle allows its weight to be reduced as much as possible. We also advise you to familiarize yourself with the classification of cars by body type.
The car's chassis deserves special attention. It consists of many mechanisms whose tasks include transmitting torque from the power unit (engine) to the drive wheels, moving the car and controlling it. These groups of mechanisms are called transmission, chassis and vehicle control mechanism.
In addition to the above components, assemblies and mechanisms, absolutely all cars are equipped with electrical equipment, consisting of sources and consumers of electric current.
The electrical equipment of the car starts and allows the engine to work, illuminates and heats the interior of the car, allows you to move without problems in the dark and in bad weather, supports the anti-theft system, takes care of our safety on the road, turns the car into a concert hall or even a cinema, and performs many other useful and very important functions.
Systems and attachments
During operation, the engine generates a large amount of heat, which, if nothing is done with it, will simply destroy the parts and components of the motor. In order to remove heat to the atmosphere, the motor is equipped with a cooling system. It comes in two types - air and liquid. If an air cooling system is used, the motor will be cooled by counter air. If liquid - coolant, antifreeze or water. They transfer heat to the atmosphere both through the walls of the cooling jacket and through the radiator.
Brief overview of types of motors
First of all, it is worth noting that the engine and motor are one and the same. Motors are often called internal combustion or electric engines. It is no secret that the engine serves as a source of energy to move the vehicle. Most cars have internal combustion engines, which can be divided into:
• Piston engines, in which expanding gases during fuel combustion force the piston to move, which in turn drives the crankshaft of the car;
• In rotary engines, the same gases drive a rotating part, the rotor itself.
If you go deeper, there are a large number of types and subtypes of engines. Based on the type of fuel, engines can be divided into diesel, gasoline, gas and gas generators.
Power and exhaust system
A power supply system is used to supply and dispense fuel. It consists of a fuel tank, fuel pumps, filters, a fuel line and a device that dispenses and mixes fuel with air. For gasoline engines, this is a carburetor or injection system, and for diesel engines, it is a high-pressure fuel pump and injectors that supply diesel fuel to the cylinders.
Chassis and electrical circuit
The chassis of a car is the chassis, suspension, steering, and axles. To dampen unevenness and ensure stability and good handling, the car's suspension consists of elastic elements, springs or leaf springs, as well as shock absorbers that prevent the body from swaying, but contribute to a smooth ride.
The steering of a car consists of a system of rods and levers, a steering mechanism, a steering column and a steering wheel. Modern cars are equipped with power steering, hydraulic or electric.
Also for control and safety, each vehicle has a braking system, which is operated by a pedal and a hand-operated parking brake lever. The system can lock the wheels as you press the brake pedal.
Also, every modern car has a safety system that can protect the driver from injury and damage and make driving safer in principle.
A simplified vehicle electrical system is shown in the photo. This is a rather complex and multi-level organism that supports and provides electricity to all consumer points, and its main elements are a generator and a battery.
In a nutshell, this is how every modern machine has worked for over a hundred years. Technologies and design solutions change, but only one thing remains unchanged - the car has firmly entered the life of modern people and without it our world would not be complete.
1.Main components and systems
Despite the fact that today there are a huge number of different brands and models of cars, almost all of them are built on the same principle. We are talking about passenger vehicles. The car diagram is divided into several parts:
•
Vehicle body or supporting structure. Today, the car body is its basis, to which almost all units and components are attached. The body, in turn, consists of a stamped bottom, front and rear side members, roof, engine compartment and other attachments. By attached components we mean doors, fenders, hood, trunk lid, etc. This division is quite arbitrary, since all the parts of the car are, one way or another, interconnected;
• Car chassis. The name speaks for itself and suggests that the chassis consists of many components and assemblies with which the car is able to move. Its main components are considered to be front and rear suspensions, drive axles and wheels. The chassis of the car also includes the frame, to which most units are also attached. The frame is the predecessor of the body.
• With the help of drive axles, the load is transferred from the frame or body to the wheels and vice versa. As for the suspension, many cars have MacPherson strut suspension, which significantly improves vehicle handling. There are also independent (each wheel is individually attached to the body) and dependent (can be in the form of a beam or a drive axle, considered obsolete) suspensions;
• Vehicle transmission. The transmission of a car is usually considered to be the power train. Its main task is to transmit torque from the crankshaft to the drive wheels. In turn, the transmission also consists of several parts, in particular the gearbox, clutch, driveline, differential, axle shafts and final drive. The latter are connected to the wheel hubs;
• Car engine. The main task and purpose of the engine is to convert thermal energy into mechanical energy. This energy is then transmitted through the transmission to the wheels of the car;
• Control mechanism. Actually, the control mechanism itself consists of a brake system and a steering system;
• Vehicle electrical equipment. No modern car can do without electrics, the main parts of which are the battery, electrical wiring, alternator and engine management system. These are only the main parts of the car, each of which provides a system within a system and sometimes more than one. Some parts are worth going into more detail.
Features of a manual transmission
A manual transmission is a type of transmission in which the gears are switched and torque is transmitted manually by the driver by selecting a gear, according to an assessment of current conditions and the characteristics of further actions.
In simpler terms, the purpose of a manual transmission is to regulate the speed range and select its direction.
The number of stages in a manual transmission ranges from four to seven, in addition to neutral and rear.
A special feature of vehicles with manual transmission is the presence of a clutch pedal, in addition to the brake and gas pedals, which are available in all types of transport. The gear change is carried out with the clutch pedal depressed.
Advantages of transport with manual transmission:
The disadvantages of manual transmission include:
Clutch
In simple terms, the clutch is designed to briefly separate the engine from the transmission and then reconnect them. The clutch consists of a clutch mechanism and a drive mechanism. The drive is designed to transmit forces from the driver to a specific mechanism. In a car, each mechanism has its own drive, thanks to which it comes into action.
The clutch mechanism is a device in which the process of transmitting torque through friction occurs. The components of the clutch mechanism are the crankcase, casing, drive, driven and pressure plates.
All of the above is just the tip of the iceberg, since each of the points contains dozens more sub-points. For a general understanding of the structure of a car, it is enough to know its main components and assemblies. Now you know exactly how and why your car moves, brakes and consumes gas.
Subscribe to our feeds on Facebook, Vkontakte and Instagram: all the most interesting automotive events in one place.
This article is intended for beginners who need to learn how to understand cars, as well as distinguish between types of bodies.
Many people think that cars are very similar to each other, and the main differences are only the lighting and trunk. But today we will try to master the basics that will help you clarify the situation at least a little.
Each model and brand of car has certain features. However, they also have a lot in common. If you intend to have a good understanding of vehicles and distinguish between existing types of car bodies, then let's get started!
The purpose of gears and pedals in a car with manual transmission
The most widespread are 5-6 speed manual transmissions. The gear selection lever is used to ensure interaction between the engine and the manual transmission.
The purpose of the pedals in a car with a manual transmission
To avoid confusion and addiction, the pedal arrangement is identical in all types of transport with manual transmission.
There are 3 pedals in front of the driver's feet:
It is necessary to place your feet on the pedals as in the figure below.
Assignment of gears
Each step must be used for movement within certain parameters. Despite the differences between machines in power, dynamic characteristics and other parameters, there are general principles for choosing stages and the conditions required for this.
When moving to any stage, the engine speed should be in the range of 2500-3000 rpm. - with a calm, even ride and 3500-4500 rpm. — when accelerating or in a more dynamic driving style.
Gears and their characteristics with a calm driving style (using the example of a five-speed manual transmission):
Attention! The more power a vehicle has, the higher the speed the steps should be increased.
Reference. In cars with diesel engines, the speed range is much lower than that of gasoline engines. This is due to the peculiarity of the engine and the achievement of maximum torque (which means more power) at lower speeds, so diesel engines are more torquey and powerful.
Speed Arrangement Options
1) The rear stage is parallel to the first. In the absence of special protection for selecting the rear stage (a button on the handle or pressing on it), a novice driver may confuse the rear with the first when choosing and start moving in the wrong direction, which can provoke an accident.
2) Having the rear stage opposite the fifth stage prevents you from starting in the wrong direction.
Driving a vehicle with a manual transmission has many of its own nuances, after mastering which the driver will be able to fully control the car under any conditions and will not be afraid of driving in difficult conditions.
How to learn to understand cars from scratch? Detailed
How to learn to understand cars inside, outside and under the hood?
The ability to understand machines is a fairly broad concept. For some, it is enough to distinguish one model from another. The same people whose profession is related to cars put a much broader meaning into this concept:
- body type;
- car class;
- engine type - injection, carburetor, diesel, one- or two-stroke, hybrid, electric car;
- transmission - manual, automatic, variator, robotic, preselective (dual clutch).
If you work, for example, in a company that sells spare parts or in an auto shop, then according to your job description you are simply required to have extensive knowledge:
- thoroughly know the model range of a particular automaker - that is, they must know the difference between various engines, for example VAZ-2104 - VAZ-21073, VAZ-21067, their volume, fuel, features;
- technical features of various units;
- design and device features.
If you have ever had to buy spare parts, then you know that it is enough for a good specialist to show this or that spare part - the brake wheel cylinder, the second gear gear, the main or intermediate shaft of the gearbox, the clutch cable, the release bearing, the feredo disc - he will name them without any problems brand, will tell you what car it is from, and most importantly, will tell you exactly what it is. He will also easily select the part you need from the catalog - from a rubber sealing ring or cuff, to an assembled distributor or gearbox rocker.
It is clear that such a skill comes only with experience. We will try to give basic recommendations on our website Vodi.su.
What not to do with a manual transmission
A manual transmission is a reliable type of transmission, but improper operation can significantly reduce its service life and lead to significant damage.
What not to do with a manual transmission:
If you follow some rules and drive thoughtfully, the experience of driving a car with a manual transmission will come quickly, despite the apparent complexity of such a transmission.
The main advantage of a car with a manual transmission is complete control over it, which is realized only after driving kilometers.
Remote engine start: device, types and principle of operation
Imagine the inside of a car that has been sitting in the cold all night. Goosebumps involuntarily run through your skin at the thought of a frozen steering wheel and seat. In winter, car owners have to leave early in order to warm up the engine and interior of their car. Unless, of course, the car has a remote engine start system that allows you to start the engine while sitting in a warm kitchen and leisurely finishing your morning coffee.
Remote start system design
The entire remote start system is housed in a compact plastic housing. Inside there is an electronic board that, once connected to the car, communicates with a group of sensors. The autostart unit is connected to the standard electrical wiring of the vehicle using a set of wires. The autostart system can be installed in a car together with an alarm system or completely autonomously. The module connects to any type of engine (petrol and diesel, turbocharged and naturally aspirated) and gearbox (manual, automatic, robot, CVT). There are no technical requirements for the car.
Car manufacturers
The next step is to remember the main companies involved in the production of cars. The most famous automakers: Mercedes, Audi, Toyota, Volkswagen, Lexus, Renault, Mazda, Chevrolet and others. The easiest way to help you remember all car manufacturers is by the icons on the front of the car.
The badge and body are just visual differences between the cars. Therefore, in order to have a good understanding of cars, you also need to pay a lot of attention to studying the technical parameters of the car - gearbox, engine, and also the chassis. You need to understand that you won’t be able to learn everything in just a few days, so we recommend that you be patient and regularly visit our Autopub (pay attention to the “Useful Tips” and “Device” sections)! Together with us you will learn how to properly maintain and repair your “iron horse”. After some time, you will be able to become one of the experts in the current automotive industry.
More detailed information about car badges and emblems can be found in the corresponding section of our website.
We recommend starting with an article about what classes of cars exist, since many beginners often ask this question. Subscribe to updates and stay with us!
Operating principle of the autostart system
A command given by the driver from the remote control or received from a timer causes the security alarm to be turned off and the lock to be unlocked. The starter rotor is set in motion. Successful engine starting is confirmed by the flashing of the vehicle's signal lights and the flickering of the LED indicator on the control key fob.
After the power unit is activated, the starter is turned off. If the automatic system fails to start the engine the first time, repeated attempts are made to turn it on with a gradual increase in the starter cranking intervals.
There are specially designed autostart systems that can independently determine the reasons for engine failure. Having completed the required diagnostics, such programs notify the driver about detected problems.
During the frosty period, automatic engine starting, carried out at certain time intervals, becomes especially important. This useful feature helps prevent overcooling of the power unit.
Also, talented inventors have developed a program that provides for the autostart system to be activated when the engine reaches a certain temperature. This option prevents the oil from freezing in the engine by periodically warming up the unit when it gets significantly colder.
Using autorun correctly
There are several algorithms for the correct operation of autostart, if followed, unforeseen situations will not occur (for example, the car moving independently). These algorithms are different for vehicles with manual and automatic transmissions.
Algorithm for manual transmission:
engage neutral gear, engage the parking brake, get out of the car, close the doors, turn on the alarm, activate the engine autostart system.
Many car enthusiasts are accustomed to leaving the gear in gear when turning off the engine. When installing autostart, they will have to get used to leaving the car in “neutral”, otherwise the autostart module will not activate. However, manufacturers of autostart systems for cars with manual transmission have solved this problem by equipping the device with the so-called “software neutral”, which will not turn off the engine until neutral gear is engaged.
Algorithm for automatic transmission:
Switch the gearbox selector to Parking mode, get out of the car, close the doors, turn on the alarm, activate the engine autostart system.
If you do not perform at least one of the above actions, the autostart system will not be activated.
Pros of autorun
— warmed up engine and car interior in winter/cooled interior in summer; — saving time; — the presence of a turbo timer mode (optional), which allows you to gradually stop the engine turbine, which has a positive effect on the resource of the unit.
Disadvantages of autorun
— temporary deactivation of the standard immobilizer and alarm shock sensor; — increased fuel consumption; — icing when starting the exhaust pipe in winter due to water condensation formed in the exhaust system (formed when the engine is idling for a long time).
Types of remote start system
Today there are two types of remote engine starting in a car. Driver controlled starting system. This scheme is the most optimal and safe. But it is feasible only if the owner of the car is at a short distance from the car (within 400 meters). The driver himself controls the start of the engine by pressing a button on the key fob or in an application on his smartphone. Only after receiving a command from the driver does the engine begin to operate.
Programmed engine activation depending on the situation. If the driver is far away (for example, the car was left overnight in a paid parking lot, and not in the yard near the house), the start of the internal combustion engine can be set to certain conditions: start at a given time; when the engine temperature drops to certain values; when the battery charge level decreases, etc. Autostart programming is also carried out using an application on a smartphone.
Features of autostart without alarm
The device for remotely starting a car engine without an alarm system is represented by a separate module designed to remotely start a car in the absence of the driver or when he is at a certain distance from the vehicle.
It is distinguished by a very convenient and understandable design, extreme ease of use, coupled with fairly high reliability and quite acceptable functionality.
The basis for installing such a system is one of the existing types of car alarms, in the absence of the use of its equipment. The considered type of remote activation of the power unit is capable of implementing the following functions:
It should be noted that using a mobile phone as a control panel has advanced functions.
To the options listed above is added the ability to automatically start the power unit upon an alarm signal or upon a command sent by a special call or SMS.